eee9219ed8256639a0bf5e6db6db4acf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Presentation for Adam Smith Conference THE ROLE OF ALTERNATIVE INVESTMENT IN SWF MANAGEMENT Vavilov A. P.
Presentation for Adam Smith Conference THE ROLE OF ALTERNATIVE INVESTMENT IN SWF MANAGEMENT Vavilov A. P.
 1. Financial assets of Russia n n n The volume of Stabfund (Stabilization fund) by the beginning of 2008 – $ 157. 5 bn. The Reserve Fund (RF) – 10% of GDP; the predicted amount by the beginning of 2008 г. - $ 122 bn. The predicted amount of the National Welfare Fund (NWF) – $ 30 -40 bn.
1. Financial assets of Russia n n n The volume of Stabfund (Stabilization fund) by the beginning of 2008 – $ 157. 5 bn. The Reserve Fund (RF) – 10% of GDP; the predicted amount by the beginning of 2008 г. - $ 122 bn. The predicted amount of the National Welfare Fund (NWF) – $ 30 -40 bn.
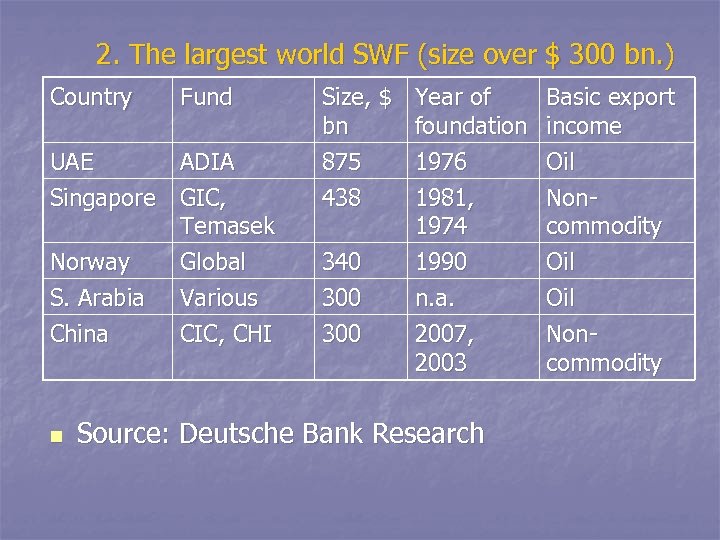 2. The largest world SWF (size over $ 300 bn. ) Country Fund UAE ADIA Singapore GIC, Temasek Norway Global S. Arabia China n Various CIC, CHI Size, $ bn 875 438 340 300 Year of foundation 1976 1981, 1974 1990 Basic export income Oil Noncommodity Oil n. a. 2007, 2003 Oil Noncommodity Source: Deutsche Bank Research
2. The largest world SWF (size over $ 300 bn. ) Country Fund UAE ADIA Singapore GIC, Temasek Norway Global S. Arabia China n Various CIC, CHI Size, $ bn 875 438 340 300 Year of foundation 1976 1981, 1974 1990 Basic export income Oil Noncommodity Oil n. a. 2007, 2003 Oil Noncommodity Source: Deutsche Bank Research
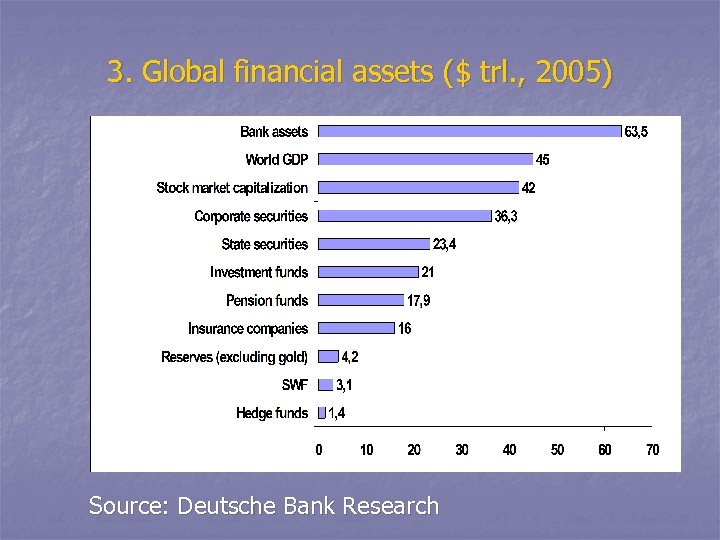 3. Global financial assets ($ trl. , 2005) Source: Deutsche Bank Research
3. Global financial assets ($ trl. , 2005) Source: Deutsche Bank Research
 4. The new rules for the Sovereign Oil and Gas Fund of Russia n RF is 10% of GDP; NWF is residual. n NWF will not increase if the oil price drops below 50 -52 $/bar. n On the contrary, the RF in real terms will grow automatically with GDP growth and ruble appreciation. n The ration of RF to NWF will be around 4: 1. n For a moderate proportion of shares and debt instruments in the NWF as 50%: 50%, the fraction of shares in the Russian SWF will be only 12. 5%.
4. The new rules for the Sovereign Oil and Gas Fund of Russia n RF is 10% of GDP; NWF is residual. n NWF will not increase if the oil price drops below 50 -52 $/bar. n On the contrary, the RF in real terms will grow automatically with GDP growth and ruble appreciation. n The ration of RF to NWF will be around 4: 1. n For a moderate proportion of shares and debt instruments in the NWF as 50%: 50%, the fraction of shares in the Russian SWF will be only 12. 5%.
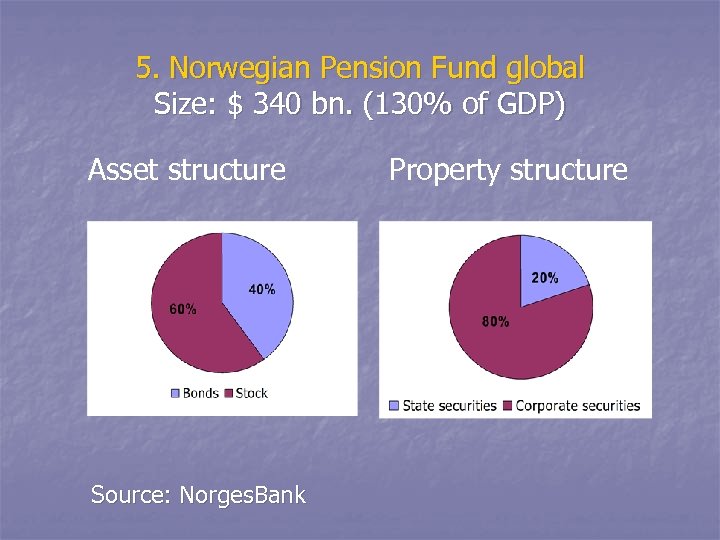 5. Norwegian Pension Fund global Size: $ 340 bn. (130% of GDP) Asset structure Source: Norges. Bank Property structure
5. Norwegian Pension Fund global Size: $ 340 bn. (130% of GDP) Asset structure Source: Norges. Bank Property structure
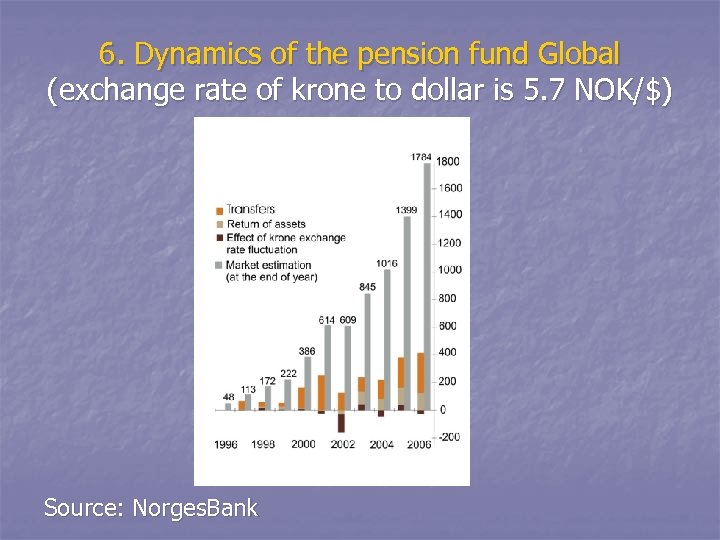 6. Dynamics of the pension fund Global (exchange rate of krone to dollar is 5. 7 NOK/$) Source: Norges. Bank
6. Dynamics of the pension fund Global (exchange rate of krone to dollar is 5. 7 NOK/$) Source: Norges. Bank
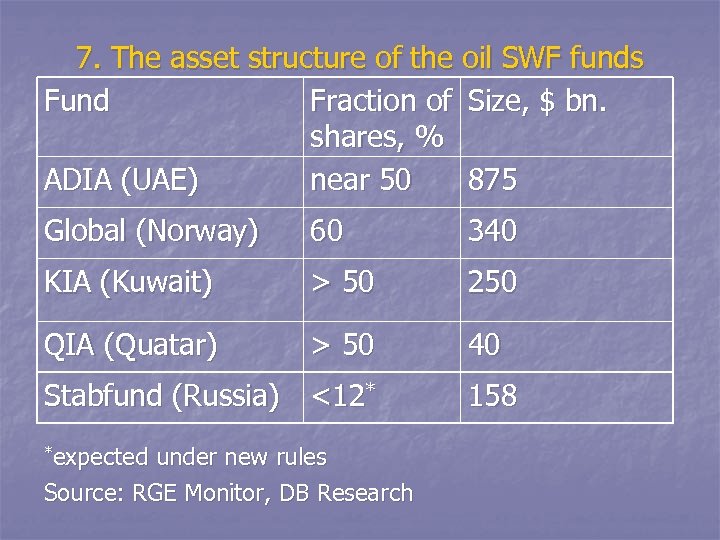 7. The asset structure of the oil SWF funds Fund Fraction of Size, $ bn. shares, % ADIA (UAE) near 50 875 Global (Norway) 60 340 KIA (Kuwait) > 50 250 QIA (Quatar) > 50 40 Stabfund (Russia) <12* *expected under new rules Source: RGE Monitor, DB Research 158
7. The asset structure of the oil SWF funds Fund Fraction of Size, $ bn. shares, % ADIA (UAE) near 50 875 Global (Norway) 60 340 KIA (Kuwait) > 50 250 QIA (Quatar) > 50 40 Stabfund (Russia) <12* *expected under new rules Source: RGE Monitor, DB Research 158
 8. Does Russia really need the financial reserve 10% of GDP? n n A) Protection against possible financial crisis? B) Total official foreign reserves ($ 476 bn. ) should be taken into account; C) The liquidity of state assets is the problem for monetary authority rather than the Fiscal authority; D) Political economy: liquid state assets are weakly protected from lobbyist pressure.
8. Does Russia really need the financial reserve 10% of GDP? n n A) Protection against possible financial crisis? B) Total official foreign reserves ($ 476 bn. ) should be taken into account; C) The liquidity of state assets is the problem for monetary authority rather than the Fiscal authority; D) Political economy: liquid state assets are weakly protected from lobbyist pressure.
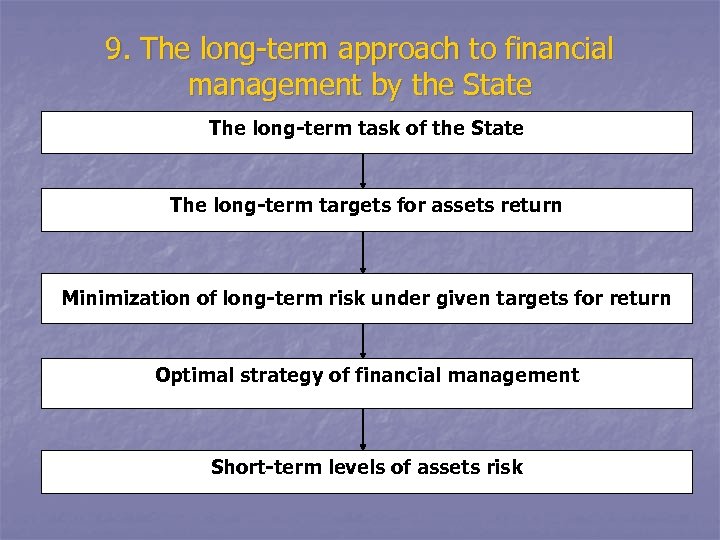 9. The long-term approach to financial management by the State The long-term task of the State The long-term targets for assets return Minimization of long-term risk under given targets for return Optimal strategy of financial management Short-term levels of assets risk
9. The long-term approach to financial management by the State The long-term task of the State The long-term targets for assets return Minimization of long-term risk under given targets for return Optimal strategy of financial management Short-term levels of assets risk
 10. A dynamic model of financial management Informal description A) The target level of NWF by some year; B) The target level of long-term return on asset portfolio of the state; C) The objective function is minimum of integral risk (time-weighted volatility of return); D) The dynamic budget constraint of the fiscal authority; F) The short-term risk-return ratios are determined from the global portfolio.
10. A dynamic model of financial management Informal description A) The target level of NWF by some year; B) The target level of long-term return on asset portfolio of the state; C) The objective function is minimum of integral risk (time-weighted volatility of return); D) The dynamic budget constraint of the fiscal authority; F) The short-term risk-return ratios are determined from the global portfolio.
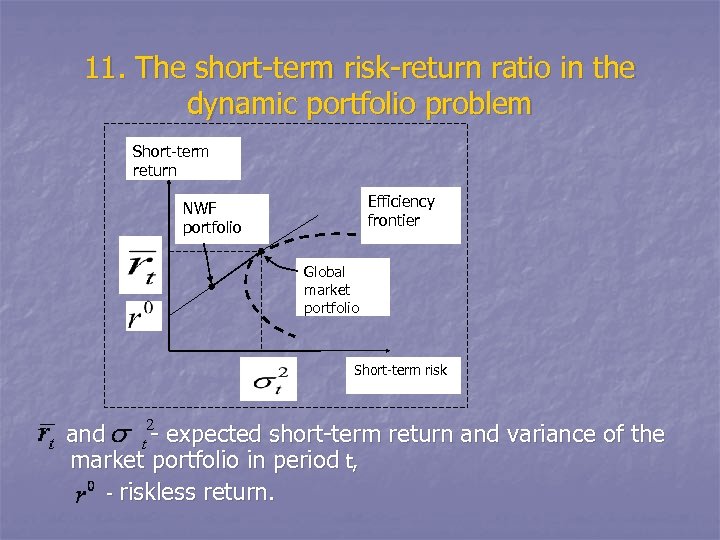 11. The short-term risk-return ratio in the dynamic portfolio problem Short-term return Efficiency frontier NWF portfolio Global market portfolio Short-term risk and - expected short-term return and variance of the market portfolio in period t, - riskless return.
11. The short-term risk-return ratio in the dynamic portfolio problem Short-term return Efficiency frontier NWF portfolio Global market portfolio Short-term risk and - expected short-term return and variance of the market portfolio in period t, - riskless return.
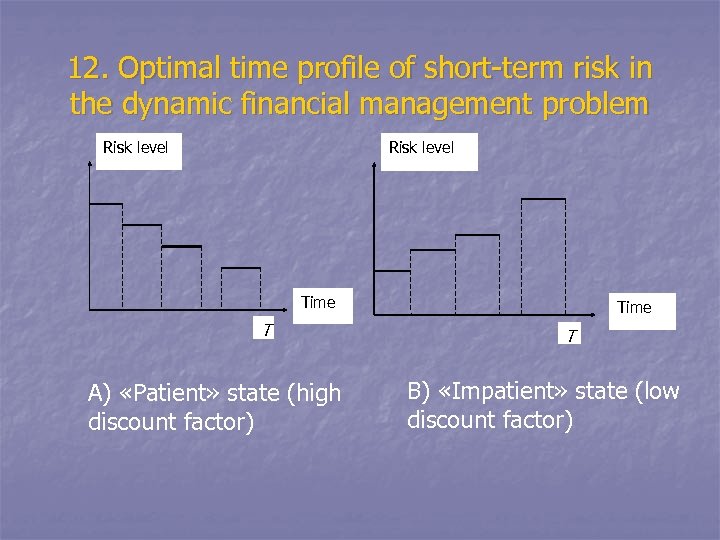 12. Optimal time profile of short-term risk in the dynamic financial management problem Risk level Time T A) «Patient» state (high discount factor) Time T B) «Impatient» state (low discount factor)
12. Optimal time profile of short-term risk in the dynamic financial management problem Risk level Time T A) «Patient» state (high discount factor) Time T B) «Impatient» state (low discount factor)
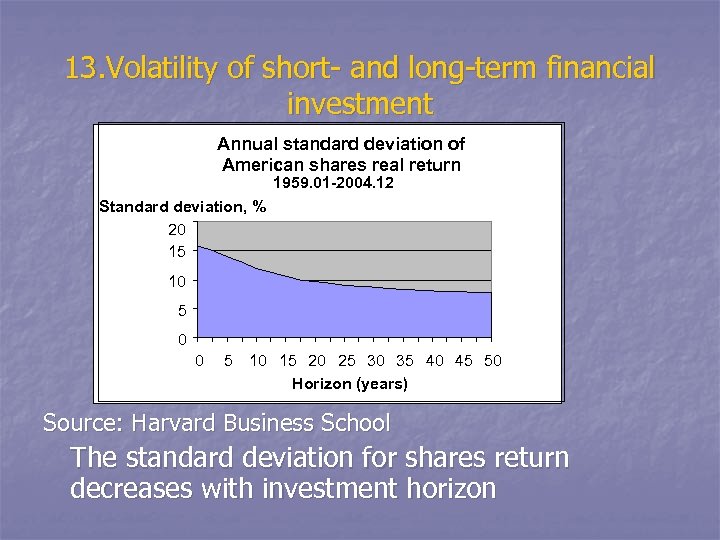 13. Volatility of short- and long-term financial investment Annual standard deviation of American shares real return 1959. 01 -2004. 12 Standard deviation, % 20 15 10 5 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 Horizon (years) Source: Harvard Business School The standard deviation for shares return decreases with investment horizon
13. Volatility of short- and long-term financial investment Annual standard deviation of American shares real return 1959. 01 -2004. 12 Standard deviation, % 20 15 10 5 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 Horizon (years) Source: Harvard Business School The standard deviation for shares return decreases with investment horizon
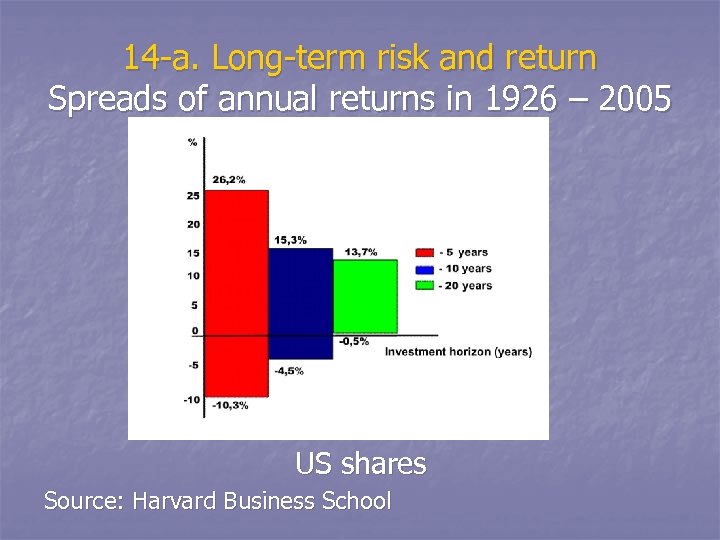 14 -а. Long-term risk and return Spreads of annual returns in 1926 – 2005 US shares Source: Harvard Business School
14 -а. Long-term risk and return Spreads of annual returns in 1926 – 2005 US shares Source: Harvard Business School
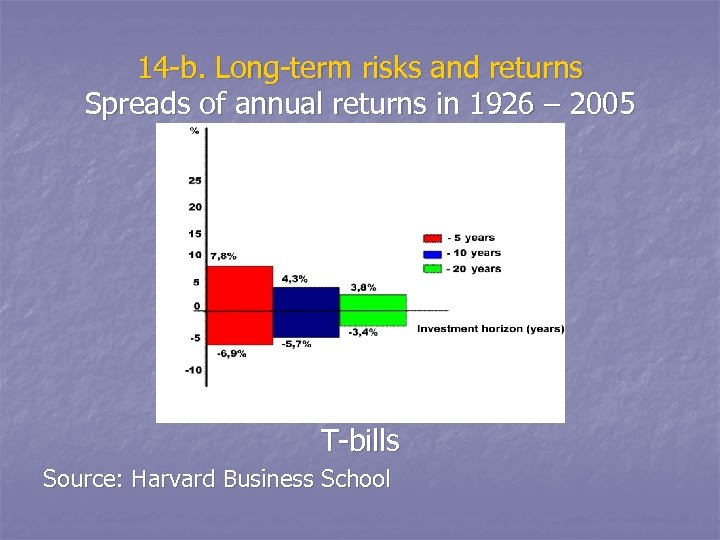 14 -b. Long-term risks and returns Spreads of annual returns in 1926 – 2005 T-bills Source: Harvard Business School
14 -b. Long-term risks and returns Spreads of annual returns in 1926 – 2005 T-bills Source: Harvard Business School
 15. Principles of dynamic portfolio management А) Standard diversification for short term riskreturn management based on global market portfolio; Б) Passive portfolio management through selection of “beta” (the major part); В) Active portfolio management and hedging through selection of “alfa” (the minor part). Excess return equation: Excess return Market risk premium
15. Principles of dynamic portfolio management А) Standard diversification for short term riskreturn management based on global market portfolio; Б) Passive portfolio management through selection of “beta” (the major part); В) Active portfolio management and hedging through selection of “alfa” (the minor part). Excess return equation: Excess return Market risk premium
 16. Implementation 1: Making beta 1. Standardized formal procedures of passive management (should be specified in the budget code) 2. 70 -80% of government assets should be invested in a globally diversified market portfolio including corporate equities, bonds, commodities, real estate, derivatives (Portfolio of Norwegian fund Global embraces 3500 issuers. ) 3. Passive style of management to ensure market returns. Long-term contracting with large global financial intermediaries
16. Implementation 1: Making beta 1. Standardized formal procedures of passive management (should be specified in the budget code) 2. 70 -80% of government assets should be invested in a globally diversified market portfolio including corporate equities, bonds, commodities, real estate, derivatives (Portfolio of Norwegian fund Global embraces 3500 issuers. ) 3. Passive style of management to ensure market returns. Long-term contracting with large global financial intermediaries
 17. Implementation 2: Making alpha 1. Alternative (market-neutral) instruments The state agency provides collateral. 2. Incentive problems (e. g. making beta instead of alpha). Solution: a) managerial fees and risk sharing between the government agency and the financial intermediary; b) specification of investment style in the short-term (annual) contracts 3. The issues of monitoring and control. Solution: deals should pass through a special account of the state agency (like Swedish pension fund AP-7). Transparency will remove unjustified political pressure on financial management.
17. Implementation 2: Making alpha 1. Alternative (market-neutral) instruments The state agency provides collateral. 2. Incentive problems (e. g. making beta instead of alpha). Solution: a) managerial fees and risk sharing between the government agency and the financial intermediary; b) specification of investment style in the short-term (annual) contracts 3. The issues of monitoring and control. Solution: deals should pass through a special account of the state agency (like Swedish pension fund AP-7). Transparency will remove unjustified political pressure on financial management.


