Prepared by: 11BD01049 Zholgaliyev Aben Checked by: Prof.


Prepared by: 11BD01049 Zholgaliyev Aben Checked by: Prof. Dr. Jim Lee Pump Stations
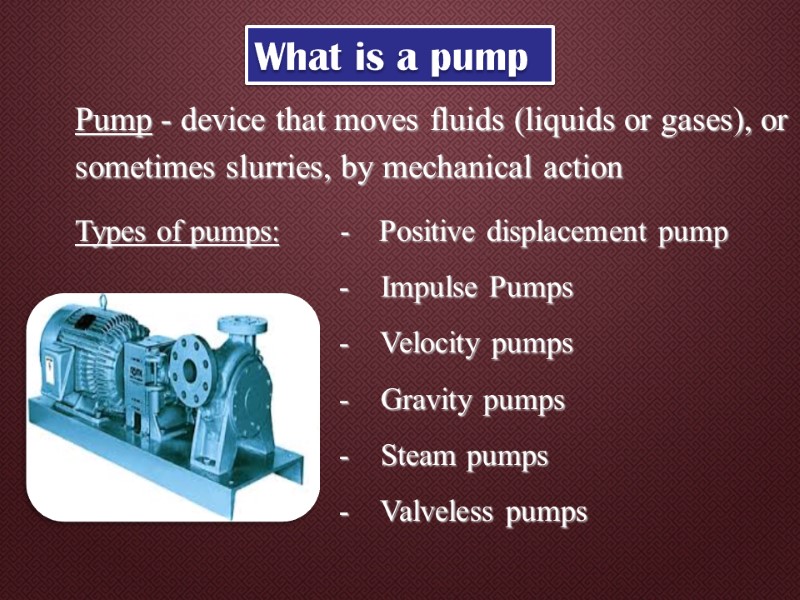
Pump - device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action Types of pumps: - Positive displacement pump - Impulse Pumps - Velocity pumps - Gravity pumps - Steam pumps - Valveless pumps What is a pump

Positive displacement pump types - Rotary positive displacement pumps - Reciprocating positive displacement pumps - Various positive displacement pumps - Gear pump - Screw pump - Progressing cavity pump - Roots-type pumps - Peristaltic pump - Plunger pumps - Triplex-style plunger pumps - Rope pumps - Flexible impeller pump - Rotolliptic pumps

A positive displacement pump makes a fluid move by trapping a fixed amount and forcing (displacing) that trapped volume into the discharge pipe. Positive displacement pump

Impulse pumps use pressure created by gas (usually air). In some impulse pumps the gas trapped in the liquid (usually water), is released and accumulated somewhere in the pump, creating a pressure that can push part of the liquid upwards. Impulse Pumps
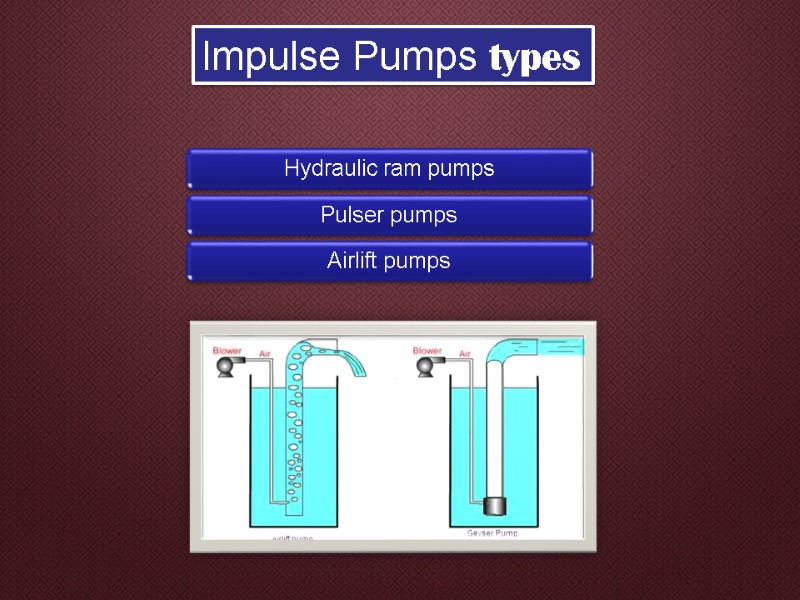
Impulse Pumps types
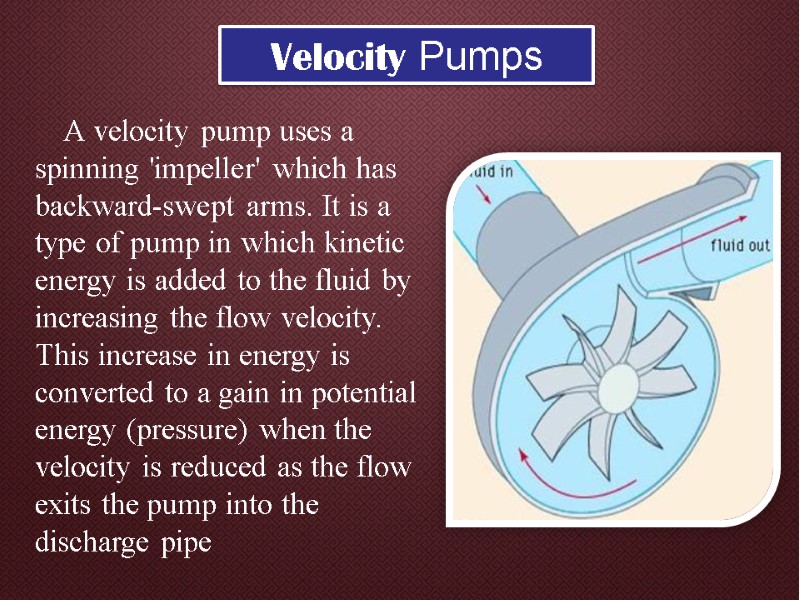
A velocity pump uses a spinning 'impeller' which has backward-swept arms. It is a type of pump in which kinetic energy is added to the fluid by increasing the flow velocity. This increase in energy is converted to a gain in potential energy (pressure) when the velocity is reduced as the flow exits the pump into the discharge pipe Velocity Pumps
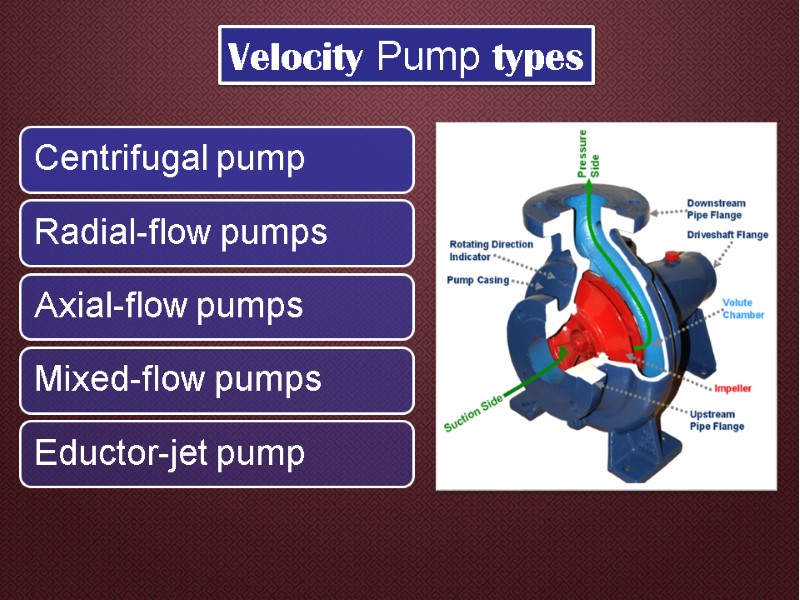
Velocity Pump types

Requirements to pumps Requirements: providing rather high pressures and good supply; economic; long duration and reliability of continuous work; use of the maximum frequency of rotation of impeller; compactness; speed of assembly and breakdown;
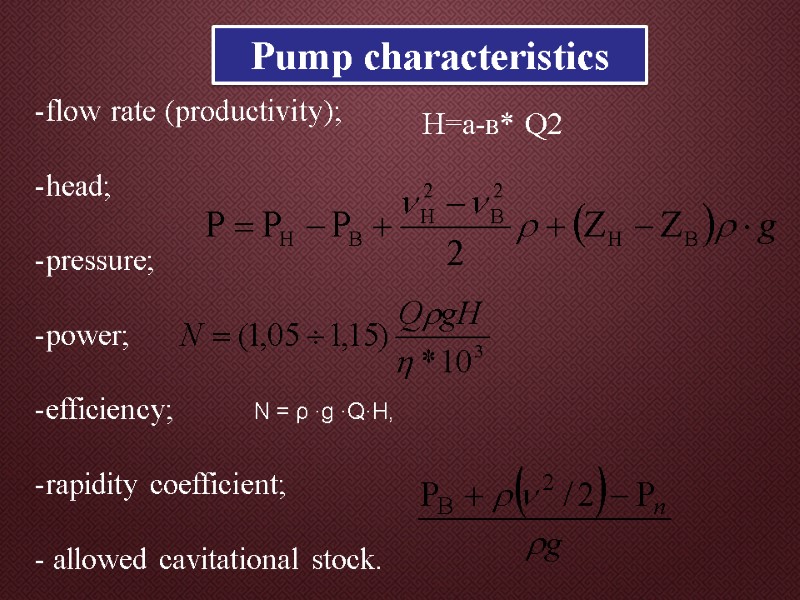
Pump characteristics flow rate (productivity); head; pressure; power; efficiency; rapidity coefficient; - allowed cavitational stock. N = ρ ·g ·Q·H, Н=а-в* Q2

Pump Station Pumping stations are facilities including pumps and equipment for pumping fluids from one place to another. Types of pump station: head(main) pump station intermediate pump stations
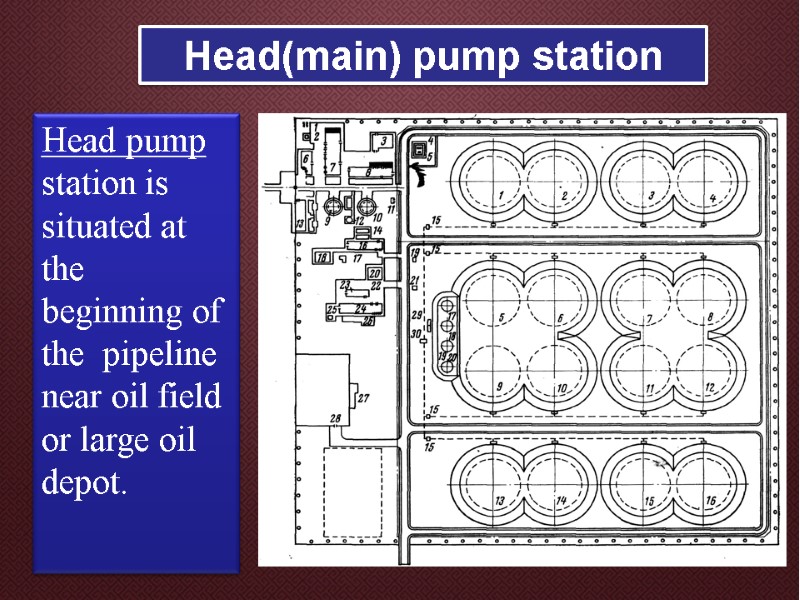
Head(main) pump station Head pump station is situated at the beginning of the pipeline near oil field or large oil depot.
Head(main) pump station Consists of: pump guild, reservoir park, knot of start of clearing devices, network of technological pipelines, platform of filters and counters, pressure control units, transformer substation, complex of constructions on preparation of water and on providing station with water, a sewerage network, a boiler room, objects of auxiliary appointment, the engineering laboratory case, fire-prevention depot, a communication center, workshops, an administrative complex and warehouses.
Intermediate pump station Intermediate pump stations intend for maintenance of necessary pressure in the pipeline in the course of transfer. Unlike head pump stations, as a rule, there are not reservoir park, retaining and oil metering station.
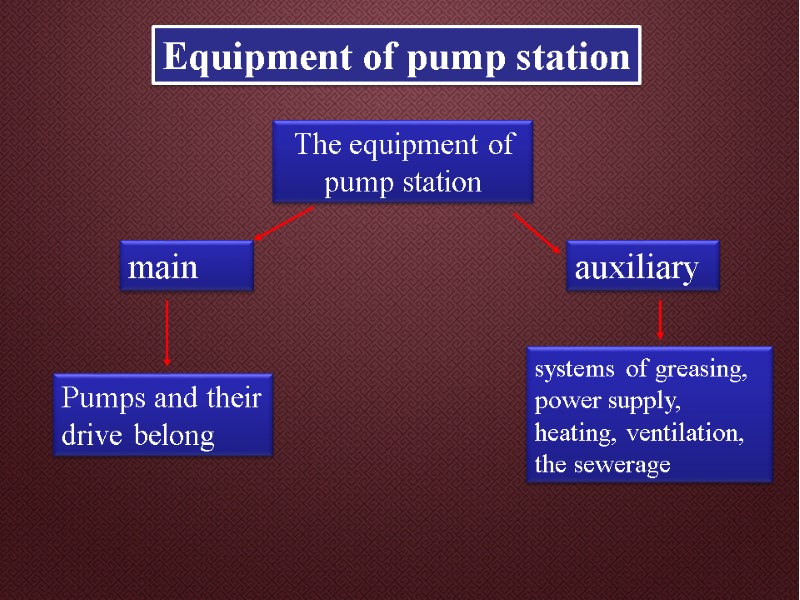
Equipment of pump station The equipment of pump station main auxiliary Pumps and their drive belong systems of greasing, power supply, heating, ventilation, the sewerage
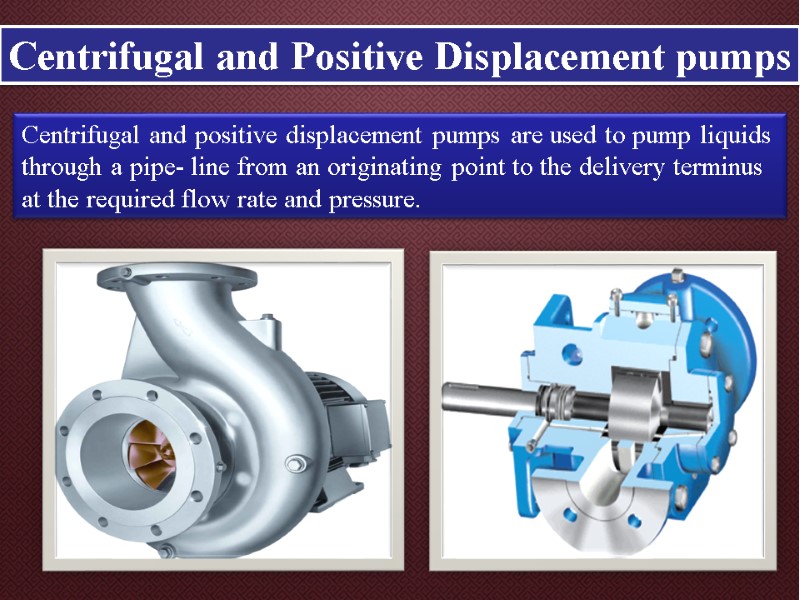
Centrifugal and Positive Displacement pumps Centrifugal and positive displacement pumps are used to pump liquids through a pipe- line from an originating point to the delivery terminus at the required flow rate and pressure.
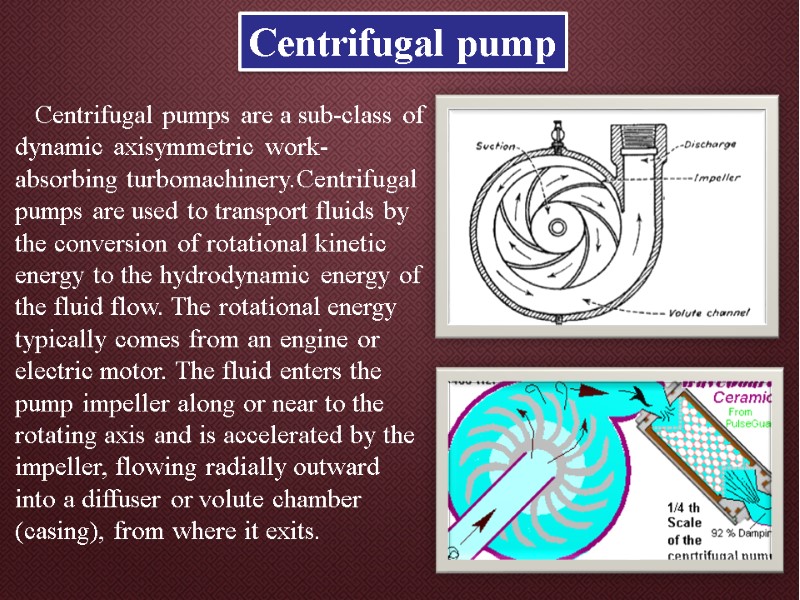
Centrifugal pump Centrifugal pumps are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery.Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. The fluid enters the pump impeller along or near to the rotating axis and is accelerated by the impeller, flowing radially outward into a diffuser or volute chamber (casing), from where it exits.

Problems with pumps - Cavitation—the net positive suction head (NPSH) of the system is too low for the selected pump - Wear of the impeller—can be worsened by suspended solids - Corrosion inside the pump caused by the fluid properties - Overheating due to low flow - Leakage along rotating shaft - Lack of prime—centrifugal pumps must be filled (with the fluid to be pumped) in order to operate - Surge
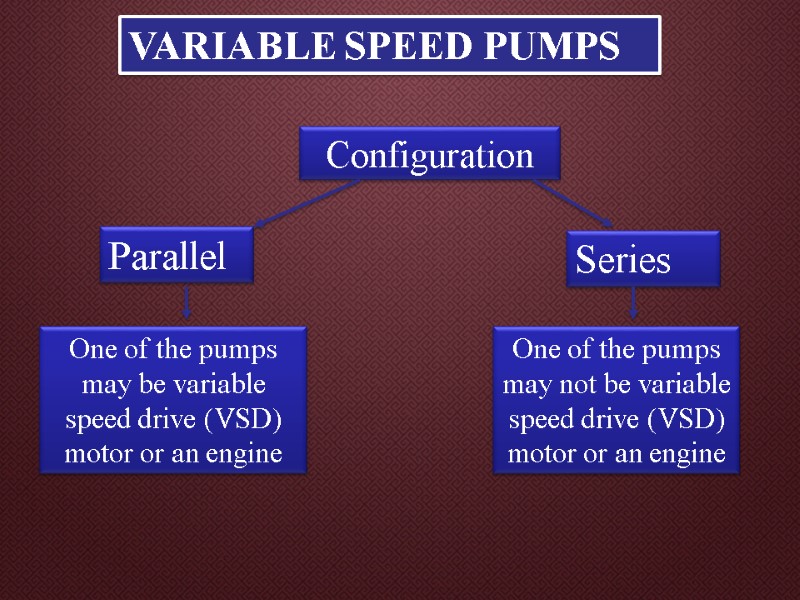
VARIABLE SPEED PUMPS Configuration Parallel Series One of the pumps may be variable speed drive (VSD) motor or an engine One of the pumps may not be variable speed drive (VSD) motor or an engine

thank you for your attention
7736-pump_stations.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

