a48ed6a509923c19c5edbb4fb2d854d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Presentation on Business Friendly Regulatory Environment for improving Investment Climate by M Velmurugan IES Additional Director – Guidance Bureau Industries Department Govt. of Tamil Nadu India Guidance Bureau

Presentation Structure v. Determinants of Investment climate v. Regulatory environment in Pre-Liberalization era v. Post-liberalization and investment climate v. Present regulatory Environment and new Approval Process v. Business deregulation

Impact of Streamlining Regulatory environment v Streamline regulatory environment and Business deregulation have made Tamil Nadu an attractive Investment destination v Growth rates and per capita Income have increased v Surge in Foreign Investment flows v Improvement in overall Competitiveness and adoption of Best Practices v Increase in Exports – both Commodities and Services
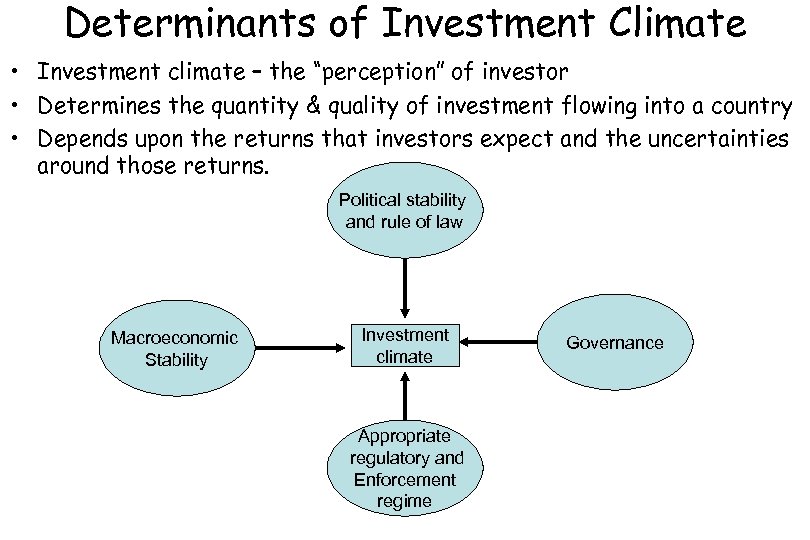
Determinants of Investment Climate • Investment climate – the “perception” of investor • Determines the quantity & quality of investment flowing into a country • Depends upon the returns that investors expect and the uncertainties around those returns. Political stability and rule of law Macroeconomic Stability Investment climate Appropriate regulatory and Enforcement regime Governance

Regulatory Environment in India’s Pre-Liberalization Ø Pre-dominant role for public sector, Ø Overwhelming regulation and Licensing of Industries Ø Import-substitution strategy was adopted vis-a-vis Export Promotion as Growth strategy. This was keeping the economy out of line with global trends Ø Govt. decided micro industrial conditions: Too much regulation Ø What to produce & capacity? ( licensing ) Ø Where to produce ? ( choice of location ) Ø Who should Produce? ( Public or Private sector ) Ø What Technology to be adopted? (Indigenous or Imported) Ø Foreign Exchange rationed and controlled rigidly Ø All these led to delays and red-tapism, Monolithic public sector with disincentives to private enterprise

Post-Liberalization and Investment climate • Pre-dominant role for private sector, • Regulations drastically pruned and Licensing Raj dismantled • Export Promotion became Growth strategy. This was keeping the economy in line with global trends • Restrictions on Foreign Investment removed • QRs governing imports removed and import tariffs brought down to bound tariff lines • Current account convertibility and moving towards capital account convertibility also • Infrastructure & Financial sector liberalization • As a result, India has emerged as one of the fastest growing economies with 6%+ growth rate
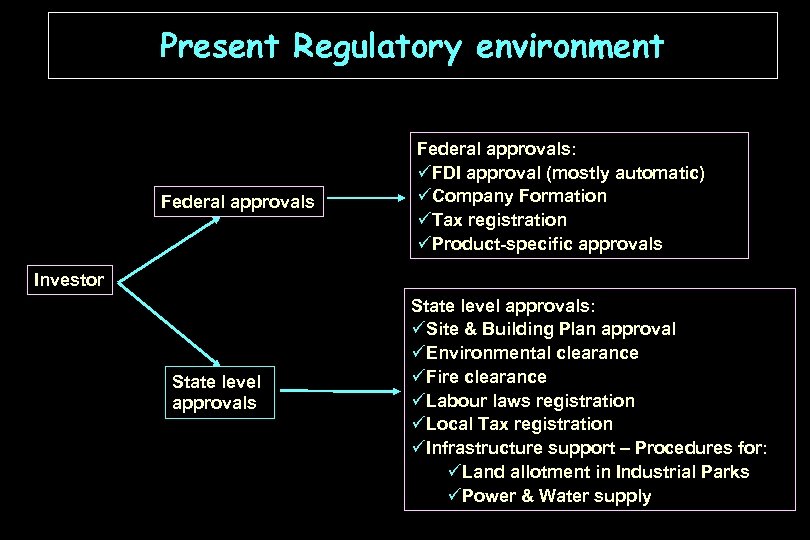
Present Regulatory environment Federal approvals: üFDI approval (mostly automatic) üCompany Formation üTax registration üProduct-specific approvals Investor State level approvals: üSite & Building Plan approval üEnvironmental clearance üFire clearance üLabour laws registration üLocal Tax registration üInfrastructure support – Procedures for: üLand allotment in Industrial Parks üPower & Water supply
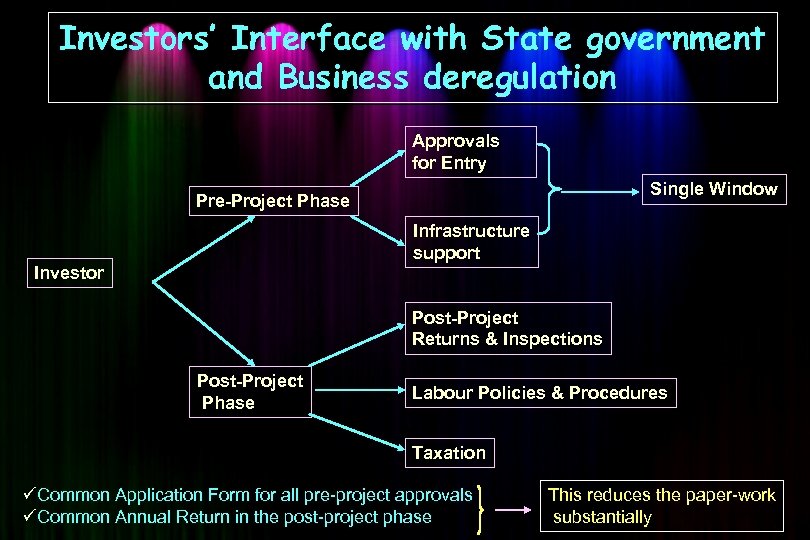
Investors’ Interface with State government and Business deregulation Approvals for Entry Single Window Pre-Project Phase Infrastructure support Investor Post-Project Returns & Inspections Post-Project Phase Labour Policies & Procedures Taxation üCommon Application Form for all pre-project approvals üCommon Annual Return in the post-project phase This reduces the paper-work substantially
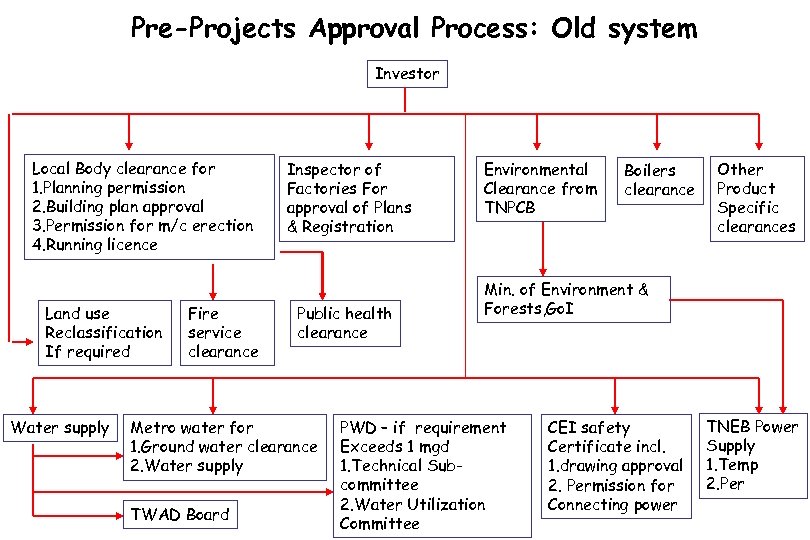
Pre-Projects Approval Process: Old system Investor Local Body clearance for 1. Planning permission 2. Building plan approval 3. Permission for m/c erection 4. Running licence Land use Reclassification If required Water supply Fire service clearance Inspector of Factories For approval of Plans & Registration Public health clearance Metro water for 1. Ground water clearance 2. Water supply TWAD Board Environmental Clearance from TNPCB Boilers clearance Other Product Specific clearances Min. of Environment & Forests, Go. I PWD – if requirement Exceeds 1 mgd 1. Technical Subcommittee 2. Water Utilization Committee CEI safety Certificate incl. 1. drawing approval 2. Permission for Connecting power TNEB Power Supply 1. Temp 2. Per

Investor fills Common Application Form Single Window Documentation centre Scrutiny by Single Window agency and Nodal officers Composite Approval by Single Window Committee Project implementation by Investor Single Window Committee gives approval in 30 days subject to: ØProject is non-polluting ØIt is proposed to be located in Industrial park / industrial use zone ØIt conforms to building plan norms Time: 30 days For Rectification of defects if any State level: New Approval process

State level: New Approval process • Under old system, approvals were to be obtained in “sequential process” that delayed the projects • Parallel Processing: Under New system, Single Window committees give composite in-principle approval to enable project promoters to go ahead with project implementation • Agencies that provide Infrastructure support – Land, Power, water, etc. , and Statutory approvals process & “simultaneously and parallely” • Time limits defined for such “parallel processing” • For mega projects, state government offers “MOU Facility” that commits timely support of state government • Dedicated project monitoring committees constituted to steer MOU projects till commissioning

Single window Mechanism – New system • Single window approval system covers both pre-project approvals and infrastructure support • Single Window Committees: – State Investment Promotion Board – for projects above Rs. 1000 million (US $ 25 million) – Projects Approvals authority – for projects above Rs. 250 million (US $ 5 million) – Investment Facilitation committee for projects between Rs. 50250 million (US $ 1 -5 million) – District Level Single Window Committees for projects up to Rs. 50 million ( Less than US $ ! Million) • Common Application Form for getting all pre-project clearances and Infrastructure support at the State level • Single agency designated for documentation • Web-based application form and Tracking

Pre-project approvals: Time Limits for approvals Nature of clearance Time limit Approval from local body including building plan permission, fire service clearance, etc 30 days Approval for change of land use 45 days Power supply: Temporary Connection Permanent supply 1 week 45 days Allotment of land / shed in industrial parks 5 days Permission to draw water from public sources 30 days Environmental clearance Green category Orange category Red category – if not referred to Mo. E&F, Go. I Registration under Factories Act 1 week 4 weeks 8 weeks 2 weeks

Some Projects handled under Single Window • • Ford Motors, USA Hyundai Motors, South Korea St. Gobain, France Xansa, UK Visteon, USA ( 2 Projects) Matsushita, Japan HM-Mitsubishi ILGIN, South Korea : $350 million : $720 million : $125 million : $47 million : $120 million : $12 million : $ 50 million : $ 10 million. and many auto components manufacturers and IT projects
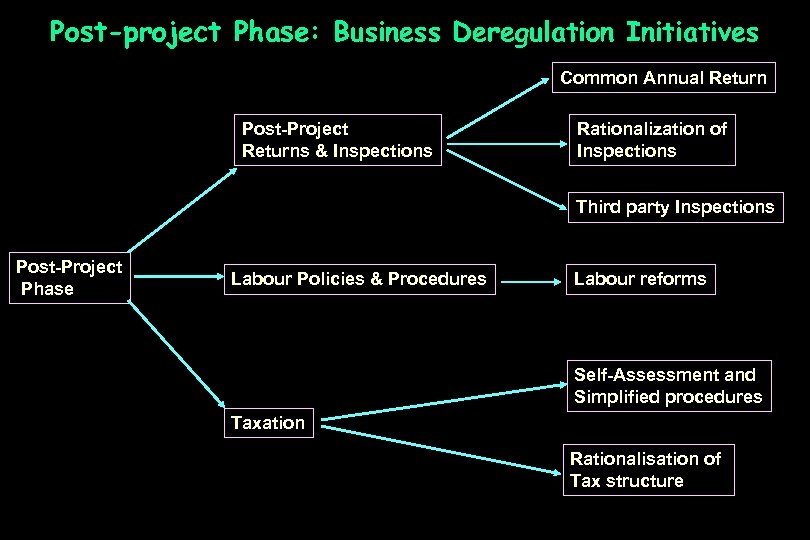
Post-project Phase: Business Deregulation Initiatives Common Annual Return Post-Project Returns & Inspections Rationalization of Inspections Third party Inspections Post-Project Phase Labour Policies & Procedures Labour reforms Self-Assessment and Simplified procedures Taxation Rationalisation of Tax structure

Business Deregulation • Labour reforms as apart of Second generation reforms on the anvil in the New Industrial policy • Reduction of Paper-work: Introduction of Common Annual Return under Labour Laws in lieu of 50+ multiple returns. This entails substantial reduction in paper work on the part of industries. • Enforcement of Stringent penalties to discourage unlawful strikes, including wildcat strikes & lockouts, go-slow tactics, intimidation, etc. • Self-Regulation in lieu of Government Regulation and adoption of “Traffic Signal approach”. • Green channel approach for small and Tiny industries

Business Deregulation – Other initiatives • Self-Assessment and declaration to all industries / business with turnover up to Rs. 100 million • Computerization of Tax administration and Rationalization of tax structure / Simplification of procedures Expert Committee recommendations • Tax inspections only random – only with authorization from competent authority • e-governance: Transparency and web-based info dissemination – all agencies have websites and Citizens charter • Private sector consultative mechanism: High Power Committee to carry forward business deregulation • Industry-specific policy initiatives to address special problems of such industries

The streamlining Process continues…. Thank you Please visit our websites: www. tidco. com www. tamilnadunri. com www. sipcot. com www. elcot. com www. tn. gov. in www. itparkchennai. com
a48ed6a509923c19c5edbb4fb2d854d5.ppt