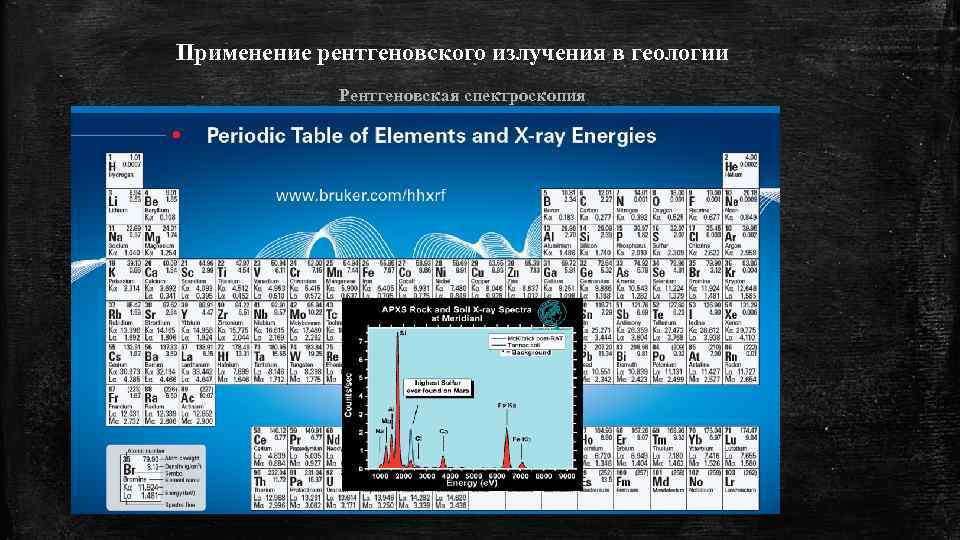
 Применение рентгеновского излучения в геологии Рентгеновская спектроскопия
Применение рентгеновского излучения в геологии Рентгеновская спектроскопия
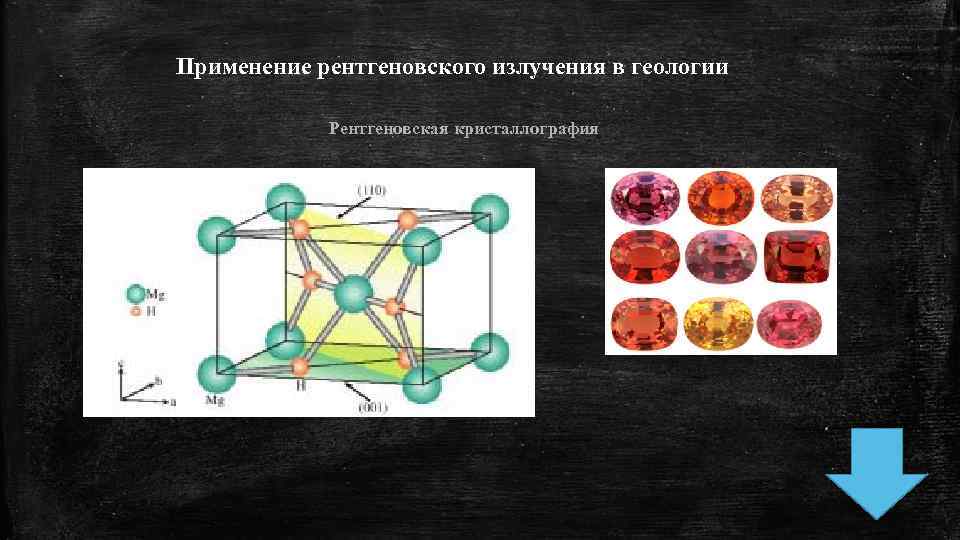 Применение рентгеновского излучения в геологии Рентгеновская кристаллография
Применение рентгеновского излучения в геологии Рентгеновская кристаллография
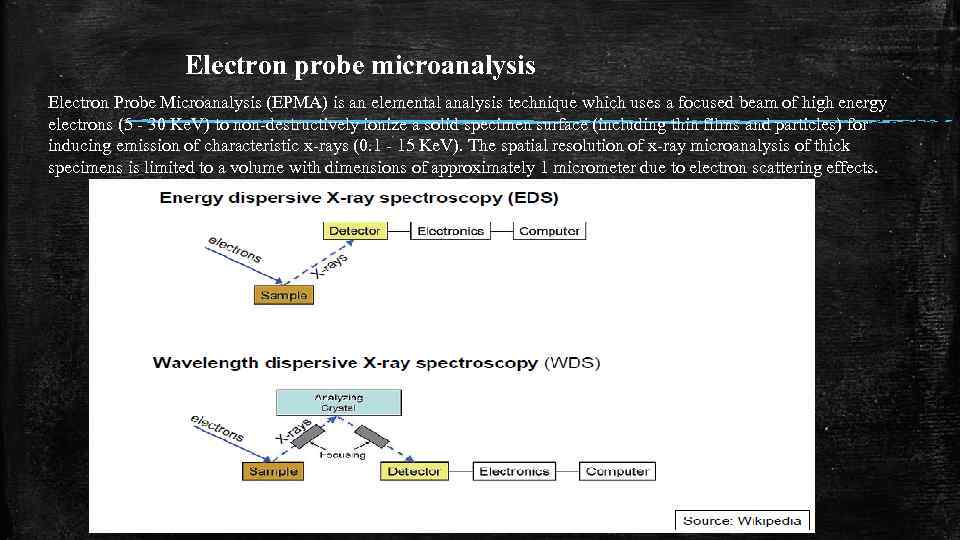 Electron probe microanalysis Electron Probe Microanalysis (EPMA) is an elemental analysis technique which uses a focused beam of high energy electrons (5 - 30 Ke. V) to non-destructively ionize a solid specimen surface (including thin films and particles) for inducing emission of characteristic x-rays (0. 1 - 15 Ke. V). The spatial resolution of x-ray microanalysis of thick specimens is limited to a volume with dimensions of approximately 1 micrometer due to electron scattering effects.
Electron probe microanalysis Electron Probe Microanalysis (EPMA) is an elemental analysis technique which uses a focused beam of high energy electrons (5 - 30 Ke. V) to non-destructively ionize a solid specimen surface (including thin films and particles) for inducing emission of characteristic x-rays (0. 1 - 15 Ke. V). The spatial resolution of x-ray microanalysis of thick specimens is limited to a volume with dimensions of approximately 1 micrometer due to electron scattering effects.
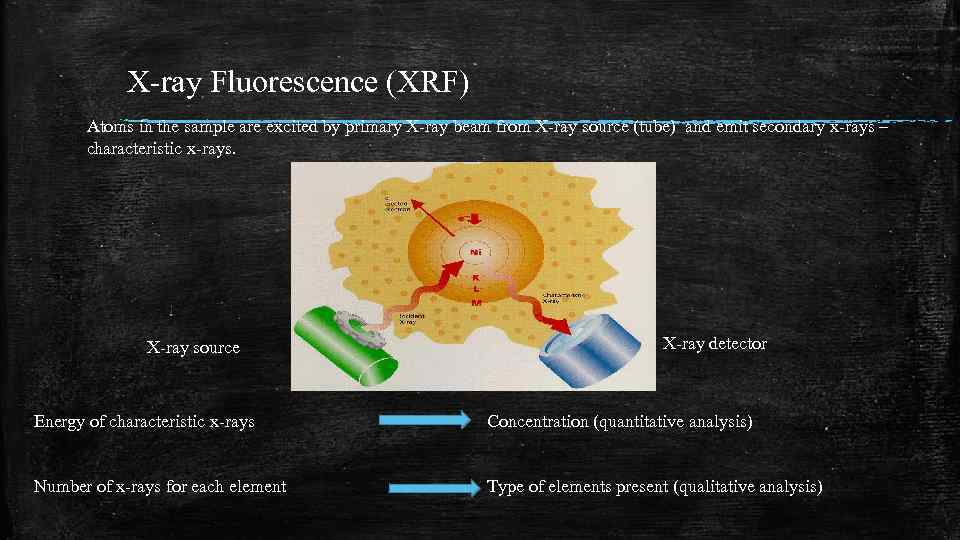 X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) Atoms in the sample are excited by primary X-ray beam from X-ray source (tube) and emit secondary x-rays – characteristic x-rays. X-ray source X-ray detector Energy of characteristic x-rays Concentration (quantitative analysis) Number of x-rays for each element Type of elements present (qualitative analysis)
X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) Atoms in the sample are excited by primary X-ray beam from X-ray source (tube) and emit secondary x-rays – characteristic x-rays. X-ray source X-ray detector Energy of characteristic x-rays Concentration (quantitative analysis) Number of x-rays for each element Type of elements present (qualitative analysis)
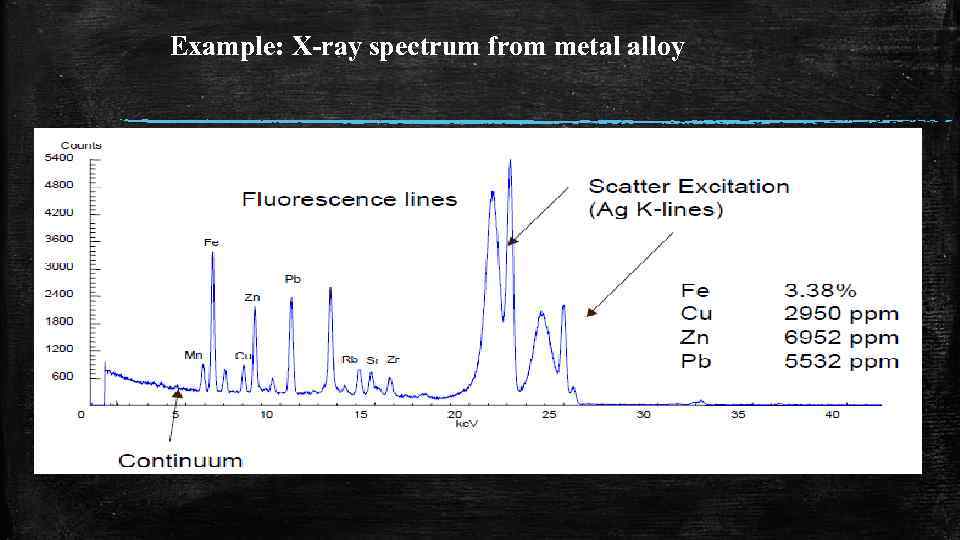 Example: X-ray spectrum from metal alloy
Example: X-ray spectrum from metal alloy
 Analytical characteristics of XRF • • • instrumental analytical technique with multi-element capability elemental analysis of solids and liquids minimal sample treatment can be operated without vacuum concentration range: ppm to % (trace, minor and major elem. ) element range: from boron to uranium (in theory)
Analytical characteristics of XRF • • • instrumental analytical technique with multi-element capability elemental analysis of solids and liquids minimal sample treatment can be operated without vacuum concentration range: ppm to % (trace, minor and major elem. ) element range: from boron to uranium (in theory)
 Types of XRF instruments How can we classify XRF methods? Based on the excitation • Tube excited XRF • Radio-isotope excited XRF • Secondary target, • Synchrotron, • Total reflection. . . Based on the detection • Wavelength dispersive (WD-XRF) • Energy dispersive (ED-XRF) • Filter instruments (proportional counter)
Types of XRF instruments How can we classify XRF methods? Based on the excitation • Tube excited XRF • Radio-isotope excited XRF • Secondary target, • Synchrotron, • Total reflection. . . Based on the detection • Wavelength dispersive (WD-XRF) • Energy dispersive (ED-XRF) • Filter instruments (proportional counter)
 Analytical characteristics of XRF • • • instrumental analytical technique with multi-element capability elemental analysis of solids and liquids minimal sample treatment can be operated without vacuum concentration range: ppm to % (trace, minor and major elem. ) element range: from boron to uranium (in theory)
Analytical characteristics of XRF • • • instrumental analytical technique with multi-element capability elemental analysis of solids and liquids minimal sample treatment can be operated without vacuum concentration range: ppm to % (trace, minor and major elem. ) element range: from boron to uranium (in theory)
 Summary in short: • • • 1. in XRF x-rays are used to excite the sample 2. characteristic x-rays are measured in the form of a spectrum 3. the spectrum tells which elements are present and how much 4. element range: B – U; concentration range ppm - % 5. used in various fields 6. there are wavelength and energy-dispersive instruments
Summary in short: • • • 1. in XRF x-rays are used to excite the sample 2. characteristic x-rays are measured in the form of a spectrum 3. the spectrum tells which elements are present and how much 4. element range: B – U; concentration range ppm - % 5. used in various fields 6. there are wavelength and energy-dispersive instruments
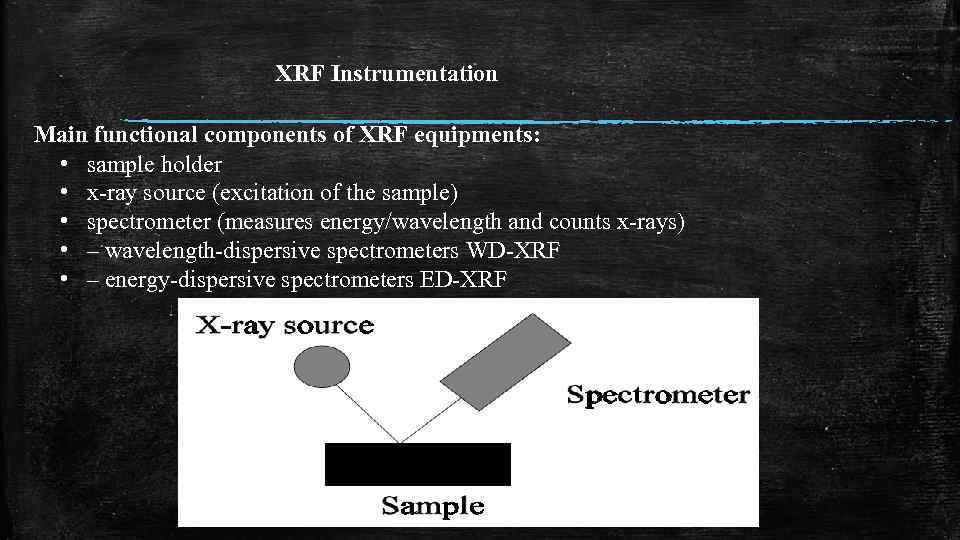 XRF Instrumentation Main functional components of XRF equipments: • sample holder • x-ray source (excitation of the sample) • spectrometer (measures energy/wavelength and counts x-rays) • – wavelength-dispersive spectrometers WD-XRF • – energy-dispersive spectrometers ED-XRF
XRF Instrumentation Main functional components of XRF equipments: • sample holder • x-ray source (excitation of the sample) • spectrometer (measures energy/wavelength and counts x-rays) • – wavelength-dispersive spectrometers WD-XRF • – energy-dispersive spectrometers ED-XRF
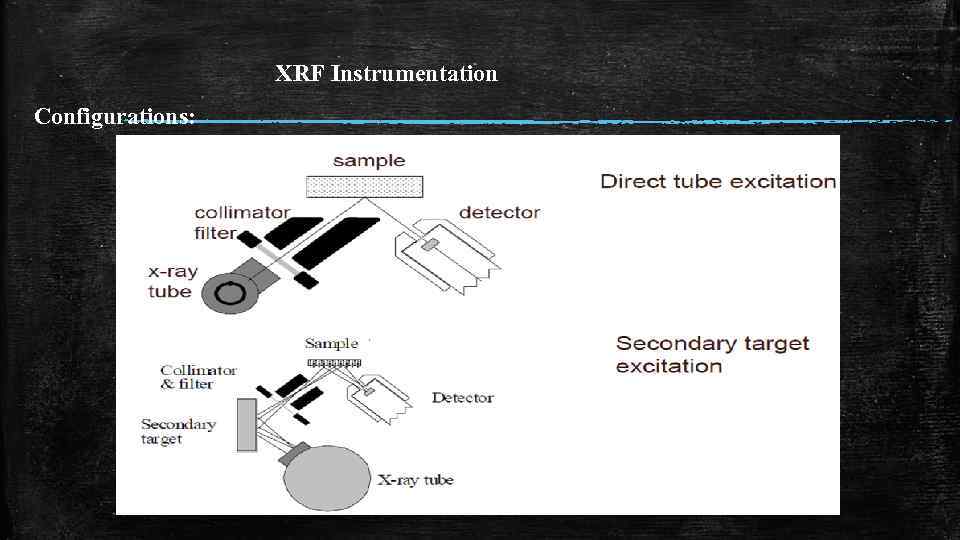 XRF Instrumentation Configurations:
XRF Instrumentation Configurations:
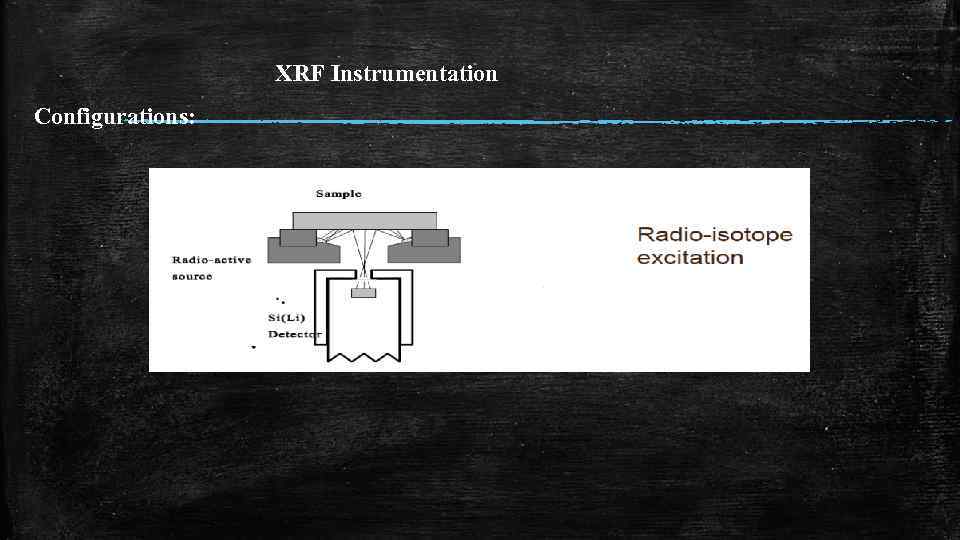 XRF Instrumentation Configurations:
XRF Instrumentation Configurations: