797a48c946fce6b474a459bc35fafc2e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 77

Presented by Angie Song Jon Rogosich Amy Benner

Geography n Russia is in Northern Asia, bordering the Arctic Ocean, between Europe & the North Pacific Ocean n Largest country in terms of area: 17, 075, 200 km 2 n Slightly less than twice that of the United States n Russian border is the world’s longest (57, 792 km) n Natural resources: Oil.
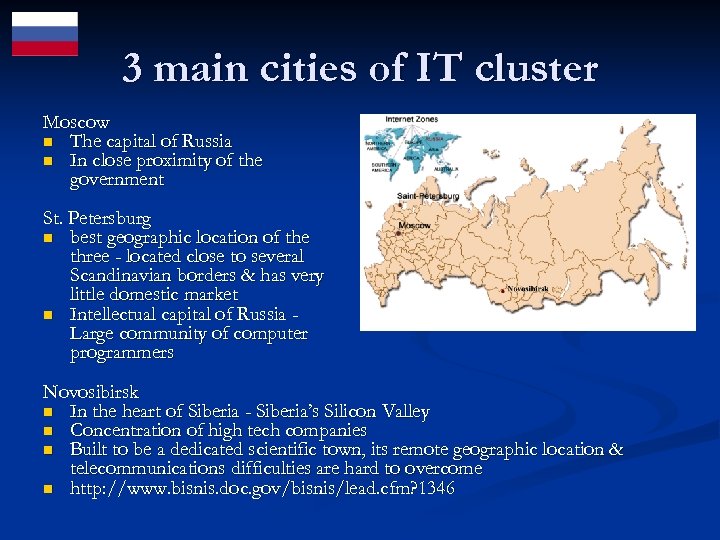
3 main cities of IT cluster Moscow n The capital of Russia n In close proximity of the government St. Petersburg n best geographic location of the three - located close to several Scandinavian borders & has very little domestic market n Intellectual capital of Russia Large community of computer programmers Novosibirsk n In the heart of Siberia - Siberia’s Silicon Valley n Concentration of high tech companies n Built to be a dedicated scientific town, its remote geographic location & telecommunications difficulties are hard to overcome n http: //www. bisnis. doc. gov/bisnis/lead. cfm? 1346

IT Penetration Outside of Major Cities n Tver Region n n n Gross regional product ~ $2 billion 44% percent of the population live below the poverty line Many young persons leave to work/live in Moscow Limited natural resources in area prompted IT Efforts Region's new governor, Dmitry Zelenin, launched an unprecedented campaign to bring in the United Nations and UNICEF to help stimulate the local economy. Recovery Plan: Includes setting up techno parks, plots of land that are specially outfitted, legally cleared and strategically marketed to technology-heavy companies.

Transportation n Roads inadequate in quality & quantity n Railroad system in need of large-scale repair n Major international airports in Moscow and St. Petersburg n Importing products into Russia through Russian customs is often timely & costly

Demographics § Population 146, 001, 176 § § ½ of the United States population Age Structure 0 -14 years: 18% 15 -64 years: 69% 65 years: 13% § Literacy About 98 % of population over age fifteen are literate

Socio-Cultural Picture Languages o o Russian ~100 others spoken Ethnic Groups Russian 81. 5% Tatar 3. 8% Ukranian 3% Chuvash 1. 2% Bashkir 0. 9% Byelorussian 0. 8% Moldovian 0. 7%

Model for Global IT Environment Political System Key MIS Management Issues Multinational Business and IT Strategy

History n n 1917 February Revolution ~ Defeats of the Russian Army in WWI led to rioting in Russian Empire and the overthrow of 300 year old Romanov Dynasty Communists under Lenin seized power and formed USSR (1917) n n New Economic Policy, partial return to market economy, widespread sense of optimism & opportunity Stalin’s brutal rule (1928 -53)strengthened Russian dominance of Soviet Union at a cost of tens of millions of lives Khruschev & Brezhnev followed - economy deteriorated, political climate pessimistic Mikhail Gorbachev & the End of Communism (1991) n Introduced glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) in an attempt to modernize Communism

History of Telecommunications n n During the Soviet period, all means of communications controlled by the state Centralization of communications in Moscow led to development of satellite communications n n Began with launch of Molniya satellite communications system in 1965 In 1980’s, priority given to military and government applications Since the breakup of the Soviet Union, there has been reorganization & modernization of Russia’s communications systems In the mid-1990’s, Russian laws and regulations limited foreign participation in the supply of equipment and services

Government & Politics Government type: federation n Declared Independence from Soviet Union August 24, 1991 n Current constitution adopted December 12, 1993 n Divided into executive, legislative, & judicial branches n

Government Policies n Legislation to strengthen the financial sector n n Deposit Insurance Law n n Tax reforms Currency Regulation and Control Law Little ICT policy prior to Putin’s presidency n Okinawa Charter of the Information Society 2000 n Electronic Russia 2002 -2010

IT Policies n “Electronic Russia 2001 -10 Plan” n $2. 6 Billion program intended to boost ecommerce and internet use in the country n n Phase 2 - $804 M n n Phase 1 - $230 M Phase 3 - $1, 595 M Program addresses 4 key areas in ICT n Regulatory environment and institutional framework n Internet Infrastructure n E-Government n E-Education

IT Policies n “Electronic Russia 2001 -10 Plan” n Timeline: n 2002 – refine the plan, identify necessary feasibility studies and define pilot projects n 2003 -2004 conducted n 2005 begin – Studies and pilot projects – full implementation expected to
Model for Global IT Environment Level of Economic Growth Political System Key MIS Management Issues Multinational Business and IT Strategy

Economy

Economy

Economy
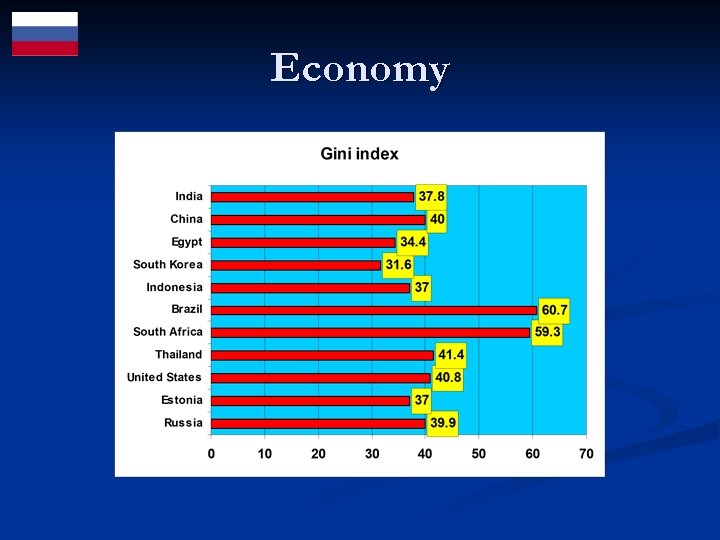
Economy
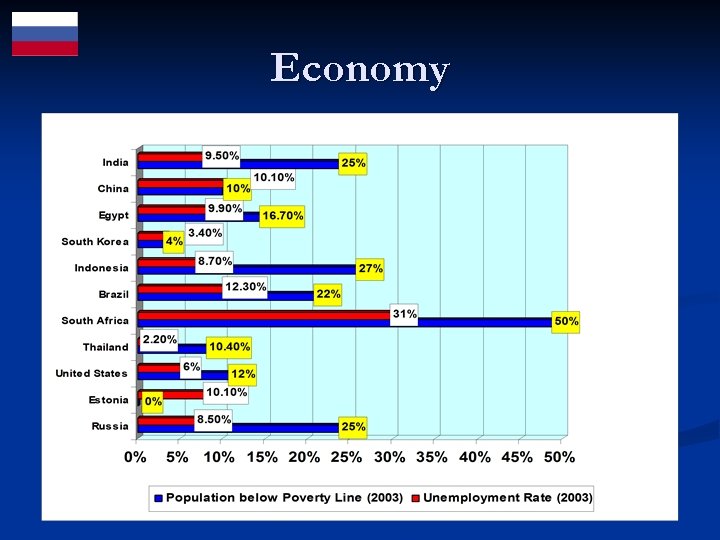
Economy

Financial Crisis of 1998 n n n After shock of the Asian crisis. Interest rates tripled in less than a year Possible Causes: n n n The Asian crisis exposed Russia’s budget deficit was huge at 8. 2 percent of GDP Large short-term foreign debt the government crisis shook investor confidence strikes aggravated the situation. Hurt by a law limiting foreign ownership in Unified Energy System, Russia’s second largest company.

Economy n n Under President Putin (elected 2000) Russia’s economy growing. 5 years of Economic growth ~ due to boom in oil exports n n In 2003, Russia’s real GDP grew by 7. 3%, surpassing average growth rates in all other G 8 countries, and marking the country’s fifth consecutive year of economic expansion. Russia’s economic growth over the last five years has been fueled primarily by energy exports, particularly the boom in Russian oil production and relatively high world oil prices. This type of growth has made the Russian economy dangerously dependent on oil and natural gas exports, and especially vulnerable to fluctuations in world oil prices. The World Bank predicts that the oil and gas sector may have accounted for up to 25% of GDP in 2003—while employing less than 1% of the population. Recent growth due to relatively cheap ruble

Economy n Since Financial Crisis of 1998: n n n n Recipient of Economic aid § § n GDP growth has averaged 6. 5% annually Real fixed capital investments have averaged gains greater than 10% since 2000 Real personal incomes have averaged increases over 12%. Russia’s international financial position has improved since the 1998 financial crisis, with its foreign debt declining from 90% of GDP to approx. 28%. Strong oil export earnings have allowed Russia to increase its foreign reserves from only $12 billion to some $80 billion. Renewed government effort to advance structural reforms, have raised business and investor confidence in Russia's economic prospects. 2001 from US, $979 million (including $750 million in non-proliferation subsidies) 2001 from EU, $200 million EU is Russia’s main trading partner (accounting for more than 50% of overall trade)

Risks for Russian Economy n Capital Flight n n n Cautious Optimism Political Fear? n n n "Clearly, the risk for the Russian economy is capital flight and Russia not continuing with the very healthy investment growth needed to sustain economic growth, " says Christopher Granville, chief strategist at Russian investment bank United Financial Group. “ (Businessweek “A Fear Rises In Russia” Oct 28, 2003) The October 2003 arrest of oil tycoon & ‘richest businessman in Russia” Mikhail Khodorkavsky (CEO and major shareholder of leading Russian oil outfit, Yukos) Many Russian’s felt that Khodorkovsky's arrest (on charges of fraud, tax evasion, and forgery) was politically motivated because he has been a sharp critic of Putin's policies. Distrust, Who’s next? How strictly will punishment be enforced? Gains from oil dependent on world demand price

IT Economy n Growth Trend Since the August 1998 financial crisis, the Russian Internet market has grown by three times, to 3 million permanent users. n Since 2000, the population's incomes have grown by 50%, so food and clothes are no longer the dominate expenditure for the average Russian family, they can invest in owning a computer n A modest government forecast presented by the Economic Development and Trade Ministry shows that the number of Internet-users in Russia will increase by three times in two-three years. (2003) n Russia’s economy would look 3 to 4 times larger if its large underground economy were taken into account n

IT Financing Capital Sources n n Market-Based Commercialization Initiative US Import Export Bank FDI into IT n n FDI (confidence) into Russia grew by ~14% in 2003 n Key investment was British Petroleum’s investment (first multibillion dollar investment in Russia’s history) Few US companies have actually made direct investments in to the Russian IT market. n Sun, Microsoft, Intel

IT Financing cont. n June 2003 extension of cooperation agreement between the Government of Finland the IFC for eastern Europe (International Finance Corporation is the financing arm of the World Bank group) n To provide technical assistance programs in Northwest Russia n Purpose to develop the private sector focusing on partnerships between Finnish and Russian businesses n To develop the local Information and Communication technology industry in NW Russia and to assist Finnish companies to develop relationships with Russian firms.

Current Investors in Russia’s IT n Microsoft n n n Microsoft’s Windows XP Starter Edition Pilot Program to launch early 2005 n Scaled down in cost and program to meet more ‘basic’ computing needs n Pilot programs in Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Brazil & People’s Republic of China, India (areas of software piracy) n Ship low cost PC’s loaded w/ XP Starter Edition to Russia to test whether consumers will pay for low cost computing Offers courses for engineers at companies that buy their technology 2003 sales in Russia grew 80%

Current Investors in Russia’s IT n Intel n n n Sun n n 2001 -2003, sales have doubled Hewlett Packard n n Set up in Russia in 1991. In Dec. 2002 ran pilot tests in Moscow & St. Petersburg where Russians could buy computers with down payments-successfully showed those w/ down payment of $99 sold out of PCs compared to those offered w/ down payment of $199 Implemented “Teach to the Future” program that trained 7, 000 Russian teachers (02’) and 20, 000 in 2003, in using computers and the Web Created labs at Russian universities to familiarize students w/ technology Currently, Russia is Intel’s fasting growing market Become a ‘favorite’ of local businesses b/c they offer tech support regionally and not just major cities IBM, Xerox, SAP

Model for Global IT Environment Level of Economic Growth Political System Culture Key MIS Management Issues Multinational Business and IT Strategy

Hofstede’s Dimensions Russia Power Distance n n 90 40 Attire n n US Suits are very important and formal business attire is expected for all meetings Hierarchy is of great importance Communication n n Only close friends and relatives use first names Appropriate to use just your last name in an introduction to a business acquaintance It is important to learn the titles of those that you are working with Russians appreciate foreigners attempting to speak their language

Hofstede’s Dimensions Russia Uncertainty Avoidance n n US 70 46 In most offices, the addressee opens his or her mail, causing delays. It’s advisable to get straight to the point in business letters and correspondence. Allowing your Russian contact to get to know you personally is essential for successfully conducting business Contracts should be clear, concise, and translated into both Russian and English Contracts without actual handwritten signature considered valueless

Hofstede’s Dimensions Uncertainty Avoidance cont’d n The series of events in Russian history has led to Russians having very little trust n Lack of trust worsened because rapid economical, political, and cultural changes n Low credit card penetration n Many save most of their money in USD under the mattress (Nazarova and Lakaeva, 2000) n Supply chain partners often rely on flea market mode of transaction (inspection, cash payment, trade) n Limits overall economic growth & e-commerce development

Hofstede’s Dimensions Russia Individualism n 91 Russian culture values comfortable situations more than higher salaries, so if a business person is comfortable in a team and the salary is adequate for them, then they are less inclined to try to gain advancement Communism history n n n 42 Teamwork n n US classless society Goal of communism is a non-hierarchical society Severe climatic conditions necessitated collaboration

Culture Implications for IT n Click & mortar shops n n Do well due to poor IT infrastructure in some regions Customers come to a partner store and see product info through an on-line system Appealing because Russians, with high UAI, like to physically see product (displays), able to see a physical store, can easily pay in cash Lock -in values n n n shopping bonus points wide-range of services/one stop shopping ease of use

Culture Implications for IT n It is possible to find most things one needs in Moscow and St. Petersburg. However, finding it is usually a challenge because of smaller stores, poor organization, underdeveloped phone books n n e-Commerce websites which help customers find products e-Commerce websites that provide one location for many products

Hofstede’s Dimensions Russia Masculinity n Mission statements US 37 62 Russians like to have the idea that they are working for a larger purpose, so missions statements usually have less to do with individual firm success and goals than western firms n Relationships takes longer to develop and require more effort than in the West n

Education n n n An important legacy of the Soviet Union is the widespread, yet basic educational system Constitution guarantees right to free preschool, basic general, and secondary vocational education Basic general education mandatory until age fifteen In 1995 about 500 postsecondary schools in operation, including forty-two universities. Private schools and universities emerging in mid-1990 s. Russian IT professionals have minimum 5 years of university-level training

IT and Education n Russia’s schools have one computer for every 500 students One in 50 schools has Internet access In comparison, almost all elementary and secondary schools in the US had Internet access by 2001 Source: June 2001 State Council report

IT Training In a poll of 102 countries, Russia was 76 in computer ownership and 59 in lowest computer utilization n Due to the fact that Russia has a limited amount of computers, there is low IT knowledge among the population n The high level of education among the population and the decline of ISP rates makes the potential for IT competency extremely high n

IT Workforce n Number of IT graduates increasing n n n A study done by Auriga, Inc. revealed that in 2004 the number of Russian IT graduates with Master’s degrees in Computer Science or with software engineering majors will amount to 68, 126 people, up 6. 9% from 2003. Russia’s potential fresh IT labor supply represented by higher education graduates will amount to a total of 225, 831 people by the end of the 20032004 academic year, up 11. 2 % from the 2002 -2003 academic year Success stories of Russian High Tech n n Eli Lily, the leading pharmaceutical company, uses ERP systems designed by a Moscow company Poly. Analyst, one of the most popular programs for data mining in the US was developed by a Moscow company Graffiti was developed by Russian engineers (Para. Graf) Tetris was developed by a Russian software engineer who is now head of computer games department at Microsoft

Technology Picture Telecommunication Infrastructure (million) n Main Phone lines : 35. 5 (2002) n Cell phone usage : 17. 6 Internet Diffusion n Number of websites n Internet users (millions) n PCs per 100 people ð ð 16, 964, 567 6 4. 29 < 5% of Russian households have PCs, and >60% for US ~ 97% software piracy Source: CIA Factbook
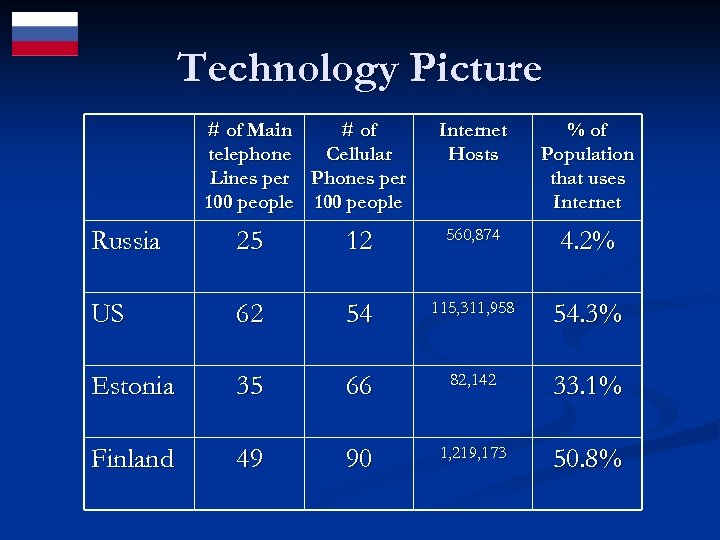
Technology Picture # of Main # of telephone Cellular Lines per Phones per 100 people Internet Hosts % of Population that uses Internet Russia 25 12 560, 874 4. 2% US 62 54 115, 311, 958 54. 3% Estonia 35 66 82, 142 33. 1% Finland 49 90 1, 219, 173 50. 8%

ICT Readiness World Economic Forum’s Annual Global IT Report 2002 -2003 n n n Countries were ranked based on 64 criteria & divided into 3 indexes - environment, readiness and usage Ranked 69 out of 82 (US was 2 nd and Estonia 24 th) n 68 th in terms of market, political, regulatory and infrastructure landscape n 60 th in openness toward new technologies n 78 th in usage rates n 29 th in the number of skilled scientists and engineers Only 3. 7% of Russia’s GDP is invested in Information and Communication Technology, compared to New Zealand’s 13. 6%

Technology Forecast n Forecasts indicate that by 2010: Number of main telephone lines will increase to 33% n Number of cellular subscribers will increase to 15% n The percentage of the population that uses the Internet will increase to 18% n

Telecommunications n Telecommunications infrastructure undersized & largely out of date Inconsistent quality and accessibility n Major population centers (Moscow/ St. Petersburg) well served, however estimated 54, 000 small communities have no telephone access whatsoever (2002) n High demand for internet access n Long delays in allocating a private fixed line fuelled growth in number of cellular phones n 6 million Russians on waiting list for basic phone service (2002) n Cellular market = 35% of Russia’s telecommunication market by value (2002) n

Telecommunications n n Post financial crisis, Russia has spent ~ $2 billion annually on telecommunications equipment. About $40 billion needed over the next decade to invest in telecommunication networks to remedy past deficiencies & meet new subscriber needs (Country Commerce) Approximately 60% of telecommunication equipment imported since domestic products not price competitive Cell phone use n Moscow near saturation (at 30%). National penetration rate of cell phone use still low at 5. 4%

Internet Use n n Slow to take off n Poor telecommunications infrastructure n Low computer use in households (less than 5% of households have a PC) n Lack of payments systems n High fees Demand for internet access outstripping the domestic supply of high-seed PCs Security & trust issues Minimal broadband infrastructure

Technology Forecast n By 2010: Number of main telephone lines will increase to 33% n Number of cellular subscribers will increase to 15% n The percentage of the population that uses the Internet will increase to 18% n

E-Commerce Picture n n Currently small specialized companies dominate (DVDs, books, software, Prepaid phone cards) Also several e-commerce companies in the grocery trade in Moscow & St. Petersburg ~85% of online sales are paid in cash Online debit- and credit-card transactions remain limited

E-Commerce Picture Barriers to E-commerce n n n n Weak legal framework and legislation Difficult to obtain PCs for households & small businesses Weak telecommunications infrastructure, especially outside major cities Lacks reliable, affordable Internet access Electronic payment systems not widely available Lack of stable, trustworthy banking sector to back electronic payment systems Poor penetration of credit card use

E-Commerce Picture Factors to Stimulate E-Commerce Russians are literate and well educated n Intellectual property laws among the best n Ready market for web-based retail sites outside main cities n

Websites n n n Russian Information Agency Personal Classifieds Moscow Lifestyle - The Russia Journal Demos-Internet n Internet Service Provider n One of the oldest network companies Golden Telecom, Inc. n n Largest independent facilities-based provider of integrated telecommunications and internet services to businesses and other highusage customers and telecommunications operators http: //www. relcom. ru/ n Internet service provider in Moscow & St. Petersburg

Websites n http: //www. Tenderonline. ru n companies post business proposals online n organizations can participate online in contract venders as suppliers or customers n http: //www. xxl. ru n leading Internet shopping site n http: //www. Cyberplat. ru n leading Russian online payments system n Paypal vs. Cyberplat

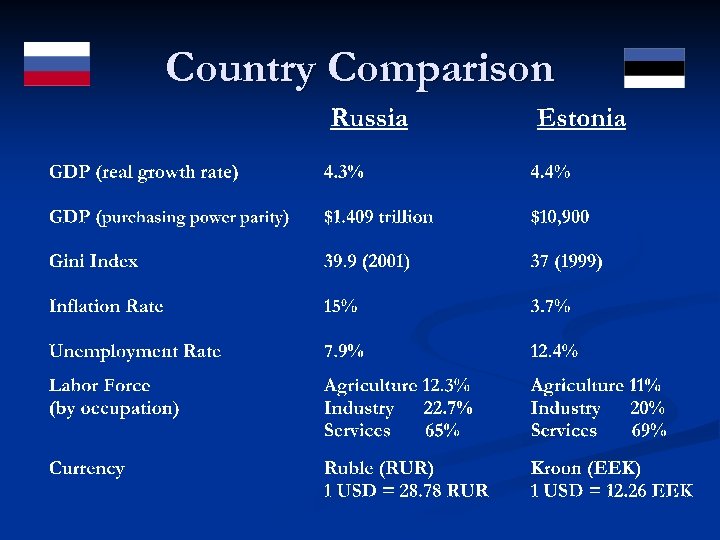
Country Comparison Russia and Estonia

Estonia Background n n n Estonia attained independence in 1918 after centuries of Danish, Swedish, German, and Russian rule Estonia was forced to incorporate into the USSR in 1940 In 1991 Estonia regained its freedom with the collapse of the Soviet Union After the last Russian troops left in 1994, Estonia has been free to promote economic and political ties with Western Europe Joined both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004

Estonia Background n n n Patterned itself after its developed neighbors, such as Finland Created Technology Parks in order to accelerate scientific research to move the economy forward. Estonia created the first Technology Park in 1992, Tartu Science Park n Research that is being undertaken by the resident companies concerns laser technologies, electronics, & software development. Tallinn Technical University Innovation Centre Foundation n Major areas of research are software development, internet services, electronics, and mechanical engineering. In addition, Estonian government is creating business incubators to improve R&D development, develop businesses in underdeveloped regions, and support development of technology-based entrepreneurship

Country Comparison
Country Comparison

Country Comparison Source: 2003 CIA Factbook

SWOT Analysis Russia’s IT

IT Strengths n n n n Proximity of St. Petersburg to Finland Well educated & literate employee base(especially in science, engineering and technology) Large state technological universities encourage R&D and IT Competitive wages for outsourcing Developing Russian-language Web content Strong supply of Current investors Distribution system is expanding from just Moscow & St. Petersburg, regional warehouses being set up and secure transportation being arranged

IT Strengths n n n Russian government is drafting a federal policy on internet use and creating a legal framework to stimulate e-commerce development Russia has started privatization and joint ventures in the telecommunications industry Potential of B 2 B arrangements & emergence of B 2 C in major cities Ready market for web-based retail sites Large potential for growth

IT Weaknesses n n n Software piracy Poor infrastructure Low PC-penetration n n n 30 million PC’s in Russia today (1/5 of population) 2003 data Lack of electronic payments system Insufficient nationwide delivery mode Poor image Lack of English-language skills Low level of average disposable income, low consumer purchasing power (but rising)

IT Weaknesses n Expensive~ Make it affordable n n Inconsistent government policies Government driven vs. business driven development n n n The average computer and access to the Internet costs an average of 75% of average monthly income Outside of Moscow, monthly income levels rose 29. 5% between 02 -03’ to $155. Government Selective Entrepreneurs, thinkers, not encouraged (Hoefstede’s culture—risk takers? Immature business and project-management skills Lack competitiveness: Current lack of capable and modern manufacturing facilities for (majority 10+ years old) Unavailable investors and financial assistance internally

IT Opportunities in Russia n n n Basic tech products: super servers, printers, computer peripherals aren’t produced domestically n Imports of servers grew 80% in 2003 For wireless or landline phone networks isn’t produced domestically ERP software (enterprise resource planning) For US suppliers and manufactures of electronic components and electronic manufacturing equipment Equipment manufacturers could form joint ventures w/ Russian manufacturers in order to obtain status as a domestic manufacturer and meet the Ministry of Communications requirements Decrease digital divide

IT Investment Opportunities n At this point, B 2 B prospects are much more appealing than B 2 C because: n n n weak consumer purchasing power low use of credit cards lack of trust in the banking system poor delivery system Major end users for IT are government, educational institutions and computer manufacturers

IT Investment Opportunities n Software Market - Outsourcing n n Russian specialists have proved to be skilled innovators and developers in the field of software development Software development has grown 40% over the past 3 years (Kozuharov) Outsourcing to Russia can cost 1/5 of labor costs in the US, even considering the added expense of managing an offshore operation (Horowitz) How does an investment in Russia compare with a similar investment in China or India? n Political advantage over China n Geographical advantage over India

IT Investment Opportunities n Software Market - Production n n n Russia is generally well known for computer programming Software Market not as established as in other western markets Not as profitable as hardware supplies because of high rate of piracy However, increasing interest in brand-named, powerful PCs should improve the software market Market for domestic software development is limited to accounting software Market for software import is legal software for Russian banks General application solutions, systems software, and hardware supporting software also in demand

IT Investment Opportunities n Hardware Production Customs duty on imported hardware & peripherals is 10% n Domestic computer hardware market dominated by imports from US companies n In the past few years: n n computer manufacturing & assembly up 20 -30% n infrastructure market up 30% n IT industry as a whole up 30 -40%

IT Investment Opportunities n Cellular Phone Production n n Opportunity exists due to the state of the fixed line infrastructure Cell-phone use in Moscow and St Petersburg is nearly as prevalent as in New York City In 2002, Russians bought 1 million wireless phones per month Mobile-communications hardware is among the most in demand in Russia according to IDC Officials have welcomed foreign participation in cellular phone production

IT Threats in Russia n n n n High installation costs Complex regulatory environment difficult to enter Perceived as risky place to do business (lingering negative imagecommunists) Negative Internal image- until 1990 s entrepreneurs considered crooks Global demand for oil drops~hurt flourishing economy and decrease available capital to invest Software piracy huge problem (still 87%+ of corporations using pirated versions of Windows operating systems Poor transportation infrastructure makes deliveries slow & expensive

IT Threats in Russia cont. n n n Until government makes export laws easier, domestic production of high tech components isn’t profitable The wide distribution of income requires a market differentiation strategy different from that in the West- more investment required to know the target market Russia’s lack of operational and financial transparency hinders FDI Russian telecommunications equipment and services market not easy to enter-Russia doesn’t recognize foreign test data Investors may be deterred b/c obtaining approvals and licensing can be a long & costly process Russia has no $

Global IT Value Chain SUPPLIERS Value Adding Investments Software Outsourcing OPERATIONS BUYER Value Multiplying Investments Value Delivery Investments R&D centers for hardware development Sales Offices for Banking software, Brandname computers, Cell phones Cell phone manufacturing

Recommendations n Russia is a good choice/location… n n n to outsource software * for a software sales office selling n Banking software n General application solutions, systems software, & hardware supporting applications for a direct investment into accounting software market for a hardware sales office selling brand-named computers with pre-installed versions of popular software for a R&D center for hardware development for a sales office or manufacturing of cellular phones

Questions/Comments?

References n n n n Jason Horowitz, Manager, Russia Program Office, Sun Microsystems, Incs. , personal communication, June 2001. Fey, Carl and Rachel Doern. e. Commerce in Russia Retrieved October 12, 2004 from http: //www. bdforum. org/download. asp? id=10 “Development of information-communication technologies in Russia in the process of setting up of the Global Information Society” United Nations Conference on Trade and Development Science & Technology for Development Network. http: //r 0. unctad. org/stdev/un/russia. htm “E-Russia Federal Program” New Economy Foundation. Dec 28, 2002. http: //www. neweco. ru Skiden, Ulla. “E-Russia Program to put the Country Online” Center for Digital Government. Jul 2003. Lakaeva, Irina and Inna Nazarova. “Overview of Electronic Commerce in Russia” BISNIS and the US Commercial Service. Moscow: Aug 30, 2000. Lakaeva, Irina. “Trends in the Russian IT Market” US Commercial Service Moscow. 2002. www. buyusa. gov/russia/en/ Kozuharov, Simone (2004, July). Russia to Cash In on IT Growth. The Saint Petersburg Times. Retrieved from http: //www. outsourcing-russia. com/kb/docs/russia/r 06074 -01. html.
797a48c946fce6b474a459bc35fafc2e.ppt