149df17bc88551d957cbc1a102b49638.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Présentation des grilles de calcul et initiation à la grille de calcul EGEE Lyon, 17 mars 2010 Sylvain Reynaud
Présentation des grilles de calcul et initiation à la grille de calcul EGEE Lyon, 17 mars 2010 Sylvain Reynaud
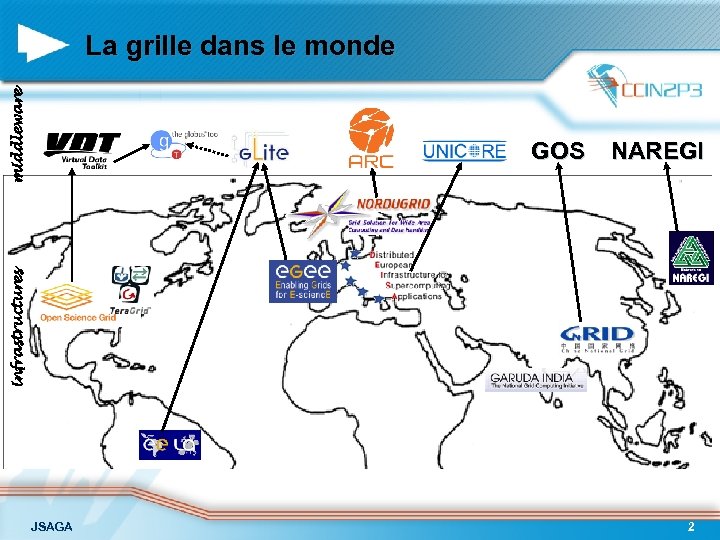 middleware La grille dans le monde NAREGI infrastructures GOS JSAGA 2
middleware La grille dans le monde NAREGI infrastructures GOS JSAGA 2
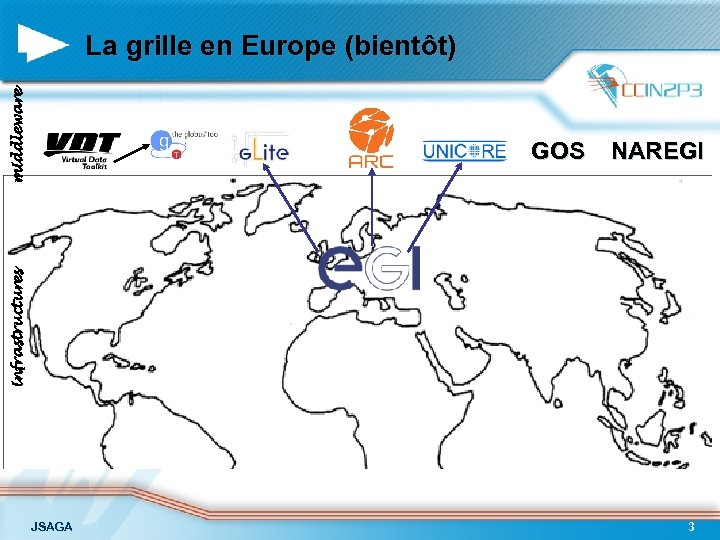 middleware La grille en Europe (bientôt) NAREGI infrastructures GOS JSAGA 3
middleware La grille en Europe (bientôt) NAREGI infrastructures GOS JSAGA 3
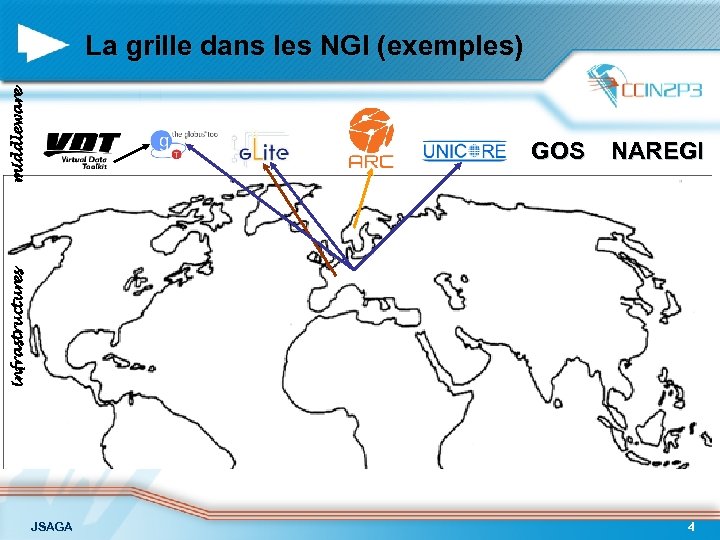 middleware La grille dans les NGI (exemples) NAREGI infrastructures GOS JSAGA 4
middleware La grille dans les NGI (exemples) NAREGI infrastructures GOS JSAGA 4
 Standardisation n Besoins et concepts communs n Une communauté d'industriels et de chercheurs définit des standards – pour l'architecture globale d'une grille (Open Grid Service Architecture) – pour chaque composant d'un middleware de grille JSAGA 5
Standardisation n Besoins et concepts communs n Une communauté d'industriels et de chercheurs définit des standards – pour l'architecture globale d'une grille (Open Grid Service Architecture) – pour chaque composant d'un middleware de grille JSAGA 5
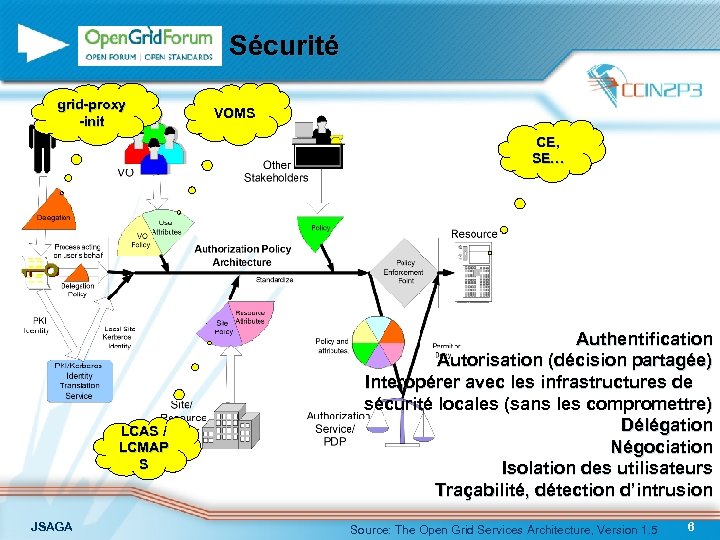 Sécurité grid-proxy -init VOMS CE, SE… LCAS / LCMAP S JSAGA Authentification Autorisation (décision partagée) Interopérer avec les infrastructures de sécurité locales (sans les compromettre) Délégation Négociation Isolation des utilisateurs Traçabilité, détection d’intrusion Source: The Open Grid Services Architecture, Version 1. 5 6
Sécurité grid-proxy -init VOMS CE, SE… LCAS / LCMAP S JSAGA Authentification Autorisation (décision partagée) Interopérer avec les infrastructures de sécurité locales (sans les compromettre) Délégation Négociation Isolation des utilisateurs Traçabilité, détection d’intrusion Source: The Open Grid Services Architecture, Version 1. 5 6
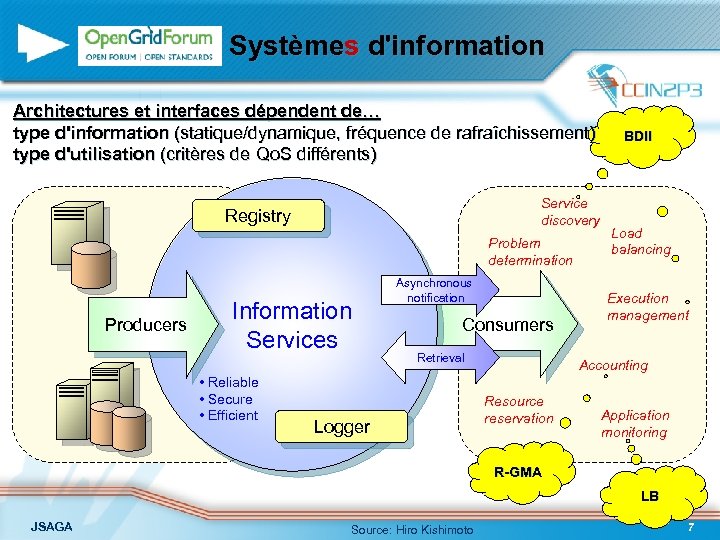 Systèmes d'information Architectures et interfaces dépendent de… type d'information (statique/dynamique, fréquence de rafraîchissement) type d'utilisation (critères de Qo. S différents) Service discovery Registry Problem determination Producers Information Services • Reliable • Secure • Efficient Asynchronous notification Consumers Retrieval Logger BDII Load balancing Execution management Accounting Resource reservation Application monitoring R-GMA LB JSAGA Source: Hiro Kishimoto 7
Systèmes d'information Architectures et interfaces dépendent de… type d'information (statique/dynamique, fréquence de rafraîchissement) type d'utilisation (critères de Qo. S différents) Service discovery Registry Problem determination Producers Information Services • Reliable • Secure • Efficient Asynchronous notification Consumers Retrieval Logger BDII Load balancing Execution management Accounting Resource reservation Application monitoring R-GMA LB JSAGA Source: Hiro Kishimoto 7
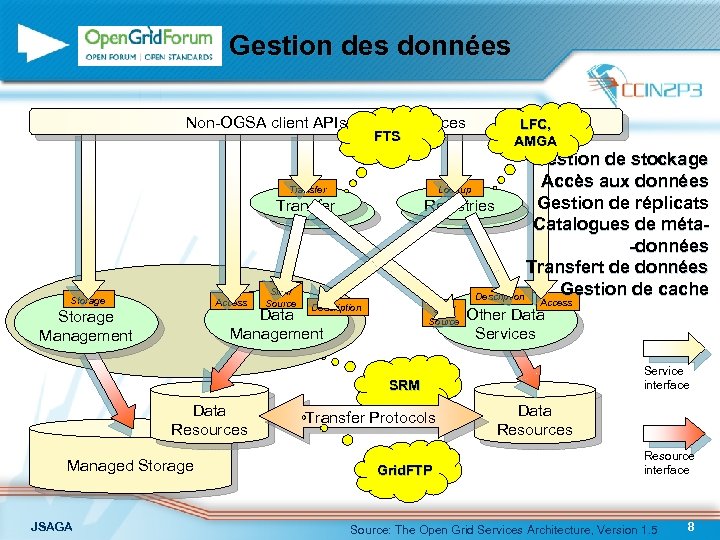 Gestion des données Non-OGSA client APIs & other services FTS Gestion de stockage Accès aux données Lookup Gestion de réplicats Registries Catalogues de méta-données Transfert de données Gestion de cache Description Transfer Storage Access Sink/ Source Description Sink/ Source Data Management Storage Management LFC, AMGA Access Other Data Services Service interface SRM Data Resources Managed Storage JSAGA Transfer Protocols Grid. FTP Data Resources Resource interface Source: The Open Grid Services Architecture, Version 1. 5 8
Gestion des données Non-OGSA client APIs & other services FTS Gestion de stockage Accès aux données Lookup Gestion de réplicats Registries Catalogues de méta-données Transfert de données Gestion de cache Description Transfer Storage Access Sink/ Source Description Sink/ Source Data Management Storage Management LFC, AMGA Access Other Data Services Service interface SRM Data Resources Managed Storage JSAGA Transfer Protocols Grid. FTP Data Resources Resource interface Source: The Open Grid Services Architecture, Version 1. 5 8
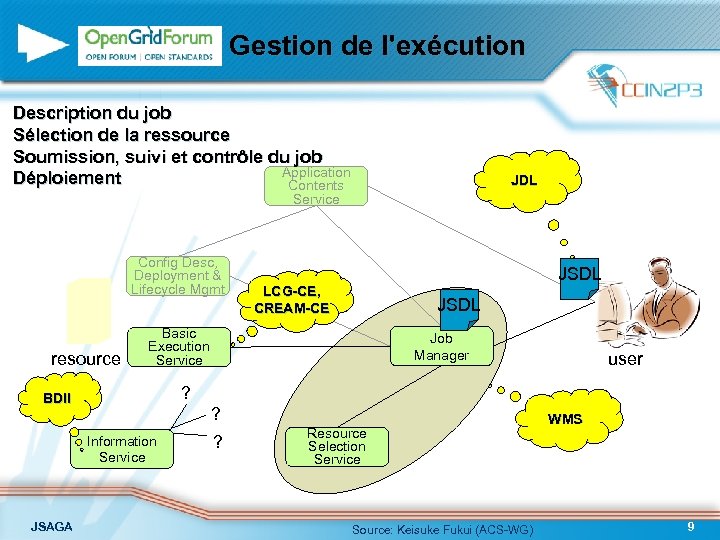 Gestion de l'exécution Description du job Sélection de la ressource Soumission, suivi et contrôle du job Application Déploiement Contents JDL Service Config Desc, Deployment & Lifecycle Mgmt resource LCG-CE, CREAM-CE JSDL Basic Execution Service Job Manager user ? BDII ? Information Service JSAGA JSDL ? Resource Selection Service Source: Keisuke Fukui (ACS-WG) WMS 9
Gestion de l'exécution Description du job Sélection de la ressource Soumission, suivi et contrôle du job Application Déploiement Contents JDL Service Config Desc, Deployment & Lifecycle Mgmt resource LCG-CE, CREAM-CE JSDL Basic Execution Service Job Manager user ? BDII ? Information Service JSAGA JSDL ? Resource Selection Service Source: Keisuke Fukui (ACS-WG) WMS 9
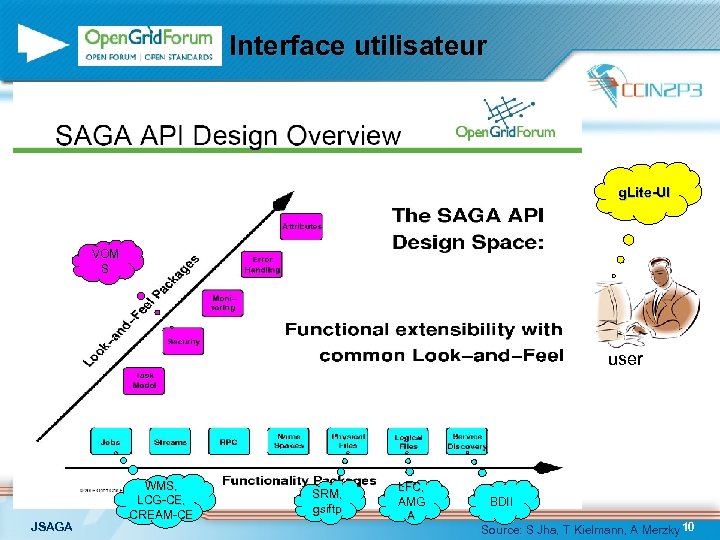 Interface utilisateur g. Lite-UI VOM S user JSAGA WMS, LCG-CE, CREAM-CE SRM, gsiftp LFC, AMG A BDII Source: S Jha, T Kielmann, A Merzky 10
Interface utilisateur g. Lite-UI VOM S user JSAGA WMS, LCG-CE, CREAM-CE SRM, gsiftp LFC, AMG A BDII Source: S Jha, T Kielmann, A Merzky 10
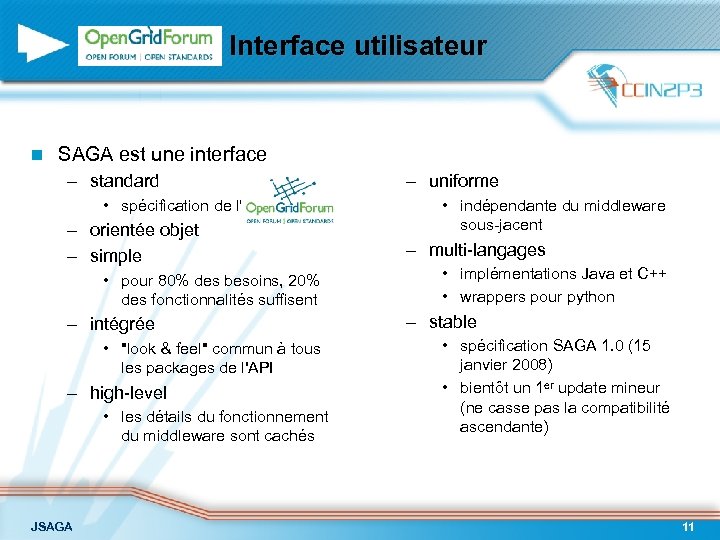 Interface utilisateur n SAGA est une interface – standard • spécification de l' – orientée objet – simple • pour 80% des besoins, 20% des fonctionnalités suffisent – intégrée • "look & feel" commun à tous les packages de l'API – high-level • les détails du fonctionnement du middleware sont cachés JSAGA – uniforme • indépendante du middleware sous-jacent – multi-langages • implémentations Java et C++ • wrappers pour python – stable • spécification SAGA 1. 0 (15 janvier 2008) • bientôt un 1 er update mineur (ne casse pas la compatibilité ascendante) 11
Interface utilisateur n SAGA est une interface – standard • spécification de l' – orientée objet – simple • pour 80% des besoins, 20% des fonctionnalités suffisent – intégrée • "look & feel" commun à tous les packages de l'API – high-level • les détails du fonctionnement du middleware sont cachés JSAGA – uniforme • indépendante du middleware sous-jacent – multi-langages • implémentations Java et C++ • wrappers pour python – stable • spécification SAGA 1. 0 (15 janvier 2008) • bientôt un 1 er update mineur (ne casse pas la compatibilité ascendante) 11
 Interface utilisateur n Exemple de code en Java (data management) Session session = Session. Factory. create. Session(true); URL url = URLFactory. create. URL("gsiftp: //cclcgseli 01. in 2 p 3. fr/t mp/"); // instanciation de l'objet SAGA à l'aide d'une fabrique NSDirectory dir = NSFactory. create. NSDirectory(session, url); tenu du iste le con l ftp: //… ertoire gsi rép // utilisation de l'objet SAGA List
Interface utilisateur n Exemple de code en Java (data management) Session session = Session. Factory. create. Session(true); URL url = URLFactory. create. URL("gsiftp: //cclcgseli 01. in 2 p 3. fr/t mp/"); // instanciation de l'objet SAGA à l'aide d'une fabrique NSDirectory dir = NSFactory. create. NSDirectory(session, url); tenu du iste le con l ftp: //… ertoire gsi rép // utilisation de l'objet SAGA List
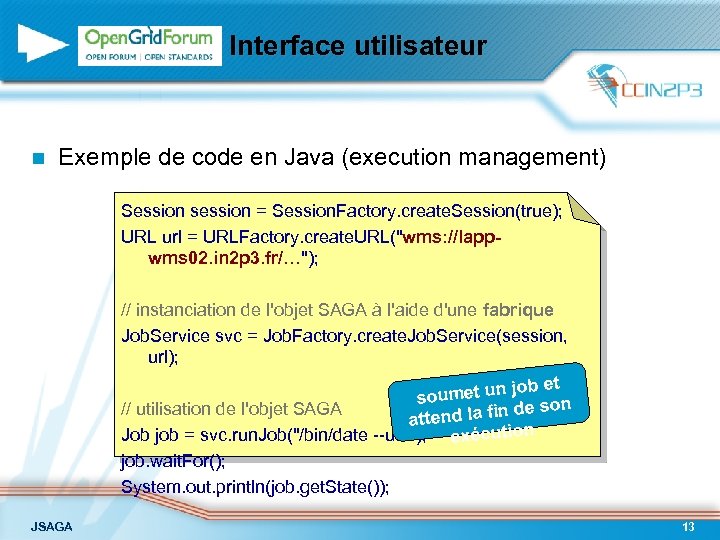 Interface utilisateur n Exemple de code en Java (execution management) Session session = Session. Factory. create. Session(true); URL url = URLFactory. create. URL("wms: //lappwms 02. in 2 p 3. fr/…"); // instanciation de l'objet SAGA à l'aide d'une fabrique Job. Service svc = Job. Factory. create. Job. Service(session, url); job et soumet un e son // utilisation de l'objet SAGA end la fin d att Job job = svc. run. Job("/bin/date --utc"); exécution job. wait. For(); System. out. println(job. get. State()); JSAGA 13
Interface utilisateur n Exemple de code en Java (execution management) Session session = Session. Factory. create. Session(true); URL url = URLFactory. create. URL("wms: //lappwms 02. in 2 p 3. fr/…"); // instanciation de l'objet SAGA à l'aide d'une fabrique Job. Service svc = Job. Factory. create. Job. Service(session, url); job et soumet un e son // utilisation de l'objet SAGA end la fin d att Job job = svc. run. Job("/bin/date --utc"); exécution job. wait. For(); System. out. println(job. get. State()); JSAGA 13
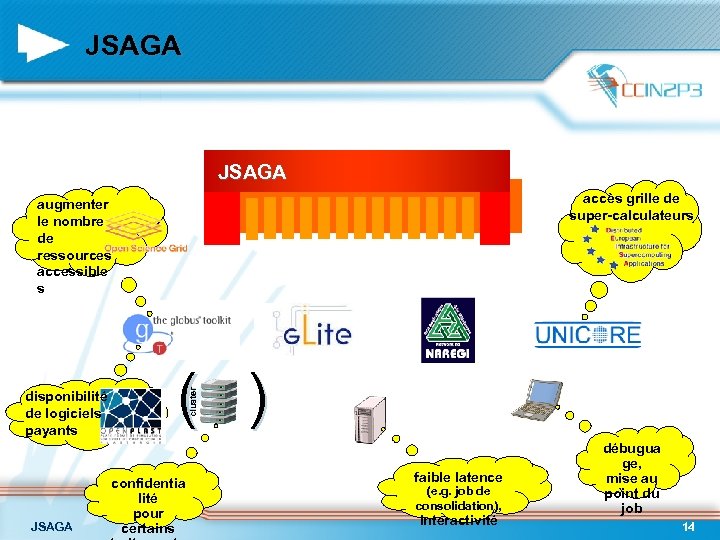 JSAGA accès grille de super-calculateurs augmenter le nombre de ressources accessible s JSAGA ( ) cluster disponibilité de logiciels payants confidentia lité pour certains faible latence (e. g. job de consolidation), interactivité débugua ge, mise au point du job 14
JSAGA accès grille de super-calculateurs augmenter le nombre de ressources accessible s JSAGA ( ) cluster disponibilité de logiciels payants confidentia lité pour certains faible latence (e. g. job de consolidation), interactivité débugua ge, mise au point du job 14
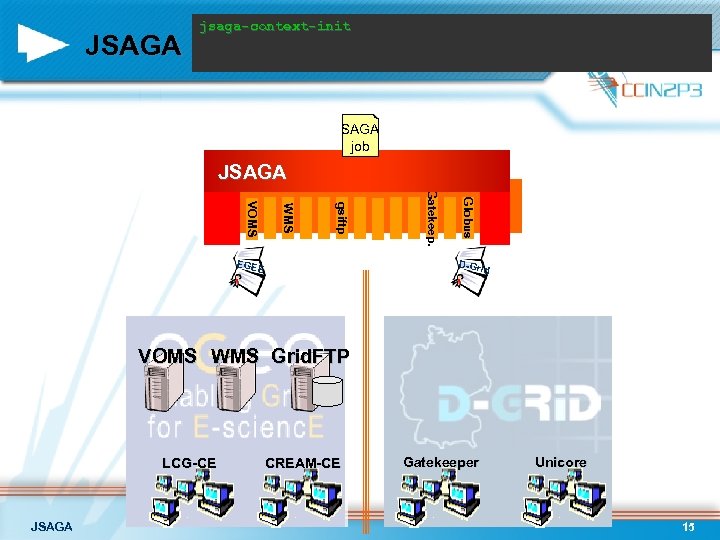 JSAGA jsaga-context-init SAGA job JSAGA Globus Gatekeep. gsiftp WMS VOMS EGEE D-Gri d VOMS WMS Grid. FTP LCG-CE JSAGA CREAM-CE Gatekeeper Unicore 15
JSAGA jsaga-context-init SAGA job JSAGA Globus Gatekeep. gsiftp WMS VOMS EGEE D-Gri d VOMS WMS Grid. FTP LCG-CE JSAGA CREAM-CE Gatekeeper Unicore 15
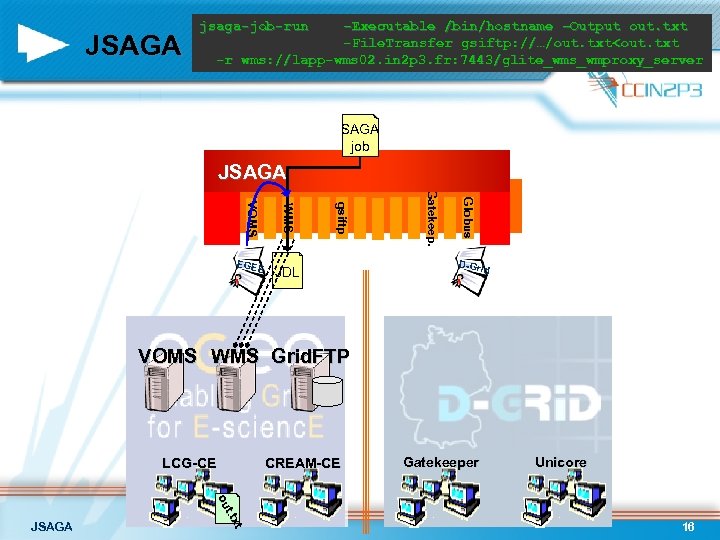 JSAGA jsaga-job-run –Executable /bin/hostname –Output out. txt -File. Transfer gsiftp: //…/out. txt
JSAGA jsaga-job-run –Executable /bin/hostname –Output out. txt -File. Transfer gsiftp: //…/out. txt
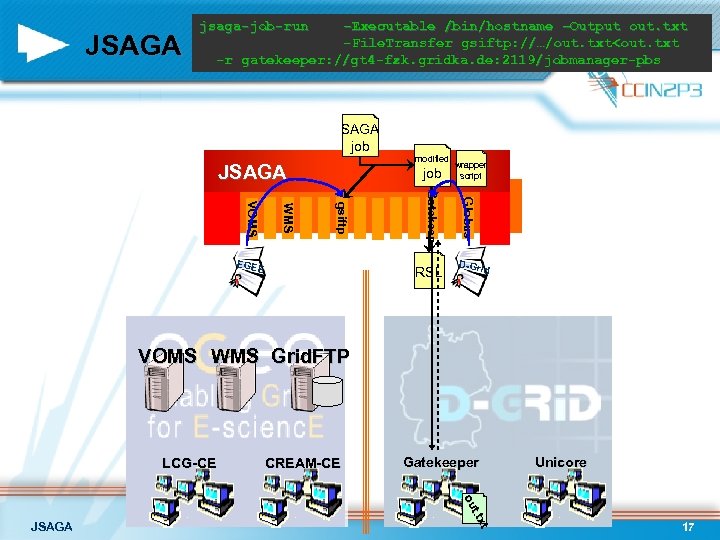 JSAGA jsaga-job-run –Executable /bin/hostname –Output out. txt -File. Transfer gsiftp: //…/out. txt
JSAGA jsaga-job-run –Executable /bin/hostname –Output out. txt -File. Transfer gsiftp: //…/out. txt
 Architecture logicielle JSAGA interface JSAGA implementation 18
Architecture logicielle JSAGA interface JSAGA implementation 18
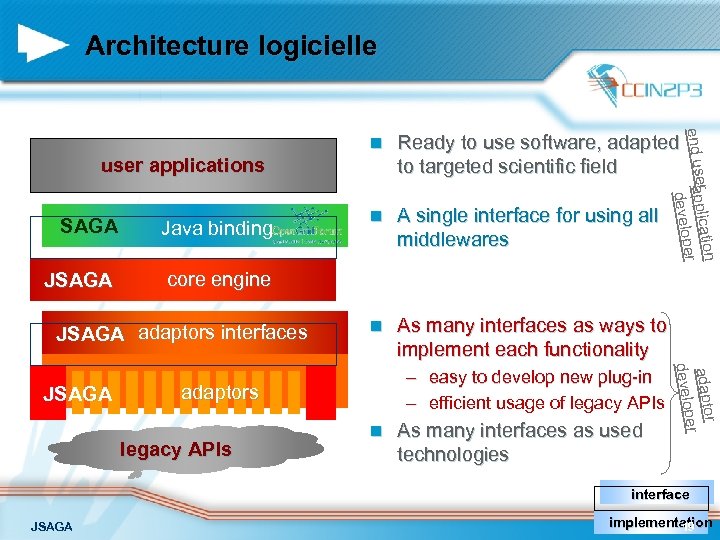 Architecture logicielle n er licatio end us app loper deve n Ready to use software, adapted to targeted scientific field n A single interface for using all middlewares n As many interfaces as ways to implement each functionality user applications SAGA Java binding JSAGA core engine JSAGA adaptors interfaces adaptors legacy APIs n As many interfaces as used technologies r adapto per develo JSAGA – easy to develop new plug-in – efficient usage of legacy APIs interface JSAGA implementation 19
Architecture logicielle n er licatio end us app loper deve n Ready to use software, adapted to targeted scientific field n A single interface for using all middlewares n As many interfaces as ways to implement each functionality user applications SAGA Java binding JSAGA core engine JSAGA adaptors interfaces adaptors legacy APIs n As many interfaces as used technologies r adapto per develo JSAGA – easy to develop new plug-in – efficient usage of legacy APIs interface JSAGA implementation 19
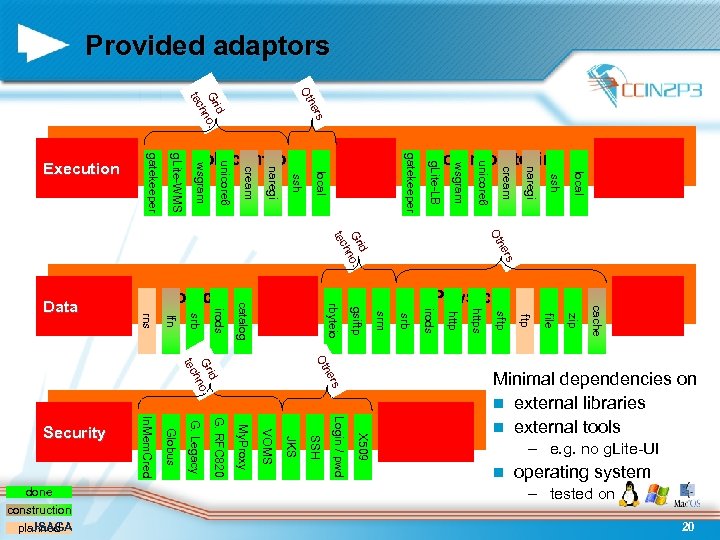 Provided adaptors Ot rs he id Gr no. h tec local ssh naregi cream unicore 6 wsgram g. Lite-LB gatekeeper local ssh naregi cream unicore 6 wsgram g. Lite-WMS gatekeeper he Ot rs id Gr no. h tec cache zip file ftp sftp https http irods srb srm gsiftp rbyteio catalog irods srb lfn rns rs he Ot id Gr no. h tec – e. g. no g. Lite-UI In. Mem. Cred Globus G. Legacy G. RFC 820 My. Proxy VOMS JKS SSH Login / pwd X 509 operating system n – tested on 20 done construction JSAGA planned Minimal dependencies on n external libraries n external tools Security Physical Logical Data Job monitoring Job control Execution
Provided adaptors Ot rs he id Gr no. h tec local ssh naregi cream unicore 6 wsgram g. Lite-LB gatekeeper local ssh naregi cream unicore 6 wsgram g. Lite-WMS gatekeeper he Ot rs id Gr no. h tec cache zip file ftp sftp https http irods srb srm gsiftp rbyteio catalog irods srb lfn rns rs he Ot id Gr no. h tec – e. g. no g. Lite-UI In. Mem. Cred Globus G. Legacy G. RFC 820 My. Proxy VOMS JKS SSH Login / pwd X 509 operating system n – tested on 20 done construction JSAGA planned Minimal dependencies on n external libraries n external tools Security Physical Logical Data Job monitoring Job control Execution
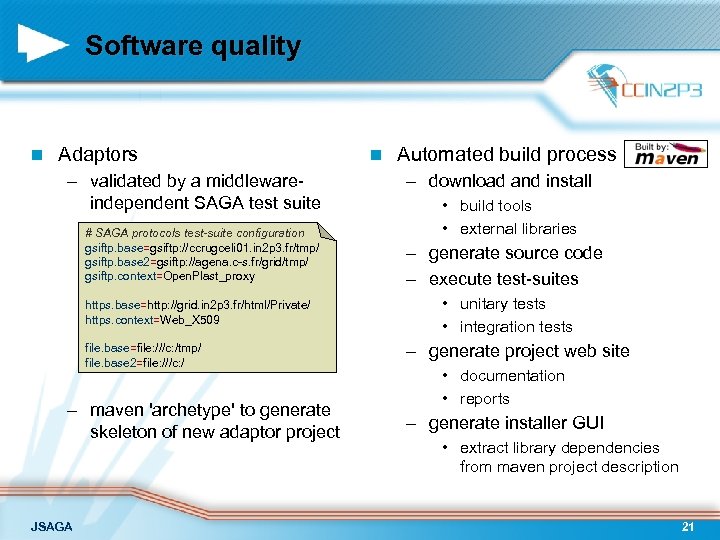 Software quality n Adaptors – validated by a middlewareindependent SAGA test suite # SAGA protocols test-suite configuration gsiftp. base=gsiftp: //ccrugceli 01. in 2 p 3. fr/tmp/ gsiftp. base 2=gsiftp: //agena. c-s. fr/grid/tmp/ gsiftp. context=Open. Plast_proxy https. base=http: //grid. in 2 p 3. fr/html/Private/ https. context=Web_X 509 file. base=file: ///c: /tmp/ file. base 2=file: ///c: / – maven 'archetype' to generate skeleton of new adaptor project JSAGA n Automated build process – download and install • build tools • external libraries – generate source code – execute test-suites • unitary tests • integration tests – generate project web site • documentation • reports – generate installer GUI • extract library dependencies from maven project description 21
Software quality n Adaptors – validated by a middlewareindependent SAGA test suite # SAGA protocols test-suite configuration gsiftp. base=gsiftp: //ccrugceli 01. in 2 p 3. fr/tmp/ gsiftp. base 2=gsiftp: //agena. c-s. fr/grid/tmp/ gsiftp. context=Open. Plast_proxy https. base=http: //grid. in 2 p 3. fr/html/Private/ https. context=Web_X 509 file. base=file: ///c: /tmp/ file. base 2=file: ///c: / – maven 'archetype' to generate skeleton of new adaptor project JSAGA n Automated build process – download and install • build tools • external libraries – generate source code – execute test-suites • unitary tests • integration tests – generate project web site • documentation • reports – generate installer GUI • extract library dependencies from maven project description 21
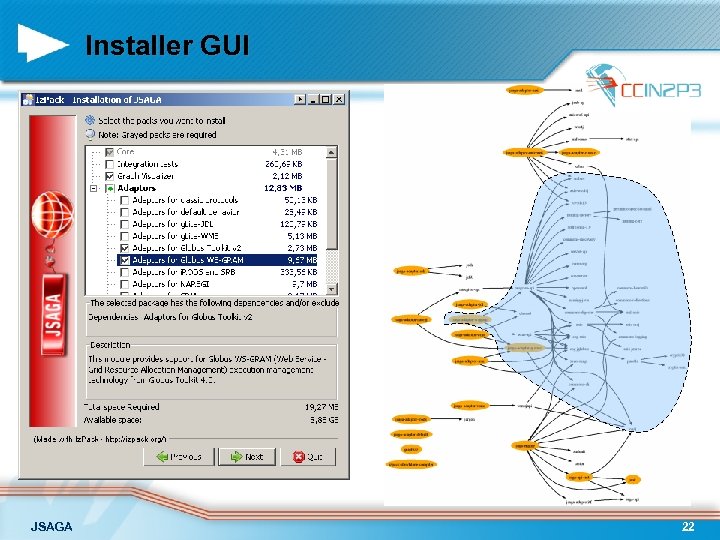 Installer GUI JSAGA 22
Installer GUI JSAGA 22
 Licenses n LGPL license – for the core engine and for most adaptors n Optional licenses – for adaptors having external dependencies, which license is not compatible with LGPL – then, end-user must… • either accept the terms of the license agreement, • or go back to previous screen and uncheck the adaptor(s) JSAGA 23
Licenses n LGPL license – for the core engine and for most adaptors n Optional licenses – for adaptors having external dependencies, which license is not compatible with LGPL – then, end-user must… • either accept the terms of the license agreement, • or go back to previous screen and uncheck the adaptor(s) JSAGA 23
 Applications – Commandes en ligne n JSAGA provides command line interfaces for… – security • jsaga-context-init • jsaga-context-info • jsaga-context-destroy – execution management • • n jsaga-job-run jsaga-job-status jsaga-job-cancel jsaga-job-output – data management • • • jsaga-cat jsaga-cp jsaga-ls jsaga-mkdir jsaga-mv jsaga-rmdir jsaga-stat jsaga-test jsaga-logical Also useful as code examples to start with SAGA JSAGA 24
Applications – Commandes en ligne n JSAGA provides command line interfaces for… – security • jsaga-context-init • jsaga-context-info • jsaga-context-destroy – execution management • • n jsaga-job-run jsaga-job-status jsaga-job-cancel jsaga-job-output – data management • • • jsaga-cat jsaga-cp jsaga-ls jsaga-mkdir jsaga-mv jsaga-rmdir jsaga-stat jsaga-test jsaga-logical Also useful as code examples to start with SAGA JSAGA 24
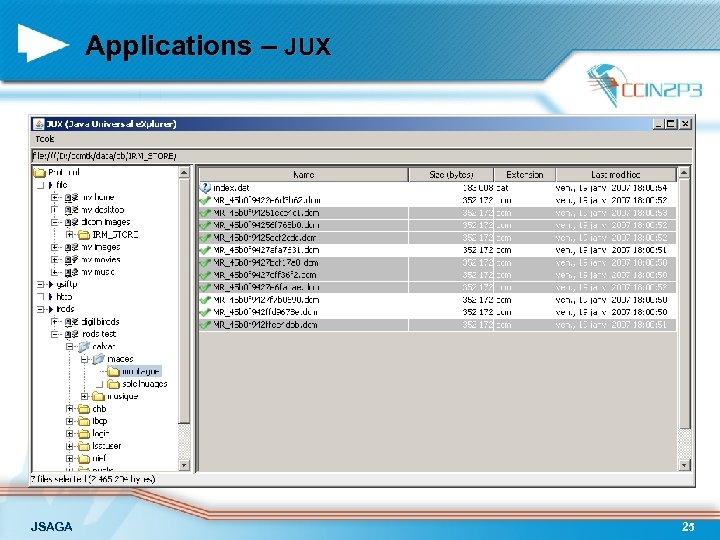 Applications – JUX JSAGA 25
Applications – JUX JSAGA 25
 Applications – autres exemples n Elis@ n • a web portal for submitting jobs to industrial and research grid infrastructures • a set of tools, including a workflow engine providing distributed computing facilities, for managing simulation experiments / n JJS (Java Job Submission) • a tool for running efficiently short-life jobs on EGEE JSAGA Sim. Explorer n j. CAE (Java CAE) • Computer Aided Engineering on distributed computing environment 26
Applications – autres exemples n Elis@ n • a web portal for submitting jobs to industrial and research grid infrastructures • a set of tools, including a workflow engine providing distributed computing facilities, for managing simulation experiments / n JJS (Java Job Submission) • a tool for running efficiently short-life jobs on EGEE JSAGA Sim. Explorer n j. CAE (Java CAE) • Computer Aided Engineering on distributed computing environment 26
 ank Th u! yo JSAGA 27
ank Th u! yo JSAGA 27
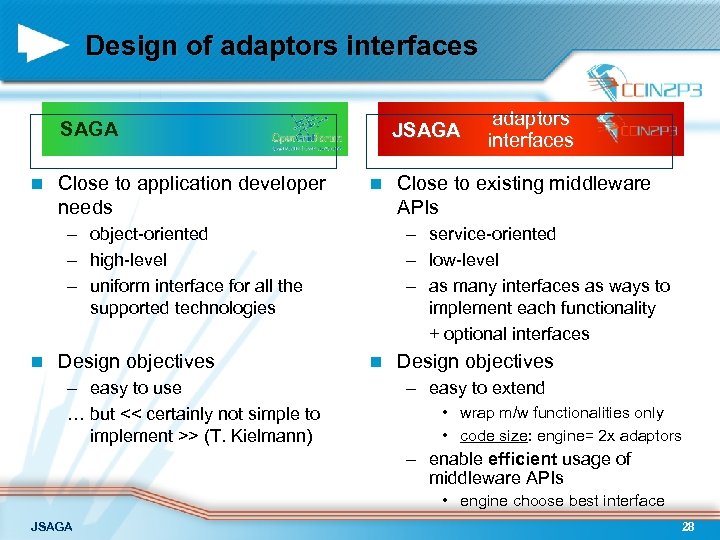 Design of adaptors interfaces SAGA n Close to application developer needs JSAGA n – object-oriented – high-level – uniform interface for all the supported technologies n Design objectives – easy to use … but << certainly not simple to implement >> (T. Kielmann) adaptors interfaces Close to existing middleware APIs – service-oriented – low-level – as many interfaces as ways to implement each functionality + optional interfaces n Design objectives – easy to extend • wrap m/w functionalities only • code size: engine= 2 x adaptors – enable efficient usage of middleware APIs • engine choose best interface JSAGA 28
Design of adaptors interfaces SAGA n Close to application developer needs JSAGA n – object-oriented – high-level – uniform interface for all the supported technologies n Design objectives – easy to use … but << certainly not simple to implement >> (T. Kielmann) adaptors interfaces Close to existing middleware APIs – service-oriented – low-level – as many interfaces as ways to implement each functionality + optional interfaces n Design objectives – easy to extend • wrap m/w functionalities only • code size: engine= 2 x adaptors – enable efficient usage of middleware APIs • engine choose best interface JSAGA 28
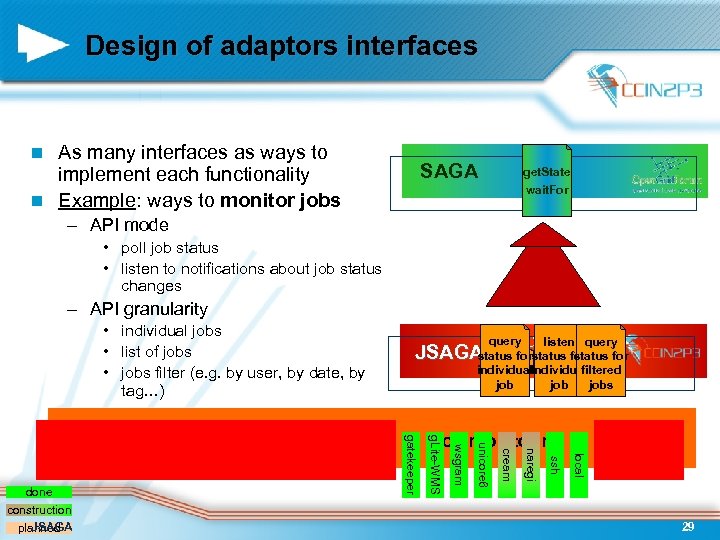 Design of adaptors interfaces As many interfaces as ways to implement each functionality n Example: ways to monitor jobs n SAGA get. State wait. For – API mode • poll job status • listen to notifications about job status changes – API granularity • individual jobs • list of jobs • jobs filter (e. g. by user, by date, by tag…) individual filtered job jobs local ssh naregi cream unicore 6 wsgram Job monitoring g. Lite-WMS gatekeeper done construction JSAGA planned query listen query adaptors JSAGA interfaces for status 29
Design of adaptors interfaces As many interfaces as ways to implement each functionality n Example: ways to monitor jobs n SAGA get. State wait. For – API mode • poll job status • listen to notifications about job status changes – API granularity • individual jobs • list of jobs • jobs filter (e. g. by user, by date, by tag…) individual filtered job jobs local ssh naregi cream unicore 6 wsgram Job monitoring g. Lite-WMS gatekeeper done construction JSAGA planned query listen query adaptors JSAGA interfaces for status 29
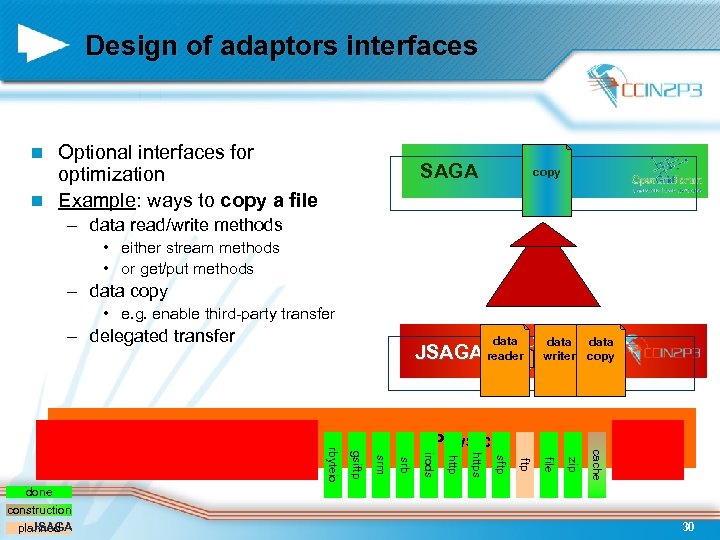 Design of adaptors interfaces Optional interfaces for optimization n Example: ways to copy a file n SAGA copy – data read/write methods • either stream methods • or get/put methods – data copy • e. g. enable third-party transfer – delegated transfer dataadaptors data JSAGA reader writer copy interfaces cache zip file ftp sftp https http irods srb srm gsiftp rbyteio done construction JSAGA planned Physical 30
Design of adaptors interfaces Optional interfaces for optimization n Example: ways to copy a file n SAGA copy – data read/write methods • either stream methods • or get/put methods – data copy • e. g. enable third-party transfer – delegated transfer dataadaptors data JSAGA reader writer copy interfaces cache zip file ftp sftp https http irods srb srm gsiftp rbyteio done construction JSAGA planned Physical 30
 Provided adaptors n SAGA hides most of the differences between the technologies n Information on remaining differences is available – on JSAGA web site, for each adaptor module • Frequently Asked Questions • Configuration example – with command line jsaga-help • supported protocols • associated security contexts • context attr. usage/defaults JSAGA usage: jsaga-help -a
Provided adaptors n SAGA hides most of the differences between the technologies n Information on remaining differences is available – on JSAGA web site, for each adaptor module • Frequently Asked Questions • Configuration example – with command line jsaga-help • supported protocols • associated security contexts • context attr. usage/defaults JSAGA usage: jsaga-help -a


