f4f089443b77fe2ae90a888cf04dc839.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Presentation and Management of Raised Intracranial Pressure Amro Al-Habib MD, FRCSC, MPH Neurosurgery
Presentation and Management of Raised Intracranial Pressure Amro Al-Habib MD, FRCSC, MPH Neurosurgery
 Basics n Components of cranium n Brain 1400 ml n CSF 75 -100 ml n Blood 75 ml Monro-Kellie Doctrine n n n These contents are incompressible Therefore, change in volume of the brain is associated with change in CSF or blood volume
Basics n Components of cranium n Brain 1400 ml n CSF 75 -100 ml n Blood 75 ml Monro-Kellie Doctrine n n n These contents are incompressible Therefore, change in volume of the brain is associated with change in CSF or blood volume
 Pressure-Volume n Increase in volume in one compartment leads to change in volume in the other ones. n n E. g. brain tumor ---> CSF volume then blood volume For how long could this go on?
Pressure-Volume n Increase in volume in one compartment leads to change in volume in the other ones. n n E. g. brain tumor ---> CSF volume then blood volume For how long could this go on?
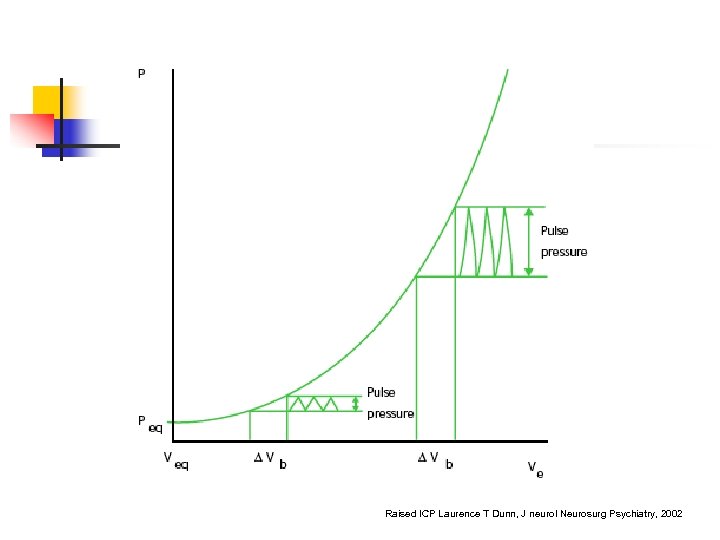 Raised ICP Laurence T Dunn, J neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2002
Raised ICP Laurence T Dunn, J neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2002
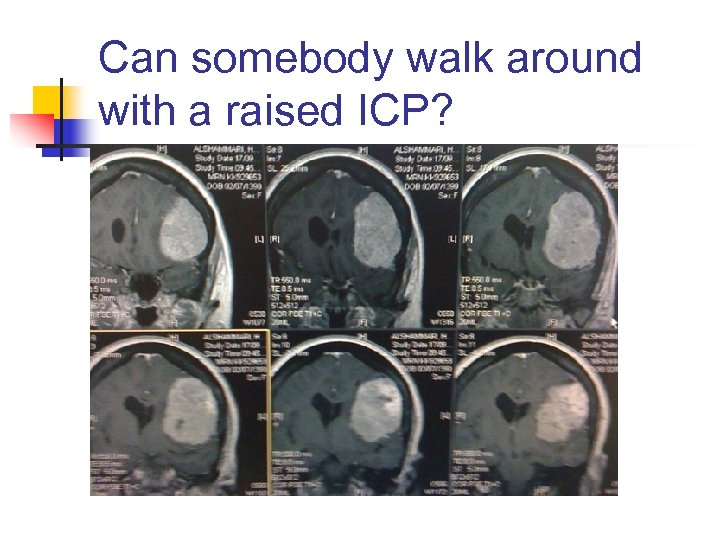 Can somebody walk around with a raised ICP?
Can somebody walk around with a raised ICP?
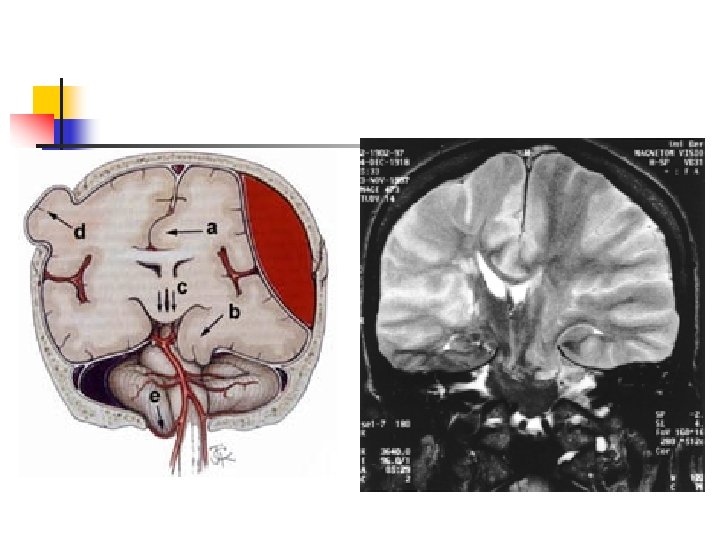
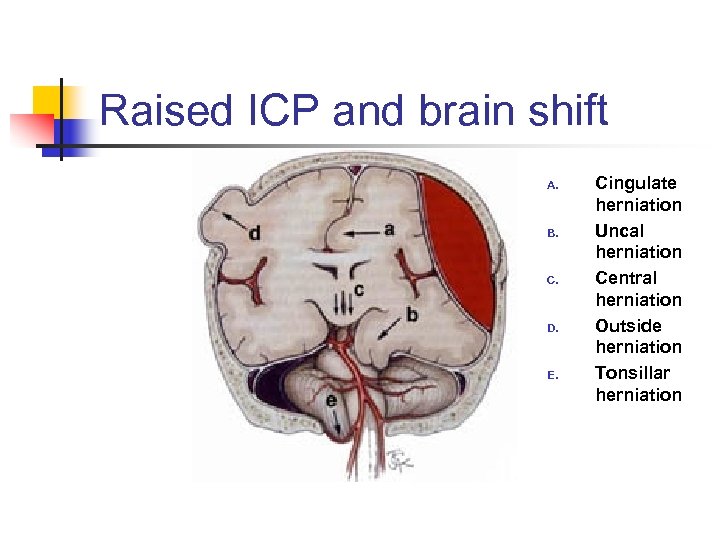 Raised ICP and brain shift A. B. C. D. E. Cingulate herniation Uncal herniation Central herniation Outside herniation Tonsillar herniation
Raised ICP and brain shift A. B. C. D. E. Cingulate herniation Uncal herniation Central herniation Outside herniation Tonsillar herniation
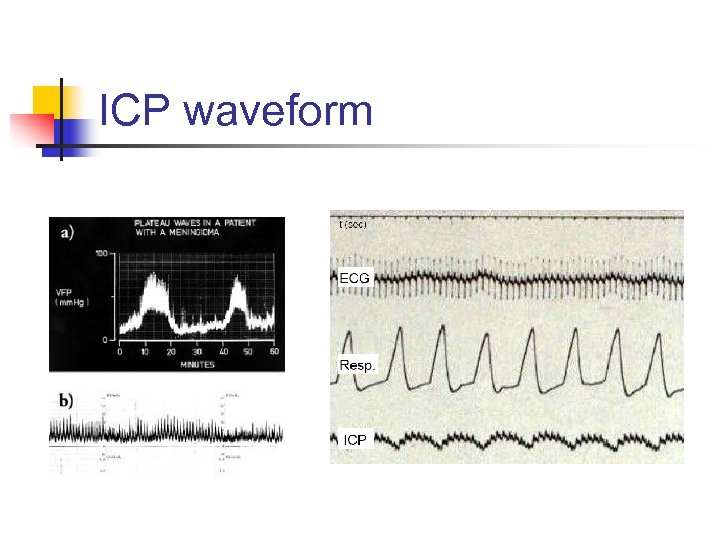 ICP waveform
ICP waveform
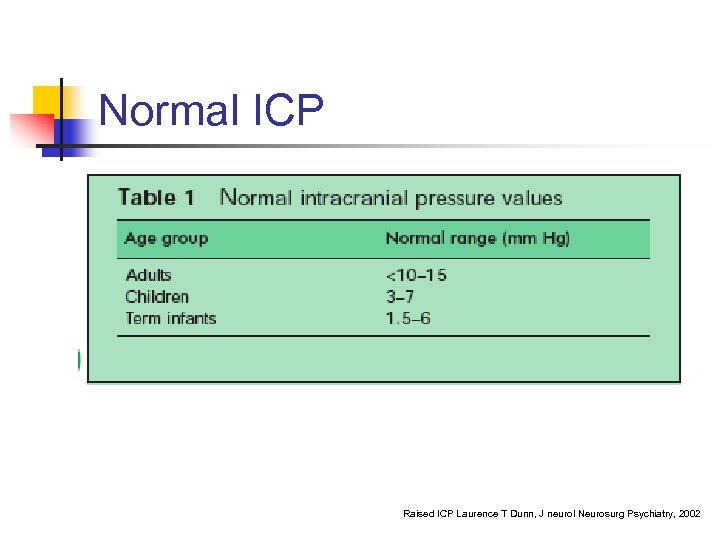 Normal ICP Raised ICP Laurence T Dunn, J neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2002
Normal ICP Raised ICP Laurence T Dunn, J neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2002
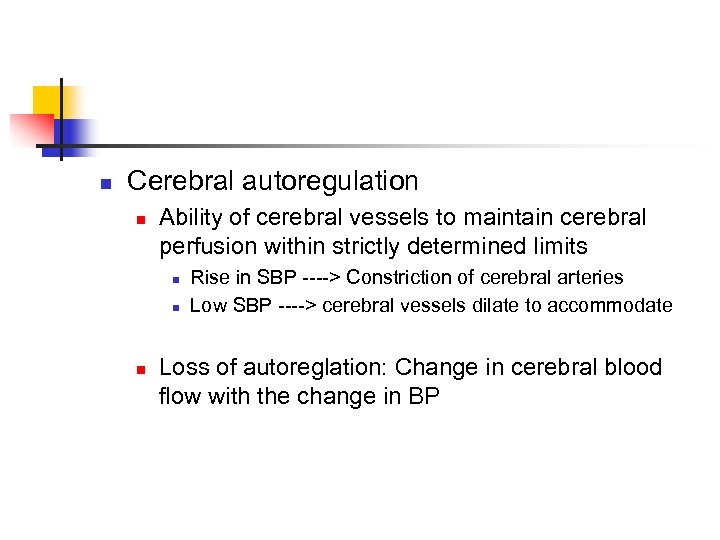 n Cerebral autoregulation n Ability of cerebral vessels to maintain cerebral perfusion within strictly determined limits n n n Rise in SBP ----> Constriction of cerebral arteries Low SBP ----> cerebral vessels dilate to accommodate Loss of autoreglation: Change in cerebral blood flow with the change in BP
n Cerebral autoregulation n Ability of cerebral vessels to maintain cerebral perfusion within strictly determined limits n n n Rise in SBP ----> Constriction of cerebral arteries Low SBP ----> cerebral vessels dilate to accommodate Loss of autoreglation: Change in cerebral blood flow with the change in BP
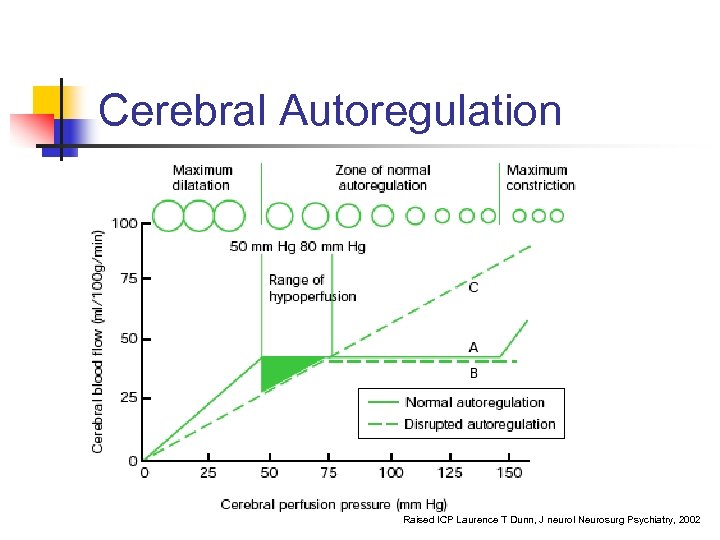 Cerebral Autoregulation Raised ICP Laurence T Dunn, J neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2002
Cerebral Autoregulation Raised ICP Laurence T Dunn, J neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2002
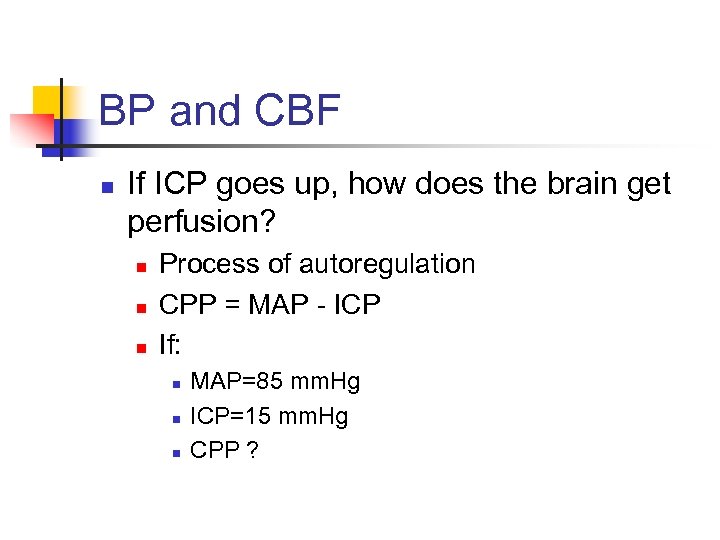 BP and CBF n If ICP goes up, how does the brain get perfusion? n n n Process of autoregulation CPP = MAP - ICP If: n n n MAP=85 mm. Hg ICP=15 mm. Hg CPP ?
BP and CBF n If ICP goes up, how does the brain get perfusion? n n n Process of autoregulation CPP = MAP - ICP If: n n n MAP=85 mm. Hg ICP=15 mm. Hg CPP ?
 n CPP 50 -140 mm. Hg
n CPP 50 -140 mm. Hg
 n 20 year old man. Had car accident (MVC) as unrestrained driver. He presented with BP 75/30, HR 125 bpm. Unconscious, with right hemiplegia. What is going on?
n 20 year old man. Had car accident (MVC) as unrestrained driver. He presented with BP 75/30, HR 125 bpm. Unconscious, with right hemiplegia. What is going on?
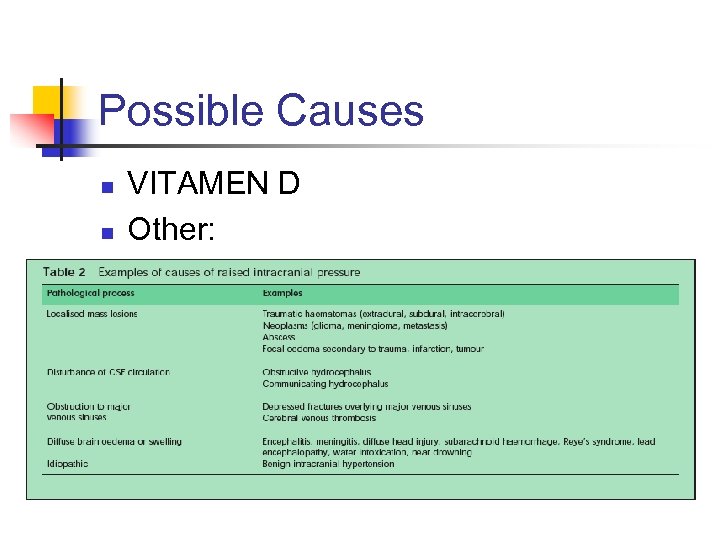 Possible Causes n n VITAMEN D Other:
Possible Causes n n VITAMEN D Other:
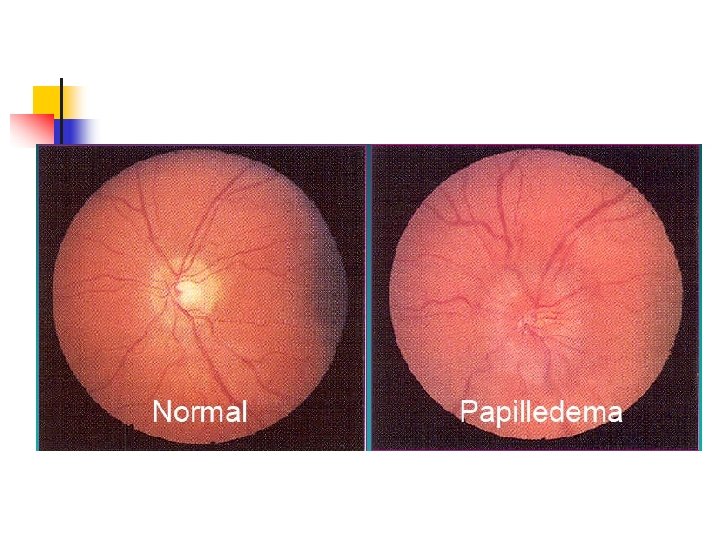
 Clinical Presentation of raised ICP n Headache, vomiting, papilloedema n Headache n n Early morning Throbbing / Bursting sneezing, coughing Papilleodema n n Reliable but may take several days Associated fundal hge indicates acute and severe rise in ICP
Clinical Presentation of raised ICP n Headache, vomiting, papilloedema n Headache n n Early morning Throbbing / Bursting sneezing, coughing Papilleodema n n Reliable but may take several days Associated fundal hge indicates acute and severe rise in ICP
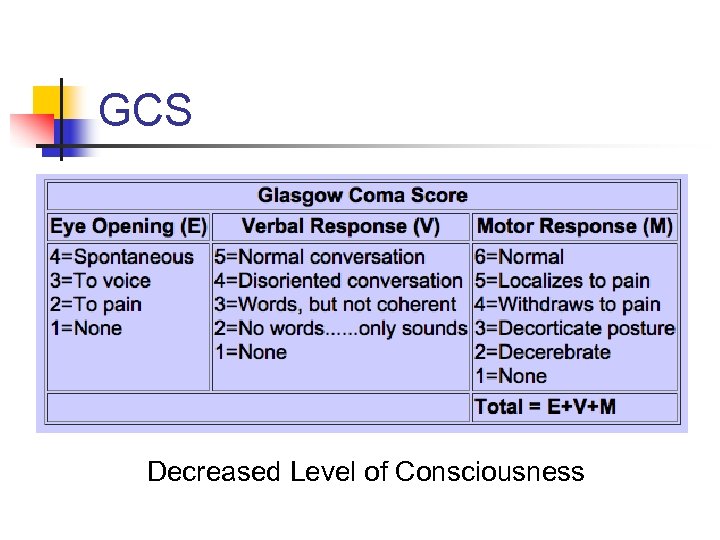 GCS Decreased Level of Consciousness
GCS Decreased Level of Consciousness
 n Neurological: n n n Pupillary dilation Hemiplegia Cranial nerve deficit
n Neurological: n n n Pupillary dilation Hemiplegia Cranial nerve deficit
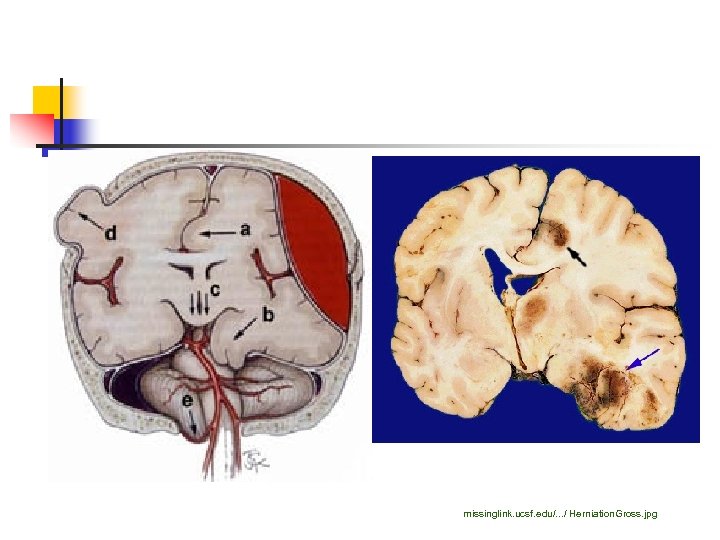 missinglink. ucsf. edu/. . . / Herniation. Gross. jpg
missinglink. ucsf. edu/. . . / Herniation. Gross. jpg
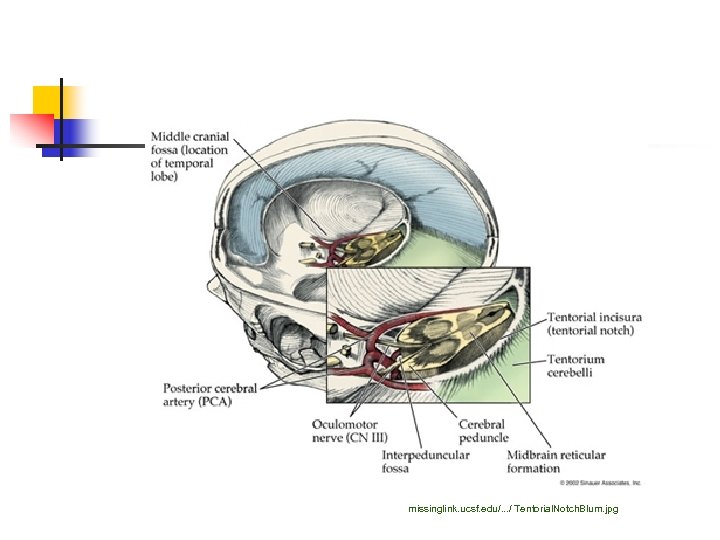 missinglink. ucsf. edu/. . . / Tentorial. Notch. Blum. jpg
missinglink. ucsf. edu/. . . / Tentorial. Notch. Blum. jpg
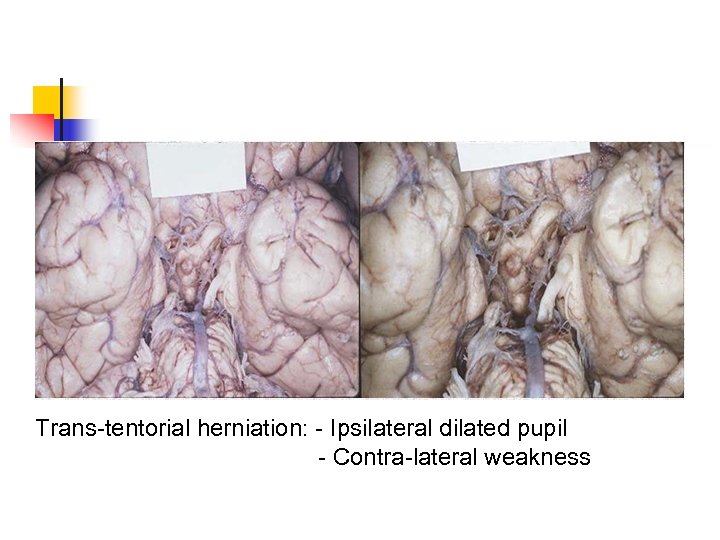 Trans-tentorial herniation: - Ipsilateral dilated pupil - Contra-lateral weakness
Trans-tentorial herniation: - Ipsilateral dilated pupil - Contra-lateral weakness
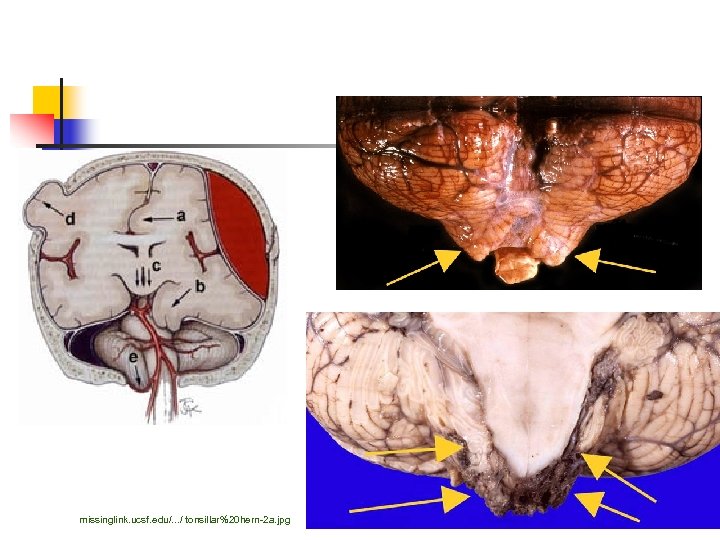 missinglink. ucsf. edu/. . . / tonsillar%20 hern-2 a. jpg
missinglink. ucsf. edu/. . . / tonsillar%20 hern-2 a. jpg
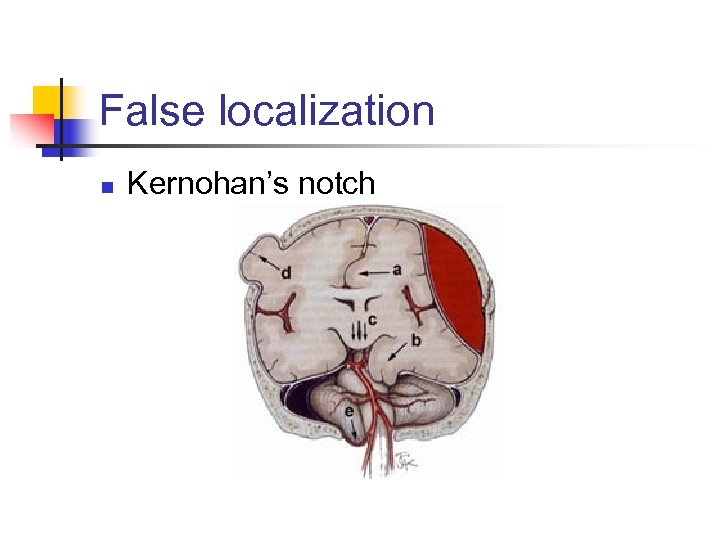 False localization n Kernohan’s notch
False localization n Kernohan’s notch
 n Systemic: n Raised BP (recall: CPP=MAP-ICP) n Respiratory change: n Cheyne-Stokes breathing: n n Oscillating periods of apnea-tachypnea Respiratory centers compromise
n Systemic: n Raised BP (recall: CPP=MAP-ICP) n Respiratory change: n Cheyne-Stokes breathing: n n Oscillating periods of apnea-tachypnea Respiratory centers compromise
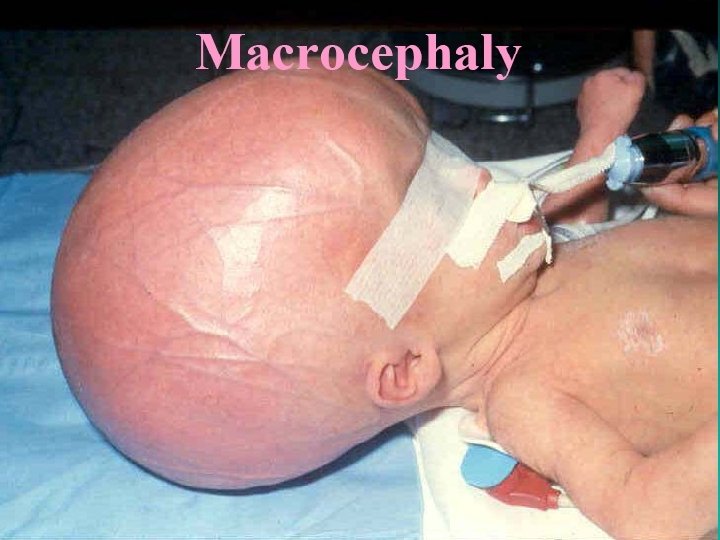
 Raised ICP in infants n n Widened sutures Increased Head circumference Dilated head veins “Sun set” eyes
Raised ICP in infants n n Widened sutures Increased Head circumference Dilated head veins “Sun set” eyes
 Investigations n n URGENT CT head NO Lumbar Puncture
Investigations n n URGENT CT head NO Lumbar Puncture
 What is the treatment of high ICP? n General measures: n n n n Head elevation (30 degrees) No neck compression Mannitol for patients who have decreased LOC (or Furosemide) Steroids (Dexamethazone) for tumors Hyperventilation: controlled to PCO 2 35 -40 mm. Hg Sedation, muscle relaxants Hypothermia Barbiturates: terminal option
What is the treatment of high ICP? n General measures: n n n n Head elevation (30 degrees) No neck compression Mannitol for patients who have decreased LOC (or Furosemide) Steroids (Dexamethazone) for tumors Hyperventilation: controlled to PCO 2 35 -40 mm. Hg Sedation, muscle relaxants Hypothermia Barbiturates: terminal option
 What is the treatment of high ICP? n Specific treatment: n Depends on the cause n VITAMEN D
What is the treatment of high ICP? n Specific treatment: n Depends on the cause n VITAMEN D
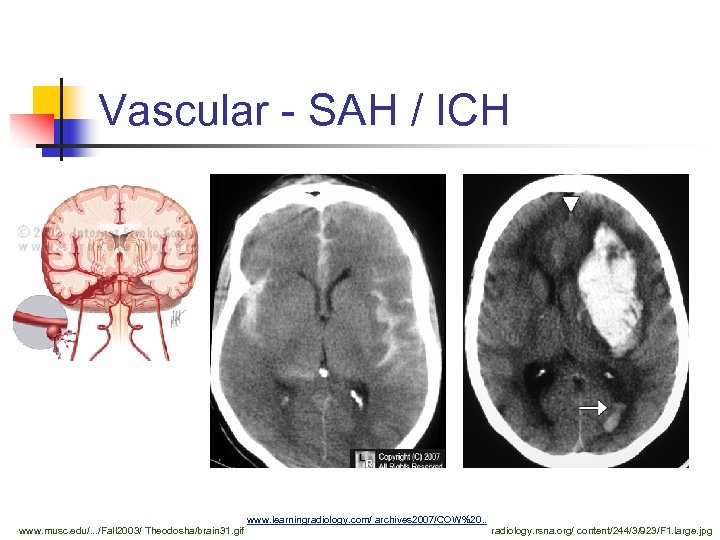 Vascular - SAH / ICH www. musc. edu/. . . /Fall 2003/ Theodosha/brain 31. gif www. learningradiology. com/ archives 2007/COW%20. . radiology. rsna. org/ content/244/3/923/F 1. large. jpg
Vascular - SAH / ICH www. musc. edu/. . . /Fall 2003/ Theodosha/brain 31. gif www. learningradiology. com/ archives 2007/COW%20. . radiology. rsna. org/ content/244/3/923/F 1. large. jpg
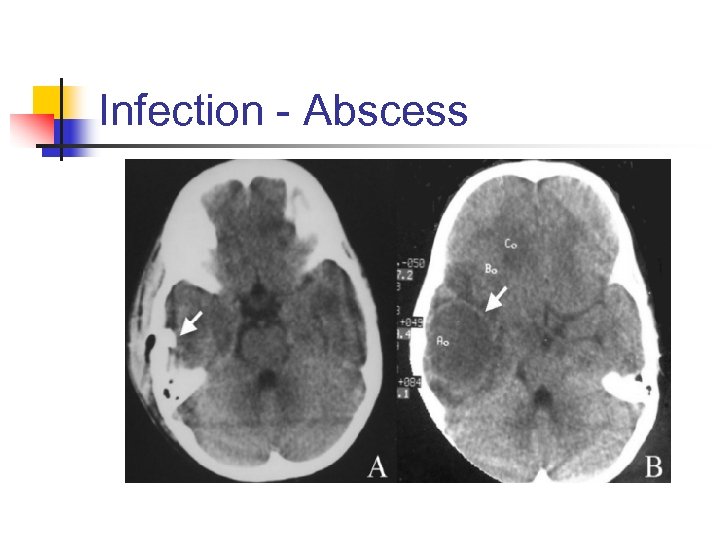 Infection - Abscess
Infection - Abscess
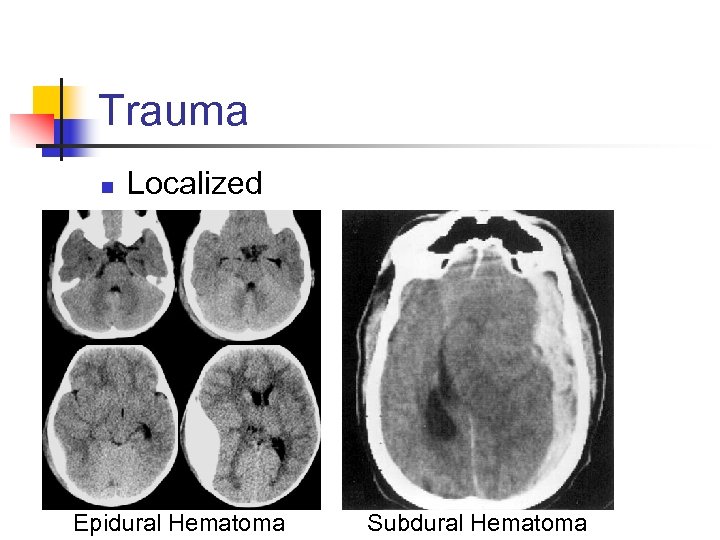 Trauma n Localized Epidural Hematoma Subdural Hematoma
Trauma n Localized Epidural Hematoma Subdural Hematoma
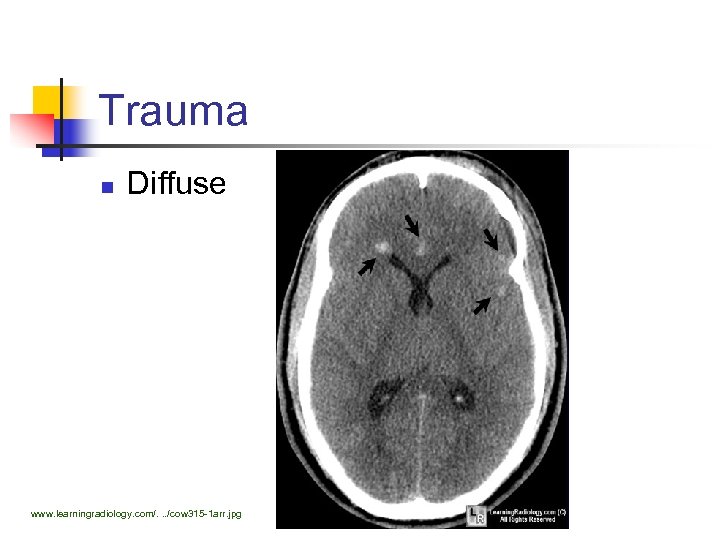 Trauma n Diffuse www. learningradiology. com/. . . /cow 315 -1 arr. jpg
Trauma n Diffuse www. learningradiology. com/. . . /cow 315 -1 arr. jpg
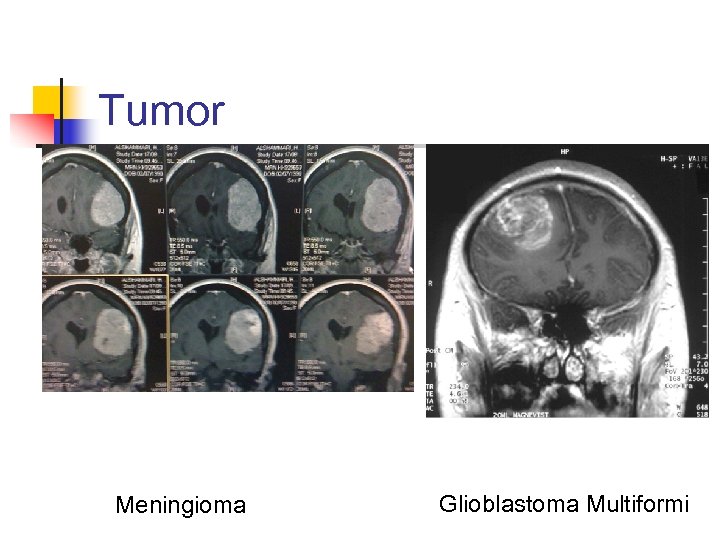 Tumor Meningioma Glioblastoma Multiformi
Tumor Meningioma Glioblastoma Multiformi
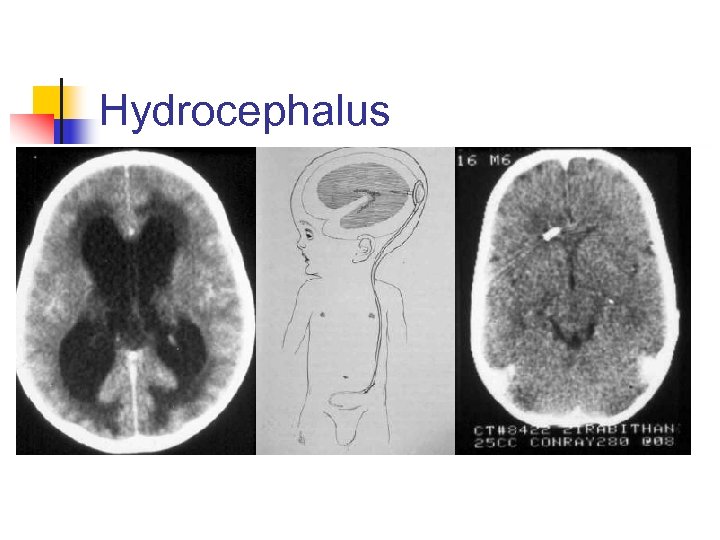 Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
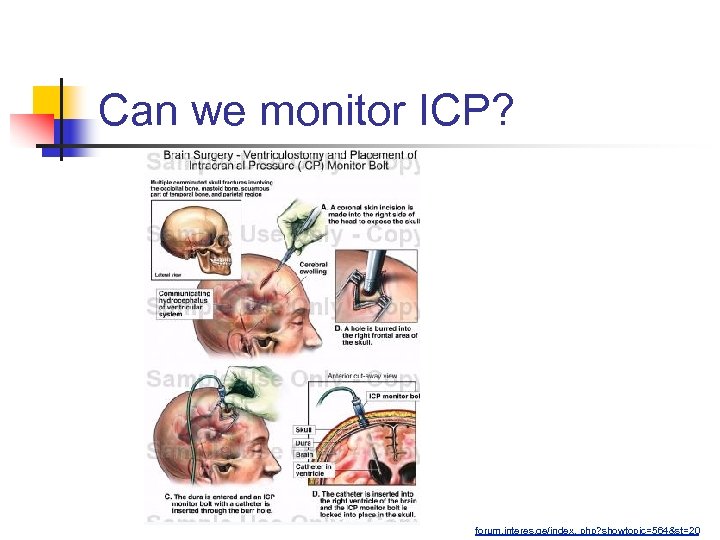 Can we monitor ICP? forum. interes. ge/index. php? showtopic=564&st=20
Can we monitor ICP? forum. interes. ge/index. php? showtopic=564&st=20


