4189871d4d688d128252957d1cb2f9ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 PRESENTATION ON Indian Power Sector GHG Reduction Strategy by Mr. V. S. Verma Member (Planning) Central Electricity Authority International Workshop on Carbon Capture and Storage in Power Sector 22 -23 rd January 2008
PRESENTATION ON Indian Power Sector GHG Reduction Strategy by Mr. V. S. Verma Member (Planning) Central Electricity Authority International Workshop on Carbon Capture and Storage in Power Sector 22 -23 rd January 2008
 INDIAN POWER SCENERIO
INDIAN POWER SCENERIO
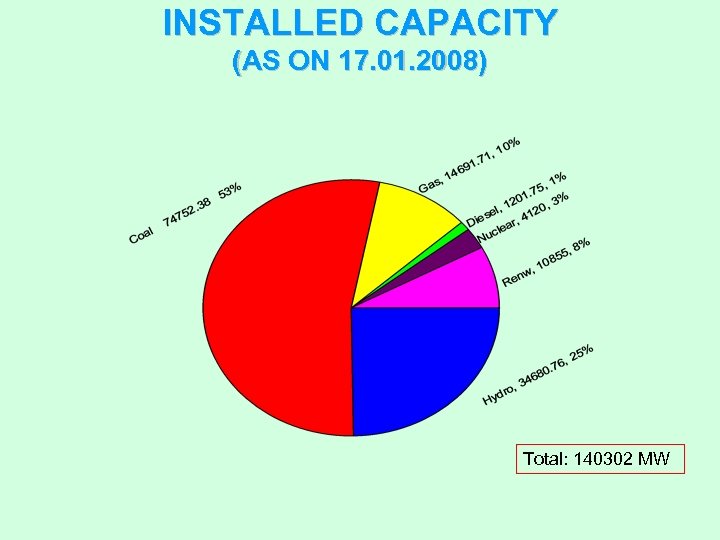 INSTALLED CAPACITY (AS ON 17. 01. 2008) Total: 140302 MW
INSTALLED CAPACITY (AS ON 17. 01. 2008) Total: 140302 MW
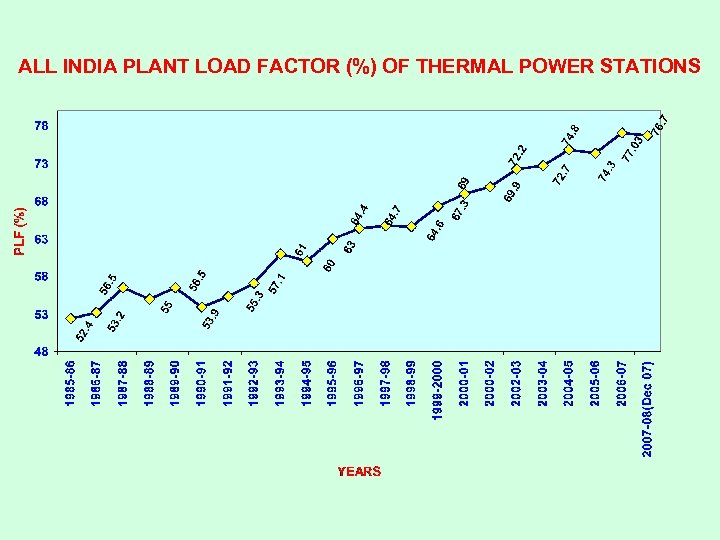 ALL INDIA PLANT LOAD FACTOR (%) OF THERMAL POWER STATIONS
ALL INDIA PLANT LOAD FACTOR (%) OF THERMAL POWER STATIONS
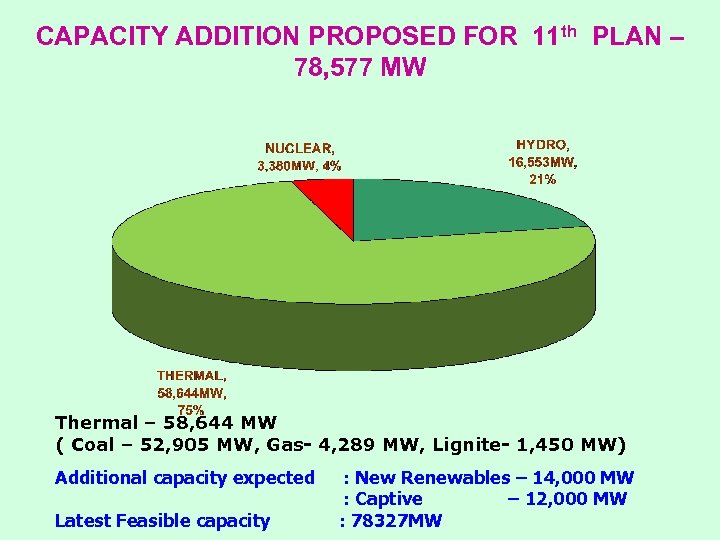 CAPACITY ADDITION PROPOSED FOR 11 th PLAN – 78, 577 MW Thermal – 58, 644 MW ( Coal – 52, 905 MW, Gas- 4, 289 MW, Lignite- 1, 450 MW) Additional capacity expected Latest Feasible capacity : New Renewables – 14, 000 MW : Captive – 12, 000 MW : 78327 MW
CAPACITY ADDITION PROPOSED FOR 11 th PLAN – 78, 577 MW Thermal – 58, 644 MW ( Coal – 52, 905 MW, Gas- 4, 289 MW, Lignite- 1, 450 MW) Additional capacity expected Latest Feasible capacity : New Renewables – 14, 000 MW : Captive – 12, 000 MW : 78327 MW
 11 TH PLAN PROGRAMME (AS ON 17. 01. 2008) • 10 th Plan capacity addition only 21, 180 MW. About 11, 000 MW slippages due to causes attributable to equipment suppliers and contractors. • 11 th Plan - 78, 577 MW Proposed: Latest Total : 78327 MW - 6886 MW capacity already commissioned - 59991 MW (77%) under construction - 11450 MW - Letter of awards yet to be placed - Coal linkages available for 96% of coal based plants - 92% hydro capacity under construction/commissioned - All gas based projects under execution or gas tied up from local sources • Additional 13, 000 MW gas based projects if gas available for long term at reasonable price
11 TH PLAN PROGRAMME (AS ON 17. 01. 2008) • 10 th Plan capacity addition only 21, 180 MW. About 11, 000 MW slippages due to causes attributable to equipment suppliers and contractors. • 11 th Plan - 78, 577 MW Proposed: Latest Total : 78327 MW - 6886 MW capacity already commissioned - 59991 MW (77%) under construction - 11450 MW - Letter of awards yet to be placed - Coal linkages available for 96% of coal based plants - 92% hydro capacity under construction/commissioned - All gas based projects under execution or gas tied up from local sources • Additional 13, 000 MW gas based projects if gas available for long term at reasonable price
 NON-CONVENTIONAL ENERGY PLANTS NON CONVENTIONAL ENERGY PLANTS Ø Installed Capacity at the end of 10 th Plan( as on 31. 12. 2007)- 10, 855. 3 MW. Ø 11 th Plan target- 14, 000 MW Wind Power-10, 500 MW Biomass Power, Baggasse Co-generation and Biomass Gasifiers- 2, 100 MW Small Hydro (up to 25 MW)-1400 MW
NON-CONVENTIONAL ENERGY PLANTS NON CONVENTIONAL ENERGY PLANTS Ø Installed Capacity at the end of 10 th Plan( as on 31. 12. 2007)- 10, 855. 3 MW. Ø 11 th Plan target- 14, 000 MW Wind Power-10, 500 MW Biomass Power, Baggasse Co-generation and Biomass Gasifiers- 2, 100 MW Small Hydro (up to 25 MW)-1400 MW
 India’s Position • • • No obligation to reduce emissions Per capita Carbon di-oxide emission of India is amongst the lowest in the world. Contributes around 4% of world total. Country wise per capita CO 2 emission in 2004 (tonnes of CO 2/annum) – – – India 1. 2 USA 20. 6 U. K 9. 8 China 3. 8 World 4. 5 Source: UNDP Human Development report 2007/08
India’s Position • • • No obligation to reduce emissions Per capita Carbon di-oxide emission of India is amongst the lowest in the world. Contributes around 4% of world total. Country wise per capita CO 2 emission in 2004 (tonnes of CO 2/annum) – – – India 1. 2 USA 20. 6 U. K 9. 8 China 3. 8 World 4. 5 Source: UNDP Human Development report 2007/08
 Average Emissions from Power Sector • With continuous Effort of Government of India average emission rate is showing declining trend indicating larger commitment • Weighted average emissions rate (t. CO 2/MWh) 2003 -04 --- 0. 85 2004 -05 --- 0. 84 2005 -06 --- 0. 82 2006 -07 --- 0. 80
Average Emissions from Power Sector • With continuous Effort of Government of India average emission rate is showing declining trend indicating larger commitment • Weighted average emissions rate (t. CO 2/MWh) 2003 -04 --- 0. 85 2004 -05 --- 0. 84 2005 -06 --- 0. 82 2006 -07 --- 0. 80
 Status of Clean Development Mechanism Projects (CDM) in India 1. National CDM Authority (NCDMA) already given Host country approvals to more than 700 Projects 2. 296 Indian CDM projects already registered with CDM Executive Board out of World Total of 868 projects (35%) 3. Main Projects: Waste heat recovery, Small Hydro, Biomass based Power Generation, Wind Power and Energy Efficiency improvement in Industries like cement etc.
Status of Clean Development Mechanism Projects (CDM) in India 1. National CDM Authority (NCDMA) already given Host country approvals to more than 700 Projects 2. 296 Indian CDM projects already registered with CDM Executive Board out of World Total of 868 projects (35%) 3. Main Projects: Waste heat recovery, Small Hydro, Biomass based Power Generation, Wind Power and Energy Efficiency improvement in Industries like cement etc.
 Indian Scenario-CDM • Exists high potential of Carbon credits. • Baseline Carbon di-oxide emissions from power sector already in place- First CDM country • Wide spectrum of projects with different sizes • Dynamic, Transparent & Speedy processing by Indian National CDM Authority (NCDMA) for Host Country Approval • Vast Technical Human Resource • Strong Industrial Base
Indian Scenario-CDM • Exists high potential of Carbon credits. • Baseline Carbon di-oxide emissions from power sector already in place- First CDM country • Wide spectrum of projects with different sizes • Dynamic, Transparent & Speedy processing by Indian National CDM Authority (NCDMA) for Host Country Approval • Vast Technical Human Resource • Strong Industrial Base
 GOVERNMENT’S STRAGTEGY/INITIATIVE FOR GHG REDUCTION
GOVERNMENT’S STRAGTEGY/INITIATIVE FOR GHG REDUCTION
 Main Sectors of Green House Gases Emissions – Energy Sector – Transport Sector – Agriculture Sector – Industrial Sector • Power sector is estimated to contribute around 50% of total CO 2 Emissions
Main Sectors of Green House Gases Emissions – Energy Sector – Transport Sector – Agriculture Sector – Industrial Sector • Power sector is estimated to contribute around 50% of total CO 2 Emissions
 Major Initiatives • Improvement in efficiency and performance of existing units - through renovation and Modernisation schemes - Partnership in excellence. - Establishment of Energy Efficiency cells at thermal power stations • Energy Conservation through legislation • Promotion to Renewable Energy Sources • 50, 000 MW Hydro Initiative launched
Major Initiatives • Improvement in efficiency and performance of existing units - through renovation and Modernisation schemes - Partnership in excellence. - Establishment of Energy Efficiency cells at thermal power stations • Energy Conservation through legislation • Promotion to Renewable Energy Sources • 50, 000 MW Hydro Initiative launched
 Major Initiatives Cont… Publication of Carbon di-oxide Baseline Emission database for Indian Power sector by Central Electricity Authority – Facilitate prospective project Developers for consistent and accurate quantification of Carbon di-oxide emission by their projects thereby reducing the project development cost – Enhance acceptability of Indian CDM projects Would help expedite the clearance /approval process
Major Initiatives Cont… Publication of Carbon di-oxide Baseline Emission database for Indian Power sector by Central Electricity Authority – Facilitate prospective project Developers for consistent and accurate quantification of Carbon di-oxide emission by their projects thereby reducing the project development cost – Enhance acceptability of Indian CDM projects Would help expedite the clearance /approval process
 Major Initiatives Cont… • Higher size thermal Supercritical units (660/800 MW) for improved efficiency in XIth Plan (2007 -2012) and beyond - Efficiency gain of about 2% - 11 Nos. of 660 MW (under XIth Plan) - 1 No. of 800 MW (under XIth Plan) • 52905 MW Coal fired Units • 16553 MW Hydro • 3880 Nuclear
Major Initiatives Cont… • Higher size thermal Supercritical units (660/800 MW) for improved efficiency in XIth Plan (2007 -2012) and beyond - Efficiency gain of about 2% - 11 Nos. of 660 MW (under XIth Plan) - 1 No. of 800 MW (under XIth Plan) • 52905 MW Coal fired Units • 16553 MW Hydro • 3880 Nuclear
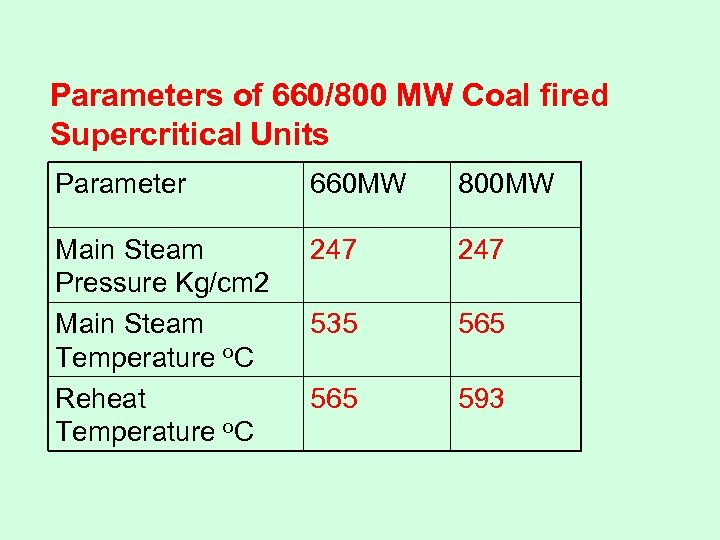 Parameters of 660/800 MW Coal fired Supercritical Units Parameter 660 MW 800 MW Main Steam Pressure Kg/cm 2 Main Steam Temperature o. C Reheat Temperature o. C 247 535 565 593
Parameters of 660/800 MW Coal fired Supercritical Units Parameter 660 MW 800 MW Main Steam Pressure Kg/cm 2 Main Steam Temperature o. C Reheat Temperature o. C 247 535 565 593
 Major Initiatives Cont… • Participating in Asia Pacific Partnership (APP) of USAID for Clean Development and Climate – To accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy technologies. - US, Australia, Japan, South Korea, China and India - MOP coordinates Power Generation and Transmission task force -Work on Efficiency improvement of two thermal power plants namely Ropar and Kolaghat Thermal Power station already started.
Major Initiatives Cont… • Participating in Asia Pacific Partnership (APP) of USAID for Clean Development and Climate – To accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy technologies. - US, Australia, Japan, South Korea, China and India - MOP coordinates Power Generation and Transmission task force -Work on Efficiency improvement of two thermal power plants namely Ropar and Kolaghat Thermal Power station already started.
 Major Initiatives Cont… • Adoption of Clean Coal Technologies – Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) – Suitable for Indian Coal/ Imported Coal – Demonstration project 100 MW by BHEL • Ultra Mega Projects(4000 MW capacity) at various pithead and coastal locations
Major Initiatives Cont… • Adoption of Clean Coal Technologies – Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) – Suitable for Indian Coal/ Imported Coal – Demonstration project 100 MW by BHEL • Ultra Mega Projects(4000 MW capacity) at various pithead and coastal locations
 Major Initiatives Cont… • Promotion of CDM Projects in Pipeline (In power sector) - NTPC- North Karanpura (3*660 MW) Supercritical technology – NTPC – R & M of Badarpur 2* 210 MW – NHPC –Nimoo Bazgo 45 MW HEP – NHPC – Chutak 44 MW HEP – BBMB – Uprating of Ganguwal Power House, Kotla Power House, Bhakra Left Bank House
Major Initiatives Cont… • Promotion of CDM Projects in Pipeline (In power sector) - NTPC- North Karanpura (3*660 MW) Supercritical technology – NTPC – R & M of Badarpur 2* 210 MW – NHPC –Nimoo Bazgo 45 MW HEP – NHPC – Chutak 44 MW HEP – BBMB – Uprating of Ganguwal Power House, Kotla Power House, Bhakra Left Bank House
 Major Initiatives Cont… • Member of Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum (CSLF) – Development of cost effective technologies for separation and capture of CO 2 • Participating in Future. Gen Project of US – 275 MW coal fired Zero Emission power plant – India contributing US$10 Million
Major Initiatives Cont… • Member of Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum (CSLF) – Development of cost effective technologies for separation and capture of CO 2 • Participating in Future. Gen Project of US – 275 MW coal fired Zero Emission power plant – India contributing US$10 Million
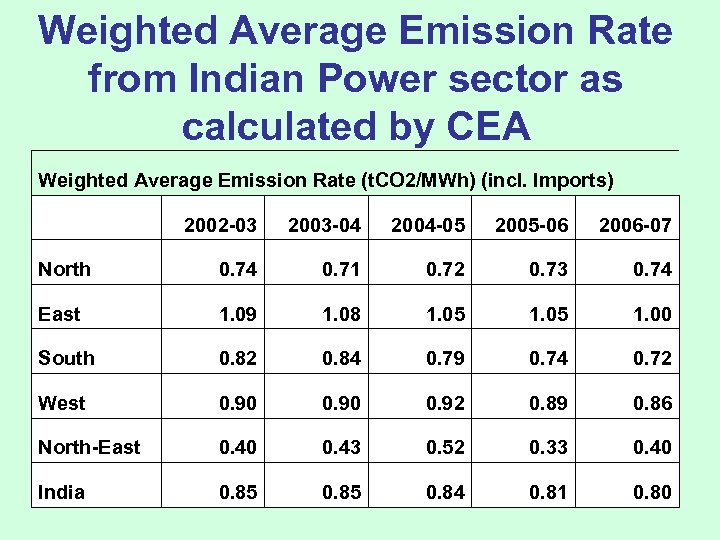 Weighted Average Emission Rate from Indian Power sector as calculated by CEA Weighted Average Emission Rate (t. CO 2/MWh) (incl. Imports) 2002 -03 2003 -04 2004 -05 2005 -06 2006 -07 North 0. 74 0. 71 0. 72 0. 73 0. 74 East 1. 09 1. 08 1. 05 1. 00 South 0. 82 0. 84 0. 79 0. 74 0. 72 West 0. 90 0. 92 0. 89 0. 86 North-East 0. 40 0. 43 0. 52 0. 33 0. 40 India 0. 85 0. 84 0. 81 0. 80
Weighted Average Emission Rate from Indian Power sector as calculated by CEA Weighted Average Emission Rate (t. CO 2/MWh) (incl. Imports) 2002 -03 2003 -04 2004 -05 2005 -06 2006 -07 North 0. 74 0. 71 0. 72 0. 73 0. 74 East 1. 09 1. 08 1. 05 1. 00 South 0. 82 0. 84 0. 79 0. 74 0. 72 West 0. 90 0. 92 0. 89 0. 86 North-East 0. 40 0. 43 0. 52 0. 33 0. 40 India 0. 85 0. 84 0. 81 0. 80



