0908b3dbc636b15bbabead0f2d4d9bf3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Presentation to the Health Portfolio Committee NHLS Annual Report 2010/2011 Sagie Pillay CEO Adv Sesi Baloyi Board Chair Nov 9, 2011 1
Presentation to the Health Portfolio Committee NHLS Annual Report 2010/2011 Sagie Pillay CEO Adv Sesi Baloyi Board Chair Nov 9, 2011 1
 OUR MONEY Clean audit For the fifth year in succession, the NHLS received a clean audit report. The NHLS posted an accounting surplus R 264 million. Affordable prices Prices for the priority programmes of HIV, TB and pap smears were reduced, on average, by 10%, resulting in R 217, 7 million savings to provincial health departments. Overall, test prices decreased by 1%, well below the inflation rate increase of 4. 1%. 2
OUR MONEY Clean audit For the fifth year in succession, the NHLS received a clean audit report. The NHLS posted an accounting surplus R 264 million. Affordable prices Prices for the priority programmes of HIV, TB and pap smears were reduced, on average, by 10%, resulting in R 217, 7 million savings to provincial health departments. Overall, test prices decreased by 1%, well below the inflation rate increase of 4. 1%. 2
 Cash flow The accounting surplus of R 264 m did not materialise into cash due to the poor payment pattern by certain provinces. Debtors have increased by R 340 m, resulting in a cash deficit of R 83 m, despite reducing capital expenditure to R 122 m (R 98 m lower than 2010). Segmental analysis of net cash deficit This net cash deficit of R 83 m is made up as follows: Subsidy to National Institute for Communicable Diseases Subsidy to National Institute for Occupational Health and the National Cancer Registry Funding of teaching and training, and research Laboratory services NHLS is mandated by the NHLS Act of 2000 to fund the Institutes and teaching, training and research from the laboratory test fee-for-service. The impact of this on test prices is 14%. 3
Cash flow The accounting surplus of R 264 m did not materialise into cash due to the poor payment pattern by certain provinces. Debtors have increased by R 340 m, resulting in a cash deficit of R 83 m, despite reducing capital expenditure to R 122 m (R 98 m lower than 2010). Segmental analysis of net cash deficit This net cash deficit of R 83 m is made up as follows: Subsidy to National Institute for Communicable Diseases Subsidy to National Institute for Occupational Health and the National Cancer Registry Funding of teaching and training, and research Laboratory services NHLS is mandated by the NHLS Act of 2000 to fund the Institutes and teaching, training and research from the laboratory test fee-for-service. The impact of this on test prices is 14%. 3
 Turnover for the year increased by R 397 m or 13% from R 3, 049 m to R 3, 446 m. The increase was attributable to the conversion of the Kwa. Zulu -Natal flat-rate billing model to the fee-for-service model from 1 April 2010. Gross margin as a percentage of turnover increased by 2. 2% from 29. 1% in 2010 to 31. 3% in 2011. This increase is attributable largely to the change in sales mix. Overheads increased by R 98 m or 10% from R 938 m to R 1, 036 m. This is largely attributable to an increase in temporary employee numbers as well as salary increases. The planned implementation of Oracle Release 12 led to a R 15 m increase in software development expenses. Other significant increases related to an increase in the cost of utilities, salaries increased due to OSD. 4
Turnover for the year increased by R 397 m or 13% from R 3, 049 m to R 3, 446 m. The increase was attributable to the conversion of the Kwa. Zulu -Natal flat-rate billing model to the fee-for-service model from 1 April 2010. Gross margin as a percentage of turnover increased by 2. 2% from 29. 1% in 2010 to 31. 3% in 2011. This increase is attributable largely to the change in sales mix. Overheads increased by R 98 m or 10% from R 938 m to R 1, 036 m. This is largely attributable to an increase in temporary employee numbers as well as salary increases. The planned implementation of Oracle Release 12 led to a R 15 m increase in software development expenses. Other significant increases related to an increase in the cost of utilities, salaries increased due to OSD. 4
 Working capital management Inventory of R 73 m (2009 - 2010 - R 69 m) is managed at 31 days which is 19 days better than the prior year of 50 days. Debtors of R 1, 786 m (2010 - R 1, 328 m) are at 154 days (2009 - 2010 - 126 days) due to the poor payment pattern of certain provinces. This has resulted in creditor days worsening from 45 days on 2010 to 62 days this year. Capital expenditure During the current financial year, capital expenditure amounted to R 122 m compared to the prior year amount of R 213 m and was funded purely from internal resources. Capital expenditure was spent as follows to maintain existing infrastructure: 5
Working capital management Inventory of R 73 m (2009 - 2010 - R 69 m) is managed at 31 days which is 19 days better than the prior year of 50 days. Debtors of R 1, 786 m (2010 - R 1, 328 m) are at 154 days (2009 - 2010 - 126 days) due to the poor payment pattern of certain provinces. This has resulted in creditor days worsening from 45 days on 2010 to 62 days this year. Capital expenditure During the current financial year, capital expenditure amounted to R 122 m compared to the prior year amount of R 213 m and was funded purely from internal resources. Capital expenditure was spent as follows to maintain existing infrastructure: 5
 2010 – 2011 Financial highlights POSITIVES: Unqualified Audit Opinion – 5 th year in a row Test Prices decreased by 1% NEGATIVES: Growth in revenue, whilst still positive, is declining Debtors collections is poor Capital Expenditure % of Turnover of 3% is the lowest in last 5 years 6
2010 – 2011 Financial highlights POSITIVES: Unqualified Audit Opinion – 5 th year in a row Test Prices decreased by 1% NEGATIVES: Growth in revenue, whilst still positive, is declining Debtors collections is poor Capital Expenditure % of Turnover of 3% is the lowest in last 5 years 6
 5 Year financial summary 2007 2008 2009 Turnover 1 735 414 2010 2011 2 667 398 3 033 151 3 455 924 29% Growth % 2 236 963 19% 14% Materials 430 427 614 354 804 586 904 034 867 799 Overheads 1 122 738 1 425 376 1 422 827 1 804 505 2 105 271 Net Capital Expenditure 125 385 122 669 176 527 213 326 108 058 Invested in Debtors 76 350 115 468 379 855 -9 201 458 005 (19 486) (40 904) (116 397) 120 487 (83 209) 7% 5% 7% 7% 3% Net Cash Generated/(Utilised) Net Capital Expenditure % of Turnover 7
5 Year financial summary 2007 2008 2009 Turnover 1 735 414 2010 2011 2 667 398 3 033 151 3 455 924 29% Growth % 2 236 963 19% 14% Materials 430 427 614 354 804 586 904 034 867 799 Overheads 1 122 738 1 425 376 1 422 827 1 804 505 2 105 271 Net Capital Expenditure 125 385 122 669 176 527 213 326 108 058 Invested in Debtors 76 350 115 468 379 855 -9 201 458 005 (19 486) (40 904) (116 397) 120 487 (83 209) 7% 5% 7% 7% 3% Net Cash Generated/(Utilised) Net Capital Expenditure % of Turnover 7
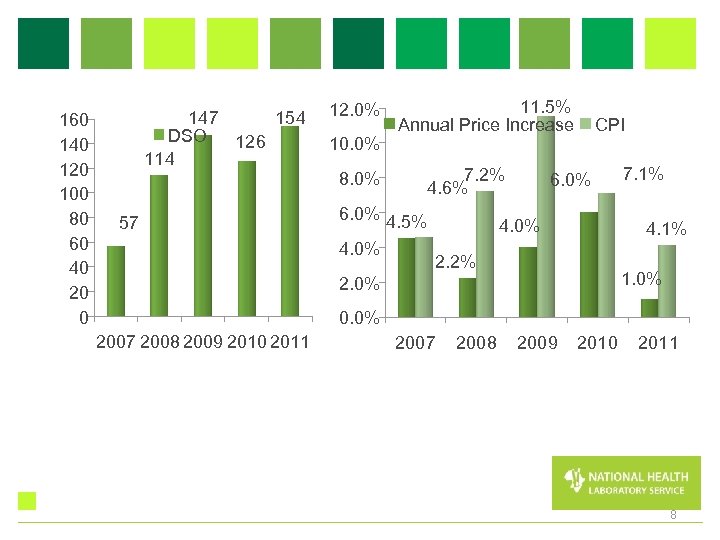 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 147 154 DSO 126 114 57 12. 0% 10. 0% 8. 0% 11. 5% Annual Price Increase 7. 2% 4. 6% 6. 0% 4. 5% 4. 0% CPI 6. 0% 4. 0% 7. 1% 4. 1% 2. 2% 1. 0% 2. 0% 0. 0% 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 8
160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 147 154 DSO 126 114 57 12. 0% 10. 0% 8. 0% 11. 5% Annual Price Increase 7. 2% 4. 6% 6. 0% 4. 5% 4. 0% CPI 6. 0% 4. 0% 7. 1% 4. 1% 2. 2% 1. 0% 2. 0% 0. 0% 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 8
 Annual price increase Year 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 Annual Price Increase 4. 5% 2. 2% 4. 0% 6. 0% 1. 0% CPI 4. 6% 7. 2% 11. 5% 7. 1% 4. 1% 12. 0% 10. 0% 11. 5% Annual Price Increase 7. 1% 6. 0% 7. 2% 8. 0% 6. 0%4. 5% 4. 6% 4. 0% 2. 2% 2. 0% CPI 4. 0% 4. 1% 1. 0% 0. 0% 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 9
Annual price increase Year 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 Annual Price Increase 4. 5% 2. 2% 4. 0% 6. 0% 1. 0% CPI 4. 6% 7. 2% 11. 5% 7. 1% 4. 1% 12. 0% 10. 0% 11. 5% Annual Price Increase 7. 1% 6. 0% 7. 2% 8. 0% 6. 0%4. 5% 4. 6% 4. 0% 2. 2% 2. 0% CPI 4. 0% 4. 1% 1. 0% 0. 0% 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 9
 DSO Year 2007 2008 2009 DSO 57 114 147 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 2010 126 2011 154 147 DSO 126 2009 2010 114 57 2008 2011 10
DSO Year 2007 2008 2009 DSO 57 114 147 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 2010 126 2011 154 147 DSO 126 2009 2010 114 57 2008 2011 10
 HUMAN RESOURCES Scarce skills development The NHLS is committed to increase its training of the next generation of world class pathologists. During the past year the following increases in the scarce-skilled areas were achieved: Pathologists and medical officers: 8. 7% (207 to 225) Registrars 2, 9% (207 to 213) Medical scientists: 2, 4% (207 to 213) Medical technologists: 2. 2% (1385 to 1415) Medical technicians: 23, 5% (528 to 625) 11
HUMAN RESOURCES Scarce skills development The NHLS is committed to increase its training of the next generation of world class pathologists. During the past year the following increases in the scarce-skilled areas were achieved: Pathologists and medical officers: 8. 7% (207 to 225) Registrars 2, 9% (207 to 213) Medical scientists: 2, 4% (207 to 213) Medical technologists: 2. 2% (1385 to 1415) Medical technicians: 23, 5% (528 to 625) 11
 Workplace Skills Plan The were 4, 796 training occurrences at a cost of R 39, 543, 687; that is 2, 8% of payroll compared to the 1% stipulated by the Skills Development Act. Employment equity reached an 83% representation of black males and females. 12
Workplace Skills Plan The were 4, 796 training occurrences at a cost of R 39, 543, 687; that is 2, 8% of payroll compared to the 1% stipulated by the Skills Development Act. Employment equity reached an 83% representation of black males and females. 12
 Workforce Profile The overall headcount increased by 2. 8% in the reporting period compared to 2. 4% in 2009/10. Executive complement was fully filled. Pathologists and medical officers increased by 8. 7% (18), making the total 225. The increase was mainly among Africans, Indians and Coloured females. Registrars increased by 2. 9% mainly among African, Coloured and Indian females including Coloured males. African females in particular increased in number from 40 to 49. 13
Workforce Profile The overall headcount increased by 2. 8% in the reporting period compared to 2. 4% in 2009/10. Executive complement was fully filled. Pathologists and medical officers increased by 8. 7% (18), making the total 225. The increase was mainly among Africans, Indians and Coloured females. Registrars increased by 2. 9% mainly among African, Coloured and Indian females including Coloured males. African females in particular increased in number from 40 to 49. 13
 Five-year trend Pathologists by Gender 250 225 215 201 207 200 165 150 131 124 118 115 100 90 86 91 89 2008/09 91 124 215 2009/10 89 118 207 94 75 50 0 MALE FEMALE TOTAL 2006/07 75 90 165 2007/08 86 115 2010/11 94 131 225 14
Five-year trend Pathologists by Gender 250 225 215 201 207 200 165 150 131 124 118 115 100 90 86 91 89 2008/09 91 124 215 2009/10 89 118 207 94 75 50 0 MALE FEMALE TOTAL 2006/07 75 90 165 2007/08 86 115 2010/11 94 131 225 14
 Five-year trend Pathologist by Race 160 133 120 140 138 129 130 120 2006/07 100 2007/08 80 2008/09 41 50 38 60 40 2009/10 35 21 2 045 7 COLOURED 16 14 INDIAN WHITE 21 32 38 2010/11 AFRICAN 15
Five-year trend Pathologist by Race 160 133 120 140 138 129 130 120 2006/07 100 2007/08 80 2008/09 41 50 38 60 40 2009/10 35 21 2 045 7 COLOURED 16 14 INDIAN WHITE 21 32 38 2010/11 AFRICAN 15
 Five-year trend Registrars by Gender 250 210 201 207 213 200 165 149 150 127 129 115 100 90 86 83 75 78 64 50 0 MALE FEMALE TOTAL 2006/07 75 90 165 2007/08 86 115 201 2008/09 83 127 210 2009/10 78 129 207 2010/11 64 149 213 16
Five-year trend Registrars by Gender 250 210 201 207 213 200 165 149 150 127 129 115 100 90 86 83 75 78 64 50 0 MALE FEMALE TOTAL 2006/07 75 90 165 2007/08 86 115 201 2008/09 83 127 210 2009/10 78 129 207 2010/11 64 149 213 16
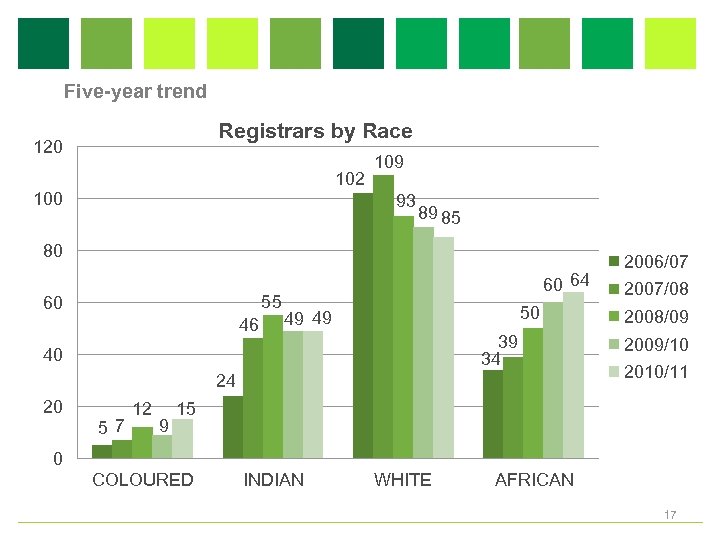 Five-year trend Registrars by Race 120 102 100 109 93 89 85 80 55 60 46 60 64 50 49 49 39 34 40 24 20 57 12 9 2006/07 2007/08 2008/09 2009/10 2010/11 15 0 COLOURED INDIAN WHITE AFRICAN 17
Five-year trend Registrars by Race 120 102 100 109 93 89 85 80 55 60 46 60 64 50 49 49 39 34 40 24 20 57 12 9 2006/07 2007/08 2008/09 2009/10 2010/11 15 0 COLOURED INDIAN WHITE AFRICAN 17
 Workforce profile • An increase of 2. 4% (5) medical scientists was recorded in 2010/11 compared 2009/10. Africans showed the most increase in numbers followed by Indians and then Coloured. This category was dominated by white females, whose numbers are stabilizing. • An increase of 2. 2% (30) medical technologists successfully completed the internship programme, mostly African males and females. The drop in number from 129 in the previous year was due to the low national pass rate of 47%. NHLS has achieved a 53% pass rate, 6% above the national mark. • A significant increase of 23. 5% (124) medical technicians was recorded, mostly NHLS laboratory support staff, who enrolled for further training to enhance capacity in the laboratories. African shows a significant increase, followed by Indian and Coloured. White medical technicians’ numbers remain constant and lower. 18
Workforce profile • An increase of 2. 4% (5) medical scientists was recorded in 2010/11 compared 2009/10. Africans showed the most increase in numbers followed by Indians and then Coloured. This category was dominated by white females, whose numbers are stabilizing. • An increase of 2. 2% (30) medical technologists successfully completed the internship programme, mostly African males and females. The drop in number from 129 in the previous year was due to the low national pass rate of 47%. NHLS has achieved a 53% pass rate, 6% above the national mark. • A significant increase of 23. 5% (124) medical technicians was recorded, mostly NHLS laboratory support staff, who enrolled for further training to enhance capacity in the laboratories. African shows a significant increase, followed by Indian and Coloured. White medical technicians’ numbers remain constant and lower. 18
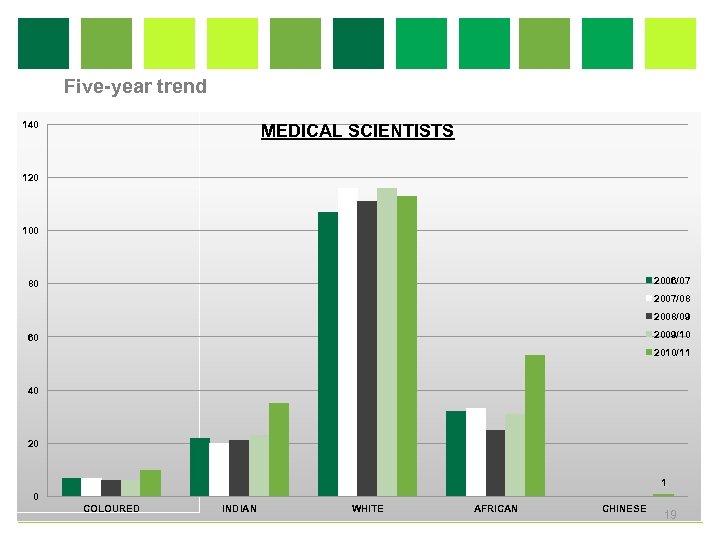 Five-year trend 140 MEDICAL SCIENTISTS 120 100 2006/07 80 2007/08 2008/09 2009/10 60 2010/11 40 20 1 0 COLOURED INDIAN WHITE AFRICAN CHINESE 19
Five-year trend 140 MEDICAL SCIENTISTS 120 100 2006/07 80 2007/08 2008/09 2009/10 60 2010/11 40 20 1 0 COLOURED INDIAN WHITE AFRICAN CHINESE 19
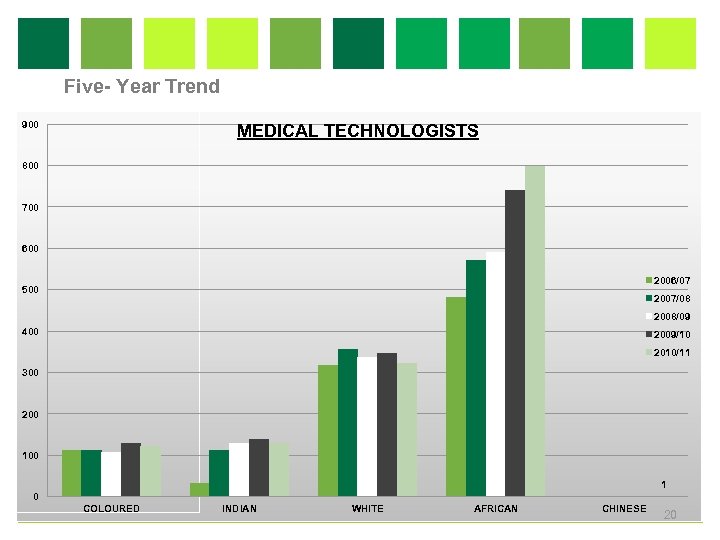 Five- Year Trend 900 MEDICAL TECHNOLOGISTS 800 700 600 2006/07 500 2007/08 2008/09 400 2009/10 2010/11 300 200 1 0 COLOURED INDIAN WHITE AFRICAN CHINESE 20
Five- Year Trend 900 MEDICAL TECHNOLOGISTS 800 700 600 2006/07 500 2007/08 2008/09 400 2009/10 2010/11 300 200 1 0 COLOURED INDIAN WHITE AFRICAN CHINESE 20
 MEDICAL TECHNICIANS 600 500 400 2006/07 2007/08 2008/09 300 2009/10 2010/11 200 100 0 COLOURED INDIAN WHITE AFRICAN 21
MEDICAL TECHNICIANS 600 500 400 2006/07 2007/08 2008/09 300 2009/10 2010/11 200 100 0 COLOURED INDIAN WHITE AFRICAN 21
 Core skills training • A total of 1, 042 registrars , interns and students was recorded at the end of the 2010/11 financial year compared to 1, 025 in 2009/10. Registrars in training in 2010/11 were 213 compared to 207 in 2010/11. • Medical scientist interns number reduced by 12. 2% (9); this is line with the current organisational needs. • The total recorded for student medical technologists is 2. 9 % lower than the previous year. This is a result of reduced numbers qualifying for admission into the tertiary institutions; hence 61 new bursaries were awarded to matriculants in 2010/11 compared to 74 in the previous financial year. 16 out of the 61 bursars (26%), were attracted from the rural areas. • Student medical technicians increased by 8. 6%. This is a combination of student medical technologist who opt for the technician level qualification and skills development of serving laboratory employees. 22
Core skills training • A total of 1, 042 registrars , interns and students was recorded at the end of the 2010/11 financial year compared to 1, 025 in 2009/10. Registrars in training in 2010/11 were 213 compared to 207 in 2010/11. • Medical scientist interns number reduced by 12. 2% (9); this is line with the current organisational needs. • The total recorded for student medical technologists is 2. 9 % lower than the previous year. This is a result of reduced numbers qualifying for admission into the tertiary institutions; hence 61 new bursaries were awarded to matriculants in 2010/11 compared to 74 in the previous financial year. 16 out of the 61 bursars (26%), were attracted from the rural areas. • Student medical technicians increased by 8. 6%. This is a combination of student medical technologist who opt for the technician level qualification and skills development of serving laboratory employees. 22
 Skills Development and grants • A total of R 39, 6 million was invested in various technical and managerial skills development initiatives. This is 2. 8% of the payroll compared to the legislated 1%. NHLS has earned mandatory grants which are re-invested in the training of staff. • Under the newly established NHLS Learning Academy: • 58 employees were enrolled on various leadership and management development programmes funded by the NHLS • A total of 4796 short term skills initiatives were funded and implemented • Grants were received from various donors to enhance skills development: HWSETA: 44 phlebotomy technicians, DST: 10 additional medical technologists and scientists Basil Read: 5 medical technologist and 1 post-graduate student CDC: Improvement of training laboratories. 23
Skills Development and grants • A total of R 39, 6 million was invested in various technical and managerial skills development initiatives. This is 2. 8% of the payroll compared to the legislated 1%. NHLS has earned mandatory grants which are re-invested in the training of staff. • Under the newly established NHLS Learning Academy: • 58 employees were enrolled on various leadership and management development programmes funded by the NHLS • A total of 4796 short term skills initiatives were funded and implemented • Grants were received from various donors to enhance skills development: HWSETA: 44 phlebotomy technicians, DST: 10 additional medical technologists and scientists Basil Read: 5 medical technologist and 1 post-graduate student CDC: Improvement of training laboratories. 23
 Employment equity, skills development and transformation (EESDT) structure was devolved into the regions during the 2010/11 financial year with a central committee that oversees the organisational activities. The Department of Labour conducted a workshop on the Legislated Employment Equity Framework to guide the EESDT Committee. The representation of Black employees within the NHLS continues to improve from 81% to 83% over the past three financial years. The representation of Black executive and management appointments in 2010/11 was 67%, of which 72% of these were female. The representation of female in top and senior management positions was recorded at 47% in 2010/11, an improvement from the 45% recorded in the previous reporting period. The executive team recorded 25% female representation. 24
Employment equity, skills development and transformation (EESDT) structure was devolved into the regions during the 2010/11 financial year with a central committee that oversees the organisational activities. The Department of Labour conducted a workshop on the Legislated Employment Equity Framework to guide the EESDT Committee. The representation of Black employees within the NHLS continues to improve from 81% to 83% over the past three financial years. The representation of Black executive and management appointments in 2010/11 was 67%, of which 72% of these were female. The representation of female in top and senior management positions was recorded at 47% in 2010/11, an improvement from the 45% recorded in the previous reporting period. The executive team recorded 25% female representation. 24
 ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Training of scarce skills The NHLS trains all pathologists in South Africa. Bilateral agreements were developed to govern the relationships between the NHLS and nine university affiliates which share joint responsibilities towards service, teaching and research. A bilateral agreement was drafted to regulate the NHLS’s relationship with eight Universities of technology regarding the training and qualifying of medical technologists. 25
ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Training of scarce skills The NHLS trains all pathologists in South Africa. Bilateral agreements were developed to govern the relationships between the NHLS and nine university affiliates which share joint responsibilities towards service, teaching and research. A bilateral agreement was drafted to regulate the NHLS’s relationship with eight Universities of technology regarding the training and qualifying of medical technologists. 25
 Research The NHLS is renowned for its cutting edge research in fields particularly benefitting South Africa and its people. A total of 177 new grants to fund such research projects to the value of R 178, 399, 660 were awarded by local and international agencies. NHLS researchers published 486 research projects in peerreviewed journals and academic text books. 26
Research The NHLS is renowned for its cutting edge research in fields particularly benefitting South Africa and its people. A total of 177 new grants to fund such research projects to the value of R 178, 399, 660 were awarded by local and international agencies. NHLS researchers published 486 research projects in peerreviewed journals and academic text books. 26
 QUALITY ASSURANCE Doing it better An external survey showed a 6. 9% improvement in customer satisfaction from 59. 7% to 66. 6% over the previous year. By year-end 72 laboratories had been accredited against a target of 184 by the 2014/2015 financial year. The total number of enrolments in the NHLS proficiency testing schemes increased by 9% to 2, 599. 27
QUALITY ASSURANCE Doing it better An external survey showed a 6. 9% improvement in customer satisfaction from 59. 7% to 66. 6% over the previous year. By year-end 72 laboratories had been accredited against a target of 184 by the 2014/2015 financial year. The total number of enrolments in the NHLS proficiency testing schemes increased by 9% to 2, 599. 27
 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (IT) Improving service delivery A specimen tracking project was initiated and piloted in Kwa. Zulu-Natal. The specimens and laboratory reports are scanned by the driver at the point of collection and delivery; the information is then transmitted via a cellular data connection to Trak. Care Lab laboratory information system (LIS). Turnaround times are therefore measured more accurately, and the loss of specimens and reports while in transit is eliminated. The information will be used to produce audit and turnaround time reports in an effort to improve the overall service to the NHLS customers. 28
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (IT) Improving service delivery A specimen tracking project was initiated and piloted in Kwa. Zulu-Natal. The specimens and laboratory reports are scanned by the driver at the point of collection and delivery; the information is then transmitted via a cellular data connection to Trak. Care Lab laboratory information system (LIS). Turnaround times are therefore measured more accurately, and the loss of specimens and reports while in transit is eliminated. The information will be used to produce audit and turnaround time reports in an effort to improve the overall service to the NHLS customers. 28
 Saving test costs To save costs for the Department of Health, an electronic gatekeeping (EGK) system was piloted and implemented at Tygerberg and Groote Schuur hospitals in the Western Cape. EGK uses the LIS to approve or reject laboratory tests based on the protocols for patient management devised by the hospital. Cell phone technology employed Phase one of the Mobilabs project which gives access to laboratory results through cell phones, was rolled out to 213 clinicians in the Eastern Cape and 110 in the Free State. In addition, 361 cell phones and 232 laptops were installed in hospital wards and in clinics in the Eastern Cape and Free State, respectively, enabling clinicians to access electronic results. 29
Saving test costs To save costs for the Department of Health, an electronic gatekeeping (EGK) system was piloted and implemented at Tygerberg and Groote Schuur hospitals in the Western Cape. EGK uses the LIS to approve or reject laboratory tests based on the protocols for patient management devised by the hospital. Cell phone technology employed Phase one of the Mobilabs project which gives access to laboratory results through cell phones, was rolled out to 213 clinicians in the Eastern Cape and 110 in the Free State. In addition, 361 cell phones and 232 laptops were installed in hospital wards and in clinics in the Eastern Cape and Free State, respectively, enabling clinicians to access electronic results. 29
 COMMUNICATIONS The Communications, Marketing and Public Relations department was added to the corporate structure in 2010 to create a single brand identity for the National Health Laboratory Service, to elevate its profile, to improve both the internal and external communication and develop a stakeholder relations strategy. Customer Satisfaction Survey A new measurement tool was developed to survey the satisfaction levels of a wider sample of customers for the NHLS. The tool will be implemented in the next financial year. 30
COMMUNICATIONS The Communications, Marketing and Public Relations department was added to the corporate structure in 2010 to create a single brand identity for the National Health Laboratory Service, to elevate its profile, to improve both the internal and external communication and develop a stakeholder relations strategy. Customer Satisfaction Survey A new measurement tool was developed to survey the satisfaction levels of a wider sample of customers for the NHLS. The tool will be implemented in the next financial year. 30
 Media An annual advertising budget of R 400 000. 00 the NHLS generated advertising value equivalent (AVE) in excess of R 3 million across all three mediums of print, electronic and broadcast. The NHLS is proud to have gained considerable awareness in the general press from the outstanding surveillance and research work being conducted. Internal communications support was offered with the development of an extensive internal campaign in delivering feedback from the Culture and Climate Survey Feedback road shows. 31
Media An annual advertising budget of R 400 000. 00 the NHLS generated advertising value equivalent (AVE) in excess of R 3 million across all three mediums of print, electronic and broadcast. The NHLS is proud to have gained considerable awareness in the general press from the outstanding surveillance and research work being conducted. Internal communications support was offered with the development of an extensive internal campaign in delivering feedback from the Culture and Climate Survey Feedback road shows. 31
 Our Priorities • Because HIV, tuberculosis (TB) and cervical cancer are three biggest disease burdens in South Africa, the NHLS established the National Priority Programmes (NPP) Unit early in 2011 to make the diagnosis of these diseases more accessible and affordable to our people. During the year, the NHLS conducted: • 5. 7 million HIV tests • 5. 9 million TB tests • 13% more cervical cytology tests 32
Our Priorities • Because HIV, tuberculosis (TB) and cervical cancer are three biggest disease burdens in South Africa, the NHLS established the National Priority Programmes (NPP) Unit early in 2011 to make the diagnosis of these diseases more accessible and affordable to our people. During the year, the NHLS conducted: • 5. 7 million HIV tests • 5. 9 million TB tests • 13% more cervical cytology tests 32
 National Priority Programmes Strategic Alignment of HIV and TB activities 80%TB patients are HIV-co-infected • Greatest laboratory synergies likely to arise in molecular testing at both a POC and centralized laboratory level • Laboratory planning needs to occur around mutual technology platforms, skill and support needs. 33
National Priority Programmes Strategic Alignment of HIV and TB activities 80%TB patients are HIV-co-infected • Greatest laboratory synergies likely to arise in molecular testing at both a POC and centralized laboratory level • Laboratory planning needs to occur around mutual technology platforms, skill and support needs. 33
 400, 000 CD 4 Test Volumes FY 2010/2011 350, 000 300, 000 250, 000 200, 000 150, 000 100, 000 50, 000 Ja n 11 Fe b 11 M ar -1 1 -1 0 D ec -1 0 N ov -1 0 O ct 10 Se p- 10 Au g- -1 0 Ju l 0 Ju n 1 ay - M Ap r-1 0 10 - 34
400, 000 CD 4 Test Volumes FY 2010/2011 350, 000 300, 000 250, 000 200, 000 150, 000 100, 000 50, 000 Ja n 11 Fe b 11 M ar -1 1 -1 0 D ec -1 0 N ov -1 0 O ct 10 Se p- 10 Au g- -1 0 Ju l 0 Ju n 1 ay - M Ap r-1 0 10 - 34
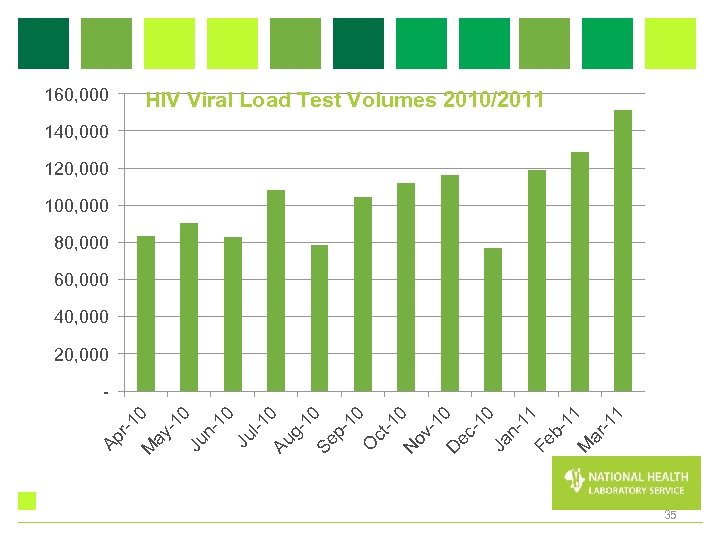 160, 000 HIV Viral Load Test Volumes 2010/2011 140, 000 120, 000 100, 000 80, 000 60, 000 40, 000 20, 000 Ap r-1 M 0 ay -1 0 Ju n 10 Ju l-1 0 Au g 10 Se p 10 O ct -1 0 N ov -1 0 D ec -1 0 Ja n 11 Fe b 11 M ar -1 1 - 35
160, 000 HIV Viral Load Test Volumes 2010/2011 140, 000 120, 000 100, 000 80, 000 60, 000 40, 000 20, 000 Ap r-1 M 0 ay -1 0 Ju n 10 Ju l-1 0 Au g 10 Se p 10 O ct -1 0 N ov -1 0 D ec -1 0 Ja n 11 Fe b 11 M ar -1 1 - 35
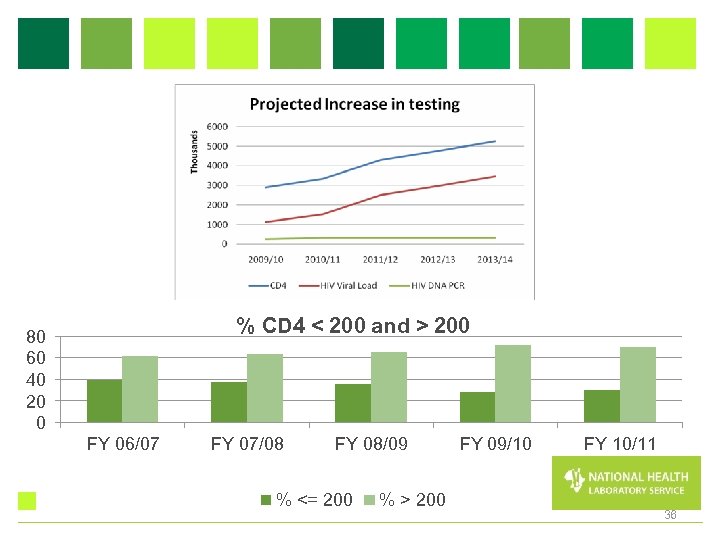 % CD 4 < 200 and > 200 80 60 40 20 0 FY 06/07 FY 07/08 FY 08/09 % <= 200 % > 200 FY 09/10 FY 10/11 36
% CD 4 < 200 and > 200 80 60 40 20 0 FY 06/07 FY 07/08 FY 08/09 % <= 200 % > 200 FY 09/10 FY 10/11 36
 National Priority Programmes Tuberculosis VOLUMES PER ANNUM Year CULTURE MICROSCOPY DST LPA DST MGIT 2004 273 829 1 815 333 34 542 2005 349 246 2 300 241 36 871 2006 481 757 2 720 813 48 049 2007 581 671 2 927 017 5 963 64 943 2008 729 424 3 373 134 23 126 58 887 2009 759 643 3 276 347 61 423 39 334 2010 931 542 3 501 652 94 649 34 980 37
National Priority Programmes Tuberculosis VOLUMES PER ANNUM Year CULTURE MICROSCOPY DST LPA DST MGIT 2004 273 829 1 815 333 34 542 2005 349 246 2 300 241 36 871 2006 481 757 2 720 813 48 049 2007 581 671 2 927 017 5 963 64 943 2008 729 424 3 373 134 23 126 58 887 2009 759 643 3 276 347 61 423 39 334 2010 931 542 3 501 652 94 649 34 980 37
 National Priority Programmes Tuberculosis 6, 000 Number of New MDR-TB Patients/Year 5, 000 4, 000 MDR 3, 000 XDR 2, 000 1, 000 , 0 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 38
National Priority Programmes Tuberculosis 6, 000 Number of New MDR-TB Patients/Year 5, 000 4, 000 MDR 3, 000 XDR 2, 000 1, 000 , 0 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 38
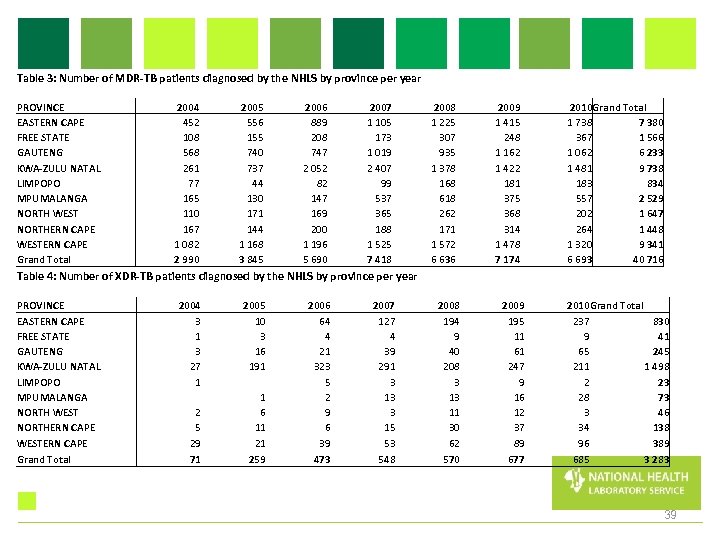 Table 3: Number of MDR-TB patients diagnosed by the NHLS by province per year PROVINCE EASTERN CAPE FREE STATE GAUTENG KWA-ZULU NATAL LIMPOPO MPUMALANGA NORTH WEST NORTHERN CAPE WESTERN CAPE Grand Total 2004 452 108 568 261 77 165 110 167 1 082 2 990 2005 556 155 740 737 44 130 171 144 1 168 3 845 2006 889 208 747 2 052 82 147 169 200 1 196 5 690 2007 1 105 173 1 019 2 407 99 537 365 188 1 525 7 418 2008 1 225 307 935 1 378 168 618 262 171 1 572 6 636 2009 1 415 248 1 162 1 422 181 375 368 314 1 478 7 174 2010 Grand Total 1 738 7 380 367 1 566 1 062 6 233 1 481 9 738 183 834 557 2 529 202 1 647 264 1 448 1 320 9 341 6 693 40 716 Table 4: Number of XDR-TB patients diagnosed by the NHLS by province per year PROVINCE EASTERN CAPE FREE STATE GAUTENG KWA-ZULU NATAL LIMPOPO MPUMALANGA NORTH WEST NORTHERN CAPE WESTERN CAPE Grand Total 2004 3 1 3 27 1 2 5 29 71 2005 10 3 16 191 1 6 11 21 259 2006 64 4 21 323 5 2 9 6 39 473 2007 127 4 39 291 3 13 3 15 53 548 2008 194 9 40 208 3 13 11 30 62 570 2009 195 11 61 247 9 16 12 37 89 677 2010 Grand Total 237 830 9 41 65 245 211 1 498 2 23 28 73 3 46 34 138 96 389 685 3 283 39
Table 3: Number of MDR-TB patients diagnosed by the NHLS by province per year PROVINCE EASTERN CAPE FREE STATE GAUTENG KWA-ZULU NATAL LIMPOPO MPUMALANGA NORTH WEST NORTHERN CAPE WESTERN CAPE Grand Total 2004 452 108 568 261 77 165 110 167 1 082 2 990 2005 556 155 740 737 44 130 171 144 1 168 3 845 2006 889 208 747 2 052 82 147 169 200 1 196 5 690 2007 1 105 173 1 019 2 407 99 537 365 188 1 525 7 418 2008 1 225 307 935 1 378 168 618 262 171 1 572 6 636 2009 1 415 248 1 162 1 422 181 375 368 314 1 478 7 174 2010 Grand Total 1 738 7 380 367 1 566 1 062 6 233 1 481 9 738 183 834 557 2 529 202 1 647 264 1 448 1 320 9 341 6 693 40 716 Table 4: Number of XDR-TB patients diagnosed by the NHLS by province per year PROVINCE EASTERN CAPE FREE STATE GAUTENG KWA-ZULU NATAL LIMPOPO MPUMALANGA NORTH WEST NORTHERN CAPE WESTERN CAPE Grand Total 2004 3 1 3 27 1 2 5 29 71 2005 10 3 16 191 1 6 11 21 259 2006 64 4 21 323 5 2 9 6 39 473 2007 127 4 39 291 3 13 3 15 53 548 2008 194 9 40 208 3 13 11 30 62 570 2009 195 11 61 247 9 16 12 37 89 677 2010 Grand Total 237 830 9 41 65 245 211 1 498 2 23 28 73 3 46 34 138 96 389 685 3 283 39
 60, 000 Cervical Screening Test Volumes 2010/2011 50, 000 40, 000 30, 000 20, 000 10, 000 Apr-10 May-10 Jun-10 Jul-10 Aug-10 Sep-10 Oct-10 Nov-10 Dec-10 Jan-11 Feb-11 Mar-11 §Total number of Cervical Screening determinations Apr ‘ 10– Mar ‘ 11: 582 005 40
60, 000 Cervical Screening Test Volumes 2010/2011 50, 000 40, 000 30, 000 20, 000 10, 000 Apr-10 May-10 Jun-10 Jul-10 Aug-10 Sep-10 Oct-10 Nov-10 Dec-10 Jan-11 Feb-11 Mar-11 §Total number of Cervical Screening determinations Apr ‘ 10– Mar ‘ 11: 582 005 40
 The Gynae (PAP) smears indicate all Gynae cases and smears received (some cases have >1 smear). 41
The Gynae (PAP) smears indicate all Gynae cases and smears received (some cases have >1 smear). 41
 Gene Xpert Rollout (GX) Together with the Department of Health, the NHLS was the first laboratory diagnostic service provider on the African continent to introduce GX technology for the diagnosis of TB and rifampicin resistance. This is groundbreaking technology that produces a result in two hours. Microscopy and cultures can take up to between 48 hours and four weeks, respectively. 42
Gene Xpert Rollout (GX) Together with the Department of Health, the NHLS was the first laboratory diagnostic service provider on the African continent to introduce GX technology for the diagnosis of TB and rifampicin resistance. This is groundbreaking technology that produces a result in two hours. Microscopy and cultures can take up to between 48 hours and four weeks, respectively. 42
 Information Management: Monthly reports In support of the NPP, the NHLS’s Corporate Data warehouse improved the provision of information to the Department of Health on multidrug-resistant TB and early diagnosis of HIV-infection in infants at 6 weeks. Monthly management summary reports by facility and by province are now automatically circulated to the provincial and national health departments. An antiretroviral hotline was also launched which enables clinicians who have registered on the system, to obtain results telephonically. 43
Information Management: Monthly reports In support of the NPP, the NHLS’s Corporate Data warehouse improved the provision of information to the Department of Health on multidrug-resistant TB and early diagnosis of HIV-infection in infants at 6 weeks. Monthly management summary reports by facility and by province are now automatically circulated to the provincial and national health departments. An antiretroviral hotline was also launched which enables clinicians who have registered on the system, to obtain results telephonically. 43
 REGIONS Better and faster Processing specimens to the testing laboratories and delivering results to clinics in the shortest possible time was one of the main objectives for laboratories in the four NHLS regions. Many of these laboratories are in very remote areas. Courier services to and from laboratories were overhauled with daily or twice daily pick and delivery times. Remarkable improvements in turnaround times, particularly for the priority programmes of HIV and TB, have been noted which means that appropriate treatment can be started earlier. In Gauteng, Free State and Northern Cape, for example, HIV PCR for babies increased by 12% - thus an improvement in the coverage of babies born to HIV-positive mothers. 44
REGIONS Better and faster Processing specimens to the testing laboratories and delivering results to clinics in the shortest possible time was one of the main objectives for laboratories in the four NHLS regions. Many of these laboratories are in very remote areas. Courier services to and from laboratories were overhauled with daily or twice daily pick and delivery times. Remarkable improvements in turnaround times, particularly for the priority programmes of HIV and TB, have been noted which means that appropriate treatment can be started earlier. In Gauteng, Free State and Northern Cape, for example, HIV PCR for babies increased by 12% - thus an improvement in the coverage of babies born to HIV-positive mothers. 44
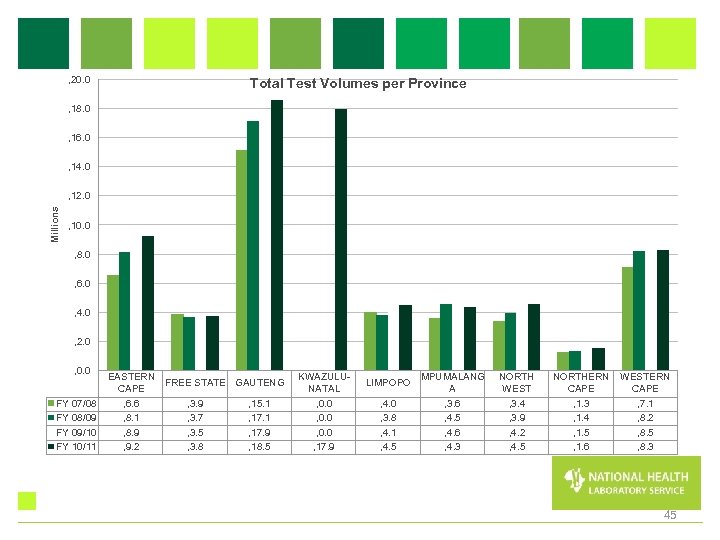 , 20. 0 Total Test Volumes per Province , 18. 0 , 16. 0 , 14. 0 Millions , 12. 0 , 10. 0 , 8. 0 , 6. 0 , 4. 0 , 2. 0 , 0. 0 FY 07/08 FY 08/09 FY 09/10 FY 10/11 EASTERN FREE STATE GAUTENG CAPE , 6. 6 , 3. 9 , 15. 1 , 8. 1 , 3. 7 , 17. 1 , 8. 9 , 3. 5 , 17. 9 , 9. 2 , 3. 8 , 18. 5 KWAZULUNATAL , 0. 0 , 17. 9 LIMPOPO , 4. 0 , 3. 8 , 4. 1 , 4. 5 MPUMALANG A , 3. 6 , 4. 5 , 4. 6 , 4. 3 NORTH WEST , 3. 4 , 3. 9 , 4. 2 , 4. 5 NORTHERN WESTERN CAPE , 1. 3 , 7. 1 , 1. 4 , 8. 2 , 1. 5 , 8. 5 , 1. 6 , 8. 3 45
, 20. 0 Total Test Volumes per Province , 18. 0 , 16. 0 , 14. 0 Millions , 12. 0 , 10. 0 , 8. 0 , 6. 0 , 4. 0 , 2. 0 , 0. 0 FY 07/08 FY 08/09 FY 09/10 FY 10/11 EASTERN FREE STATE GAUTENG CAPE , 6. 6 , 3. 9 , 15. 1 , 8. 1 , 3. 7 , 17. 1 , 8. 9 , 3. 5 , 17. 9 , 9. 2 , 3. 8 , 18. 5 KWAZULUNATAL , 0. 0 , 17. 9 LIMPOPO , 4. 0 , 3. 8 , 4. 1 , 4. 5 MPUMALANG A , 3. 6 , 4. 5 , 4. 6 , 4. 3 NORTH WEST , 3. 4 , 3. 9 , 4. 2 , 4. 5 NORTHERN WESTERN CAPE , 1. 3 , 7. 1 , 1. 4 , 8. 2 , 1. 5 , 8. 5 , 1. 6 , 8. 3 45
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR COMMUNICABLE DISEASES (NICD) Finding the best health solutions Pulse. Net Africa, part of an international molecular subtyping network for foodborne and waterborne disease surveillance which provides early warning of disease outbreaks, emerging pathogens and acts of bioterrorism, was launched and will be run by the NICD Enteric Diseases Reference Unit. . Six other regional Pulse. Net networks exist: for the USA, Canada, Latin America, Europe, Middle East and Asia Pacific. 46
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR COMMUNICABLE DISEASES (NICD) Finding the best health solutions Pulse. Net Africa, part of an international molecular subtyping network for foodborne and waterborne disease surveillance which provides early warning of disease outbreaks, emerging pathogens and acts of bioterrorism, was launched and will be run by the NICD Enteric Diseases Reference Unit. . Six other regional Pulse. Net networks exist: for the USA, Canada, Latin America, Europe, Middle East and Asia Pacific. 46
 The Special Pathogens Unit conducted Ebola virus reservoir host studies in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Ebola haemorrhagic fever is a deadly disease of which the cause is unknown. The purpose of the mission was to try to the feasibility of conducting an international research expedition to sample bats, particularly Hypsignatus monstrosus, but also other fruit bat species implicated as potential reservoirs of Ebola virus. Rotavirus is the most common cause of severe diarrhoea among infants and young children. Comparing the number of diarrhoea cases and the detection rate of rotavirus a year after the introduction of the rotavirus vaccine, NICD surveillance found a 20% decrease in diarrhoea cases and 49% in rotavirus-positive cases for 2010 and 2009, respectively. 47
The Special Pathogens Unit conducted Ebola virus reservoir host studies in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Ebola haemorrhagic fever is a deadly disease of which the cause is unknown. The purpose of the mission was to try to the feasibility of conducting an international research expedition to sample bats, particularly Hypsignatus monstrosus, but also other fruit bat species implicated as potential reservoirs of Ebola virus. Rotavirus is the most common cause of severe diarrhoea among infants and young children. Comparing the number of diarrhoea cases and the detection rate of rotavirus a year after the introduction of the rotavirus vaccine, NICD surveillance found a 20% decrease in diarrhoea cases and 49% in rotavirus-positive cases for 2010 and 2009, respectively. 47
 2010 Football World Cup The Division of Epidemiology prepared a Synopsis Guide for 2010 Football World Cup visitors to South Africa, which was posted on the NICD website. From February to August 2010, the monthly communiqués included pre- and post- 2010 Football World Cup communicable disease alerts for healthcare workers, visitors and the general public. The Outbreak Response Unit assisted the Department of Health with monitoring and response to communicable diseases during the 2010 Football World Cup period, both directly related and unrelated to the football activities. Laboratories were supported by facilitating the collection and testing of clinical and environmental specimens during foodborne disease outbreaks and other communicable disease incidents. Daily situation reports were provided. 48
2010 Football World Cup The Division of Epidemiology prepared a Synopsis Guide for 2010 Football World Cup visitors to South Africa, which was posted on the NICD website. From February to August 2010, the monthly communiqués included pre- and post- 2010 Football World Cup communicable disease alerts for healthcare workers, visitors and the general public. The Outbreak Response Unit assisted the Department of Health with monitoring and response to communicable diseases during the 2010 Football World Cup period, both directly related and unrelated to the football activities. Laboratories were supported by facilitating the collection and testing of clinical and environmental specimens during foodborne disease outbreaks and other communicable disease incidents. Daily situation reports were provided. 48
 Disease outbreaks The Outbreak Response Unit: assisted the Department of Health in reporting, field investigation, development of clinical and laboratory guidelines, management of laboratory surveillance data and interpretation of results, and recommendations for prevention and control of a number of disease outbreaks, namely Rift Valley fever, brucellosis, rabies, foodborne diseases, enteroviral meningitis, Odyssean malaria, pertussis, diphtheria, Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever, Legionnaires’ disease and cholera. 49
Disease outbreaks The Outbreak Response Unit: assisted the Department of Health in reporting, field investigation, development of clinical and laboratory guidelines, management of laboratory surveillance data and interpretation of results, and recommendations for prevention and control of a number of disease outbreaks, namely Rift Valley fever, brucellosis, rabies, foodborne diseases, enteroviral meningitis, Odyssean malaria, pertussis, diphtheria, Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever, Legionnaires’ disease and cholera. 49
 Disease warning systems Automated systems were developed by the Corporate Data Warehouse to alert outbreak response personnel to the diagnosis of priority communicable diseases. The system provides timely notifications and patient information following the confirmation of the following infections by NHLS laboratories throughout South Africa: Salmonella Typhi, Vibrio cholerae, and Neisseria meningitidis. A similar system was designed and piloted in 2010 to send automated SMS alerts. 50
Disease warning systems Automated systems were developed by the Corporate Data Warehouse to alert outbreak response personnel to the diagnosis of priority communicable diseases. The system provides timely notifications and patient information following the confirmation of the following infections by NHLS laboratories throughout South Africa: Salmonella Typhi, Vibrio cholerae, and Neisseria meningitidis. A similar system was designed and piloted in 2010 to send automated SMS alerts. 50
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH (NIOH) Making workplaces healthier, safer A strong research thrust is on the priority diseases within South Africa with many research activities directed towards HIV and TB in the workplace. New research initiatives covering health technology assessment, biomedical waste and point-of-care have begun. A total of 326 workers were assessed for various occupational diseases mainly from the non-mining sector with a few workers with tuberculosis and occupational asthma from the mining industry. This represented an increase of 98% from the previous year. 51
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH (NIOH) Making workplaces healthier, safer A strong research thrust is on the priority diseases within South Africa with many research activities directed towards HIV and TB in the workplace. New research initiatives covering health technology assessment, biomedical waste and point-of-care have begun. A total of 326 workers were assessed for various occupational diseases mainly from the non-mining sector with a few workers with tuberculosis and occupational asthma from the mining industry. This represented an increase of 98% from the previous year. 51
 Field work was conducted to evaluate the provision of HIV and TB services in the mining sector; 60 mines and quarries in the nine provinces were visited. The final recommendations focused on the need for regulatory reform, provision of an effective surveillance system and services and development of a monitoring and evaluation system. An allergy database was developed which contains a list of the common allergy tests available in South Africa. Concerns were raised about the health risks posed by the asbestos cement pipes in one of the two Orlando Towers, a popular bungee jumping and power swinging venue in Soweto. A team from the NIOH carried out a risk assessment and monitored the air in and around the towers. The Toxicology Section has continued working in the nanotoxicology and risk assessment of nanomaterials programme within the NIOH Nanotoxicology Strategic Plan, established in 2009. 52
Field work was conducted to evaluate the provision of HIV and TB services in the mining sector; 60 mines and quarries in the nine provinces were visited. The final recommendations focused on the need for regulatory reform, provision of an effective surveillance system and services and development of a monitoring and evaluation system. An allergy database was developed which contains a list of the common allergy tests available in South Africa. Concerns were raised about the health risks posed by the asbestos cement pipes in one of the two Orlando Towers, a popular bungee jumping and power swinging venue in Soweto. A team from the NIOH carried out a risk assessment and monitored the air in and around the towers. The Toxicology Section has continued working in the nanotoxicology and risk assessment of nanomaterials programme within the NIOH Nanotoxicology Strategic Plan, established in 2009. 52
 Cancer statistics The National Cancer Registry within the NIOH is the only national source of cancer incidence statistics and the registry data are regularly used and quoted by numerous stakeholders. Regulations were drafted to set out the legal basis for the reporting of cancers by health professionals, health facilities and pathology laboratories to the registry. Cervical cancer Cervical smear screening for the National Cytology Programme, which forms part of the NHLS’ priority programmes alongside HIV and TB, increased by 13%. 53
Cancer statistics The National Cancer Registry within the NIOH is the only national source of cancer incidence statistics and the registry data are regularly used and quoted by numerous stakeholders. Regulations were drafted to set out the legal basis for the reporting of cancers by health professionals, health facilities and pathology laboratories to the registry. Cervical cancer Cervical smear screening for the National Cytology Programme, which forms part of the NHLS’ priority programmes alongside HIV and TB, increased by 13%. 53
 REACHING OUT. . to our workers NIOH Pathology section developed an outreach programme to assist mine workers in all aspects of the compensation process; 1, 502 autopsies were carried out as part of the compensation process in terms of the Occupational Diseases in Mines and Works Act The Special Bacterial Pathogens Reference Unit, NICD, trained environmental health officers from the City of Johannesburg on the dissection and storage of rodent organs for surveillance purposes; and pest control, health and veterinary personnel from the Eastern Cape on plague surveillance and management. 54
REACHING OUT. . to our workers NIOH Pathology section developed an outreach programme to assist mine workers in all aspects of the compensation process; 1, 502 autopsies were carried out as part of the compensation process in terms of the Occupational Diseases in Mines and Works Act The Special Bacterial Pathogens Reference Unit, NICD, trained environmental health officers from the City of Johannesburg on the dissection and storage of rodent organs for surveillance purposes; and pest control, health and veterinary personnel from the Eastern Cape on plague surveillance and management. 54
 The NICD’s Epidemiology Unit assisted the City of Johannesburg with training for the expanded programme on immunization as well as with epidemic preparedness response training, particularly on the measles outbreak in South Africa. The Outbreak Response Unit trained healthcare workers and doctors on how to prepare for epidemics and to manage foodborne disease outbreaks; and helped with the training in several provinces for the mass measles and polio vaccination campaign. The Chemical Pathology Division at Stellenbosch University helps the Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Society of the Western Cape to inform MS patients about recent developments on their disease. Staff members assisted clinicians at regional hospitals in the Western and Eastern Cape regions on how to efficiently use laboratory services. 55
The NICD’s Epidemiology Unit assisted the City of Johannesburg with training for the expanded programme on immunization as well as with epidemic preparedness response training, particularly on the measles outbreak in South Africa. The Outbreak Response Unit trained healthcare workers and doctors on how to prepare for epidemics and to manage foodborne disease outbreaks; and helped with the training in several provinces for the mass measles and polio vaccination campaign. The Chemical Pathology Division at Stellenbosch University helps the Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Society of the Western Cape to inform MS patients about recent developments on their disease. Staff members assisted clinicians at regional hospitals in the Western and Eastern Cape regions on how to efficiently use laboratory services. 55
 Healthcare and other support for the under-resourced sector of our population are needed as new and ambitious government HIV guidelines and earlier entry onto highly active antiretroviral treatment regimens are being implemented. Staff of the medical microbiology and virology divisions plays leading roles in HOPE Cape Town, a non-profit organisation providing outreach, education and counselling on HIV/AIDS and TB to the community in the Western Cape province. This academic and teaching connection supplies HOPE with knowledge to where it is most needed. The medical student elective programme for HOPE - KID-CRU - is very popular among overseas students and they appreciate the opportunity to see our country with all its realities in the townships. This rotation provides a further strong link between HOPE Cape Town and Stellenbosch University 56
Healthcare and other support for the under-resourced sector of our population are needed as new and ambitious government HIV guidelines and earlier entry onto highly active antiretroviral treatment regimens are being implemented. Staff of the medical microbiology and virology divisions plays leading roles in HOPE Cape Town, a non-profit organisation providing outreach, education and counselling on HIV/AIDS and TB to the community in the Western Cape province. This academic and teaching connection supplies HOPE with knowledge to where it is most needed. The medical student elective programme for HOPE - KID-CRU - is very popular among overseas students and they appreciate the opportunity to see our country with all its realities in the townships. This rotation provides a further strong link between HOPE Cape Town and Stellenbosch University 56
 …to Africa The NICD’s Respiratory and Meningeal Pathogens Reference Unit held a laboratory training workshop in The Gambia to help in the fight against pneumococcal disease in West Africa. Training on sexually transmitted infections was given to over 100 African dermato-venereologists in Moshi, Tanzania; to about 150 healthcare workers in Harare, Zimbabwe; and to technologists in microbiological surveillance in Madagascar and Zimbabwe. 57
…to Africa The NICD’s Respiratory and Meningeal Pathogens Reference Unit held a laboratory training workshop in The Gambia to help in the fight against pneumococcal disease in West Africa. Training on sexually transmitted infections was given to over 100 African dermato-venereologists in Moshi, Tanzania; to about 150 healthcare workers in Harare, Zimbabwe; and to technologists in microbiological surveillance in Madagascar and Zimbabwe. 57
 ACCOLADES Our people making us proud • Dr W Burgers, Division of Virology, University of Cape Town (UCT), was awarded a Wellcome Trust Intermediate Fellowship in Public Health and Tropical Medicine. • Dr E Gray, Immunology Laboratory, NICD, was selected by the Gates Foundation to be honoured by the Collaboration for AIDS Vaccine Discovery (CAVD) Council of Principal Investigators as a young/early career investigator who has made important scientific contributions to the work of CAVD. She received a Fogarty award to undergo two months’ training at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, USA. • Dr S Kgalamono, Occupational Medicine Section, NIOH, won one of three Young Investigators Awards at the International Mesothelioma Interest Group Conference held in Japan. 58
ACCOLADES Our people making us proud • Dr W Burgers, Division of Virology, University of Cape Town (UCT), was awarded a Wellcome Trust Intermediate Fellowship in Public Health and Tropical Medicine. • Dr E Gray, Immunology Laboratory, NICD, was selected by the Gates Foundation to be honoured by the Collaboration for AIDS Vaccine Discovery (CAVD) Council of Principal Investigators as a young/early career investigator who has made important scientific contributions to the work of CAVD. She received a Fogarty award to undergo two months’ training at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, USA. • Dr S Kgalamono, Occupational Medicine Section, NIOH, won one of three Young Investigators Awards at the International Mesothelioma Interest Group Conference held in Japan. 58
 • Ms N Mkhize, Division of Virology, UCT, received the L’Oreal Women in Science award. • Dr R Weyers, Department of Haematology and Cell Biology, University of the Free State, was one of a select group of young haemophilia therapists to receive an International ACHIEVE award and travel to Milan. • Prof A-L Williamson, Division of Virology, UCT, was awarded the Cancer Association of South Africa AG Oettlé Memorial Medal for work on the human papillomavirus, the leading cause of cervical cancer. • Dr N Wolter, Respiratory and Meningeal Pathogens Reference Unit, NICD, received the Robert Austrian Research Award 2010 in Pneumococcal Vaccinology presented to her in Tel Aviv, Israel. The award included a $25 000 grant for her research project. 59
• Ms N Mkhize, Division of Virology, UCT, received the L’Oreal Women in Science award. • Dr R Weyers, Department of Haematology and Cell Biology, University of the Free State, was one of a select group of young haemophilia therapists to receive an International ACHIEVE award and travel to Milan. • Prof A-L Williamson, Division of Virology, UCT, was awarded the Cancer Association of South Africa AG Oettlé Memorial Medal for work on the human papillomavirus, the leading cause of cervical cancer. • Dr N Wolter, Respiratory and Meningeal Pathogens Reference Unit, NICD, received the Robert Austrian Research Award 2010 in Pneumococcal Vaccinology presented to her in Tel Aviv, Israel. The award included a $25 000 grant for her research project. 59
 • Prof CA Wright, Division of Anatomical Pathology, University of Stellenbosch, was appointed as a member of the International Academy of Cytology Task Force to promote education and professional development in cytology in developing countries for the period 2010 -2013. She was also elected to the Board of the International Academy of Cytopathology. • Ms A Picton, Immunology Laboratory, NICD, was awarded a South African Fogarty AIDS and TB Training and Research Programme Fellowship to train at the University of Texas 60
• Prof CA Wright, Division of Anatomical Pathology, University of Stellenbosch, was appointed as a member of the International Academy of Cytology Task Force to promote education and professional development in cytology in developing countries for the period 2010 -2013. She was also elected to the Board of the International Academy of Cytopathology. • Ms A Picton, Immunology Laboratory, NICD, was awarded a South African Fogarty AIDS and TB Training and Research Programme Fellowship to train at the University of Texas 60
 Other proudly NHLS achievements include: • The Division of Anatomical Pathology, UCT, was placed first among the 333 international participating laboratories in the general diagnostic external quality assessment module of the Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia. • Immunopaedia, an on-line training site in immunology, developed by Prof C Gray, of the Immunology Laboratory, NICD, received the prestigious Science Prize for Online Resources in Education (SPORE). 61
Other proudly NHLS achievements include: • The Division of Anatomical Pathology, UCT, was placed first among the 333 international participating laboratories in the general diagnostic external quality assessment module of the Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia. • Immunopaedia, an on-line training site in immunology, developed by Prof C Gray, of the Immunology Laboratory, NICD, received the prestigious Science Prize for Online Resources in Education (SPORE). 61
 Our appreciation to the Honourable chair and the Committee for this opportunity to present the 2010/11 annual report THANK YOU 62
Our appreciation to the Honourable chair and the Committee for this opportunity to present the 2010/11 annual report THANK YOU 62


