79e3cafcad0dddd0d67315f6c1be4489.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Presentation/Meeting Title Presented by Name, Organization Date & Location

What is the global picture? • More than half a million women die during pregnancy and childbirth each year. • More than 10 million children die each year before their fifth birthday, almost 40% in the first month of life. • At least two-thirds of these deaths could be prevented.

What is The Partnership? • • • New global health partnership With a focus on mothers and children Merger of 3 existing partnerships Launched in September 2005 To support efforts toward achieving MDGs 4 and 5 "This is a major effort, and no one agency can do it alone. Commitment and partnership are essential. ” Ms. Thoraya Ahmed Obaid, Executive Director of UNFPA

Who is The Partnership? • • • Partner countries International organizations Non-governmental organizations Professional organizations Academic & research institutions Bilateral donors "We affirm our commitment and renew our resolve to work together for this noble cause of our sisters' and our children's life. " Smt. Sonia Gandhi, Honourable Chairperson National Advisory Council

What does The Partnership do? The Partnership aims to intensify and harmonize national, regional, global action to improve MNCH by focusing on: • Country Support • Advocacy • Effective Interventions "To accelerate progress, we • Accountability need to integrate our efforts at the global, national and community level. " Ann M. Veneman, Executive Director, UNICEF

What does The Partnership do? Country Support • Establish links with all major stakeholders. • Identify key activities and agree specific inputs. • Support country coordination mechanisms. • Establish links with other relevant programmes. • Facilitate the integration of MNCH into national context. • Address human resources challenges.

What does The Partnership do? Advocacy • Develop and promote MNCH messages. • Create tools that make the case for MNCH. • Lobby for increased resources for MNCH. • Organize high-visibility debates on MNCH. • Generate media coverage for MNCH. • Increase uptake of MNCH by civil society.

What does The Partnership do? Effective Interventions • Draw together current knowledge on interventions. • Build consensus on proven, effective interventions. • Develop a minimum package of interventions. • Identify appropriate delivery approaches. • Identify priorities for operational research. • Support the development and promotion of key publications.

What does The Partnership do? Accountability • Develop a monitoring and evaluation framework. • Develop indicators/means of verification for every milestone. • Monitor stakeholders’ delivery on commitments. • Support the development and agreement of core indicators for MNCH. • Support the improvement of models to track MNC mortality. • Link data on Partnership’s progress to future planning.

What does The Partnership offer? • • • Greater visibility of MNCH Better coordination under country leadership Increased commitment to primary health care Reduced competition & duplication More efficient use of resources Shared & agreed goals "By working with countries to increase access to existing health care solutions, this Partnership has the potential to transform millions of lives. " Dr. LEE Jong-wook, Director. General, WHO
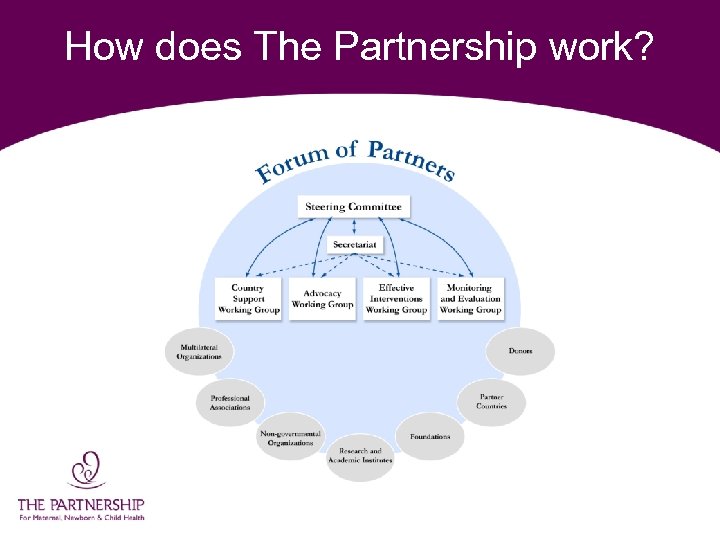
How does The Partnership work?

What is the history of it? • 1987: Safe Motherhood Initiative (SMI) and Safe Motherhood Inter-Agency Group (IAG) • 2000: Healthy Newborn Partnership is formed • 2003: SMI and IAG form the Partnership for Safe Motherhood & Newborn Health • 2004: Child Survival Partnership is formed • 2005: The Partnership for Maternal, Newborn & Child Health

What are the guiding principles? • • • Country-led Inclusive Comprehensive Flexible Collaborative Results-oriented "It is clear that the MDGs simply cannot be achieved unless the different stakeholders join together at global &, even more importantly, at country level. " Dr. Mushtaque Chowdhury, Deputy Executive Director, BRAC

A country example: Cambodia • In Cambodia, a high-level meeting held to increase political & institutional commitment to child survival. • Consensus achieved among government/partners on set of interventions to be scaled up & monitored. • Core partners re-aligned their programmatic & investment approaches to support delivery. • Agreement on one national strategy, one national coordinating mechanism, & one monitoring/ evaluation framework for all partners

A country example: Tanzania • January 2005: Ministry of Health renews resolve to reduce child mortality in Tanzania. • April 2005: Minister of Health - Honourable Min. Anna Abdallah, MP signs the Delhi Declaration on Maternal, Newborn & Child Health. • May 2005: Tanzania Partnership for Maternal, Newborn, & Child Survival is created. • June 2005: Tanzania Partnership establishes its objectives & structure.

website: www. pmnch. org email: info@pmnch. org
79e3cafcad0dddd0d67315f6c1be4489.ppt