5519cd026e810ae1d1f4412322993d8b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

PRESENTATION ON THE RESEARCH WORK PUBLISHED AT IEEE Wi. Mob, OCTOBER 2009, MARRAKECH, MOROCCO A NOVEL MULTI-HOP B 3 G ARCHITECTURE FOR ADAPTIVE GATEWAY MANAGEMENT IN HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS NETWORKS (PAPER ID: #1569229692) PUBLISHED AND PRESENTED BY: RAJAN. S B. Tech (CSE) ASSISTANT SYSTEMS ENGINEER TRAINEE (RECRUITED) TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES INDIA

AGENDA n HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS NETWORKS q q q n n n n IEEE 802. 11 -BASED WIRELESS COMPUTER NETWORKS 3 G CELLULAR NETWORK MULTI-HOP BEYOND 3 G NETWORKS MOTIVATION OF RESEARCH REVIEW OF LITERATURE PROPOSED MULTI-HOP B 3 G NETWORK ARCHITECTURE ADAPTIVE GATEWAY MANAGEMENT IN MULTI-HOP B 3 G NETWORKS RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS COMPARISON OF PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE WITH EXISTING HWN ARCHITECTURES CONCLUSIONS AND DIRECTIONS FOR FUTURE RESEARCH

INTRODUCTION n IEEE 802. 11(b)-based short range Wireless Local Area Networks q q n Unlicensed frequency: 2. 4 GHz Gross Data Rate: 11 Mbps Indoor coverage (Theoretical): 250 m Modes supported: Infrastructure, Ad hoc 3 G – Universal Mobile Telecommunication Systems (UMTS) q q Licensed Frequency values: 2 GHz (ITU-T) and 900 MHz (Ideal) Peak Data Rates for Dedicated Channel (dch) 4: n n q High-speed Data Packet Access Data Rates: n n q Uplink Data Rate: 384 Kbps Downlink Data Rate: 2 Mbps Uplink Data Rate: 2 Mbps Downlink Data Rate: 7. 2 Mbps Coverage: ~ 20 km per Base Station Transceiver

MULTI-HOP BEYOND 3 G NETWORKS n n n HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS NETWORKS (HWN): Integration of individual wireless networks for seamless connectivity with co-existence of multiple access techniques MULTI-HOP BEYOND 3 G NETWORKS: HWN formed by integration of IEEE 802. 11(b) multi-hop Mobile Ad hoc Network (MANET) and infrastructure Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) with 3 G cellular network (such as UMTS) PURPOSE: q q q Inter-group communication between nodes of spatially-apart MANETs and WLANs connected by 3 G cellular network as the backbone for anytime, anywhere data connectivity Coupling of high data rate (IEEE 802. 11 b) and wide range of communication (3 G) to facilitate extension of UMTS service over IEEE 802. 11(b) networks Elimination of dead spots in 3 G UMTS through extension of coverage by integrating with MANET/WLAN
MODEL OF A MULTI-HOP B 3 G NETWORK AND RESEARCH OBJECTIVES n RESEARCH OBJECTIVES: q q To enable dual-interface of 3 G and IEEE 802. 11 b networks on Gateway nodes of MANET/WLAN to communicate with the backbone 3 G network To select an optimal Gateway using related metrics of the MANET nodes To perform Adaptive Gateway Migration to sustain end-to-end connectivity of the integrated HWN network for data transfer To provide suitable Gateway Discovery mechanism suited for multi-hop packet transfer to the Gateway
MOTIVATION OF RESEARCH n n n GATEWAY: Dual-interfaced intermediate node in MANET that enables data transfer from nodes of the MANET across the external UMTS network Configuration and enabling of dual interfaces of 3 G and IEEE 802. 11(b) in the Gateway for hybrid interfacing with UMTS and MANET Research Issues in Gateway Management: q q Interfacing Gateway nodes dually with MANET and UMTS network interfaces, which exist in two different spectrum regions Choosing an Optimal Gateway Selection Mechanism to select a MANET Gateway to serve as a liaison with the external 3 G backbone network Gateway-centric issues such as Mobility and Depletion factors of the Gateway Choosing an Optimal Gateway Discovery Mechanism (Pro-active, Reactive, Hybrid)

REVIEW OF LITERATURE n « Simulation-based analysis of TCP over beyond 3 G Cellular Multi-hop Networks » , Anthony Lo et al. [1]: q q n « A Unified Cellular and Ad-hoc Network Architecture » , Ramachandran Ramjee et al. [2]: q n MANET – deployed as a proxy network between cellular network and mobile clients to provide high data rate services. « Issues in integrating Cellular Networks, WLANs and MANETs: A Futuristic Heterogeneous Approach » , Dave Cavalcanti et al. [3]: q q n Devised the protocol stack for IEEE 802. 11(b)- and UMTS-interfaced Gateway node. A single static Gateway node without issues of mobility and depletion Issues on integrating individual networks in Physical, MAC, Data Link, Network, Transport and Application layers Detailed Comparative study of existing HWN architectures « An architecture for connecting ad hoc networks with IPv 6 backbone using a wireless Gateway » , Nico Bayer et al. [4]: q q Dual-interface of Gateway with MANET and WLAN Access Point Wired infrastructure IPv 6 backbone network connected to WLAN AP

REVIEW OF LITERATURE n « An Optimum Multi-metrics Gateway Selection Mechanism in MANET and Infrastructured Networks Integration » , Fudhiyanto Pranata Setiawan et al. [6]: q q q n « Adaptive Distributed Gateway Discovery Scheme in Hybrid Wireless Networks » , Usman Javaid et al. [7]: q q n Gateway selection on basis of metrics such as residual energy, number of hops from source and mobility speed – Limited significance to infrastructured backbone network Multiple Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) method called Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) to outrank the optimum node MANET nodes can communicate with external network using different Gateways, one for each MANET node Combines pro-active and reactive Gateway Discovery mechanisms Describes configuration of advertisement interval and zone, corresponding to number of hops « A Module-based Wireless Node for Multi-Channel and Multi-interface support in ns 2 – Notes and Documentation » , Laurent Paquereau et al. [9]: q q Configuration of a node with dual interfaces of different networks Support for Base and Portal node configuration of IEEE 802. 11 networks.
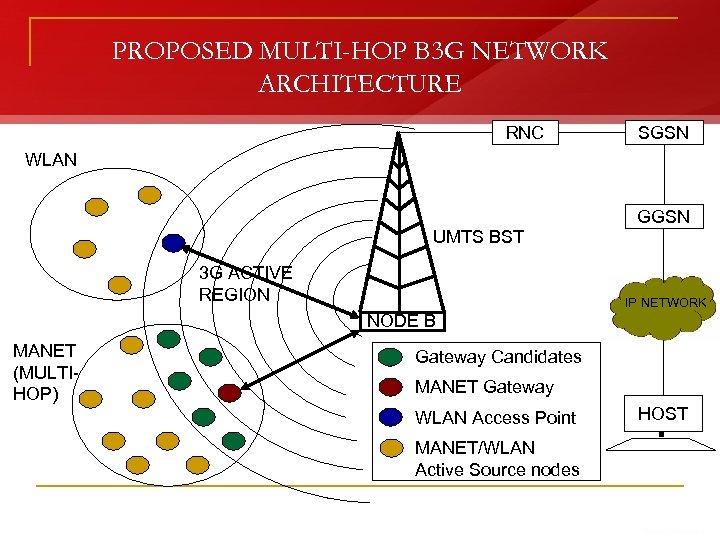
PROPOSED MULTI-HOP B 3 G NETWORK ARCHITECTURE RNC SGSN WLAN GGSN UMTS BST 3 G ACTIVE REGION IP NETWORK NODE B MANET (MULTIHOP) Gateway Candidates MANET Gateway WLAN Access Point MANET/WLAN Active Source nodes HOST
MULTI-HOP B 3 G ARCHITECTURE n Individual networks in the proposed Multi-hop B 3 G Architecture: q q q n n IEEE 802. 11(b) infrastructure-less Multi-hop MANET IEEE 802. 11(b) infrastructure single-hop WLAN 3 G UMTS Cellular backbone network Support of peer-to-peer communication in MANET and support of communication via Access Point in WLAN Components of UMTS Core Network: q q q Mobile Station (MS) Base Station Transceiver (BST) : UTRAN interface Radio Network Controller (RNC) : Co-ordinates radio resources for BST Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) : Routing within core components Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) : Communication with external network and performs packet-switching within UMTS

3 G ACTIVE REGION AND GATEWAY CANDIDATES n n n 3 G ACTIVE REGION: Region within MANET where 3 G signal strength is profound/intense GATEWAY CANDIDATES: Nodes of MANET lying within or migrating to 3 G Active Region Configuration of IEEE 802. 11 b and 3 G UMTS Network interfaces, but enabling of only IEEE 802. 11 b network interface on all nodes Additional enabling of 3 G UMTS Network interface only on GATEWAY CANDIDATES Activation of IEEE 802. 11 b and 3 G Network interfaces only on the node selected as the GATEWAY at that instance Employment of Gateway Selection Mechanism to select a single Gateway from the Gateway Candidates
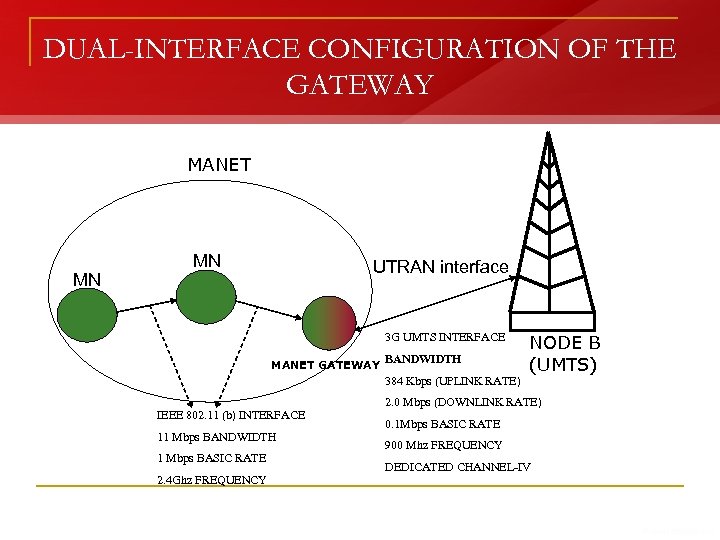
DUAL-INTERFACE CONFIGURATION OF THE GATEWAY MANET MN MN UTRAN interface 3 G UMTS INTERFACE MANET GATEWAY BANDWIDTH 384 Kbps (UPLINK RATE) IEEE 802. 11 (b) INTERFACE 11 Mbps BANDWIDTH 1 Mbps BASIC RATE 2. 4 Ghz FREQUENCY NODE B (UMTS) 2. 0 Mbps (DOWNLINK RATE) 0. 1 Mbps BASIC RATE 900 Mhz FREQUENCY DEDICATED CHANNEL-IV

ADAPTIVE GATEWAY MANAGEMENT MECHANISM n MULTI-METRIC GATEWAY SELECTION MECHANISM: q GATEWAY CANDIDATE METRICS CONSIDERED FOR SELECTION: n n ADAPTIVE GATEWAY MIGRATION MECHANISM: q q n RESIDUAL ENERGY (POSITIVE CRITERION) 3 G SIGNAL STRENGTH (POSITIVE CRITERION) MOBILITY SPEED (NEGATIVE CRITERION) ENERGY-EFFICIENT GATEWAY MIGRATION MULTI-METRIC GATEWAY MIGRATION GATEWAY DISCOVERY MECHANISMS: q q q PRO-ACTIVE REACTIVE HYBRID
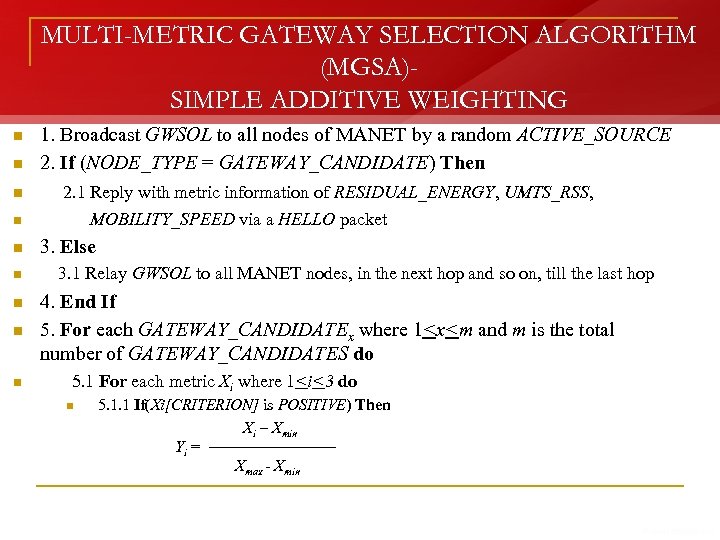
MULTI-METRIC GATEWAY SELECTION ALGORITHM (MGSA)SIMPLE ADDITIVE WEIGHTING n 1. Broadcast GWSOL to all nodes of MANET by a random ACTIVE_SOURCE 2. If (NODE_TYPE = GATEWAY_CANDIDATE) Then 2. 1 Reply with metric information of RESIDUAL_ENERGY, UMTS_RSS, n MOBILITY_SPEED via a HELLO packet n 3. Else n 3. 1 Relay GWSOL to all MANET nodes, in the next hop and so on, till the last hop n n 4. End If 5. For each GATEWAY_CANDIDATEx where 1<x<m and m is the total number of GATEWAY_CANDIDATES do n 5. 1 For each metric Xi where 1<i<3 do n n n 5. 1. 1 If(Xi[CRITERION] is POSITIVE) Then Xi – Xmin Yi = Xmax - Xmin
![MULTI-METRIC GATEWAY SELECTION ALGORITHM (MGSA). . . (Contd) q 5. 1. 2 Else If(Xi[CRITERION] MULTI-METRIC GATEWAY SELECTION ALGORITHM (MGSA). . . (Contd) q 5. 1. 2 Else If(Xi[CRITERION]](https://present5.com/presentation/5519cd026e810ae1d1f4412322993d8b/image-15.jpg)
MULTI-METRIC GATEWAY SELECTION ALGORITHM (MGSA). . . (Contd) q 5. 1. 2 Else If(Xi[CRITERION] is NEGATIVE) Then Xmax – Xi Yi = Xmax - Xmin q 5. 1. 3 End If 5. 2 End For 5. 3 Calculate weight of GATEWAY_CANDIDATEx as: 3 Wx = ∑( Xi[PRIORITY_FACTOR] * Yi ) i= 1 6. End For q q q 7. Now select the GATEWAY_CANDIDATE having the maximum Weight (Wx) as the NEW_GATEWAY 8. Use Hybrid Gateway Discovery Mechanism to advertise the GATEWAY 9. Activate UTRAN interface of the selected Gateway to communicate with 3 G
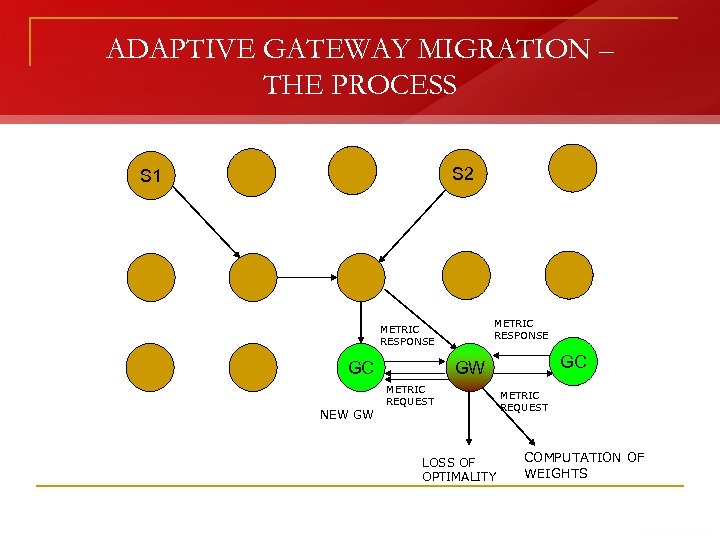
ADAPTIVE GATEWAY MIGRATION – THE PROCESS S 2 S 1 METRIC RESPONSE GC NEW GW GC GW METRIC REQUEST LOSS OF OPTIMALITY METRIC REQUEST COMPUTATION OF WEIGHTS
![MULTI-METRIC ADAPTIVE MIGRATION MECHANISM (MAGMM) n If ((GATEWAY[ENERGY] < THRESHOLD_ENERGY) Or (GATEWAY[SIGNAL_STRENGTH]<THRESHOLD_SIGNAL_STRENGTH)) Then q MULTI-METRIC ADAPTIVE MIGRATION MECHANISM (MAGMM) n If ((GATEWAY[ENERGY] < THRESHOLD_ENERGY) Or (GATEWAY[SIGNAL_STRENGTH]<THRESHOLD_SIGNAL_STRENGTH)) Then q](https://present5.com/presentation/5519cd026e810ae1d1f4412322993d8b/image-17.jpg)
MULTI-METRIC ADAPTIVE MIGRATION MECHANISM (MAGMM) n If ((GATEWAY[ENERGY] < THRESHOLD_ENERGY) Or (GATEWAY[SIGNAL_STRENGTH]<THRESHOLD_SIGNAL_STRENGTH)) Then q q q n Call MGSA to select a new GATEWAY and name it GATEWAY_ELECT Complete the on-going transmission and forward all new incoming packets to GATEWAY_ELECT Use Hybrid Gateway Discovery Mechanism to inform the MANET about GATEWAY_ELECT De-activate 3 G interface on the GATEWAY and Activate 3 G interface on the GATEWAY_ELECT sends ACK packet to GATEWAY becomes ACTIVE_SOURCE in MANET and GATEWAY_ELECT becomes the GATEWAY End If
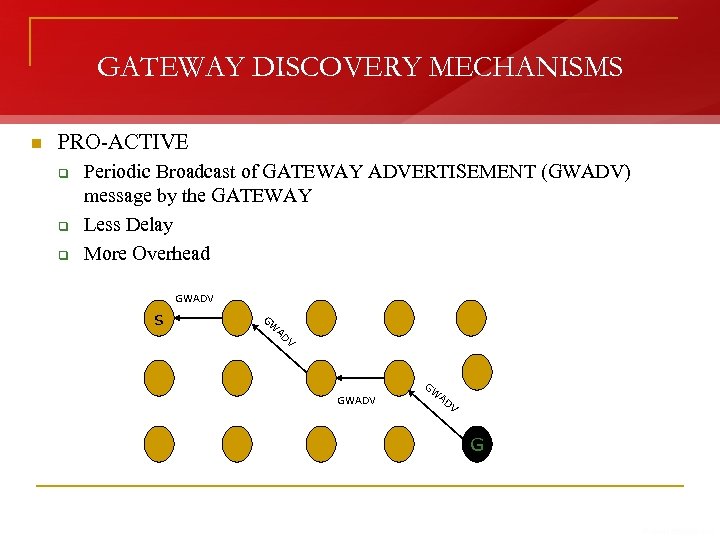
GATEWAY DISCOVERY MECHANISMS n PRO-ACTIVE q q q Periodic Broadcast of GATEWAY ADVERTISEMENT (GWADV) message by the GATEWAY Less Delay More Overhead GWADV s G W AD V GWADV GW AD V G
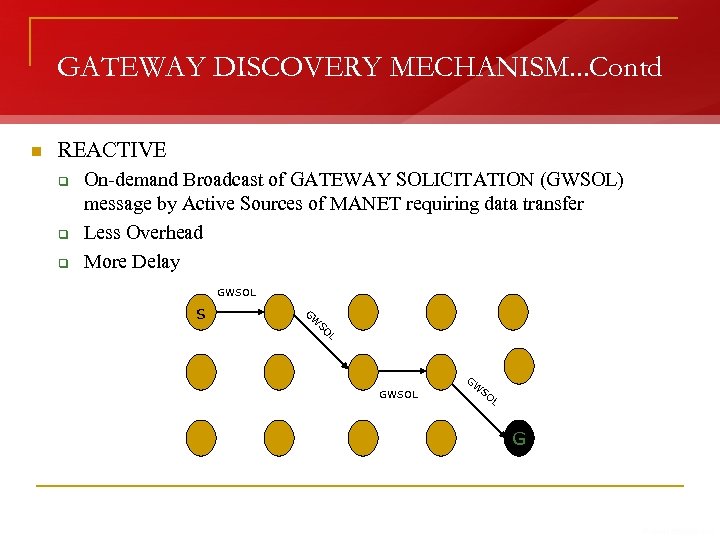
GATEWAY DISCOVERY MECHANISM. . . Contd n REACTIVE q q q On-demand Broadcast of GATEWAY SOLICITATION (GWSOL) message by Active Sources of MANET requiring data transfer Less Overhead More Delay GWSOL s G W SO L GWSOL GW SO L G
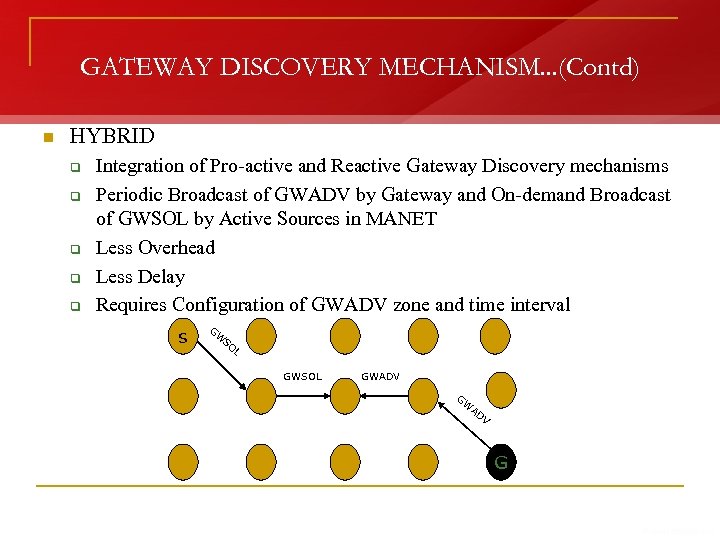
GATEWAY DISCOVERY MECHANISM. . . (Contd) n HYBRID q q q Integration of Pro-active and Reactive Gateway Discovery mechanisms Periodic Broadcast of GWADV by Gateway and On-demand Broadcast of GWSOL by Active Sources in MANET Less Overhead Less Delay Requires Configuration of GWADV zone and time interval s G W SO L GWSOL GWADV GW AD V G
HIERARCHICAL ADDRESSING MECHANISM n n Integrated Multi-hop B 3 G Network consists of individual MANET, UMTS and WLAN sub networks Configuration of a specified number of clusters within the Sub-network Specific number of nodes within every cluster Hierarchical Addressing Format: q <domain_address>. <cluster_id>. <node_id>

MAGMM METRICS n 3 PHASES: q q q n MAGMM METRICS: q q q n q q W 1 : α = 0. 2 ; β = 0. 5 ; γ = 0. 3 W 2 : α = 0. 3 ; β = 0. 2 ; γ = 0. 5 W 3 : α = 0. 33 ; β = 0. 33 ; γ = 0. 33 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF HWN PARAMETERS q q q n α = Residual Energy β = UMTS Signal Strength γ = Mobility Speed MAGMM WEIGHTING FACTORS: q n Energy-efficient Adaptive Gateway Migration Mechanism (EAGMM) Multi-metric Adaptive Gateway Migration Mechanism (MAGMM) End-to-end Polymorphic Routing Transaction Duration (TD) Data Packet Delivery Ratio (DPDR) Control Packet Overhead (CPO) Throughput Packet Drop Fraction Evaluation of Energy-efficient and Multi-metric Adaptive Gateway Migration against the number of sources generating data packets
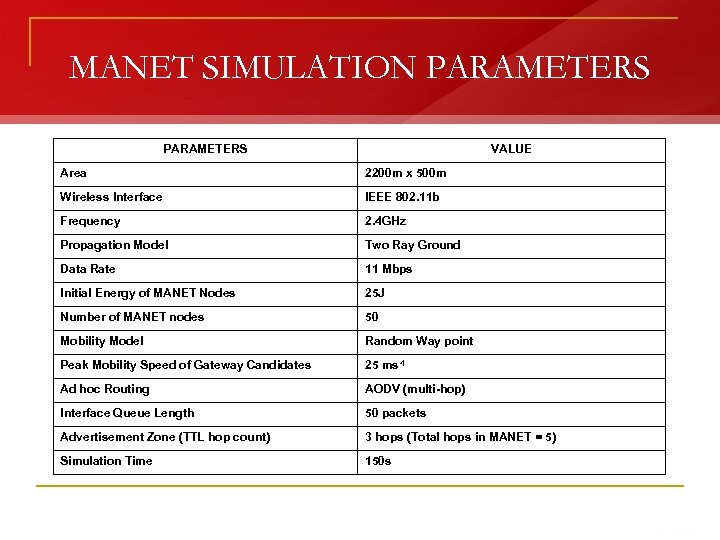
MANET SIMULATION PARAMETERS VALUE Area 2200 m x 500 m Wireless Interface IEEE 802. 11 b Frequency 2. 4 GHz Propagation Model Two Ray Ground Data Rate 11 Mbps Initial Energy of MANET Nodes 25 J Number of MANET nodes 50 Mobility Model Random Way point Peak Mobility Speed of Gateway Candidates 25 ms-1 Ad hoc Routing AODV (multi-hop) Interface Queue Length 50 packets Advertisement Zone (TTL hop count) 3 hops (Total hops in MANET = 5) Simulation Time 150 s
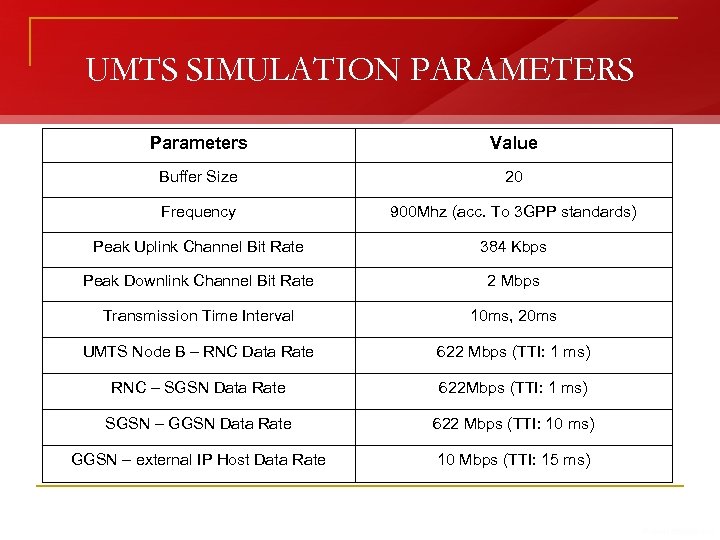
UMTS SIMULATION PARAMETERS Parameters Value Buffer Size 20 Frequency 900 Mhz (acc. To 3 GPP standards) Peak Uplink Channel Bit Rate 384 Kbps Peak Downlink Channel Bit Rate 2 Mbps Transmission Time Interval 10 ms, 20 ms UMTS Node B – RNC Data Rate 622 Mbps (TTI: 1 ms) RNC – SGSN Data Rate 622 Mbps (TTI: 1 ms) SGSN – GGSN Data Rate 622 Mbps (TTI: 10 ms) GGSN – external IP Host Data Rate 10 Mbps (TTI: 15 ms)
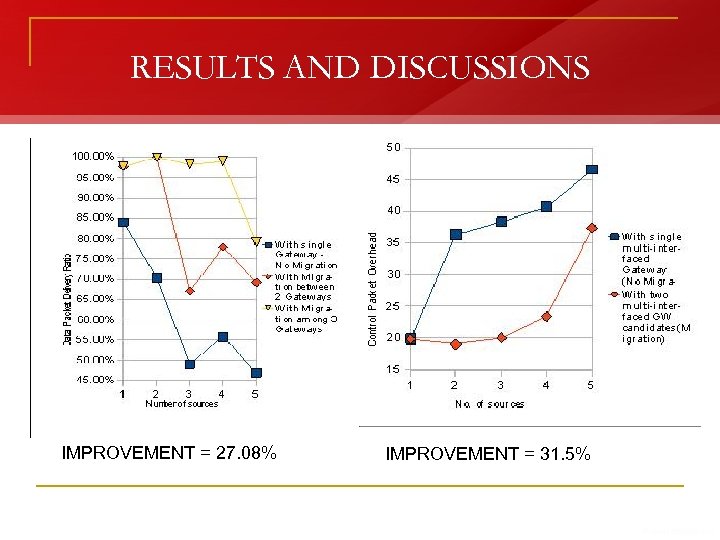
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS IMPROVEMENT = 27. 08% IMPROVEMENT = 31. 5%
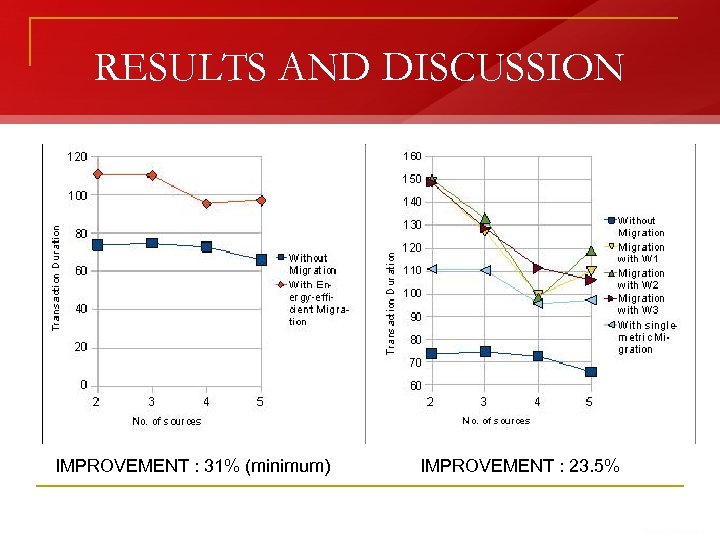
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION IMPROVEMENT : 31% (minimum) IMPROVEMENT : 23. 5%
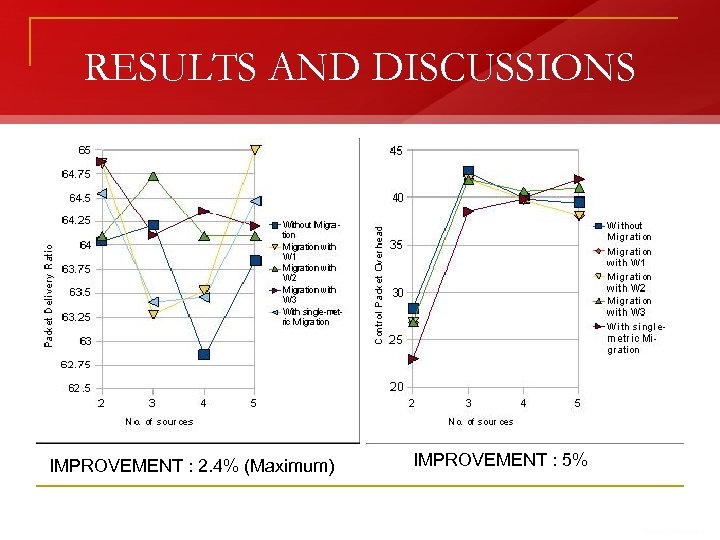
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS IMPROVEMENT : 2. 4% (Maximum) IMPROVEMENT : 5%
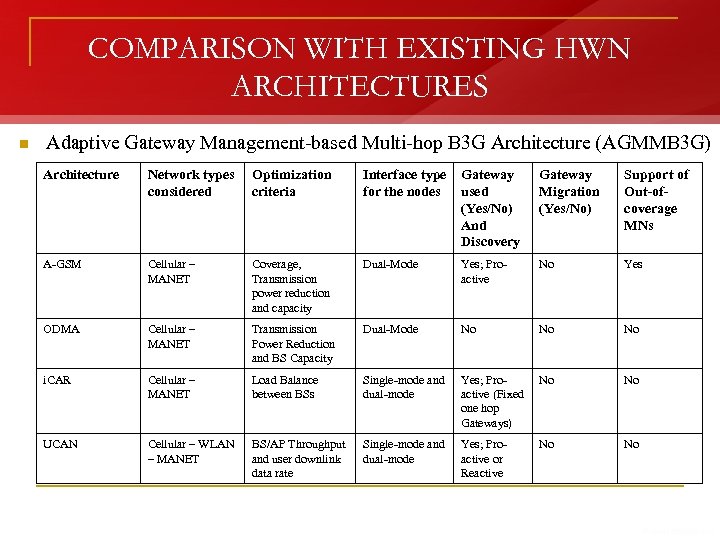
COMPARISON WITH EXISTING HWN ARCHITECTURES n Adaptive Gateway Management-based Multi-hop B 3 G Architecture (AGMMB 3 G) Architecture Network types considered Optimization criteria Interface type for the nodes Gateway used (Yes/No) And Discovery Gateway Migration (Yes/No) Support of Out-ofcoverage MNs A-GSM Cellular – MANET Coverage, Transmission power reduction and capacity Dual-Mode Yes; Proactive No Yes ODMA Cellular – MANET Transmission Power Reduction and BS Capacity Dual-Mode No No No i. CAR Cellular – MANET Load Balance between BSs Single-mode and dual-mode Yes; Proactive (Fixed one hop Gateways) No No UCAN Cellular – WLAN – MANET BS/AP Throughput and user downlink data rate Single-mode and dual-mode Yes; Proactive or Reactive No No
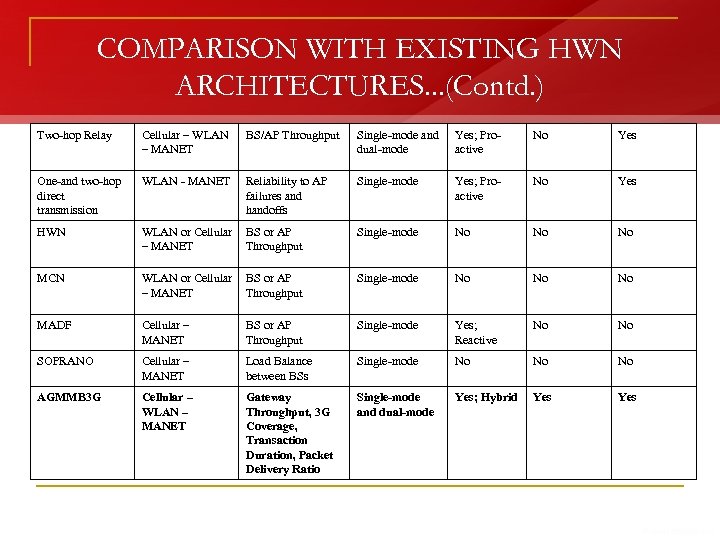
COMPARISON WITH EXISTING HWN ARCHITECTURES. . . (Contd. ) Two-hop Relay Cellular – WLAN – MANET BS/AP Throughput Single-mode and dual-mode Yes; Proactive No Yes One-and two-hop direct transmission WLAN - MANET Reliability to AP failures and handoffs Single-mode Yes; Proactive No Yes HWN WLAN or Cellular BS or AP – MANET Throughput Single-mode No No No MCN WLAN or Cellular BS or AP – MANET Throughput Single-mode No No No MADF Cellular – MANET BS or AP Throughput Single-mode Yes; Reactive No No SOPRANO Cellular – MANET Load Balance between BSs Single-mode No No No AGMMB 3 G Cellular – WLAN – MANET Gateway Throughput, 3 G Coverage, Transaction Duration, Packet Delivery Ratio Single-mode and dual-mode Yes; Hybrid Yes

CONCLUSIONS AND DIRECTIONS FOR FUTURE RESEARCH n CONCLUSION SUMMARY: q q Devised a multi-hop B 3 G Network Architecture Adaptive Gateway Management n n q q n Multi-metric Gateway Selection Algorithm (MGSA) Energy-efficient Adaptive Gateway Migration Mechanism (EAGMM) Multi-metric Adaptive Gateway Migration Mechanism (MAGMM) Hybrid Gateway Discovery Sustains connectivity of the MANET with the external UMTS for a longer time. Evaluation of multi-hop B 3 G in terms of Transaction Duration, Data Packet Delivery Ratio and Control Packet Overhead FUTURE WORK: q q Proposal of an End-to-end polymorphic routing, integrating multi-hop reactive routing in MANET, pro-active routing in 3 G UMTS, single-hop packet forwarding in WLA for data transfer in the integrated HWN Enabling Qo. S group communication for multicasting in HWN
![REFERENCES [1] Anthony Lo, Jinglong Zhou, Ignas Niemegeers, “Simulation-based Analysis of TCP over beyond REFERENCES [1] Anthony Lo, Jinglong Zhou, Ignas Niemegeers, “Simulation-based Analysis of TCP over beyond](https://present5.com/presentation/5519cd026e810ae1d1f4412322993d8b/image-31.jpg)
REFERENCES [1] Anthony Lo, Jinglong Zhou, Ignas Niemegeers, “Simulation-based Analysis of TCP over beyond 3 G Cellular Multi-Hop Networks”, In Proceedings of the 17 th Annual IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), pp. 1 -5, September 2006. [2] Maiyun Luo, Ramachandran Ramjee, Prasun Sinha, Li(Erran) Li, Songwu Lu, “A Unified Cellular and Ad-Hoc Network Architecture (UCAN)”, In Proceedings of ACM MOBICOM, pp. 353 -367, September 2003 [3] Dave Cavalcanti, Dharma Agarwal, Carlos Cordeiro, Bin Xie and Anup Kumar, “Issues in Integrating Cellular Networks, WLANs and MANETs: A Futuristic Heterogeneous Wireless Network”, In IEEE Wireless Communications Magazine, v 12 i 3. pp. 30 -41, June 2005. [4] Nico Bayer, Bangnan Xu and Sven Hische, “An Architecture for connecting Ad hoc Networks with the IPv 6 Backbone (6 Bone) using a wireless Gateway”, In Proceedings of European Wireless Conference, February 2004. [5] “Overview of the Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS)”, at http: //www. umtsworld. com/technology/overview. htm
![REFERENCES [6] Fudhiyanto Pranata Setiawan, Safdar Hussain Bouk and Iwao Sasase, “An Optimum Multiple REFERENCES [6] Fudhiyanto Pranata Setiawan, Safdar Hussain Bouk and Iwao Sasase, “An Optimum Multiple](https://present5.com/presentation/5519cd026e810ae1d1f4412322993d8b/image-32.jpg)
REFERENCES [6] Fudhiyanto Pranata Setiawan, Safdar Hussain Bouk and Iwao Sasase, “An Optimum Multiple Metrics Gateway Selection Mechanism in MANET and Infrastructured Networks Integration”, In Proceedings Of IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, pp. 2229 -2234, March 2008. [7] Usman Javaid, Djamal-Eddine Meddour, Sahibzada Ali Mahmud, Toufik Ahmed, “Adaptive Distributed Gateway Discovery Scheme in Hybrid Wireless Networks”, In Proceedings Of IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, pp. 2735 -2740, March 2008. [8] Fall, K. and Varadhan, K. “The ns Manual”. available at http: //wwwi. isi. edu/nsnam/ns/nsdocumentation. html [9] Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication Systems, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, “A Module-based Wireless Node for Multichannel Multi-interface support in ns 2 – Notes and Documentation”, Laurent Paquereau edition, March 2007. [10] Anthony Lo, Jinglou Zhou, Martin Jacobsson, Ignas Niemegeers, “ns-2 Models for Simulating a Novel Beyond 3 G Cellular Multi-hop Network”, In Proceeding series of ACM International Conference; Vol. 202, 2006.

REMAINING PORTION OF THE B. Tech PROJECT WORK – UNCOVERED IN IEEE Wi. Mob 2009 (INDICATED AS FUTURE RESEARCH)
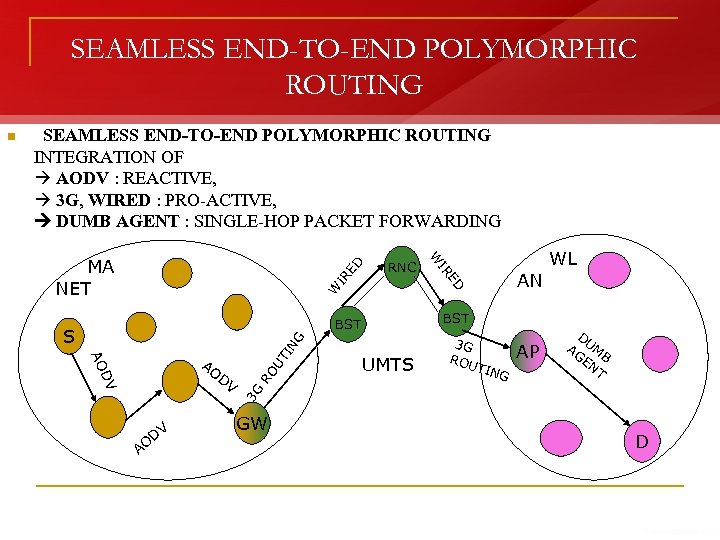
SEAMLESS END-TO-END POLYMORPHIC ROUTING INTEGRATION OF AODV : REACTIVE, 3 G, WIRED : PRO-ACTIVE, DUMB AGENT : SINGLE-HOP PACKET FORWARDING ED IR W ED DV AO DV IN G UT DV RO AO AO AN WL BST S IR RNC W MA NET UMTS 3 G ROU T ING AP D AG UM EN B T 3 G n GW D

END-TO-END POLYMORPHIC ROUTING ALGORITHM n If (source == MANET_NODE) Then q q n Else If (source == WLAN_NODE) Then q q n n Select new Gateway by Multi-metric Gateway Selection mechanism or by MAGMM, in case existing Gateway loses optimality Identify GATEWAY within MANET sub-network using Hierarchical Addressing mechanism If Gateway is determined, use reactive routing protocol to route data packets to GATEWAY Use pro-active routing to forward data from 3 G interface of the GATEWAY to UMTS BST Use DUMB_AGENT routing for single-hop packet forwarding from source to AP Use pro-active routing to forward data from 3 G interface of the AP to UMTS BST End If Identify RNC in the UMTS sub-network using Hierarchical Addressing
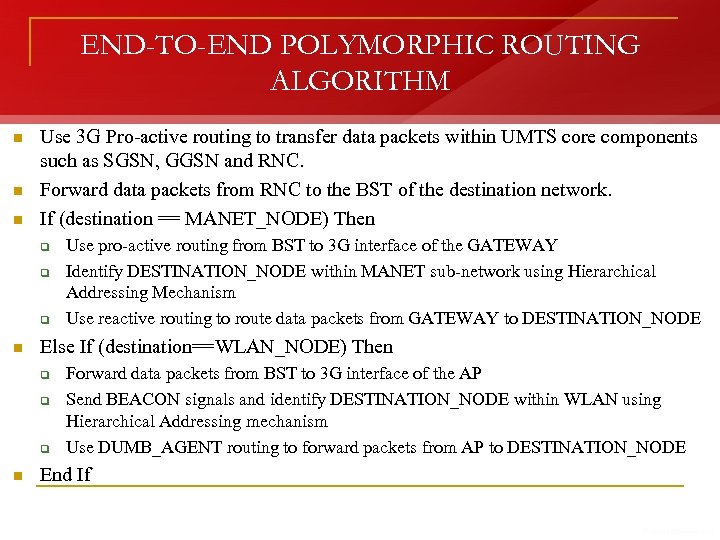
END-TO-END POLYMORPHIC ROUTING ALGORITHM n n n Use 3 G Pro-active routing to transfer data packets within UMTS core components such as SGSN, GGSN and RNC. Forward data packets from RNC to the BST of the destination network. If (destination == MANET_NODE) Then q q q n Else If (destination==WLAN_NODE) Then q q q n Use pro-active routing from BST to 3 G interface of the GATEWAY Identify DESTINATION_NODE within MANET sub-network using Hierarchical Addressing Mechanism Use reactive routing to route data packets from GATEWAY to DESTINATION_NODE Forward data packets from BST to 3 G interface of the AP Send BEACON signals and identify DESTINATION_NODE within WLAN using Hierarchical Addressing mechanism Use DUMB_AGENT routing to forward packets from AP to DESTINATION_NODE End If
END-TO-END POLYMORPHIC ROUTING ALGORITHM n n Forward data packets from RNC to the BST of the destination network. If (destination == MANET_NODE) Then q q q n Else If (destination==WLAN_NODE) Then q q q n Use pro-active routing from BST to 3 G interface of the GATEWAY Identify DESTINATION_NODE within MANET sub-network using Hierarchical Addressing Mechanism Use reactive routing to route data packets from GATEWAY to DESTINATION_NODE Forward data packets from BST to 3 G interface of the AP Send BEACON signals and identify DESTINATION_NODE within WLAN using Hierarchical Addressing mechanism Use DUMB_AGENT routing to forward packets from AP to DESTINATION_NODE End If
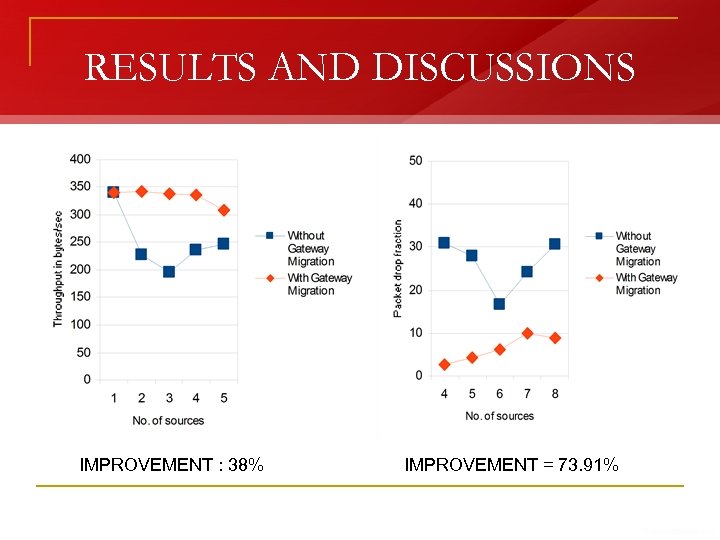
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS IMPROVEMENT : 38% IMPROVEMENT = 73. 91%

QUERIES? ? ?

THANK YOU PRESENTED BY: RAJAN. S B. Tech (CSE) RECRUITED ASSISTANT SYSTEMS ENGINEER TRAINEE TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES PUDUCHERRY, INDIA
5519cd026e810ae1d1f4412322993d8b.ppt