b399fefd9e1b9ae7fa60365e4dbee129.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
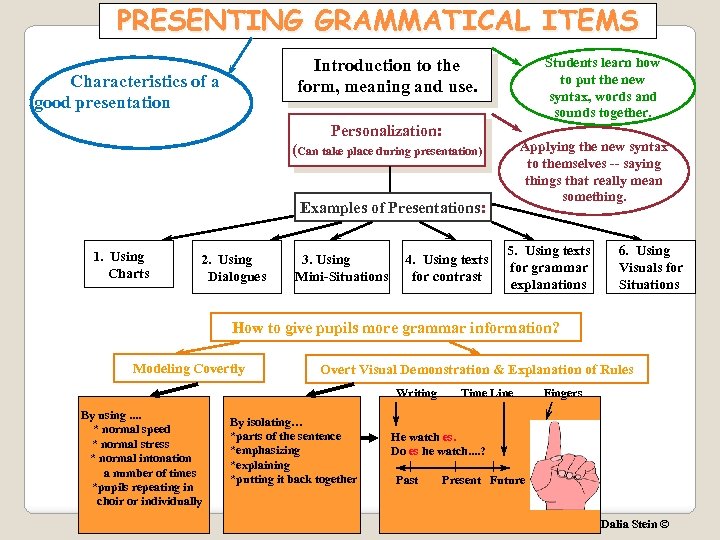 PRESENTING GRAMMATICAL ITEMS Students learn how to put the new syntax, words and sounds together. Introduction to the form, meaning and use. Characteristics of a good presentation Personalization: Applying the new syntax to themselves -- saying things that really mean something. (Can take place during presentation) Examples of Presentations: 1. Using Charts 2. Using Dialogues 3. Using Mini-Situations 4. Using texts for contrast 5. Using texts for grammar explanations 6. Using Visuals for Situations How to give pupils more grammar information? Modeling Covertly Overt Visual Demonstration & Explanation of Rules Writing By using. . * normal speed * normal stress * normal intonation a number of times *pupils repeating in choir or individually By isolating… *parts of the sentence *emphasizing *explaining *putting it back together Time Line Fingers He watch es. Do es he watch. . ? | | | Past Present Future Dalia Stein ©
PRESENTING GRAMMATICAL ITEMS Students learn how to put the new syntax, words and sounds together. Introduction to the form, meaning and use. Characteristics of a good presentation Personalization: Applying the new syntax to themselves -- saying things that really mean something. (Can take place during presentation) Examples of Presentations: 1. Using Charts 2. Using Dialogues 3. Using Mini-Situations 4. Using texts for contrast 5. Using texts for grammar explanations 6. Using Visuals for Situations How to give pupils more grammar information? Modeling Covertly Overt Visual Demonstration & Explanation of Rules Writing By using. . * normal speed * normal stress * normal intonation a number of times *pupils repeating in choir or individually By isolating… *parts of the sentence *emphasizing *explaining *putting it back together Time Line Fingers He watch es. Do es he watch. . ? | | | Past Present Future Dalia Stein ©
 Qualities of a Good Presentation A good presentation should: be clear be efficient be memorable use standard terminology use informative terminology not rely on translation
Qualities of a Good Presentation A good presentation should: be clear be efficient be memorable use standard terminology use informative terminology not rely on translation
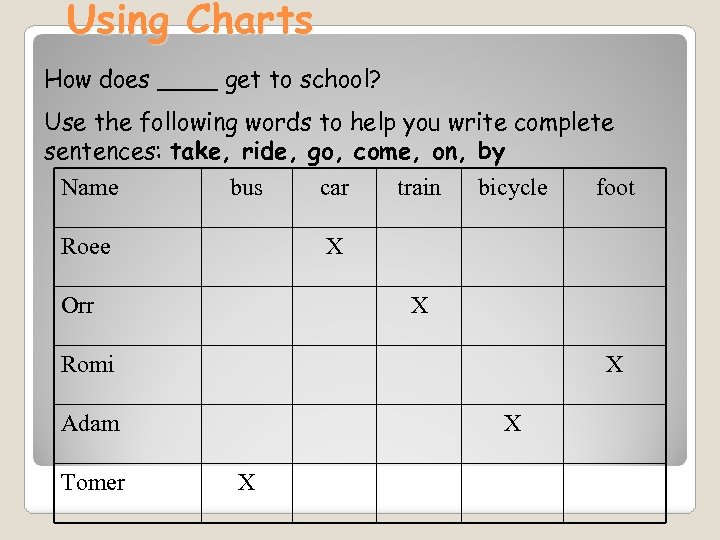 Using Charts How does ____ get to school? Use the following words to help you write complete sentences: take, ride, go, come, on, by Name bus Roee car train bicycle X Orr X Romi X Adam Tomer foot X X
Using Charts How does ____ get to school? Use the following words to help you write complete sentences: take, ride, go, come, on, by Name bus Roee car train bicycle X Orr X Romi X Adam Tomer foot X X
 Using Drawings Present Progressive Be am is are verb + ing
Using Drawings Present Progressive Be am is are verb + ing
 Using Dialogues A: Do you like spaghetti? B: Oh yes. I love it. A: How often do you eat it? B: At least once a week. A: So do I. B: Let’s go have some.
Using Dialogues A: Do you like spaghetti? B: Oh yes. I love it. A: How often do you eat it? B: At least once a week. A: So do I. B: Let’s go have some.
 Mini Situations Where are we going? Why are you going to______? What are you going to see there? What are you going to buy? Who are you going with? In each situation, the teacher can ask questions and the students answer. Then the students follow with questions and answers. You can also supply helpful vocabulary.
Mini Situations Where are we going? Why are you going to______? What are you going to see there? What are you going to buy? Who are you going with? In each situation, the teacher can ask questions and the students answer. Then the students follow with questions and answers. You can also supply helpful vocabulary.
 Using Visuals for Situations To teach the Past Progressive, use “action pictures”. Ask What did the teacher see when she entered the room? Write 4 sentence to describe the picture. Use the Past Progressive. For example: When she entered the room, 4 boys were wrestling
Using Visuals for Situations To teach the Past Progressive, use “action pictures”. Ask What did the teacher see when she entered the room? Write 4 sentence to describe the picture. Use the Past Progressive. For example: When she entered the room, 4 boys were wrestling
 Using Texts for Contrast Every day Adam gets up at 7 am. He brushes his teeth and washes his face. He dresses himself and then eats his cereal with milk. His mother takes him to school by car because his school is too far from his house. Yesterday, Adam got up at 7 a. m. He brushed his teeth and washed his face. He dressed himself and then ate his cereal and milk. His mother took him to school by car because his school was too far from his house.
Using Texts for Contrast Every day Adam gets up at 7 am. He brushes his teeth and washes his face. He dresses himself and then eats his cereal with milk. His mother takes him to school by car because his school is too far from his house. Yesterday, Adam got up at 7 a. m. He brushed his teeth and washed his face. He dressed himself and then ate his cereal and milk. His mother took him to school by car because his school was too far from his house.
 Using Texts for Grammar Explanation The teacher tells the students about a conference for children’s rights that was held in Japan, which students from all over the world attended. Uri, a representative from Israel was also there. This is the text of a conversation he had: Uri: Hello, My name's Uri. What is your name? Yamaguchi : Yamaguchi. How are you? Uri: I am fine, and you? Yamaguchi : Great. Where are you from? Uri: I am from Israel. Uri: Where is that girl from? Is she also from Japan? Yamaguchi : No, she is not from here. She is from Singapore. Uri: How old is she? Yamaguchi : She is twelve years old. Let’s identify the verb in each sentence. List the verbs. Ask if they can make a rule for the use of the verbs: am, is, are Review the rule. Give examples from the text and ask them to give some other ones. Have them copy the rule. Give drilling exercises. Ask them to write a similar dialogue of their own.
Using Texts for Grammar Explanation The teacher tells the students about a conference for children’s rights that was held in Japan, which students from all over the world attended. Uri, a representative from Israel was also there. This is the text of a conversation he had: Uri: Hello, My name's Uri. What is your name? Yamaguchi : Yamaguchi. How are you? Uri: I am fine, and you? Yamaguchi : Great. Where are you from? Uri: I am from Israel. Uri: Where is that girl from? Is she also from Japan? Yamaguchi : No, she is not from here. She is from Singapore. Uri: How old is she? Yamaguchi : She is twelve years old. Let’s identify the verb in each sentence. List the verbs. Ask if they can make a rule for the use of the verbs: am, is, are Review the rule. Give examples from the text and ask them to give some other ones. Have them copy the rule. Give drilling exercises. Ask them to write a similar dialogue of their own.
 Model sentences for oral practice + picture The old man is holding the young baby.
Model sentences for oral practice + picture The old man is holding the young baby.
 Using Demonstration Prepositions of place/direction I'm going to put the food into the plastic dish. Now it’s in the right place. Preposition of time Let’s meet on Monday at 5 o’clock.
Using Demonstration Prepositions of place/direction I'm going to put the food into the plastic dish. Now it’s in the right place. Preposition of time Let’s meet on Monday at 5 o’clock.
 Using Grammatical Explanations We use "some" when the quantity is definite for plural or uncountable in positive formation. I have some new books. She has some information for me. We use “any" when the quantity is definite for plural or uncountable in negative or question formation. . I don’t have any new books. Does she have any information?
Using Grammatical Explanations We use "some" when the quantity is definite for plural or uncountable in positive formation. I have some new books. She has some information for me. We use “any" when the quantity is definite for plural or uncountable in negative or question formation. . I don’t have any new books. Does she have any information?
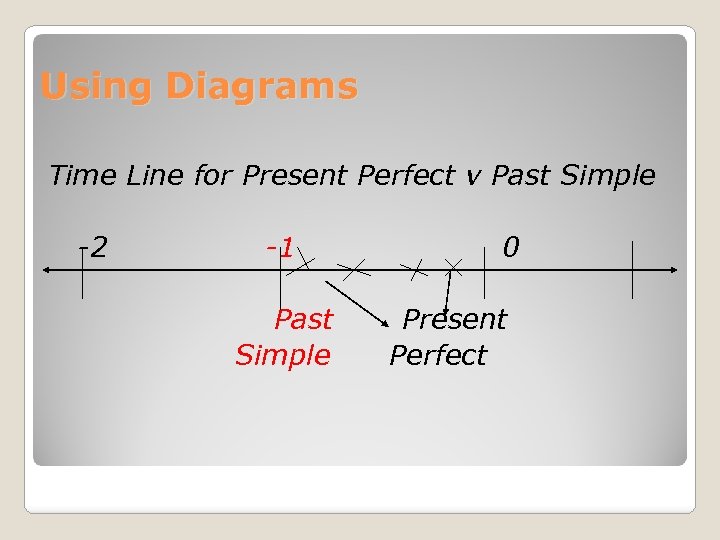 Using Diagrams Time Line for Present Perfect v Past Simple -2 -1 Past Simple 0 Present Perfect
Using Diagrams Time Line for Present Perfect v Past Simple -2 -1 Past Simple 0 Present Perfect
 Using Translation How would you say the following sentences in English? . אני רוצה שתבואו מחר . בבקשה אל תבקש ממני טובות ? מי בא לביה"ס כל יום Did you translate the sentences word for word? Which sentence is similar to Hebrew?
Using Translation How would you say the following sentences in English? . אני רוצה שתבואו מחר . בבקשה אל תבקש ממני טובות ? מי בא לביה"ס כל יום Did you translate the sentences word for word? Which sentence is similar to Hebrew?
 Using Grammatical explanations in student's mother tongue בזמן עבר, צריך להפוך את הפועל לעבר. ניתן לעשות זאת באחת מהדרכים הבאות: א. ע"י הוספת סיומת לפועל: play + ed = played ב. ע"י שינוי הפועל: , go – went, see – saw ג. את הפועל " "be משנים ל: was / were
Using Grammatical explanations in student's mother tongue בזמן עבר, צריך להפוך את הפועל לעבר. ניתן לעשות זאת באחת מהדרכים הבאות: א. ע"י הוספת סיומת לפועל: play + ed = played ב. ע"י שינוי הפועל: , go – went, see – saw ג. את הפועל " "be משנים ל: was / were


