 Presentation 4 Kunal Jain April 7, 2010 Economics 201 FS
Presentation 4 Kunal Jain April 7, 2010 Economics 201 FS
 Pairs Trading n Market Neutral Strategy looking at correlations within day-to-day price movements of certain equities Competitors in same sector ¨ Liquid Equities ¨ Used to Hedge sector- and market-risk. ¨ n Finds some sort of index or relative mean Calculate Standard Deviations ¨ Mean Reversion ¨ n When correlation breaks, one equity trades up, while other trades down: Sell outperforming stock ¨ Buy underperforming stock ¨ n Convergence Trade
Pairs Trading n Market Neutral Strategy looking at correlations within day-to-day price movements of certain equities Competitors in same sector ¨ Liquid Equities ¨ Used to Hedge sector- and market-risk. ¨ n Finds some sort of index or relative mean Calculate Standard Deviations ¨ Mean Reversion ¨ n When correlation breaks, one equity trades up, while other trades down: Sell outperforming stock ¨ Buy underperforming stock ¨ n Convergence Trade
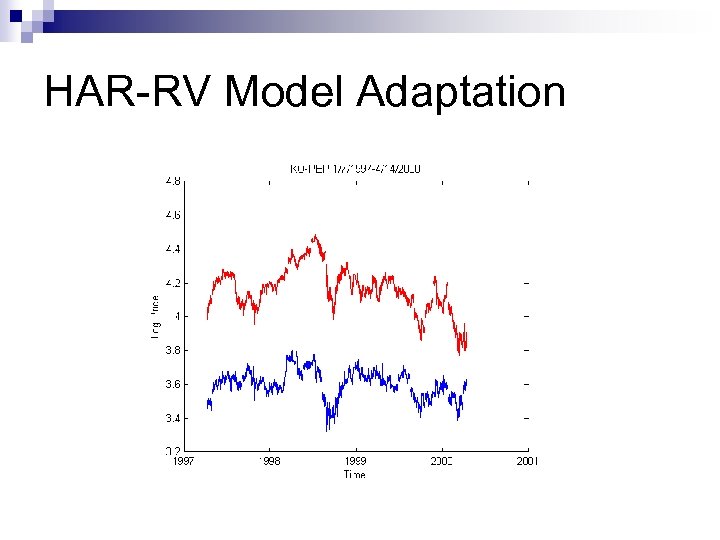 HAR-RV Model Adaptation
HAR-RV Model Adaptation
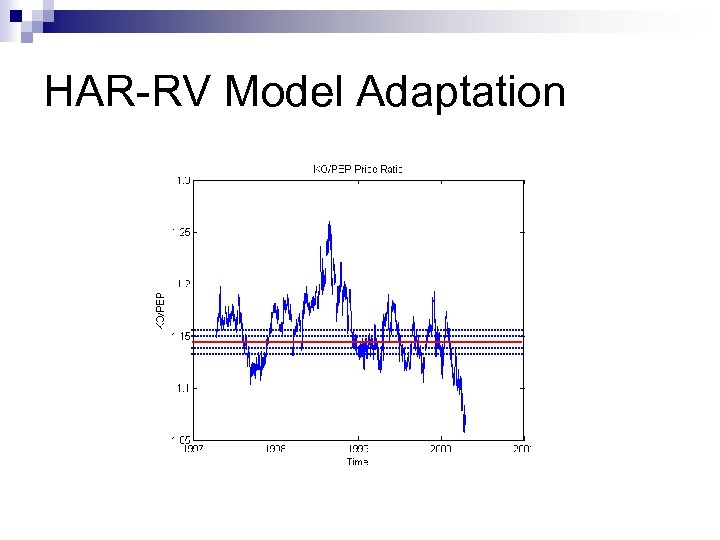 HAR-RV Model Adaptation
HAR-RV Model Adaptation
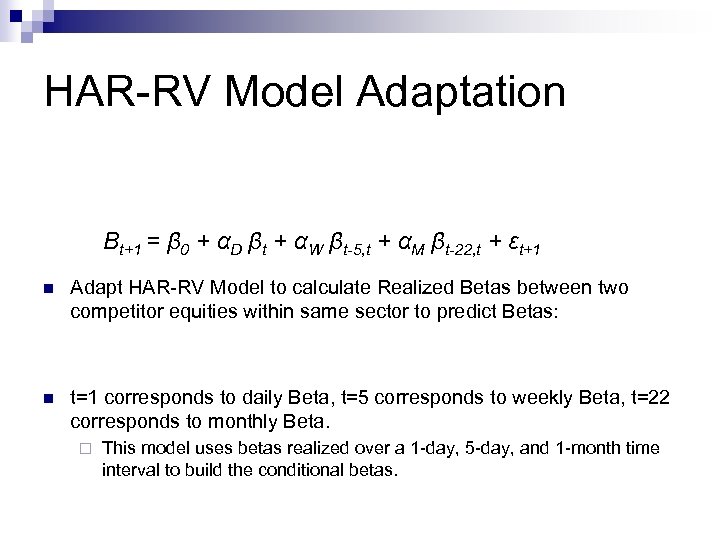 HAR-RV Model Adaptation Βt+1 = β 0 + αD βt + αW βt-5, t + αM βt-22, t + εt+1 n Adapt HAR-RV Model to calculate Realized Betas between two competitor equities within same sector to predict Betas: n t=1 corresponds to daily Beta, t=5 corresponds to weekly Beta, t=22 corresponds to monthly Beta. ¨ This model uses betas realized over a 1 -day, 5 -day, and 1 -month time interval to build the conditional betas.
HAR-RV Model Adaptation Βt+1 = β 0 + αD βt + αW βt-5, t + αM βt-22, t + εt+1 n Adapt HAR-RV Model to calculate Realized Betas between two competitor equities within same sector to predict Betas: n t=1 corresponds to daily Beta, t=5 corresponds to weekly Beta, t=22 corresponds to monthly Beta. ¨ This model uses betas realized over a 1 -day, 5 -day, and 1 -month time interval to build the conditional betas.
 HAR-RV Model Adaptation n Intuition: Test whether the HAR adaptation, using daily, weekly, monthly Betas, can be implemented specifically in terms of Pairs Trading to predict Beta and take advantage of strategy. ¨ Negates Drift associated with Pairs Trading n Unless the relative prices return closer to their historical levels, the pair trade will not be profitable Take advantage of high-frequency data ¨ Potential better ways of calculating Beta? ¨
HAR-RV Model Adaptation n Intuition: Test whether the HAR adaptation, using daily, weekly, monthly Betas, can be implemented specifically in terms of Pairs Trading to predict Beta and take advantage of strategy. ¨ Negates Drift associated with Pairs Trading n Unless the relative prices return closer to their historical levels, the pair trade will not be profitable Take advantage of high-frequency data ¨ Potential better ways of calculating Beta? ¨
 HAR-RV Model Adaptation n Chose liquid competitor equities and Time Interval Coca Cola (KO): 4/9/1997 -4/14/2000 ¨ Pepsi (PEP): 4/9/1997 -4/14/2000 ¨ n Calculate HAR-Beta coefficients (D, W, M) ¨ n Implemented in Mat. LAB Find conditional Beta using observed data and Beta-coefficients from model ¨ Found using observed Betas (Alphas) n Calculate expected relative return based on conditional Beta n Calculate/Compare actual return to estimate differential
HAR-RV Model Adaptation n Chose liquid competitor equities and Time Interval Coca Cola (KO): 4/9/1997 -4/14/2000 ¨ Pepsi (PEP): 4/9/1997 -4/14/2000 ¨ n Calculate HAR-Beta coefficients (D, W, M) ¨ n Implemented in Mat. LAB Find conditional Beta using observed data and Beta-coefficients from model ¨ Found using observed Betas (Alphas) n Calculate expected relative return based on conditional Beta n Calculate/Compare actual return to estimate differential
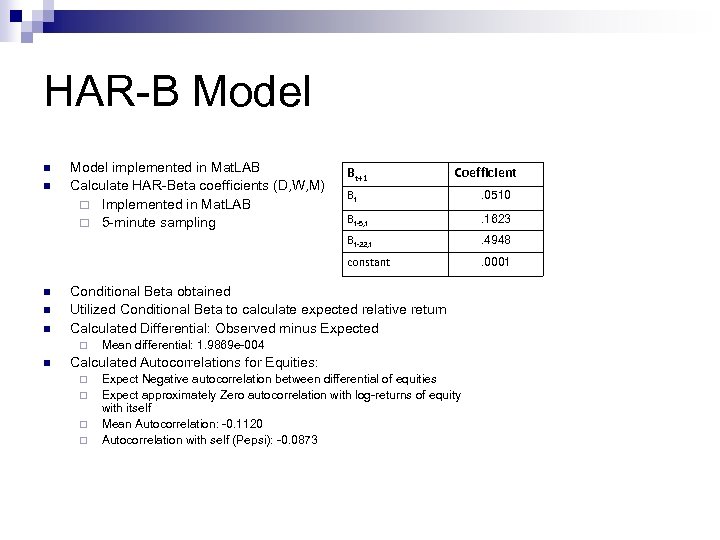 HAR-B Model n n Model implemented in Mat. LAB Calculate HAR-Beta coefficients (D, W, M) ¨ Implemented in Mat. LAB ¨ 5 -minute sampling Bt+1 Coefficient n . 1623. 4948. 0001 Conditional Beta obtained Utilized Conditional Beta to calculate expected relative return Calculated Differential: Observed minus Expected ¨ n Bt-5, t constant n . 0510 Bt-22, t n Bt Mean differential: 1. 9869 e-004 Calculated Autocorrelations for Equities: ¨ ¨ Expect Negative autocorrelation between differential of equities Expect approximately Zero autocorrelation with log-returns of equity with itself Mean Autocorrelation: -0. 1120 Autocorrelation with self (Pepsi): -0. 0873
HAR-B Model n n Model implemented in Mat. LAB Calculate HAR-Beta coefficients (D, W, M) ¨ Implemented in Mat. LAB ¨ 5 -minute sampling Bt+1 Coefficient n . 1623. 4948. 0001 Conditional Beta obtained Utilized Conditional Beta to calculate expected relative return Calculated Differential: Observed minus Expected ¨ n Bt-5, t constant n . 0510 Bt-22, t n Bt Mean differential: 1. 9869 e-004 Calculated Autocorrelations for Equities: ¨ ¨ Expect Negative autocorrelation between differential of equities Expect approximately Zero autocorrelation with log-returns of equity with itself Mean Autocorrelation: -0. 1120 Autocorrelation with self (Pepsi): -0. 0873
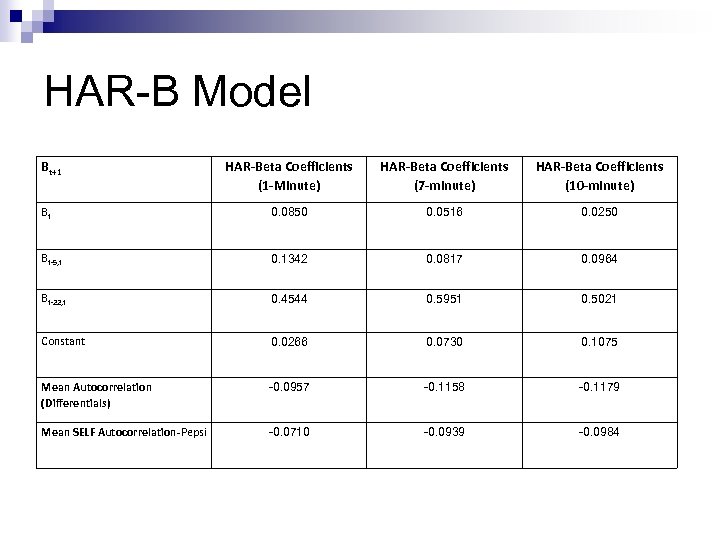 HAR-B Model Bt+1 HAR-Beta Coefficients (1 -Minute) HAR-Beta Coefficients (7 -minute) HAR-Beta Coefficients (10 -minute) Bt 0. 0850 0. 0516 0. 0250 Bt-5, t 0. 1342 0. 0817 0. 0964 Bt-22, t 0. 4544 0. 5951 0. 5021 Constant 0. 0266 0. 0730 0. 1075 Mean Autocorrelation (Differentials) -0. 0957 -0. 1158 -0. 1179 Mean SELF Autocorrelation-Pepsi -0. 0710 -0. 0939 -0. 0984
HAR-B Model Bt+1 HAR-Beta Coefficients (1 -Minute) HAR-Beta Coefficients (7 -minute) HAR-Beta Coefficients (10 -minute) Bt 0. 0850 0. 0516 0. 0250 Bt-5, t 0. 1342 0. 0817 0. 0964 Bt-22, t 0. 4544 0. 5951 0. 5021 Constant 0. 0266 0. 0730 0. 1075 Mean Autocorrelation (Differentials) -0. 0957 -0. 1158 -0. 1179 Mean SELF Autocorrelation-Pepsi -0. 0710 -0. 0939 -0. 0984
 Further Research n n n Significance Levels More Competitor Pairs Different Time Intervals Autocorrelation for all returns Calculate Strategy Returns and Profitability
Further Research n n n Significance Levels More Competitor Pairs Different Time Intervals Autocorrelation for all returns Calculate Strategy Returns and Profitability