Presentations Skills MAMA.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Presentations Skills Dr. Mitali Mittra 2012
Presentations Skills Dr. Mitali Mittra 2012
 Definitions Presentation “Something set forth to an audience for the attention of the mind “ Effective “…producing a desired result” Source: http: //www. merriam-webster. com
Definitions Presentation “Something set forth to an audience for the attention of the mind “ Effective “…producing a desired result” Source: http: //www. merriam-webster. com
 Agenda Introduction Planning Your Presentation The Presentation Sequence Creating Effective Visual Aids Presentation Techniques Practice
Agenda Introduction Planning Your Presentation The Presentation Sequence Creating Effective Visual Aids Presentation Techniques Practice
 Presentation Skills Insight "There always three speeches, for every one you actually gave. The one you practiced, the one you gave, and the one you wish you gave. " -- Dale Carnegie “It takes one hour of preparation for each minute of presentation time. " -- Wayne Burgraff
Presentation Skills Insight "There always three speeches, for every one you actually gave. The one you practiced, the one you gave, and the one you wish you gave. " -- Dale Carnegie “It takes one hour of preparation for each minute of presentation time. " -- Wayne Burgraff
 Important Points Impossible to turn into an excellent presenter over night First step is tough and then it is rewarding Rehearse! And Rehearse
Important Points Impossible to turn into an excellent presenter over night First step is tough and then it is rewarding Rehearse! And Rehearse
 Overcoming Fear “Of all the liars in the world, sometimes the worst are your own fears”. - Rudyard Kipling THE FACTS: Shaking hands, dry throat, excessive sweating, memory loss, nausea, and knocking knees NORMAL REACTION!
Overcoming Fear “Of all the liars in the world, sometimes the worst are your own fears”. - Rudyard Kipling THE FACTS: Shaking hands, dry throat, excessive sweating, memory loss, nausea, and knocking knees NORMAL REACTION!
 Overcoming Fear ●Control the symptoms ●Exercise ●On Stage- Slow down, Speak Up, Stop Bellowing
Overcoming Fear ●Control the symptoms ●Exercise ●On Stage- Slow down, Speak Up, Stop Bellowing
 Overcoming Nerves ●Positive Self-talk ●Believe in audience’s goodwill ●Believe in what you are saying ● Prepare thoroughly ● Rehearse
Overcoming Nerves ●Positive Self-talk ●Believe in audience’s goodwill ●Believe in what you are saying ● Prepare thoroughly ● Rehearse
 Developing The Attitude Remember that you know your subject Know your material well. Be the expert. Your primary duty is Understand your audience needs Prepare the message and supporting materials - deliver your message clearly and powerfuly
Developing The Attitude Remember that you know your subject Know your material well. Be the expert. Your primary duty is Understand your audience needs Prepare the message and supporting materials - deliver your message clearly and powerfuly
 Developing The Attitude Podium panic is normal, and be open about it Practice your presentation, do pilot test Get the audience to participate Establish a rapport by using names & eye contact Establish & check the equipment
Developing The Attitude Podium panic is normal, and be open about it Practice your presentation, do pilot test Get the audience to participate Establish a rapport by using names & eye contact Establish & check the equipment
 Nervous Presentation WATCH!
Nervous Presentation WATCH!
 General purposes of a presentation INFORM TEACH TRAIN MOTIVATE
General purposes of a presentation INFORM TEACH TRAIN MOTIVATE
 4 Types of Presentations More Persuasive Sales Explanatory Instructional Oral Report More Detailed
4 Types of Presentations More Persuasive Sales Explanatory Instructional Oral Report More Detailed
 4 Types of Presentations I Sales: to sell an idea or suggestion to clients, upper management, coworkers or employees. To persuade for an action or belief Explanatory: To familiarize, give an overall perspective or identify new developments. Should offer the audience new or renewed information&understanding
4 Types of Presentations I Sales: to sell an idea or suggestion to clients, upper management, coworkers or employees. To persuade for an action or belief Explanatory: To familiarize, give an overall perspective or identify new developments. Should offer the audience new or renewed information&understanding
 4 Types of Presentations II Instructional: When you want to teach others how to use something like a new procedure or a piece of hardware. Needs persuasion, detail & audience participation Oral Report: Bring the audience up to date on something with which they are already familiar. Focus on facts, figures &details involve little persuasive efforts.
4 Types of Presentations II Instructional: When you want to teach others how to use something like a new procedure or a piece of hardware. Needs persuasion, detail & audience participation Oral Report: Bring the audience up to date on something with which they are already familiar. Focus on facts, figures &details involve little persuasive efforts.
 Presentation Style VVB 7% Verbal Content
Presentation Style VVB 7% Verbal Content
 Elements of Presentation Style Vocal Techniques Loudness Pitch Rate Pause Deviations From the Norm for Emphasis
Elements of Presentation Style Vocal Techniques Loudness Pitch Rate Pause Deviations From the Norm for Emphasis
 Elements of Presentation Style Body Language n Eye Contact, Gestures, Posture Use of Space § § Can Everyone See You? Movement
Elements of Presentation Style Body Language n Eye Contact, Gestures, Posture Use of Space § § Can Everyone See You? Movement
 Build Rapport Relationship, especially one of mutual trust or emotional affinity. Listeners who trust you and feel that you care Start Before You Begin Mingle; Learn Names Opportunity to reinforce or correct audience assessment Good First Impression People Listen To People They Like
Build Rapport Relationship, especially one of mutual trust or emotional affinity. Listeners who trust you and feel that you care Start Before You Begin Mingle; Learn Names Opportunity to reinforce or correct audience assessment Good First Impression People Listen To People They Like
 Body Language NO-NO’s Lean on or grip the podium Rock or sway in place Stand immobile Use a single gesture repeatedly Examine or bite your fingernails
Body Language NO-NO’s Lean on or grip the podium Rock or sway in place Stand immobile Use a single gesture repeatedly Examine or bite your fingernails
 Body Language NO-NO’s Cross your arms in front of your chest Use obviously practiced or stilted gestures Chew gum or eat candy Click or tap your pen, pencil or pointer
Body Language NO-NO’s Cross your arms in front of your chest Use obviously practiced or stilted gestures Chew gum or eat candy Click or tap your pen, pencil or pointer
 Eye Contact Never let the listeners out of your sight. Looking them in the eye makes them feel that they are influencing what you say. Eye contact allows the presentation to approximate conversation—the audience feels much more involved.
Eye Contact Never let the listeners out of your sight. Looking them in the eye makes them feel that they are influencing what you say. Eye contact allows the presentation to approximate conversation—the audience feels much more involved.
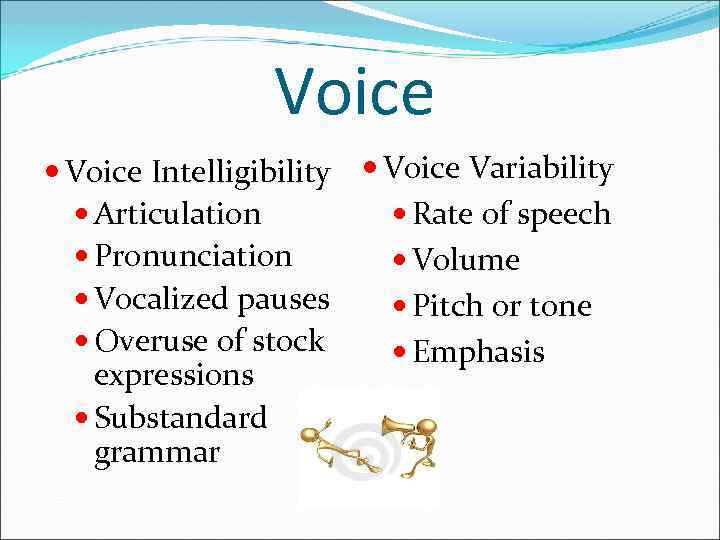 Voice Intelligibility Voice Variability Rate of speech Articulation Pronunciation Volume Vocalized pauses Pitch or tone Overuse of stock Emphasis expressions Substandard grammar
Voice Intelligibility Voice Variability Rate of speech Articulation Pronunciation Volume Vocalized pauses Pitch or tone Overuse of stock Emphasis expressions Substandard grammar
 Bad Communication
Bad Communication
 Visual Aids n n n n Power. Point Slides Overhead Trans Graphs/Charts Pictures Films/Video Flip Charts Sketches
Visual Aids n n n n Power. Point Slides Overhead Trans Graphs/Charts Pictures Films/Video Flip Charts Sketches
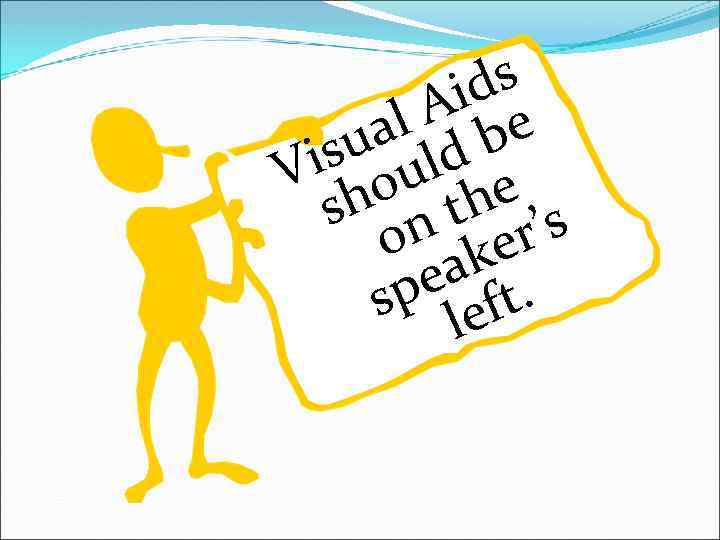 s id l A be ua ld is u V o h the s s n o ker’ ea t. sp lef
s id l A be ua ld is u V o h the s s n o ker’ ea t. sp lef
 Why to Use Visual Aids Visual aids support your ideas Visual aids add array to your presentation and the audience remember them Visual aids help demonstrate complex thoughts or concepts clearly
Why to Use Visual Aids Visual aids support your ideas Visual aids add array to your presentation and the audience remember them Visual aids help demonstrate complex thoughts or concepts clearly

 Golden Rule AVOID argument with your audience.
Golden Rule AVOID argument with your audience.
 Dealing with a questions Make an eye contact with the questioner. Don’t be bias but be attentive. Carefully listen to the question. Pause before you respond. Reply the questioner
Dealing with a questions Make an eye contact with the questioner. Don’t be bias but be attentive. Carefully listen to the question. Pause before you respond. Reply the questioner
 Easy as A B C “I can’t Answer that question Because …, but I Can tell you…”
Easy as A B C “I can’t Answer that question Because …, but I Can tell you…”
 GROUP PRESENTATIONS
GROUP PRESENTATIONS
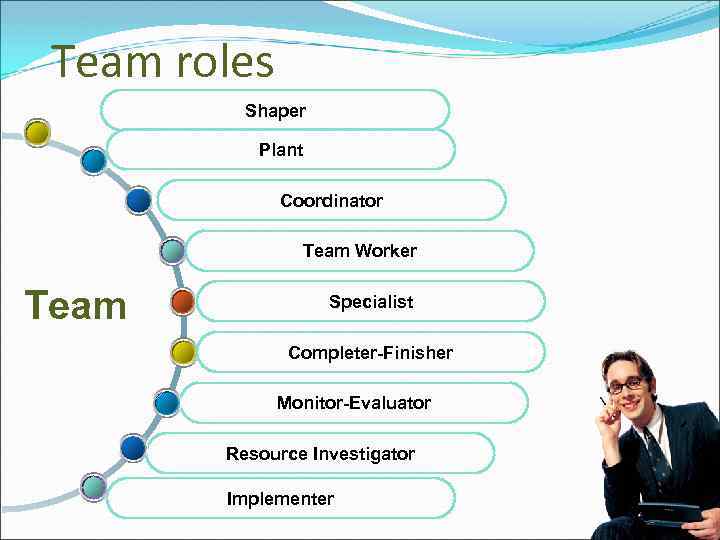 Team roles Shaper Plant Coordinator Team Worker Team Specialist Completer-Finisher Monitor-Evaluator Resource Investigator Implementer
Team roles Shaper Plant Coordinator Team Worker Team Specialist Completer-Finisher Monitor-Evaluator Resource Investigator Implementer
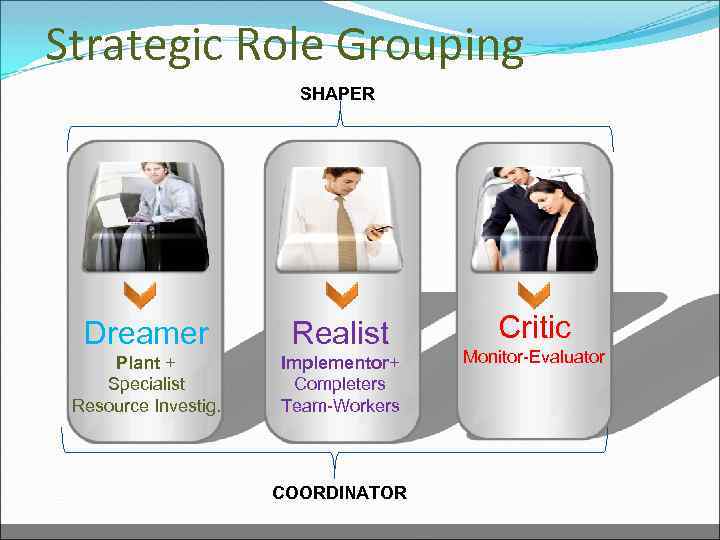 Strategic Role Grouping SHAPER Dreamer Realist Plant + Specialist Resource Investig. Implementor+ Completers Team-Workers COORDINATOR Critic Monitor-Evaluator
Strategic Role Grouping SHAPER Dreamer Realist Plant + Specialist Resource Investig. Implementor+ Completers Team-Workers COORDINATOR Critic Monitor-Evaluator
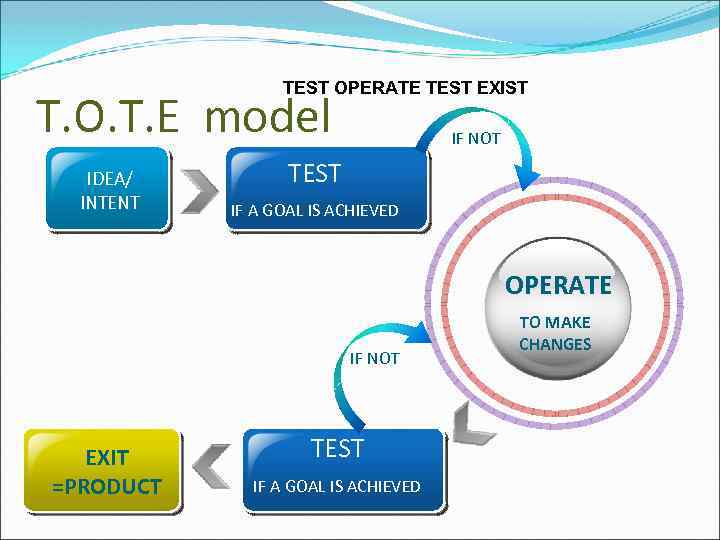 TEST OPERATE TEST EXIST T. O. T. E model IDEA/ INTENT IF NOT TEST IF A GOAL IS ACHIEVED OPERATE IF NOT EXIT =PRODUCT TEST IF A GOAL IS ACHIEVED TO MAKE CHANGES
TEST OPERATE TEST EXIST T. O. T. E model IDEA/ INTENT IF NOT TEST IF A GOAL IS ACHIEVED OPERATE IF NOT EXIT =PRODUCT TEST IF A GOAL IS ACHIEVED TO MAKE CHANGES
 Summary Dreamer Visionary Sees a big picture Believes anything is possible Realist Action oriented Short term steps Considers alternatives Critic Logical Avoids problems by finding what is missing Asks “What if” problems occur
Summary Dreamer Visionary Sees a big picture Believes anything is possible Realist Action oriented Short term steps Considers alternatives Critic Logical Avoids problems by finding what is missing Asks “What if” problems occur
 Group Exercise Break into your subgroups and identify your Dreamers, Realists and Critics Make a 10 min presentation that would cover the problem of the Moscow traffic, i. e. • The origin of the traffic • The current state of the traffic • Proposed methods to tackle the traffic with the given budget of 100 bln. USD One dreamer, one realist and one critic are to present their parts
Group Exercise Break into your subgroups and identify your Dreamers, Realists and Critics Make a 10 min presentation that would cover the problem of the Moscow traffic, i. e. • The origin of the traffic • The current state of the traffic • Proposed methods to tackle the traffic with the given budget of 100 bln. USD One dreamer, one realist and one critic are to present their parts
 Don’ts in Presentation
Don’ts in Presentation
 Remember Eight Easy Steps Activate the vital Triangle Create A Supporting Mindset Set The Scene For Interaction Look Authoritative Familiarise Yourself With Your Material Prepare Your Visuals Organise your Material Get Information
Remember Eight Easy Steps Activate the vital Triangle Create A Supporting Mindset Set The Scene For Interaction Look Authoritative Familiarise Yourself With Your Material Prepare Your Visuals Organise your Material Get Information
 Keep it. Short and. Simple
Keep it. Short and. Simple
 THANKS & BEST OF LUCK
THANKS & BEST OF LUCK


