c748aee105c17b7e64f0f51a7744101b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Price Reporting Mechanism (PRM): Lessons learnt and how to use the evidence from the PRM Technical Briefing Seminar for Consultants on Procurement and Supply Management for HIV, TB and Malaria 30 January 2006 Copenhagen Peter Graaff, AMDS, HIV AMDS
Price Reporting Mechanism (PRM): Lessons learnt and how to use the evidence from the PRM Technical Briefing Seminar for Consultants on Procurement and Supply Management for HIV, TB and Malaria 30 January 2006 Copenhagen Peter Graaff, AMDS, HIV AMDS
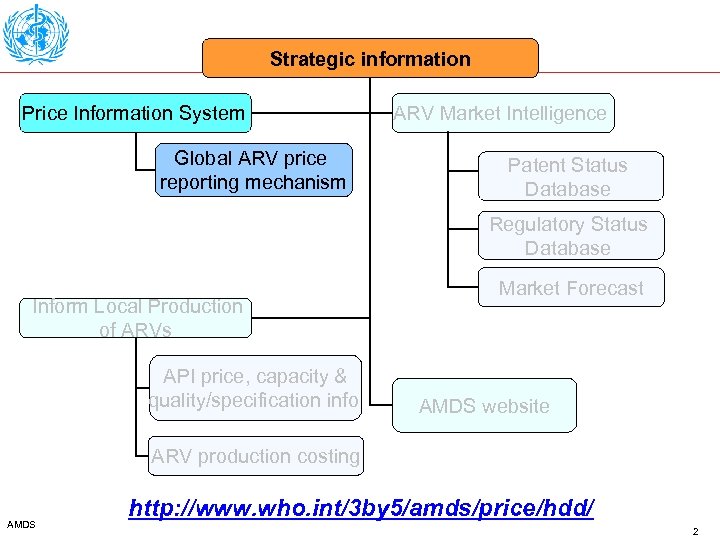 Strategic information Price Information System Global ARV price reporting mechanism ARV Market Intelligence Patent Status Database Regulatory Status Database Inform Local Production of ARVs API price, capacity & quality/specification info Market Forecast AMDS website ARV production costing AMDS http: //www. who. int/3 by 5/amds/price/hdd/ 2
Strategic information Price Information System Global ARV price reporting mechanism ARV Market Intelligence Patent Status Database Regulatory Status Database Inform Local Production of ARVs API price, capacity & quality/specification info Market Forecast AMDS website ARV production costing AMDS http: //www. who. int/3 by 5/amds/price/hdd/ 2
 Introduction and Purpose of the GPRM ÚThe Global Price Reporting Mechanism is a database that consolidates information (price, volume, …) of ARV drugs ÚInformation on other drugs (such as TB or malaria drugs) is included when available but is not actively sought AMDS 3
Introduction and Purpose of the GPRM ÚThe Global Price Reporting Mechanism is a database that consolidates information (price, volume, …) of ARV drugs ÚInformation on other drugs (such as TB or malaria drugs) is included when available but is not actively sought AMDS 3
 Background Ú Procurement decision makers should know their potential suppliers and the price they should expect to pay for their products Ú Existing information sources include: • • "Sources and prices" by UNICEF/WHO/MSF/UNAIDS "Untangling the web" by MSF The GFATM Price Reporting Mechanism Indicative prices announced by procurement organisations (IDA) or foundations (CHAI) Ú With exception of the GFATM Price Reporting Mechanism these information tools record quotes by suppliers and don't record volumes transacted. Ú The GFATM Price Reporting Mechanism has real transaction prices and volumes transacted but • Suffers from serious underreporting • GFATM represents only part of all transactions AMDS 4
Background Ú Procurement decision makers should know their potential suppliers and the price they should expect to pay for their products Ú Existing information sources include: • • "Sources and prices" by UNICEF/WHO/MSF/UNAIDS "Untangling the web" by MSF The GFATM Price Reporting Mechanism Indicative prices announced by procurement organisations (IDA) or foundations (CHAI) Ú With exception of the GFATM Price Reporting Mechanism these information tools record quotes by suppliers and don't record volumes transacted. Ú The GFATM Price Reporting Mechanism has real transaction prices and volumes transacted but • Suffers from serious underreporting • GFATM represents only part of all transactions AMDS 4
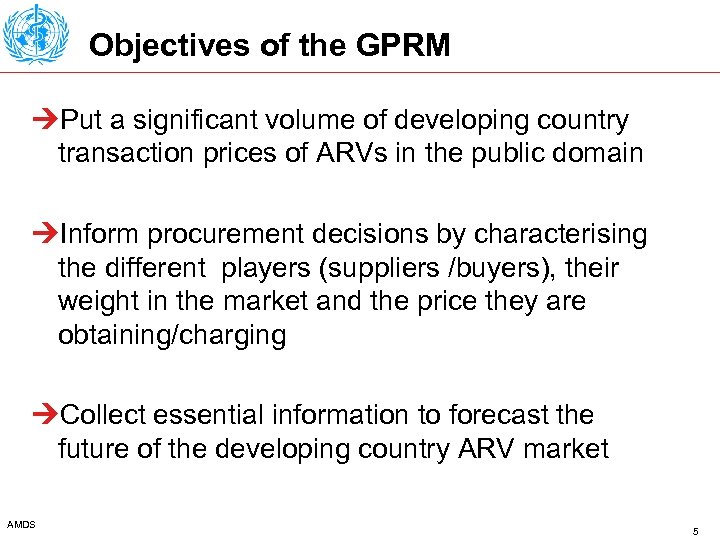 Objectives of the GPRM ÚPut a significant volume of developing country transaction prices of ARVs in the public domain ÚInform procurement decisions by characterising the different players (suppliers /buyers), their weight in the market and the price they are obtaining/charging ÚCollect essential information to forecast the future of the developing country ARV market AMDS 5
Objectives of the GPRM ÚPut a significant volume of developing country transaction prices of ARVs in the public domain ÚInform procurement decisions by characterising the different players (suppliers /buyers), their weight in the market and the price they are obtaining/charging ÚCollect essential information to forecast the future of the developing country ARV market AMDS 5
 Outcomes: 1) Process ÚCooperation of main partners (GFATM, UNICEF, IDA, CPS) secured ÚCooperation of secondary partners (MSH, JSI, Clinton Foundation CHAI, Crown Agents, CHMP) secured and growing ÚNo negative feedback from big pharmaceutical companies, positive feedback from several generic companies AMDS 6
Outcomes: 1) Process ÚCooperation of main partners (GFATM, UNICEF, IDA, CPS) secured ÚCooperation of secondary partners (MSH, JSI, Clinton Foundation CHAI, Crown Agents, CHMP) secured and growing ÚNo negative feedback from big pharmaceutical companies, positive feedback from several generic companies AMDS 6
 Outcomes: 2) Products ÚUser-friendly web based searchable database developed and online since June 2005 ÚThe GPRM is the biggest database of ARVs transaction prices available in the public domain • More than USD 160 million of procurement recorded, or about 1/3 of ARV transactions in developing countries • FTP protocol enabling main partners to upload data automatically operational • Automated report generator operational • Quarterly summary report launched AMDS 7
Outcomes: 2) Products ÚUser-friendly web based searchable database developed and online since June 2005 ÚThe GPRM is the biggest database of ARVs transaction prices available in the public domain • More than USD 160 million of procurement recorded, or about 1/3 of ARV transactions in developing countries • FTP protocol enabling main partners to upload data automatically operational • Automated report generator operational • Quarterly summary report launched AMDS 7
 Global price reporting mechanism AMDS http: //www. who. int/3 by 5/amds/price/hdd/ 8
Global price reporting mechanism AMDS http: //www. who. int/3 by 5/amds/price/hdd/ 8
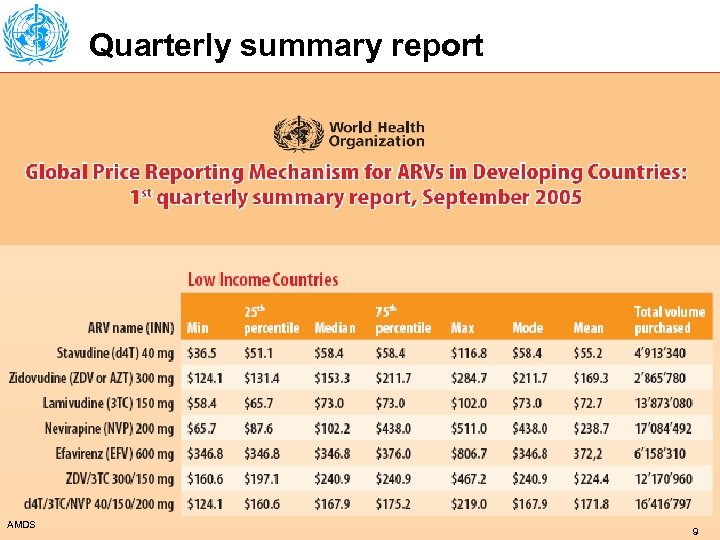 Quarterly summary report AMDS 9
Quarterly summary report AMDS 9
 Strengths ÚProcess Strength • Consolidation of WHO's collaboration with significant partner organizations ÚTechnical strengths • Size, coverage, details and volume of the database • Easy access and report generation AMDS 10
Strengths ÚProcess Strength • Consolidation of WHO's collaboration with significant partner organizations ÚTechnical strengths • Size, coverage, details and volume of the database • Easy access and report generation AMDS 10
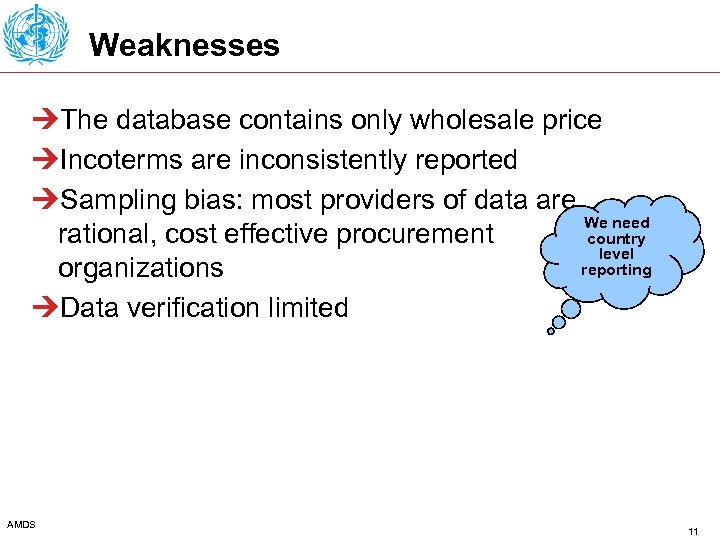 Weaknesses ÚThe database contains only wholesale price ÚIncoterms are inconsistently reported ÚSampling bias: most providers of data are We need rational, cost effective procurement country level reporting organizations ÚData verification limited AMDS 11
Weaknesses ÚThe database contains only wholesale price ÚIncoterms are inconsistently reported ÚSampling bias: most providers of data are We need rational, cost effective procurement country level reporting organizations ÚData verification limited AMDS 11
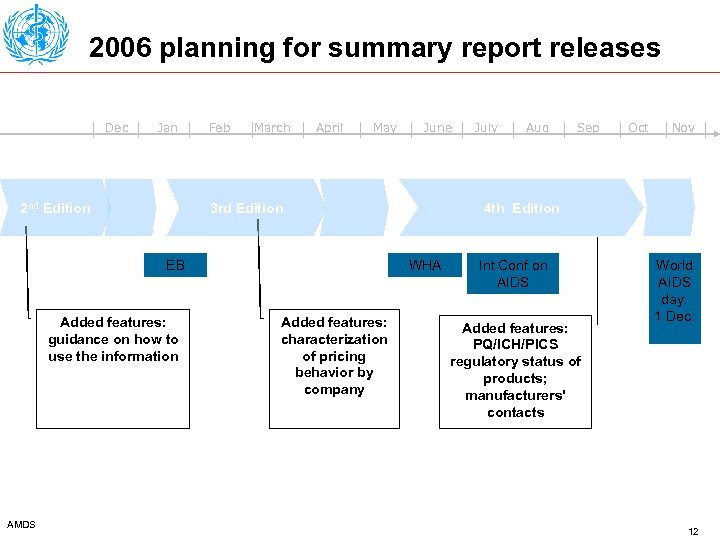 2006 planning for summary report releases Dec Jan 2 nd Edition Feb March April May 3 rd Edition EB Added features: guidance on how to use the information AMDS June Aug Sep Oct Nov 4 th Edition WHA Added features: characterization of pricing behavior by company July Int Conf on AIDS Added features: PQ/ICH/PICS regulatory status of products; manufacturers' contacts World AIDS day: 1 Dec. 12
2006 planning for summary report releases Dec Jan 2 nd Edition Feb March April May 3 rd Edition EB Added features: guidance on how to use the information AMDS June Aug Sep Oct Nov 4 th Edition WHA Added features: characterization of pricing behavior by company July Int Conf on AIDS Added features: PQ/ICH/PICS regulatory status of products; manufacturers' contacts World AIDS day: 1 Dec. 12
 For further information please visit the AMDS website http: //www. who. int/3 by 5/amds/en/ or send an e-mail to AMDS@who. int AMDS 13
For further information please visit the AMDS website http: //www. who. int/3 by 5/amds/en/ or send an e-mail to AMDS@who. int AMDS 13


