Presentations.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Presentations What makes a good presentation?
Presentations What makes a good presentation?
 Presentation is a talk or report by a company executive that introduces a new product or service to an audience of specialists in the field or to potential investors. The speaker-audience interaction takes place: the representative of a business organization talks about a certain product or service; the audience perceives and, if need be, responds by asking questions, requesting information or making comments. Presentation is an act of public speaking.
Presentation is a talk or report by a company executive that introduces a new product or service to an audience of specialists in the field or to potential investors. The speaker-audience interaction takes place: the representative of a business organization talks about a certain product or service; the audience perceives and, if need be, responds by asking questions, requesting information or making comments. Presentation is an act of public speaking.
 Presentations Informative (the central part includes descriptions, analysis, information and facts) Persuasive (the main body consists in building arguments and talking through options)
Presentations Informative (the central part includes descriptions, analysis, information and facts) Persuasive (the main body consists in building arguments and talking through options)
 Main aspects of a presentation § Delivery § Content § Use of visual aids § Body language
Main aspects of a presentation § Delivery § Content § Use of visual aids § Body language
 How to deliver a presentation Think about: § Preparing a presentation § Delivering a presentation § Visuals § Ending a presentation § Dealing with questions
How to deliver a presentation Think about: § Preparing a presentation § Delivering a presentation § Visuals § Ending a presentation § Dealing with questions
 Preparing a presentation “It usually takes more than three weeks to prepare a good impromptu speech” Mark Twain
Preparing a presentation “It usually takes more than three weeks to prepare a good impromptu speech” Mark Twain
 Planning • Know your subject. • Develop a theme. • List the key concepts and points to convey. • Begin to think about ways of illustrating the key points. • Max of 1 slide per minute, 4 key points in 45 minute presentation.
Planning • Know your subject. • Develop a theme. • List the key concepts and points to convey. • Begin to think about ways of illustrating the key points. • Max of 1 slide per minute, 4 key points in 45 minute presentation.
 Structure Topic: Aim: Main points: 1. 2. 3. Main message (conclusion): Benefit to audience:
Structure Topic: Aim: Main points: 1. 2. 3. Main message (conclusion): Benefit to audience:
 Delivering a presentation § Remember to face the audience and make eye contact with them. § Speak clearly and fairly slowly. § Use simple language with short sentences. § Emphasize key words and pause briefly between points. § Repeat key numbers or write them on a visual. § Involve the audience by asking a question from time to time.
Delivering a presentation § Remember to face the audience and make eye contact with them. § Speak clearly and fairly slowly. § Use simple language with short sentences. § Emphasize key words and pause briefly between points. § Repeat key numbers or write them on a visual. § Involve the audience by asking a question from time to time.
 Language for presentations § Signposting (typical signposts: So, Right then, let’s start; To conclude, I’d just like to go back to…) § Emphasizing (e. g. use of lexis like really, absolutely, extremely) § Rhetorical questions (What does this mean? Let me tell you…) § Metaphors § Anecdotes
Language for presentations § Signposting (typical signposts: So, Right then, let’s start; To conclude, I’d just like to go back to…) § Emphasizing (e. g. use of lexis like really, absolutely, extremely) § Rhetorical questions (What does this mean? Let me tell you…) § Metaphors § Anecdotes
 Talk, don’t read! You have several choices for how you deliver your speech Memorizing the Speech + allows eye contact - difficult for long speeches - room for precision errors - no room for improvising Reading From a Text + ensures precision - does not sound natural - no room for improvising - hinders eye contact Winging It + sounds natural - has much room for error Speaking From Slides + ensures organization + allows eye contact + allows improvising - some room for error
Talk, don’t read! You have several choices for how you deliver your speech Memorizing the Speech + allows eye contact - difficult for long speeches - room for precision errors - no room for improvising Reading From a Text + ensures precision - does not sound natural - no room for improvising - hinders eye contact Winging It + sounds natural - has much room for error Speaking From Slides + ensures organization + allows eye contact + allows improvising - some room for error
 Visuals Recurrent patterns: Have a look at this. /Take a look at this. As you can see, here… and here… Let’s take a closer look for a moment at… I’d like us to look at … in more detail. As you can see… I’d also like to draw your attention to… If you look at it more closely, you’ll notice… The graph we’re looking at very clearly demonstrates…
Visuals Recurrent patterns: Have a look at this. /Take a look at this. As you can see, here… and here… Let’s take a closer look for a moment at… I’d like us to look at … in more detail. As you can see… I’d also like to draw your attention to… If you look at it more closely, you’ll notice… The graph we’re looking at very clearly demonstrates…
 § Aids (materials, OHP, laptop, pointer, flipchart) § Rapport (eye contact, body language, mannerisms, humour) § Delivery (clarity, pronunciation, stress, pauses, intonation) § Language (accuracy, appropriacy, simplicity) vocabulary,
§ Aids (materials, OHP, laptop, pointer, flipchart) § Rapport (eye contact, body language, mannerisms, humour) § Delivery (clarity, pronunciation, stress, pauses, intonation) § Language (accuracy, appropriacy, simplicity) vocabulary,
 Summary § Before you start preparing your talk – Know your audience and select the message § Structure and preparation of slides – Select key points – Organize content – Keep story simple – Use visual aids § Rehearse, rehearse § Giving the talk – Grab and hold audience’s attention
Summary § Before you start preparing your talk – Know your audience and select the message § Structure and preparation of slides – Select key points – Organize content – Keep story simple – Use visual aids § Rehearse, rehearse § Giving the talk – Grab and hold audience’s attention
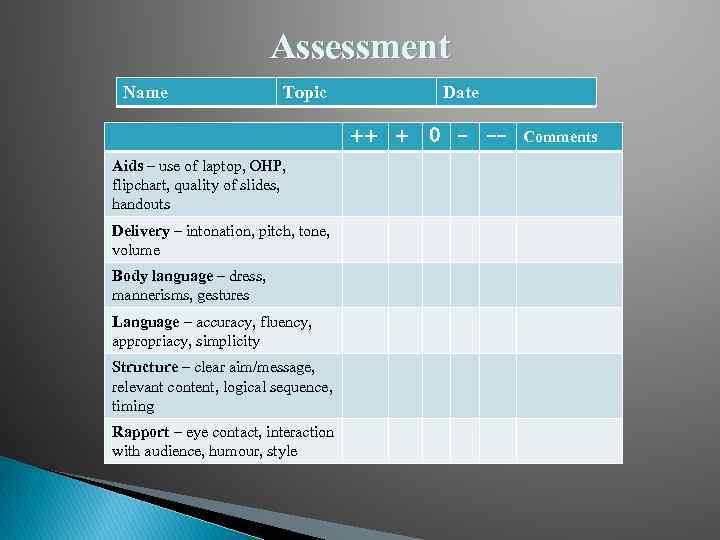 Assessment Name Topic Date ++ + Aids – use of laptop, OHP, flipchart, quality of slides, handouts Delivery – intonation, pitch, tone, volume Body language – dress, mannerisms, gestures Language – accuracy, fluency, appropriacy, simplicity Structure – clear aim/message, relevant content, logical sequence, timing Rapport – eye contact, interaction with audience, humour, style 0 - -- Comments
Assessment Name Topic Date ++ + Aids – use of laptop, OHP, flipchart, quality of slides, handouts Delivery – intonation, pitch, tone, volume Body language – dress, mannerisms, gestures Language – accuracy, fluency, appropriacy, simplicity Structure – clear aim/message, relevant content, logical sequence, timing Rapport – eye contact, interaction with audience, humour, style 0 - -- Comments


