1d7ae7aceff33e5e14dd2deea195dd11.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

Preparing for the 64 -bit Platform Ron van Moorsel, Senior DBA Consultant SQL Services Ltd Rob Hawthorne, SQL Server Solution Specialist Microsoft NZ Ltd Wednesday, 26 th July 2006

Agenda 64 -bit SQL Server ¢ ¢ ¢ Introduction Platforms Benefits Challenges and Best Practices Summary and Questions

Introduction ¢ Speaker’s Bio ¢ ¢ ¢ Ron van Moorsel ¢ Senior DBA Consultant for SQL Services Ltd ¢ SQL Server and Oracle Certified DBA since 1999 ¢ Almost 20 years IT experience, 10 years in Europe with multinationals like Philips and Nissan working with mainframes Rob Hawthorne ¢ Microsoft NZ’s SQL Server Solution Specialist ¢ Been working with SQL Server since early version 6. 0 ¢ Focused on high availability and scalability ¢ Author of “SQL Server Database Development from Scratch” Key Takeaways

Agenda 64 -bit SQL Server ¢ ¢ ¢ Introduction Platforms Benefits Challenges and Best Practices Summary and Questions
64 -bit Platforms ¢ ¢ ¢ Server platforms are now 64 -bit ready You have choices about the SQL Server configuration You even have a choice about the type of 64 -bit to run, IA 64 or x 64

Properties of Itanium (IA 64) ¢ ¢ Runs 64 -bit Windows, drivers and software specifically compiled for the Itanium instruction set Runs 32 -bit software without being recompiled Cannot act like an x 86 (32 -bit) processor or boot 32 -bit Windows Does not run versions of Windows or 64 bit drivers compiled for x 64
Intel Itanium - 2 offerings ¢ Aimed at the larger processing environments, for example: ¢ ¢ Greater than 4 CPUs (sockets) 64 CPUs Massive scalability database target market ¢ ¢ i. e. More than 5, 000 users (achieved 30, 000 concurrent users) See http: //www. tpc. org (Transaction Performance Processing Council) Future versions of the processor coming, code name “Montvale” Vendors: ¢ HP, Unisys, NEC, Fujitsu, Bull

Properties of x 64 ¢ ¢ Runs 64 -bit Windows, drivers and software specifically compiled for x 64 instruction set Runs 32 -bit software without recompilation ¢ ¢ Note: Think of a half-way house Does not run Itanium versions of Windows nor drivers compiled for Itanium ¢ Note: Specific x 64 drivers required, not all 64 bit drivers are equal!
x 64 Offerings ¢ Two chip vendors, same OS required ¢ ¢ AMD (AMD 64) Intel (EM 64 T) X 64 was the first to offer dual-core Generally aimed at <= 4 -CPUs, however… ¢ ¢ Unisys - 32 socket IBM – 16 socket
Multi-Core and Hyper-Threading ¢ Multi-Core chips scale very effectively ¢ ¢ Dual-core offers >> 50% performance benefit relative to single core SQL Server operates as though each core is a separate CPU SQL Server is priced per socket, not per core (lower TCO) Hyper-Threading does not benefit typical SQL Server workloads ¢ ¢ ¢ Generally recommend disabling Hyper. Threading Potentially overloads a single core with multiple concurrent scheduler tasks Multiple threads can thrash the CPU cache
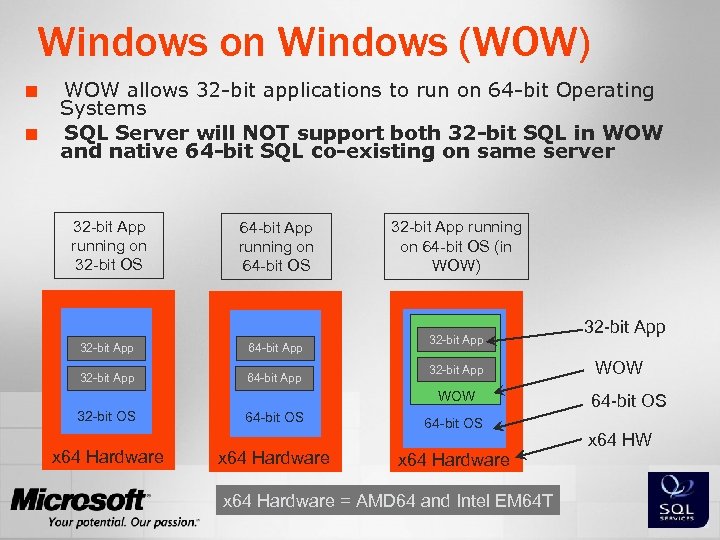
Windows on Windows (WOW) ¢ ¢ WOW allows 32 -bit applications to run on 64 -bit Operating Systems SQL Server will NOT support both 32 -bit SQL in WOW and native 64 -bit SQL co-existing on same server 32 -bit App running on 32 -bit OS 64 -bit App running on 64 -bit OS 32 -bit App 64 -bit App 32 -bit App running on 64 -bit OS (in WOW) 32 -bit App WOW 32 -bit OS x 64 Hardware 64 -bit OS x 64 Hardware = AMD 64 and Intel EM 64 T 32 -bit App WOW 64 -bit OS x 64 HW
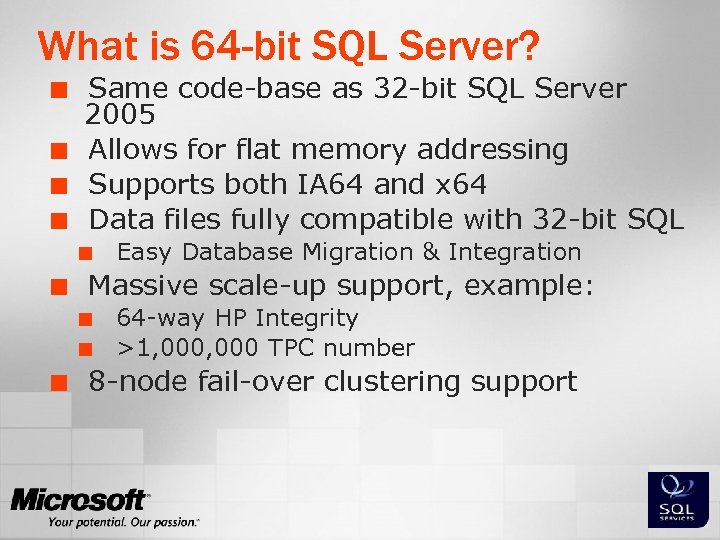
What is 64 -bit SQL Server? ¢ ¢ Same code-base as 32 -bit SQL Server 2005 Allows for flat memory addressing Supports both IA 64 and x 64 Data files fully compatible with 32 -bit SQL ¢ ¢ Massive scale-up support, example: ¢ ¢ ¢ Easy Database Migration & Integration 64 -way HP Integrity >1, 000 TPC number 8 -node fail-over clustering support

64 -bit gaps in SQL Server 2005 ¢ ¢ Visual Studio (VS) not supported on Itanium ¢ Although management tools are supported BIDS not supported on Itanium – affects SSIS ¢ Must develop and debug packages on a 32 -bit server and deploy to IA 64 ¢ Watch out for driver compatibility! x 64 BIDS runs in the WOW ¢ SSIS needs 32 -bit drivers during development and 64 -bit drivers at run time Trade off between high processor speed vs. flat memory and scale-up (1. 6 GHz vs. 3. 2 GHz)

32 -bit SQL Server on x 64 ¢ 32 -bit SQL Server 2005 (server & tools) supported on x 64 running 64 -bit Windows ¢ ¢ Under WOW 64, SQL Server can access FULL 4 GB (VAS) of RAM, as well as AWE Why would you want to run 32 -bit OS instead? ¢ ¢ ¢ Drivers Coexistence with other applications or tools that aren’t WOW-certified Warning: http: //blogs. msdn. com/slavao/archive/2006/0 3/12/550096. aspx
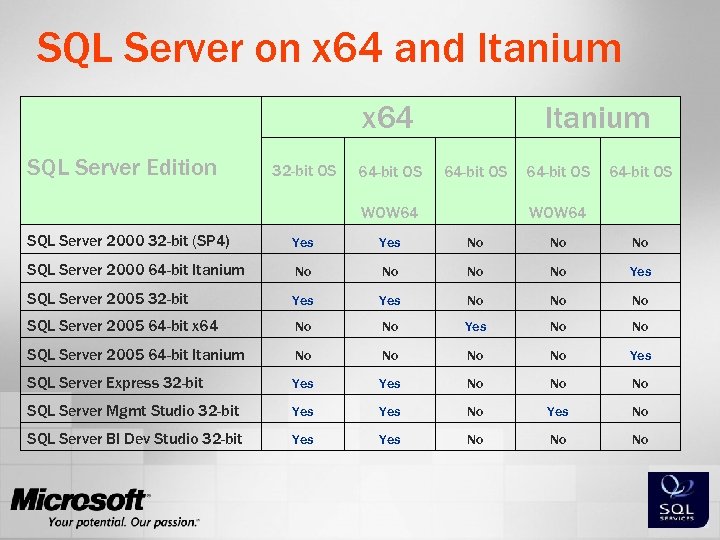
SQL Server on x 64 and Itanium x 64 SQL Server Edition Itanium 32 -bit OS 64 -bit OS WOW 64 SQL Server 2000 32 -bit (SP 4) Yes No No No SQL Server 2000 64 -bit Itanium No No Yes SQL Server 2005 32 -bit Yes No No No SQL Server 2005 64 -bit x 64 No No Yes No No SQL Server 2005 64 -bit Itanium No No Yes SQL Server Express 32 -bit Yes No No No SQL Server Mgmt Studio 32 -bit Yes No SQL Server BI Dev Studio 32 -bit Yes No No No

Agenda 64 -bit SQL Server ¢ ¢ ¢ Introduction Platforms Benefits Challenges and Best Practices Summary and Questions
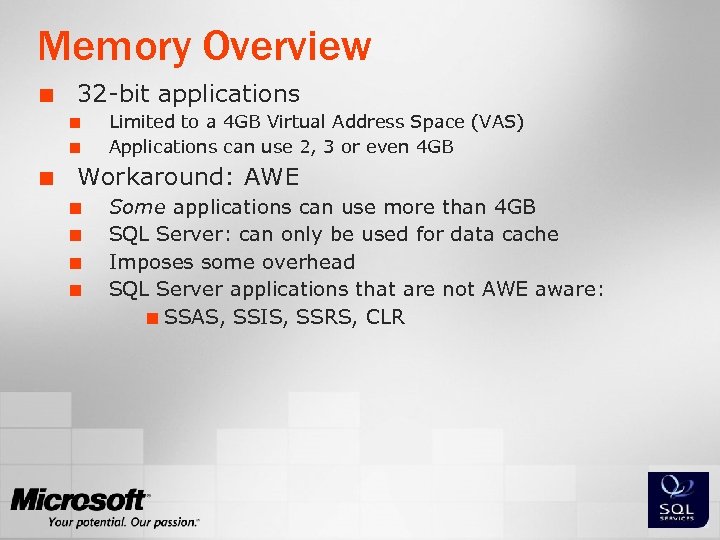
Memory Overview ¢ 32 -bit applications ¢ ¢ ¢ Limited to a 4 GB Virtual Address Space (VAS) Applications can use 2, 3 or even 4 GB Workaround: AWE ¢ ¢ Some applications can use more than 4 GB SQL Server: can only be used for data cache Imposes some overhead SQL Server applications that are not AWE aware: ¢ SSAS, SSIS, SSRS, CLR
Memory Overview – Continued ¢ 64 -bit applications like SQL Server 64 -bit ¢ Flat, huge virtual address space ¢ can ¢ ¢ use all memory available without AWE No mapping needed All SQL Server services can use all addressable memory: ¢ SSAS ¢ SSRS ¢ SSIS ¢ SSNS
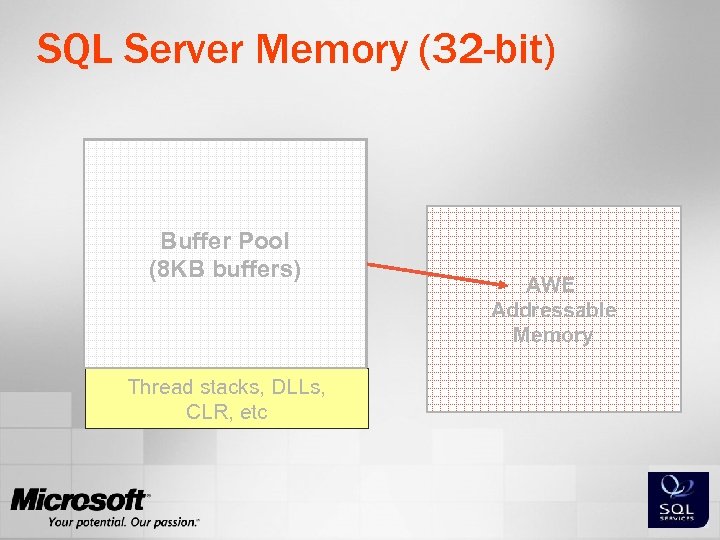
DB Page Cache Plan Cache Query Workspace. Buffer Pool (8 KB buffers) Locks Other SQL Server Memory (32 -bit) Thread stacks, DLLs, CLR, etc AWE Addressable Memory

Where Will 64 -bit SQL Server Help? Relational Engine ¢ Memory hungry workloads: ¢ ¢ ¢ Plan Cache Workspace Memory Connection Memory Lock Memory: Large-scale OLTP Data Buffer Cache High Concurrency OLTP / Large DW ¢ Row versioning: Resolve writers blocking readers issue ¢ Partitions – on one server First, measure memory pressure ¢
Where Will 64 -bit SQL Server Help? Analysis Services (SSAS) ¢ Large dimensions ¢ ¢ Large memory for Process Buffers Large cubes and fast processing ¢ ¢ SSAS 2005 queries cached in memory Frees up the Relational Engine Very large Filesystem Cache Large number of concurrent users First, measure

Where Will 64 -bit SQL Server Help? Integration Services (SSIS) ¢ Large-scale transformations: ¢ ¢ Sort Aggregate Key Lookups (cached) Packages failures due to memory constraints

Where Will 64 -bit SQL Server Help? Reporting Services (SSRS) ¢ ¢ Reporting Services cannot use AWE But on 64 -bit it can access all available memory ¢ Large and/or complex reports

Where Will 64 -bit SQL Server Help? Scale-Up, Performance and Consolidation ¢ ¢ Itanium: today’s choice for workloads requiring > 8 CPUs ¢ Itanium offers excellent scaling x 64 Xeon scaled-up servers are available x 64 offers fastest CPU performance today Consolidation of SQL Server Platforms ¢ ¢ Reduced cost of administration, licenses, etc Warning: Generally, no virtualisation of the data tier in production

Agenda 64 -bit SQL Server ¢ ¢ Introduction Platforms Benefits Challenges and Best Practices ¢ ¢ ¢ Drivers Memory Configuration NUMA Performance Summary and Questions

Challenges - Drivers ¢ 64 -bit drivers for Data Access ¢ ¢ AS and IS require 64 -bit versions of 3 rd Party Ole. DB drivers to support sources such as Oracle, Informix… No ODBC driver access for AS since Ole. DB for ODBC is not ported MS provides 32 -bit Oracle Ole. DB provider – not 64 -bit – have to get it from Oracle 64 -bit drivers and software for hardware ¢ ¢ ¢ NZ Horror stories Ask the hard questions of vendors before purchasing HCL (http: //www. microsoft. com/hcl): validate

Agenda 64 -bit SQL Server ¢ ¢ Introduction Platforms Benefits Challenges and Best Practices ¢ ¢ ¢ Drivers Memory Configuration NUMA Performance Summary and Questions
Challenges – Memory Configuration Scenarios: ¢ Multiple SQL Instances on server ¢ Multiple Service components on server, e. g. SSAS, SQL Relational Engine, SSIS Note, both 32 -bit and 64 -bit memory allocation needs to be configured appropriately – nothing new here
64 -bit Memory Configuration Integration Services ¢ ¢ Cannot impose explicit memory limits Large Sort, Aggregation and Cached Lookup operations can consume a lot of virtual memory ¢ ¢ Hint: Retrieve minimum necessary fields If still too much memory pressure, consider using DB operations instead, or running IS on a separate hardware partition or server
Memory Configuration Alternatives Integration Services ¢ Use separate hardware partitions (NUMA) or separate servers for solutions that combine Relational Engine, SSAS and SSIS ¢ ¢ Eliminates risks of cross-application memory contention But this may underutilise CPU resources OR Manage memory use explicitly for each component running on a single server Note: What isn’t an option? ¢
64 -bit Memory Configuration Relational Engine ¢ If multiple SQL Server instances share the server Or ¢ If multiple applications (SSAS, SSIS) coexist on the server: ¢ Best Practice: place memory ceiling on each SQL instance ¢ Or ¢ Lock even use a fixed memory size pages in memory to prevent OS paging of SQL under memory pressure
64 -bit Memory Configuration Analysis Services ¢ Consumes memory in two ways ¢ Virtual Memory for SSAS Service ¢ OS Memory used as Filesystem cache ¢ Potentially unbounded, may starve OS of memory ¢ If SSAS is running on a server with other critical services (SQL or SSIS): ¢ Best Practice: establish a maximum memory size for Analysis Services process and limit growth of Filesystem Cache

Agenda ¢ ¢ Introduction Platforms Benefits Challenges and Best Practices ¢ ¢ ¢ Drivers Memory Configuration NUMA Performance Summary and Questions
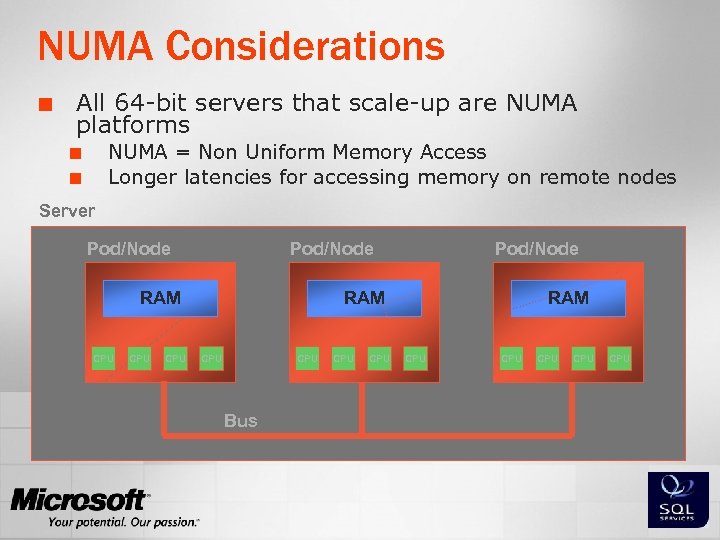
NUMA Considerations ¢ All 64 -bit servers that scale-up are NUMA platforms NUMA = Non Uniform Memory Access Longer latencies for accessing memory on remote nodes ¢ ¢ Server Pod/Node RAM CPU CPU Pod/Node RAM CPU Bus CPU RAM CPU CPU CPU
SQL Server 2005 and NUMA ¢ ¢ NUMA memory configuration is the preferred choice on SQL 2005 servers with > 4 cores Many NUMA Enhancements in Relational Engine ¢ ¢ ¢ Improved placement of objects in local cache Per-node lazywriter, free list and checkpointing Per-node resource management (threads) Per-node IO completion port A SQL connection will remain on the same NUMA node for its lifetime ¢ ¢ Potential for leveraging local cache for all of its tasks Can direct specific connections to specific nodes

Some NUMA ‘gotchas’ ¢ SSAS and SSIS are not NUMA aware ¢ ¢ No guarantees of evenly distributed memory allocation OS will tend to fill up a node’s CPUs with work before using other CPUs 1 node may be busy while the remainder are idle until the node saturates Consider starting up SQL Server and warming cache before launching SSAS ¢ ¢ ¢ May be effective in very large cube environments Avoids SSAS potentially grabbing all local memory for one node Avoids filesystem cache from stealing pages disproportionately from a single node – which could create a SQL node starved of local pages

Agenda 64 -bit SQL Server ¢ ¢ Introduction Platforms Benefits Challenges and Best Practices ¢ ¢ ¢ Drivers Memory Configuration NUMA Performance Summary and Questions

Will code run faster on 64 -bit? ¢ Maybe… Depends on a lot of factors ¢ ¢ ¢ Is memory a bottleneck? Is the application CPU-bound? Are there pointers in the working set data? Is it instruction cache bound? Is it floating point intensive? Result: Apps that are not memory constrained on 32 -bit may run ~10% less efficiently using 64 -bit edition than 32 -bit edition on the same machine ¢ You may see the CPUs busier on 64 -bit than on 32 -bit to perform equivalent workload
Performance Considerations ¢ If you are not under memory pressure, and do not need to scale up, and you want the absolutely fastest single-thread performance ¢ ¢ Use x 64 instead of IA 64 Consider using 32 -bit SQL in the WOW or on 32 -bit OS Intel’s (EM 64 T) larger L 3 cache may have a noticeable impact relative to AMD’s (AMD 64) If you need to scale up for greater throughput ¢ Use IA 64 with large number of CPUs or ¢ Consider newest scaled-up x 64 servers

64 -bit ‘gotchas’ ¢ ¢ ¢ Driver availability Developer tools support Multiple components competing for memory (nothing new here) Potential NUMA effects Most applications will run faster, but …

Agenda 64 -bit SQL Server ¢ ¢ Introduction Platforms Benefits Challenges and Best Practices ¢ ¢ ¢ Drivers Memory Configuration NUMA Performance Summary and Questions

Summary – Takeaways ¢ 64 -bit SQL Server 2005 can leverage the power of x 64 and IA 64 platforms ¢ ¢ ¢ Plan carefully – think before you buy Understand the benefits and gotchas ¢ ¢ ¢ Allows SQL Server to fully address memory available SSAS, SSIS, SSRS can really benefit from 64 -bit Recommended for high volume workloads, consolidation May not always be faster, beware of drivers Allows more effective use of row versioning giving higher volume transactional throughput Assistance is available 64 -bit will become the standard

Thank You Questions?

© 2005 -2006 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. This presentation is for informational purposes only. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, in this summary.
1d7ae7aceff33e5e14dd2deea195dd11.ppt