24bd400ed6fc4973adc3b644ec001ba9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 155

Presentation Plus! Texas and Texans Copyright © by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. Send all inquiries to: GLENCOE DIVISION Glencoe/Mc. Graw-Hill 8787 Orion Place Columbus, Ohio 43240


Chapter Introduction Section 1 Sam Houston’s Government Section 2 Lamar Becomes President Section 3 Houston Regains Presidency Section 4 Texas Becomes a State Chapter Summary Chapter Assessment Click a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides.

Chapter Objectives Section 1: Sam Houston’s Government • Characterize the problems the Republic of Texas faced during its first years. • Explain why Texans wanted the United States to annex Texas. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Chapter Objectives (cont. ) Section 2: Lamar Becomes President • Describe the policies the Lamar administration used toward Native Americans. • Contrast the programs of the Lamar and Houston administrations. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Chapter Objectives (cont. ) Section 3: Houston Regains Presidency • Summarize the ways that President Houston tried to reduce government spending. • Describe the conflicts with Mexico. • Report how Houston attempted to resolve the Texan-Native American conflicts. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Chapter Objectives (cont. ) Section 4: Texas Becomes a State • Discuss the “Texas Question. ” • Describe the annexation of Texas. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Click the Speaker button to replay the audio.

Why It Matters The victory at San Jacinto began a 10 -year period in which Texas was an independent nation. Those 10 years brought both challenges and achievements. Eventually Texas voluntarily gave up its independent status and became a part of the United States.

The Impact Today • The existence of Texas as an independent republic continues to be a source of great pride to Texans. Several organizations such as the Daughters of the Republic of Texas and the Sons of the Republic of Texas were formed to honor the people who lived in Texas at that time and to preserve Texas history. • The United States itself would have a vastly different character if Texas had chosen to remain a separate republic. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.




Guide to Reading Main Idea After gaining independence, Texans faced the challenge of building a new nation. Key Terms • capitol • annexation • expenditure • revenue • tariff Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Guide to Reading (cont. ) Reading Strategy Organizing Information As you read this section, complete a chart like the one shown on page 270 of your textbook by filling in the significance of each person listed. Read to Learn • what problems faced the Republic of Texas during its first years. • why Texans wanted the United States to annex Texas. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
Guide to Reading (cont. ) Section Theme Government and Democracy Texas leaders worked to build a successful government that would be recognized annexed by the United States.

Sam Houston Click the Speaker button to replay the audio.
Did You Know? • Between 1837 and 1841, Texas had given away 1, 162, 240 acres of land, much of it as bounty for members of the Texas army. Each member received 320 acres for each three months of service, plus 640 acres.

Houston Forms a Government • In September 1836 Texans elected Sam Houston president and Mirabeau B. Lamar as vice president. • Texans approved the Constitution of 1836 and proposed that Texas join the United States. • Houston was chosen as the capital for three years. (pages 270– 271) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Houston Forms a Government (cont. ) What action did Houston take as the newly elected president? Houston named members of the new Texas government, selected a new capital, approved Constitution, and proposed Texas join the United States. (pages 270– 271) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Houston Faces Trouble with the Army • Army commander Felix Huston wanted to invade Mexico. • President Houston intervened and sent most of the soldiers home. (page 271) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Houston Faces Trouble with the Army (cont. ) Why did Houston send the soldiers home? He sent them home so they would not invade Mexico and endanger the young republic. (page 271) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

The United States Delays Annexation • Texans wanted annexation to the United States because most Texans had emigrated from the United States and wanted its protection. • Annexation was delayed because the United States did not want to damage relations with Mexico. • Antislavery groups in the United States did not want Texas to join the Union as a slave state. (pages 271– 272) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

The United States Delays Annexation (cont. ) How would annexation damage U. S. relations with Mexico? Mexico did not recognize Texas as independent. If the United States annexed it, Mexico would consider it an annexation of part of Mexico. (pages 271– 272) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Recognition as a Nation • On March 3, 1837, President Andrew Jackson granted official recognition of Texas as a nation. • Houston appointed J. Pinckney Henderson ambassador. • Henderson arranged trade treaties with France and Great Britain. (pages 272– 273) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Recognition as a Nation (cont. ) What was Henderson’s mission in Europe? Henderson’s mission was to negotiate trade deals with France and Great Britain. (pages 272– 273) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Native American and Texan Conflicts • Native Americans resented Anglo Americans settling in Central Texas. • They led a series of raids in 1836 that lasted for several years. • In the 1836 treaty, the Cherokees promised to remain peaceful during Texas’s fight for freedom; negotiators promised the Cherokees title to their land. (pages 273– 274) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Native American and Texan Conflicts (cont. ) • Later, however, the Senate of the Republic of Texas refused to accept the treaty, and each day more settlers took Cherokee land. (pages 273– 274)

Native American and Texan Conflicts (cont. ) How were the Cherokees treated unfairly? After Houston negotiated a treaty that promised them title to their land, the Senate of the Republic of Texas did not accept the treaty, and the Cherokee continued to lose their land. (pages 273– 274) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Texas Debt Soars • Texas also had unpaid bills from the revolution. • To raise money, congress placed a tariff on imported goods. • It also imposed property taxes, business taxes, and land title fees. • The taxes were difficult to collect, and the government continued to spend more than it collected. (page 274) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Texas Debt Soars (cont. ) Why was Texas deeply in debt? It had unpaid bills left over from the revolution, and it was difficult to collect new taxes that their congress imposed. (page 274) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

The Release of Santa Anna • Santa Anna was released in November 1836. • He returned to Mexico and renounced the promises he had made in Texas. • Mexico still did not recognize Texas’s independence. (page 274) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

The Release of Santa Anna (cont. ) How much did Santa Anna’s release affect Texas-Mexico relations? It affected Texas-Mexico relations very little. Mexico still did not recognize Texas’s independence. (page 274) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
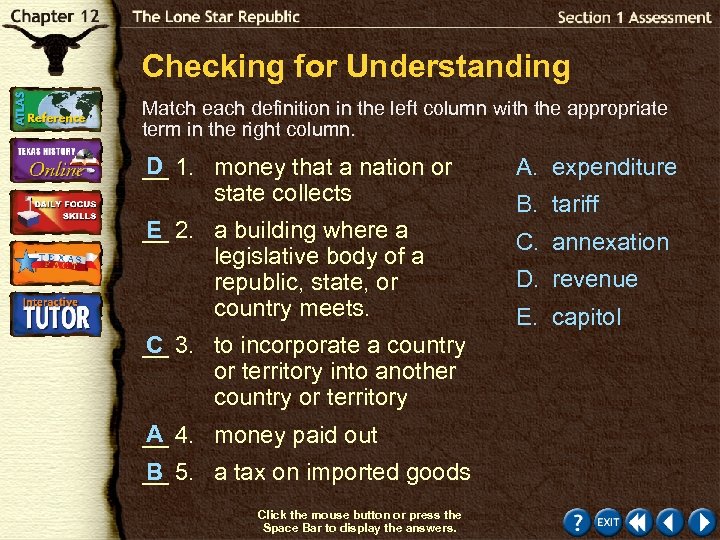
Checking for Understanding Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. D __ 1. money that a nation or state collects A. expenditure E __ 2. a building where a legislative body of a republic, state, or country meets. C. annexation C __ 3. to incorporate a country or territory into another country or territory A __ 4. money paid out B __ 5. a tax on imported goods Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. B. tariff D. revenue E. capitol

Checking for Understanding (cont. ) Reviewing Facts Who were the first president, vice president, and secretary of state of the Republic of Texas? Sam Houston was the first president, Mirabeau Lamar was the first vice president, and Stephen F. Austin was the first secretary of state. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Reviewing Themes Government and Democracy On what date did the United States recognize the government of Texas? On March 3, 1837 the United States recognized the government of Texas. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Critical Thinking Explaining Why did the Texas Congress designate Houston as the first capitol? Columbia was too small, and Houston’s founders had promised to build a handsome city if congress would locate the capital there. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Critical Thinking (cont. ) Summarizing Why did the public debt of Texas continue to increase through the years of the Republic? Debt continued to increase because expenditures were more than revenues. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

TAKS Practice Identifying Problems Give two reasons why some people in the United States opposed the annexation of Texas. There were concerns about relations with Mexico and adding a slave state. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.


Guide to Reading Main Idea President Lamar’s policies differed sharply from Houston’s policies. Key Terms • endowment fund • cabinet • redback Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Guide to Reading (cont. ) Reading Strategy Classifying Information As you read this section, complete a table like the one shown on page 275 of your textbook with the key issues, goals of Lamar’s administration, and what actions were taken. Read to Learn • what policies Lamar’s administration used toward Native Americans. • how the programs of the Lamar and Houston administrations were different. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Guide to Reading (cont. ) Section Theme Government and Democracy Government policy promoted public education.

Native American holding peace pipe Click the Speaker button to replay the audio.

Did You Know? • In 1842, when Santa Anna’s troops took San Antonio, Goliad, and Refugio, many Texans ran from their homes, much as they did during the “Runaway Scrape. ”

Mirabeau Lamar Becomes President • Texans elected Lamar president when Houston’s term ended in 1838. • Improving education was one of Lamar’s goals. • Congress set aside nearly 18, 000 acres of land in each county to support public schools. • Later governments substituted land in West Texas, the value of which multiplied when oil was discovered there in the early 1900 s. (pages 275– 276) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Mirabeau Lamar Becomes President (cont. ) Why did giving land in West Texas for support of schools prove beneficial? When oil was discovered on West Texas land owned by schools, the money from oil helped support the schools. (pages 275– 276) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

The Capital Is Moved to Austin • In 1839 Congress approved Waterloo on the Colorado as the site of a permanent capital. • The new capital was named Austin, in honor of Stephen F. Austin. (page 276) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

The Capital Is Moved to Austin (cont. ) What was the city of Austin’s former name? Waterloo was Austin’s former name. (page 276) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Lamar’s Policy toward Native Americans • Lamar reversed Houston’s policy toward Native Americans, saying Cherokees had no fair claim to Texas lands they occupied. • In 1839 he ordered Cherokees removed from Texas. • Surviving Cherokees were forced from their land moved across the Red River out of Texas. (pages 276– 277) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Lamar’s Policy toward Native Americans (cont. ) How were Lamar’s and Houston’s views about Native Americans different? Houston believed that Cherokees had land ownership rights in Texas. Lamar thought they did not, and he forced the Cherokees out of Texas. (pages 276– 277) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Raids Lead to Council House Fight • After raiding several settlements, the Comanches agreed to meet with Texas authorities. • The Comanches promised to bring their Anglo captives, but produced only one girl, Matilda Lockhart. • The angered Texans tried to take the Comanches hostage, but they resisted. • In what was called the Council House Fight, 7 Texans and 35 Comanches died. (pages 277– 278) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Raids Lead to Council House Fight (cont. ) • The Council House Fight has been called “the greatest blunder in the history of Texan-Native American relations. ” (pages 277– 278)

Raids Lead to Council House Fight (cont. ) Why were the Comanches angry after the Council House Fight? The Comanches were outraged that Texans had killed 35 of their people during a meeting that was supposed to be peaceful. (pages 277– 278) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Texas Rebuilds Its Navy • Lamar ordered a newly restored navy into Mexican waters. • He thought Mexico would recognize Texas in exchange for the promise that the navy would not invade Mexico. • Sam Houston regained the presidency in 1841 and recalled the navy. (page 278) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Texas Rebuilds Its Navy (cont. ) Why did Lamar order the Texas navy into Mexican waters? He thought a strong military presence would force Mexico to recognize Texas’s independence, but they did not. (page 278) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

The Santa Fe Expedition • Texans wanted control of Santa Fe, a trading center on the upper Rio Grande in present-day New Mexico. • In 1841 Lamar sent an expedition to Santa Fe to control the region and open up trade. • The Santa Fe expedition was plagued by misfortune and hardship; heat, shortages of water and food, and attacks by Native Americans led to suffering. (pages 278– 279) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

The Santa Fe Expedition (cont. ) • The expedition was confronted by a Mexican army that forced the Texans to march 1, 000 miles to Mexico City. • The Santa Fe expedition was a failure. (pages 278– 279) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

The Santa Fe Expedition (cont. ) Why did Texas want to control Santa Fe? Control of Santa Fe would help secure the Rio Grande as the border with Mexico. (pages 278– 279) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Financial Difficulties • Lamar’s maintenance of the navy and campaigns were expensive. • Texas was deeply in debt when Lamar left office. (page 279) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Financial Difficulties (cont. ) What policy of Lamar’s contributed to Texas’s debt? His policy of maintaining the Texas navy contributed to Texas’s debt. (page 279) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Checking for Understanding Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. A __ 1. the heads of departments A. cabinet of the executive branch B. endowment appointed by the president fund and confirmed by the C. redback Senate; a group of advisers to a political head of government C __ 2. additional money issued during Mirabeau B. Lamar’s presidency to help in easing the large public debt (redbacks quickly shrank in value) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers.
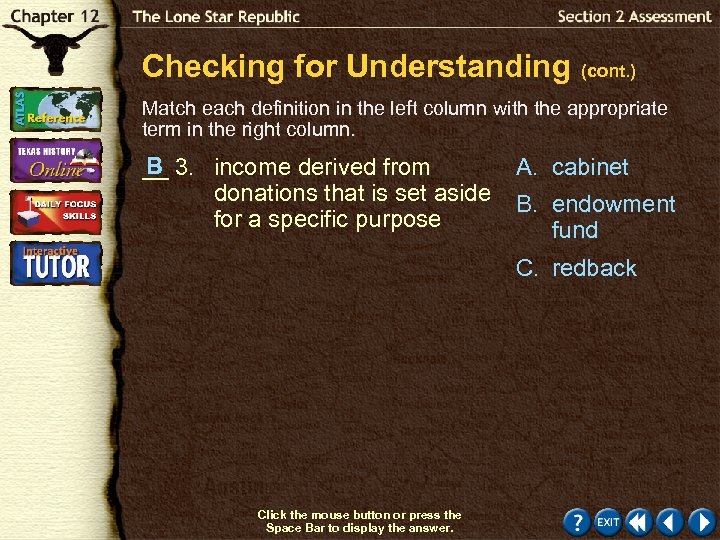
Checking for Understanding (cont. ) Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. B __ 3. income derived from donations that is set aside for a specific purpose A. cabinet B. endowment fund C. redback Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Checking for Understanding (cont. ) Reviewing Facts Why was Houston not reelected when his first term ended in 1838? The Constitution of 1836 banned consecutive terms for president. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Reviewing Themes Government and Democracy Why did the Texas Congress reserve 231, 400 acres of public land? The land was reserved as a source of funds for two universities. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Critical Thinking Explaining Why did President Lamar want to have a strong military? Lamar wanted to remove Native Americans and to force Mexico to recognize Texas. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Critical Thinking (cont. ) Evaluating Solutions How effective were President Lamar’s solutions to financial difficulties? They were not effective. He failed to borrow money and could not back up printed money. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

TAKS Practice Determining Cause and Effect What was the effect of the Council House meeting in San Antonio between Texas authorities and the Comanches? Texans attacked the Comanches in San Antonio, and the Comanches attacked Texans in revenge. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.


Guide to Reading Main Idea Sam Houston’s return to the presidency signaled a change in government’s economic and Native American policies. Key Term • archives Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Guide to Reading (cont. ) Reading Strategy Organizing Information As you read this section, complete a chart like the on page 281 of your textbook, outlining important events and their outcomes. Read to Learn • what ways President Houston tried to reduce government spending. • about conflicts with Mexico. • how Houston attempted to resolve the Texan. Native American conflicts. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Guide to Reading (cont. ) Section Theme Economic Factors Texas attempted to balance the budget, yet the debt increased.

President Sam Houston Click the Speaker button to replay the audio.

Did You Know? • Among the captives of the failed Mier Expedition was William A. A. (“Big Foot”) Wallace. When it was his turn to draw a bean, Wallace had the clever insight that black beans were bigger than white ones, so he was able to choose a white one and escape being executed by a Mexican firing squad.

A Policy of Economy • Houston eliminated government positions and cut the size of the army. • Houston tried to sell navy ships, but angry citizens of Galveston prevented the sale. (page 281) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

A Policy of Economy (cont. ) Why did the debt of the republic increase despite Houston’s attempts to cut costs? Despite Houston’s efforts, the debt of the republic increased, largely because of the high interest that had to be paid. (page 281) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

A Temporary Peace • Houston tried to renew peaceful and fair dealings with the Native Americans. • Treaties signed with various Native Americans guaranteed calm for several years. (page 282) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

A Temporary Peace (cont. ) How did the situation change for Native Americans when Houston regained office? He negotiated peace treaties that reduced the fighting for several years. (page 282) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Invasion Triggers the Archives War • A Mexican army of 500 occupied San Antonio, Goliad, and Refugio. • Houston ordered the government archives moved to Houston. • A group of Austin residents engaged in a skirmish called the Archives War with officials who tried to take away the archives. • The archives and the capital stayed in Austin. (page 282) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Invasion Triggers the Archives War (cont. ) Why did officials want to move the archives from Austin to Houston? They feared that the Mexican army would take Austin, the capital, and seize the archives, which held valuable documents about the Republic of Texas. (page 282) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Woll Invades Texas • In 1842 Mexican forces invaded Texas. • The Texas militia and the Texas Rangers drove them out of Texas. (page 282) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Woll Invades Texas (cont. ) How were the Mexican troops driven out of Texas? The Texas militia and the Texas Rangers were called to drive them out. (page 282) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

The Mier Expedition • In November, 750 militia members were sent to patrol the area from San Antonio to Laredo. • There were no signs of Mexican troops, so Somervell ordered his soldiers back to Gonzales. • About 300 of them refused and moved down the Rio Grande and attacked Mier in Mexico. • The Texans surrendered to a large army of Mexicans on December 26. (pages 282– 283) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

The Mier Expedition (cont. ) What does the Mier expedition tell you about the Texas militia? Many of them were so eager for a battle that a group of independent-minded members disobeyed orders, causing their own capture. (pages 282– 283) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

The Drawing of the Black Beans • The Mexican army marched the captives to Mexico City. • Santa Anna had ordered every 10 th Texan in captivity executed. • A prisoner drawing a black bean would be executed while those who drew a white bean would be imprisoned in Mexico City. (pages 283– 284) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

The Drawing of the Black Beans (cont. ) Why did Mexicans order officers to pick beans first? Seventeen black beans were placed on top of white beans in a mug that had not been stirred. Officers were ordered to choose first in the hope that these men would choose the black beans and would then be executed. This would weaken the armies by taking away their leaders. (pages 283– 284) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Feuds Lead to Unrest in East Texas • Two groups of settlers, the Regulators and the Moderators, had been fighting for years in the Neutral Ground Territory. • Houston sent soldiers into the Neutral Ground Territory to bring peace. • Houston persuaded the settlers that Texans should not be fighting each other. (page 284) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Feuds Lead to Unrest in East Texas (cont. ) What was Houston’s argument to the feuders? He argued that Texans should not be fighting each other. (page 284) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Checking for Understanding Using Key Terms Fill in the blank with the appropriate term. 1. _____ are official government documents. Archives Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Checking for Understanding (cont. ) Reviewing Facts Why did the capital remain in Austin instead of moving to Houston in 1842? Citizens fired on government officials trying to move the archives to Houston. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Reviewing Themes Economic Factors Public debt refers to money owed by a government. Why did the public debt of Texas continue to increase despite attempts by Houston to balance the budget? High interest had to be paid. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Critical Thinking Explaining What happened to those who drew a black bean as compared to a white bean? Why were officers more likely to draw the black bean? Black beans meant death; white beans meant prison. The Mexicans had the officers draw first and the black beans were on top. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Critical Thinking (cont. ) Analyzing How did Houston make temporary peace with the Native Americans? He acknowledged Native Americans’ rights by not allowing whites or Native American to pass into the other’s territory without permission; a white who committed a crime against a Native American would be punished; they also signed treaties. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

TAKS Practice Drawing Conclusions What had the Regulators and the Moderators been fighting over for several years? What could have prevented this conflict? They were fighting over land titles. The conflict could have been prevented by having local officials to keep peace for all Texans. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.


Guide to Reading Main Idea Efforts for Texas annexation were given a boost by the changing political atmosphere in the United States. Key Terms • manifest destiny • joint resolution Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Guide to Reading (cont. ) Reading Strategy Organizing Information As you read this section, complete a chart like the one shown on page 286 of your textbook by filling in the roles that these people played in the annexation of Texas. Read to Learn • about the “Texas Question. ” • about the annexation of Texas. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
Guide to Reading (cont. ) Section Theme Government and Democracy With the approval of the United States Congress, Texas became a state as soon as its people approved annexation and adopted a state constitution.
Sam Houston’s sword and scabbard Click the Speaker button to replay the audio.

Did You Know? • Representatives of Britain and France negotiated a deal with Mexico in which Mexico would recognize Texas’s independence. In return, Texas had to agree not to join the United States. However, the Texas Congress unanimously rejected the Mexican treaty and voted for annexation instead.

The Texas Question • The push for annexation again became a priority during Houston’s second term as president. • Those against annexation believed it would benefit Southern slaveholders and spark war with Mexico; thousands of American immigrants helped to increase the popularity of annexation and strengthen ties with the United States. • In 1844 Texas and United States representatives signed a treaty making Texas a United States territory. (pages 286– 287) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
The Texas Question (cont. ) • Texas would give its public lands to the United States, and the United States would pay all the Republic of Texas’s debts. However, the U. S. Senate rejected the treaty. (pages 286– 287)

The Texas Question (cont. ) Why did the U. S. Senate reject the treaty of the annexation of Texas? Senators did not believe that slavery should continue and that it would hurt relations between the United States and Mexico, which still believed Texas was part of Mexico. (pages 286– 287) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Polk Wins Election • James K. Polk, the Democratic presidential candidate from Tennessee, favored annexation, while Henry Clay of Kentucky, the Whig Party candidate, was against it. • Polk’s close victory showed most of the voters favored annexation. • Growing support for annexation came from settlers who wanted to live on fertile land in Western states, including Texas. (page 288) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Polk Wins Election (cont. ) • Most Americans believed the United States was destined to expand to the western coast. This belief was called manifest destiny. • Even before Polk took office, President John Tyler asked Congress to reconsider annexation. (page 288) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Polk Wins Election (cont. ) What does the term manifest destiny mean? Manifest destiny is the belief that the United States was destined to expand coast to coast. (page 288) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Congress and Texas Approve Annexation • On February 28, 1845, Congress passed a joint resolution for annexation. • The terms were more favorable than those of the 1844 treaty. • Texas could keep its public lands but should sell some to pay its debts. • Texas also could be divided into up to five states, but only with the approval of both Texas and the United States. (pages 288– 289) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Congress and Texas Approve Annexation (cont. ) • Anson Jones, elected Texas president in 1844, called a special session of Congress, which approved annexation. • On October 13, 1845, Texas approved annexation by a landslide vote. • The U. S. Congress approved a new Texas Constitution in December 1845, and President Polk signed a resolution making Texas a state. (pages 288– 289) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Congress and Texas Approve Annexation (cont. ) What do you think was the result of annexation for President Anson Jones? He would no longer be president of the Republic of Texas. (pages 288– 289) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Mexico Offers Recognition • Under pressure from Britain and France, which opposed annexation, Mexico offered to recognize Texas’s independence. • Texans rejected the offer and voted for annexation. (page 289) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Mexico Offers Recognition (cont. ) Why do you think Britain and France opposed Texas’s annexation to the United States? Possible answer: Annexing Texas would make the United States larger, wealthier, and more powerful. (page 289) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

“The Republic of Texas Is No More” • In a ceremony in front of the capitol, Anson Jones, turned over the government to J. Pinckney Henderson, the first governor of the state. • Jones declared, “the Republic of Texas is no more. ” • Texas became the twenty-eighth state. (page 289) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

“The Republic of Texas Is No More” (cont. ) Who took over the leadership of Texas? J. Pinckney Henderson, the first governor of Texas, took over the leadership of Texas. (page 289) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Checking for Understanding Using Key Terms Fill in the blanks with the appropriate terms. 1. ________ is the view that it was fated Manifest destiny that the United States should expand its borders from coast to coast. 2. A _______ is a statement passed by joint resolution both houses of a legislature that has the force of law. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers.

Checking for Understanding (cont. ) Reviewing Facts Why were some people in the United States against annexing Texas? Annexation would benefit slave owners and might cause war with Mexico. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Reviewing Themes Government and Democracy Why (to the surprise of many Texans) did the United States Senate reject the treaty of 1844 to annex Texas? The treaty was rejected because Texas would have been a slave state. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Critical Thinking Identifying Viewpoints The annexation of Texas to the U. S. caused different opinions among Texans. Why did some Texans favor annexation in 1845? Why did some Texans oppose annexation? Those who favored annexation had ties to the U. S. Those Texans who opposed annexation had disagreements with the terms. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

TAKS Practice Drawing Inferences Why do you suppose Sam Houston would not give up his sword during his inauguration ceremony? Possible answer: He might need it again to defend his country. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.


Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.



Reviewing Key Terms Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. A. B. A __ 2. money that a nation or state collects C. E __ 3. the heads of departments D. of the executive branch E. appointed by the president F. and confirmed by the G. Senate; a group of advisors to a political head of government H. I. J __ 4. official government documents J. H __ 1. a tax on imported goods Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. revenue joint resolution capitol expenditure cabinet annexation endowment fund tariff redback archives

Reviewing Key Terms (cont. ) Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. C __ 5. a building where a legislative body of a republic, state, or country meets F __ 6. to incorporate a country or territory into another country or territory I __ 7. additional money issued during Mirabeau B. Lamar’s presidency to help in easing the large public debt (redbacks quickly shrank in value) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. revenue joint resolution capitol expenditure cabinet annexation endowment fund H. tariff I. redback J. archives

Reviewing Key Terms (cont. ) Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. B __ 8. a statement passed by both houses of legislature that has the force of law G __ 9. income derived from donations that is set aside for a specific purpose D __ 10. money paid out Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. revenue joint resolution capitol expenditure cabinet annexation endowment fund H. tariff I. redback J. archives

Reviewing Key Facts List two reasons why annexation of Texas to the United States was delayed. Some Americans opposed adding new slave territory and feared damaged relations with Mexico. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Reviewing Key Facts (cont. ) Describe the actions of the Native Americans in central Texas during 1836 and 1837. The raided settlements, causing death and property loss. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Reviewing Key Facts (cont. ) Why did the government debt of Texas grow during the beginning of the republic? Money spent for government operations and services was greater than money taken in. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Reviewing Key Facts (cont. ) Describe the results of the Texas attack on the Mexican town of Mier. Texans, outnumbered and low on supplies, surrendered. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Reviewing Key Facts (cont. ) List three terms of the joint resolution for annexation. Texas was to become a state as soon as Texans approved and adopted a state constitution. Texas was to keep public lands and pay the debt. Texas could be divided into as many as five states with the approval of Texas and the United States. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Critical Thinking Synthesizing Information Why was President Houston concerned about the treatment of Native Americans? Houston respected the rights of Native Americans and wanted Anglo settlers to treat them fairly; he did not want Native Americans to become hostile. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Critical Thinking (cont. ) Determining Cause and Effect How did Santa Anna’s release affect Texas’s relations with Mexico? Santa Anna’s release did not improve Texas’s relations with Mexico. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
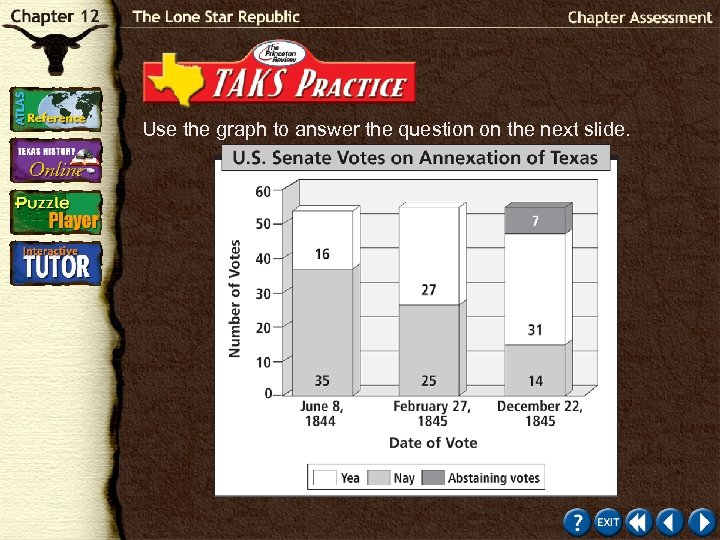
Use the graph to answer the question on the next slide.
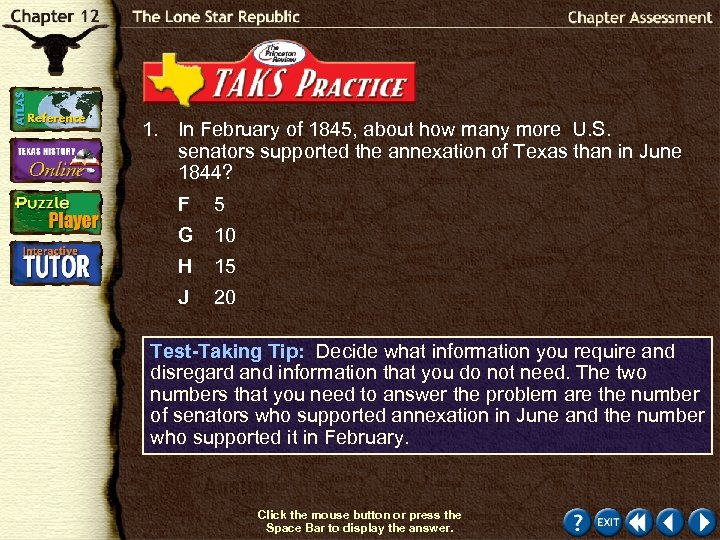
1. In February of 1845, about how many more U. S. senators supported the annexation of Texas than in June 1844? F 5 G 10 H 15 J 20 Test-Taking Tip: Decide what information you require and disregard and information that you do not need. The two numbers that you need to answer the problem are the number of senators who supported annexation in June and the number who supported it in February. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
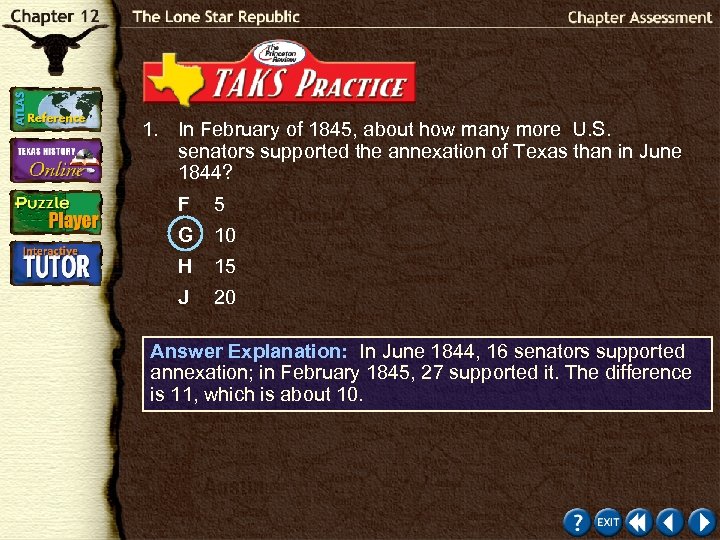
1. In February of 1845, about how many more U. S. senators supported the annexation of Texas than in June 1844? F 5 G 10 H 15 J 20 Answer Explanation: In June 1844, 16 senators supported annexation; in February 1845, 27 supported it. The difference is 11, which is about 10.

What were two defining characteristics of the Republic of Texas? Possible answer: The Republic of Texas had friction with Native Americans and a lack of funds. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.


Explore online information about the topics introduced in this chapter. Click on the Connect button to launch your browser and go to the Texas & Texans Web site. At this site, you will find interactive activities, current events information, and Web sites correlated with the chapters and units in the textbook. When you finish exploring, exit the browser program to return to this presentation. If you experience difficulty connecting to the Web site, manually launch your Web browser and go to http: //texans. glencoe. com.


Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Distinguishing Fact From Opinion Why Learn This Skill? When studying past or current events, it is important to distinguish between fact and opinion. Facts relate exactly what happened, when and where it happened, and who was involved. An opinion expresses a feeling or belief about the event. You should know how to distinguish a fact from an opinion so that you will have accurate information and not confuse the two. This feature is found on page 285 of your textbook. Click the Speaker button to replay the audio.

Distinguishing Fact From Opinion Learning the Skill Here are some ways to distinguish facts from opinions: • Check facts for accuracy by comparing them to other sources. • Can you ask questions beginning with who, what, when or where? If so, you are dealing with facts. • Identify opinions by looking for statements of feelings or beliefs. This feature is found on page 285 of your textbook. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Distinguishing Fact From Opinion Learning the Skill (cont. ) • Opinions often begin with “I believe” or “In my view. ” • Opinions often contain words like should, would, could, best, greatest, all, every, or always. This feature is found on page 285 of your textbook. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Distinguishing Fact From Opinion Practicing the Skill Read each statement on the following slides. Then write F if the statement is a fact or O if it is an opinion. This feature is found on page 285 of your textbook.

Distinguishing Fact From Opinion Practicing the Skill (cont. ) 1. Houston is the most wonderful place in the world. O 2. Comanches and Kiowas killed several settlers and kidnapped two women and several children from Parker’s Fort. F 3. There was a cowardly tribe among us, the Tonkawas. . . hated by all other Indians of every tribe. O 4. In the Council House Fight, 12 Comanche chiefs, 20 warriors, and several women and children were killed. F This feature is found on page 285 of your textbook. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers.

Distinguishing Fact From Opinion Practicing the Skill (cont. ) 5. Congress passed acts in 1839 and 1840 that set aside nearly 18, 000 acres (7, 290 hectares) of land in each Texas county for public education. F 6. She is a noble woman, wife, mother, and patriot–a woman of great thought and heart–yet the most modest and unpretentious of women–Texas is proud of her. O This feature is found on page 285 of your textbook. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers.


Jim R. Hughes was a Texas Ranger for 28 years but lived on even longer as the model for Zane Grey’s fictional hero in The Lone Star Ranger. Other Texas Rangers in fiction were Augustus Mc. Crae and W. F. Call from Larry Mc. Murtry’s Pulitzer Prize-winning novel Lonesome Dove.

Economizing Today’s Texas spending would shock Sam Houston. State expenditures reached almost $50 billion in 2000.


End of Custom Shows WARNING! Do Not Remove This slide is intentionally blank and is set to auto-advance to end custom shows and return to the main presentation.

24bd400ed6fc4973adc3b644ec001ba9.ppt