 Preparations for exam
Preparations for exam
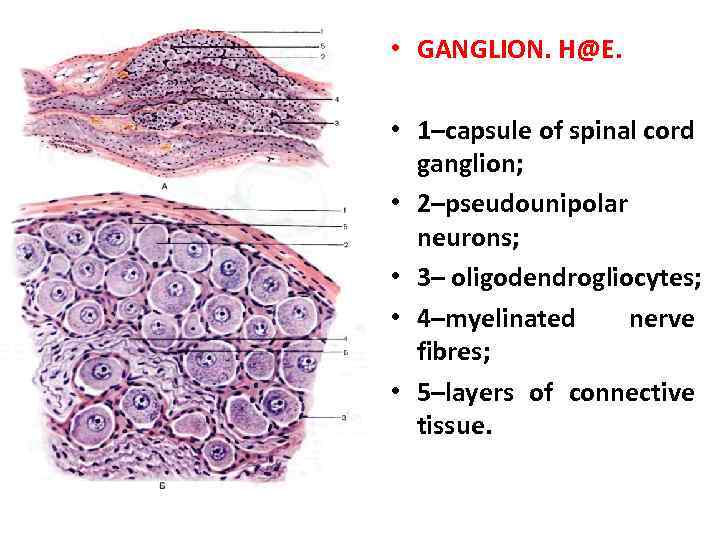 • GANGLION. H@E. • 1–capsule of spinal cord ganglion; • 2–pseudounipolar neurons; • 3– oligodendrogliocytes; • 4–myelinated nerve fibres; • 5–layers of connective tissue.
• GANGLION. H@E. • 1–capsule of spinal cord ganglion; • 2–pseudounipolar neurons; • 3– oligodendrogliocytes; • 4–myelinated nerve fibres; • 5–layers of connective tissue.
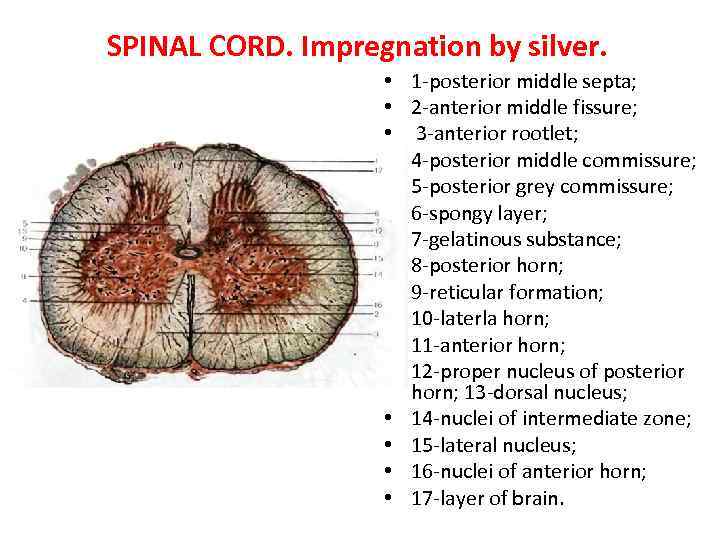 SPINAL CORD. Impregnation by silver. • • • • 1 -posterior middle septa; 2 -anterior middle fissure; 3 -anterior rootlet; 4 -posterior middle commissure; 5 -posterior grey commissure; 6 -spongy layer; 7 -gelatinous substance; 8 -posterior horn; 9 -reticular formation; 10 -laterla horn; 11 -anterior horn; 12 -proper nucleus of posterior horn; 13 -dorsal nucleus; 14 -nuclei of intermediate zone; 15 -lateral nucleus; 16 -nuclei of anterior horn; 17 -layer of brain.
SPINAL CORD. Impregnation by silver. • • • • 1 -posterior middle septa; 2 -anterior middle fissure; 3 -anterior rootlet; 4 -posterior middle commissure; 5 -posterior grey commissure; 6 -spongy layer; 7 -gelatinous substance; 8 -posterior horn; 9 -reticular formation; 10 -laterla horn; 11 -anterior horn; 12 -proper nucleus of posterior horn; 13 -dorsal nucleus; 14 -nuclei of intermediate zone; 15 -lateral nucleus; 16 -nuclei of anterior horn; 17 -layer of brain.
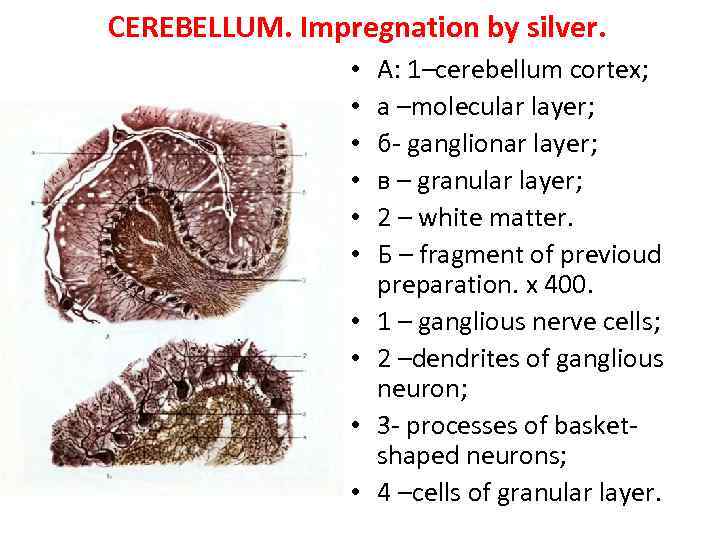 CEREBELLUM. Impregnation by silver. • • • A: 1–cerebellum cortex; а –molecular layer; б- ganglionar layer; в – granular layer; 2 – white matter. Б – fragment of previoud preparation. х 400. 1 – ganglious nerve cells; 2 –dendrites of ganglious neuron; 3 - processes of basketshaped neurons; 4 –cells of granular layer.
CEREBELLUM. Impregnation by silver. • • • A: 1–cerebellum cortex; а –molecular layer; б- ganglionar layer; в – granular layer; 2 – white matter. Б – fragment of previoud preparation. х 400. 1 – ganglious nerve cells; 2 –dendrites of ganglious neuron; 3 - processes of basketshaped neurons; 4 –cells of granular layer.
 CORTEX OF LARGE HEMISPHERES. Impregnation by silver. • • • • I – molecular layer II – external granular layer III – pyramidal layer IV – internal granular layer V – ganglious layer VI – multi-shaped layer 1 – pia matter 2 – horizontal neurons 3 – small pyramidal cells and cellsgranules 4 – small, middle and big pyramidal neurons 5 – stellate nerve cells and cellsgranules 6 - giant pyramidal neurons of Becz 7 – blood vessels 8 – stellate
CORTEX OF LARGE HEMISPHERES. Impregnation by silver. • • • • I – molecular layer II – external granular layer III – pyramidal layer IV – internal granular layer V – ganglious layer VI – multi-shaped layer 1 – pia matter 2 – horizontal neurons 3 – small pyramidal cells and cellsgranules 4 – small, middle and big pyramidal neurons 5 – stellate nerve cells and cellsgranules 6 - giant pyramidal neurons of Becz 7 – blood vessels 8 – stellate
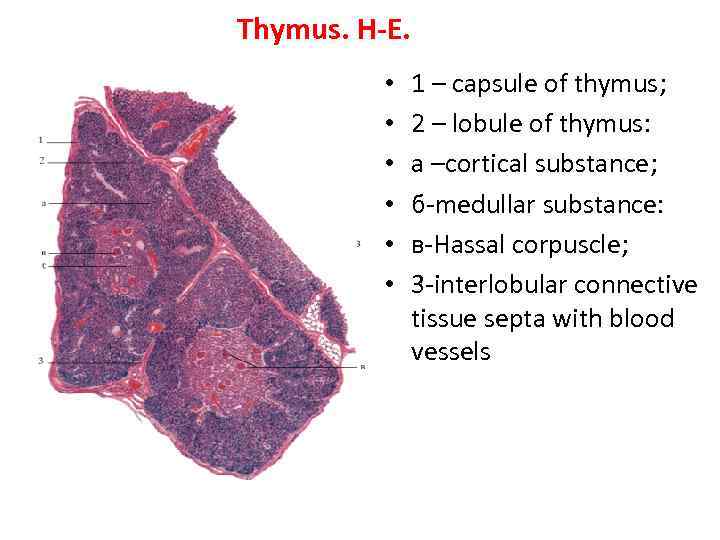 Thymus. H-E. • • • 1 – capsule of thymus; 2 – lobule of thymus: а –cortical substance; б-medullar substance: в-Hassal corpuscle; 3 -interlobular connective tissue septa with blood vessels
Thymus. H-E. • • • 1 – capsule of thymus; 2 – lobule of thymus: а –cortical substance; б-medullar substance: в-Hassal corpuscle; 3 -interlobular connective tissue septa with blood vessels
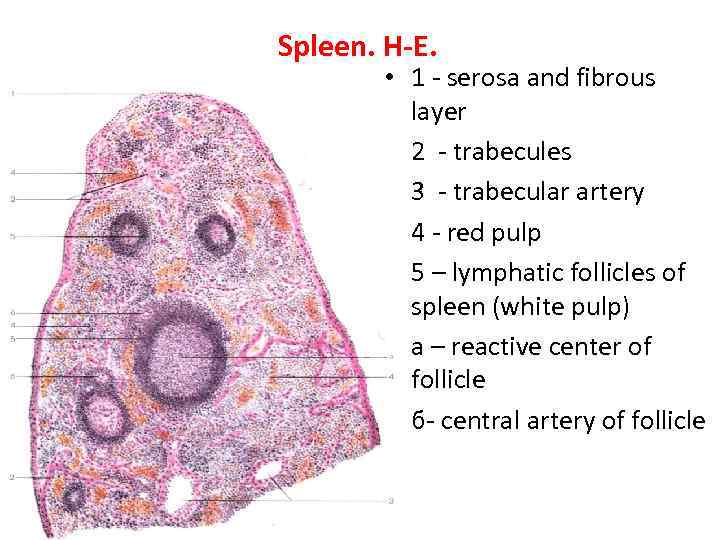 Spleen. H-E. • 1 - serosa and fibrous layer • 2 - trabecules • 3 - trabecular artery • 4 - red pulp • 5 – lymphatic follicles of spleen (white pulp) • а – reactive center of follicle • б- central artery of follicle
Spleen. H-E. • 1 - serosa and fibrous layer • 2 - trabecules • 3 - trabecular artery • 4 - red pulp • 5 – lymphatic follicles of spleen (white pulp) • а – reactive center of follicle • б- central artery of follicle
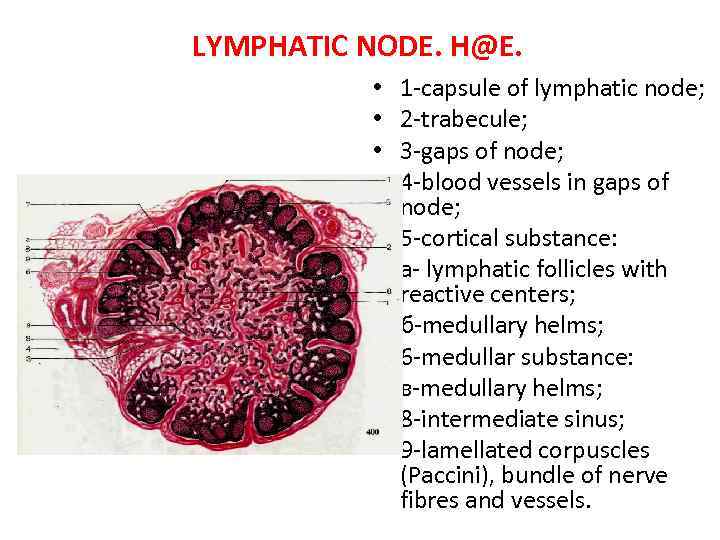 LYMPHATIC NODE. H@E. • • • 1 -capsule of lymphatic node; 2 -trabecule; 3 -gaps of node; 4 -blood vessels in gaps of node; 5 -cortical substance: a- lymphatic follicles with reactive centers; б-medullary helms; 6 -medullar substance: в-medullary helms; 8 -intermediate sinus; 9 -lamellated corpuscles (Paccini), bundle of nerve fibres and vessels.
LYMPHATIC NODE. H@E. • • • 1 -capsule of lymphatic node; 2 -trabecule; 3 -gaps of node; 4 -blood vessels in gaps of node; 5 -cortical substance: a- lymphatic follicles with reactive centers; б-medullary helms; 6 -medullar substance: в-medullary helms; 8 -intermediate sinus; 9 -lamellated corpuscles (Paccini), bundle of nerve fibres and vessels.
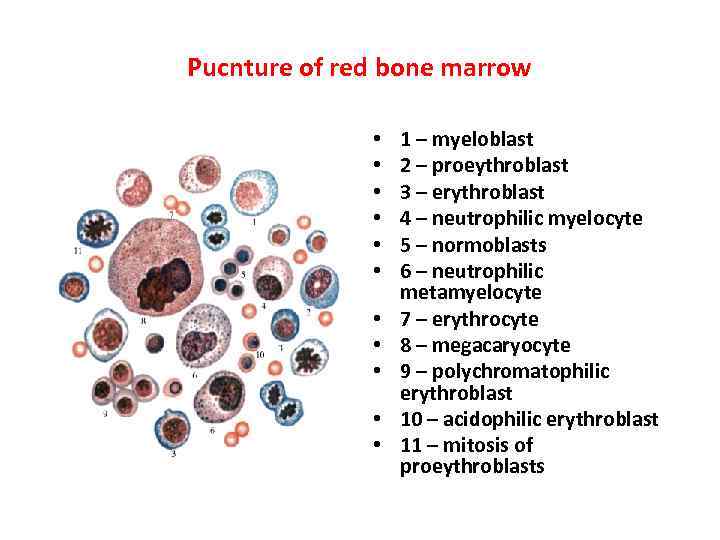 Pucnture of red bone marrow • • • 1 – myeloblast 2 – proeythroblast 3 – erythroblast 4 – neutrophilic myelocyte 5 – normoblasts 6 – neutrophilic metamyelocyte 7 – erythrocyte 8 – megacaryocyte 9 – polychromatophilic erythroblast 10 – acidophilic erythroblast 11 – mitosis of proeythroblasts
Pucnture of red bone marrow • • • 1 – myeloblast 2 – proeythroblast 3 – erythroblast 4 – neutrophilic myelocyte 5 – normoblasts 6 – neutrophilic metamyelocyte 7 – erythrocyte 8 – megacaryocyte 9 – polychromatophilic erythroblast 10 – acidophilic erythroblast 11 – mitosis of proeythroblasts
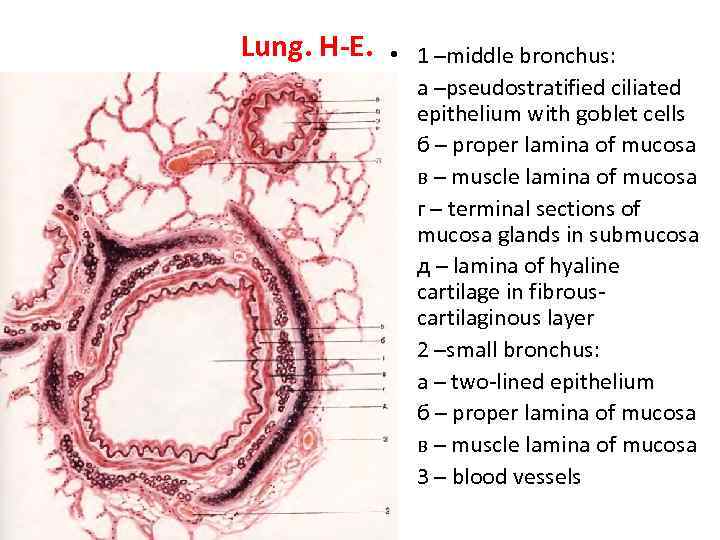 Lung. H-E. • 1 –middle bronchus: • а –pseudostratified ciliated epithelium with goblet cells • б – proper lamina of mucosa • в – muscle lamina of mucosa • г – terminal sections of mucosa glands in submucosa • д – lamina of hyaline cartilage in fibrouscartilaginous layer • 2 –small bronchus: • а – two-lined epithelium • б – proper lamina of mucosa • в – muscle lamina of mucosa • 3 – blood vessels
Lung. H-E. • 1 –middle bronchus: • а –pseudostratified ciliated epithelium with goblet cells • б – proper lamina of mucosa • в – muscle lamina of mucosa • г – terminal sections of mucosa glands in submucosa • д – lamina of hyaline cartilage in fibrouscartilaginous layer • 2 –small bronchus: • а – two-lined epithelium • б – proper lamina of mucosa • в – muscle lamina of mucosa • 3 – blood vessels
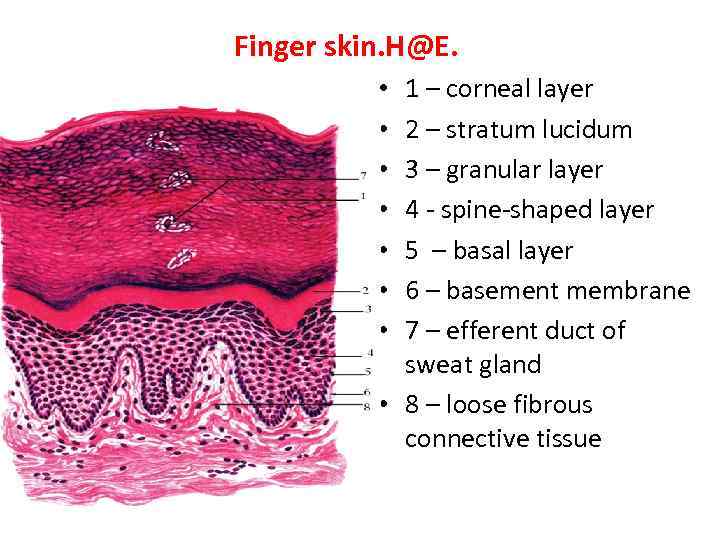 Finger skin. H@E. 1 – corneal layer 2 – stratum lucidum 3 – granular layer 4 - spine-shaped layer 5 – basal layer 6 – basement membrane 7 – efferent duct of sweat gland • 8 – loose fibrous connective tissue • •
Finger skin. H@E. 1 – corneal layer 2 – stratum lucidum 3 – granular layer 4 - spine-shaped layer 5 – basal layer 6 – basement membrane 7 – efferent duct of sweat gland • 8 – loose fibrous connective tissue • •
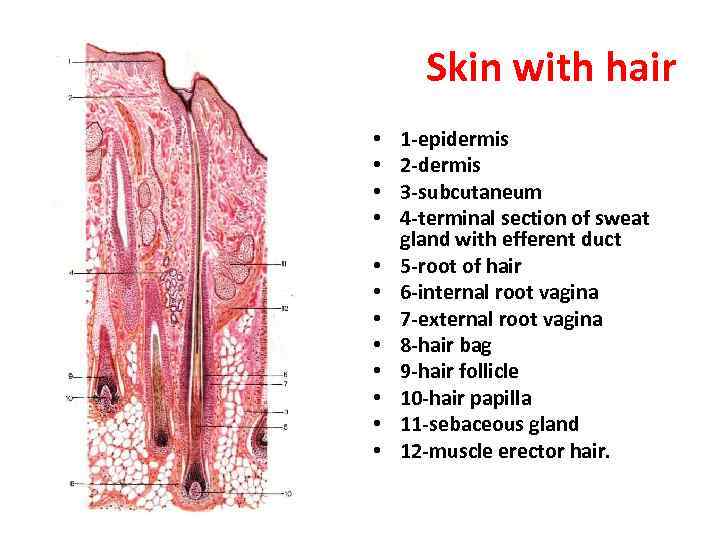 Skin with hair • • • 1 -epidermis 2 -dermis 3 -subcutaneum 4 -terminal section of sweat gland with efferent duct 5 -root of hair 6 -internal root vagina 7 -external root vagina 8 -hair bag 9 -hair follicle 10 -hair papilla 11 -sebaceous gland 12 -muscle erector hair.
Skin with hair • • • 1 -epidermis 2 -dermis 3 -subcutaneum 4 -terminal section of sweat gland with efferent duct 5 -root of hair 6 -internal root vagina 7 -external root vagina 8 -hair bag 9 -hair follicle 10 -hair papilla 11 -sebaceous gland 12 -muscle erector hair.
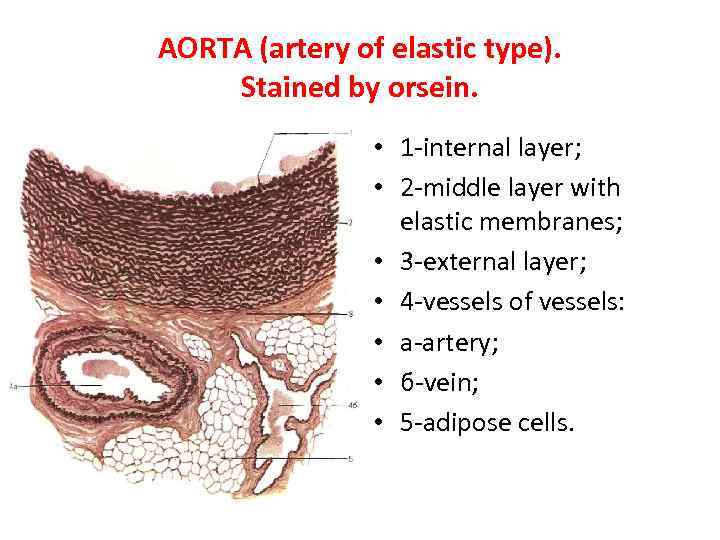 AORTA (artery of elastic type). Stained by orsein. • 1 -internal layer; • 2 -middle layer with elastic membranes; • 3 -external layer; • 4 -vessels of vessels: • a-artery; • б-vein; • 5 -adipose cells.
AORTA (artery of elastic type). Stained by orsein. • 1 -internal layer; • 2 -middle layer with elastic membranes; • 3 -external layer; • 4 -vessels of vessels: • a-artery; • б-vein; • 5 -adipose cells.
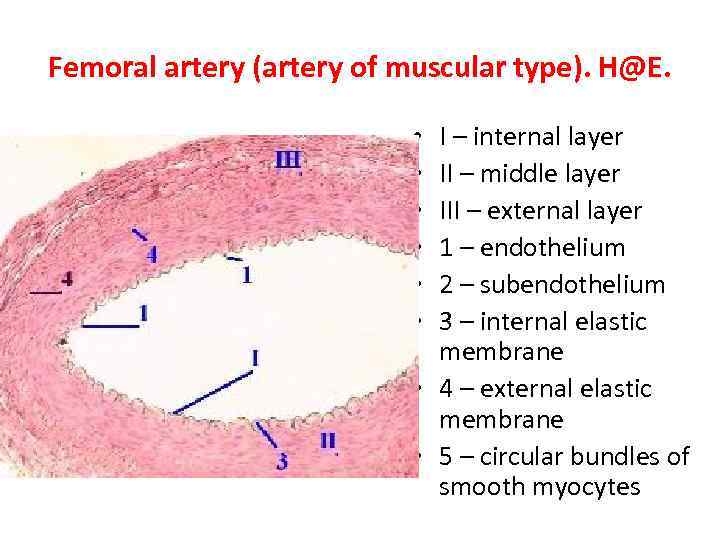 Femoral artery (artery of muscular type). H@E. I – internal layer II – middle layer III – external layer 1 – endothelium 2 – subendothelium 3 – internal elastic membrane • 4 – external elastic membrane • 5 – circular bundles of smooth myocytes • • •
Femoral artery (artery of muscular type). H@E. I – internal layer II – middle layer III – external layer 1 – endothelium 2 – subendothelium 3 – internal elastic membrane • 4 – external elastic membrane • 5 – circular bundles of smooth myocytes • • •
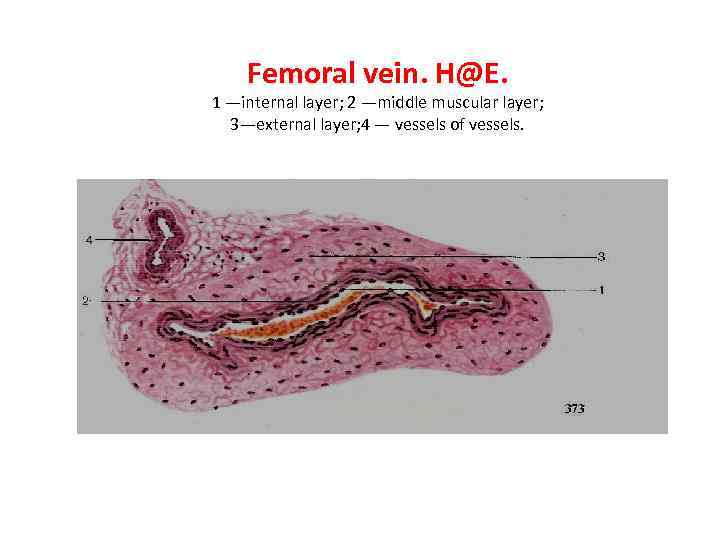 Femoral vein. H@E. 1 —internal layer; 2 —middle muscular layer; 3—external layer; 4 — vessels of vessels.
Femoral vein. H@E. 1 —internal layer; 2 —middle muscular layer; 3—external layer; 4 — vessels of vessels.
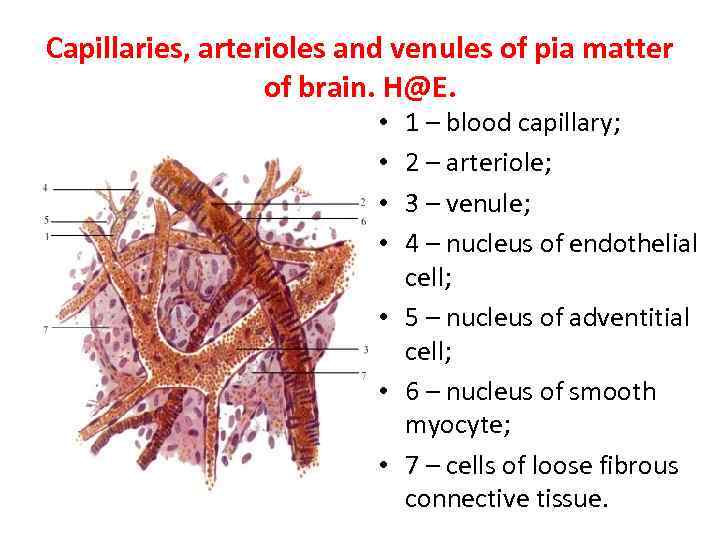 Capillaries, arterioles and venules of pia matter of brain. H@E. 1 – blood capillary; 2 – arteriole; 3 – venule; 4 – nucleus of endothelial cell; • 5 – nucleus of adventitial cell; • 6 – nucleus of smooth myocyte; • 7 – cells of loose fibrous connective tissue. • •
Capillaries, arterioles and venules of pia matter of brain. H@E. 1 – blood capillary; 2 – arteriole; 3 – venule; 4 – nucleus of endothelial cell; • 5 – nucleus of adventitial cell; • 6 – nucleus of smooth myocyte; • 7 – cells of loose fibrous connective tissue. • •
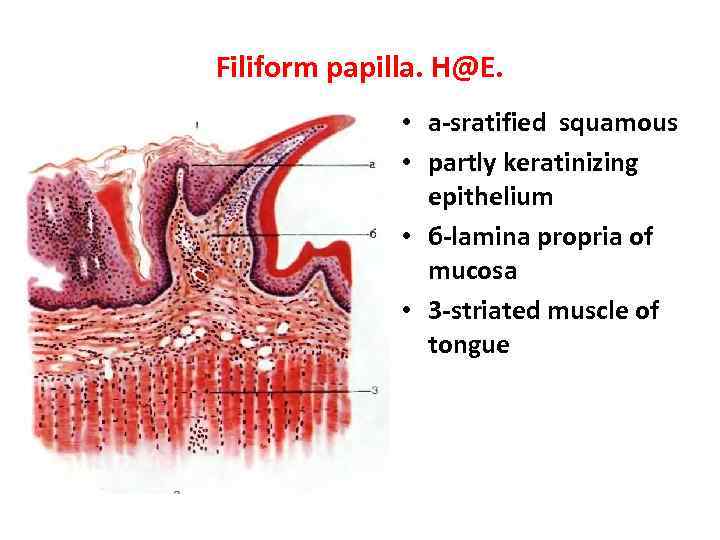 Filiform papilla. H@E. • a-sratified squamous • partly keratinizing epithelium • б-lamina propria of mucosa • 3 -striated muscle of tongue
Filiform papilla. H@E. • a-sratified squamous • partly keratinizing epithelium • б-lamina propria of mucosa • 3 -striated muscle of tongue
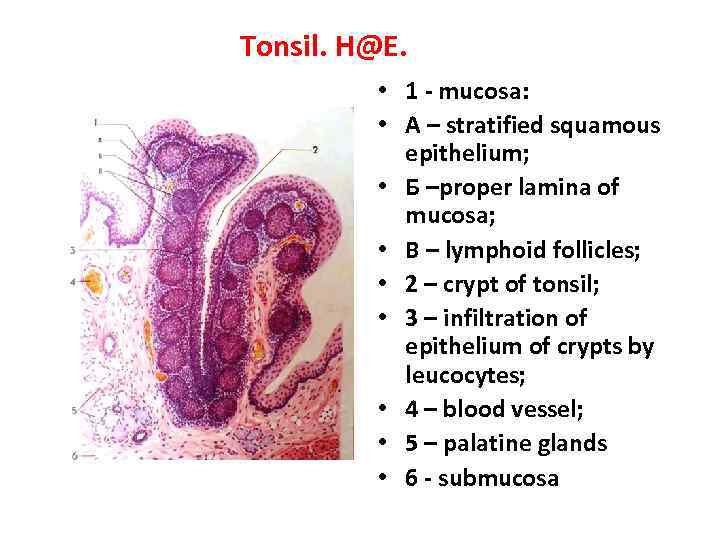 Tonsil. H@E. • 1 - mucosa: • A – stratified squamous epithelium; • Б –proper lamina of mucosa; • В – lymphoid follicles; • 2 – crypt of tonsil; • 3 – infiltration of epithelium of crypts by leucocytes; • 4 – blood vessel; • 5 – palatine glands • 6 - submucosa
Tonsil. H@E. • 1 - mucosa: • A – stratified squamous epithelium; • Б –proper lamina of mucosa; • В – lymphoid follicles; • 2 – crypt of tonsil; • 3 – infiltration of epithelium of crypts by leucocytes; • 4 – blood vessel; • 5 – palatine glands • 6 - submucosa
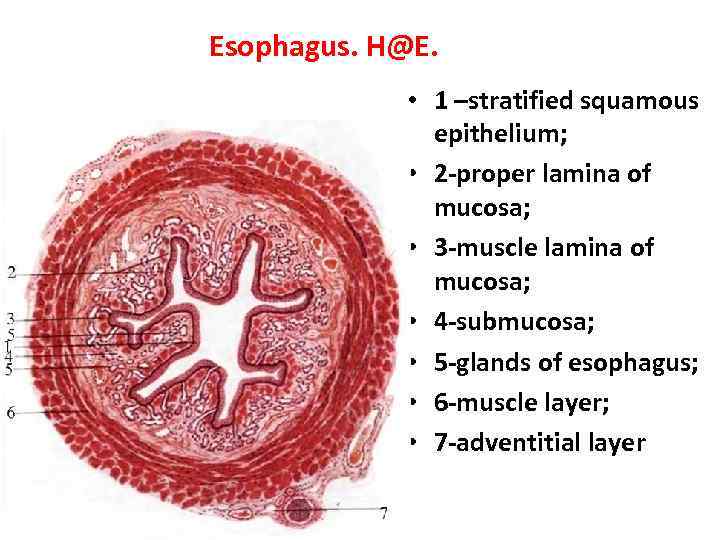 Esophagus. H@E. • 1 –stratified squamous epithelium; • 2 -proper lamina of mucosa; • 3 -muscle lamina of mucosa; • 4 -submucosa; • 5 -glands of esophagus; • 6 -muscle layer; • 7 -adventitial layer
Esophagus. H@E. • 1 –stratified squamous epithelium; • 2 -proper lamina of mucosa; • 3 -muscle lamina of mucosa; • 4 -submucosa; • 5 -glands of esophagus; • 6 -muscle layer; • 7 -adventitial layer
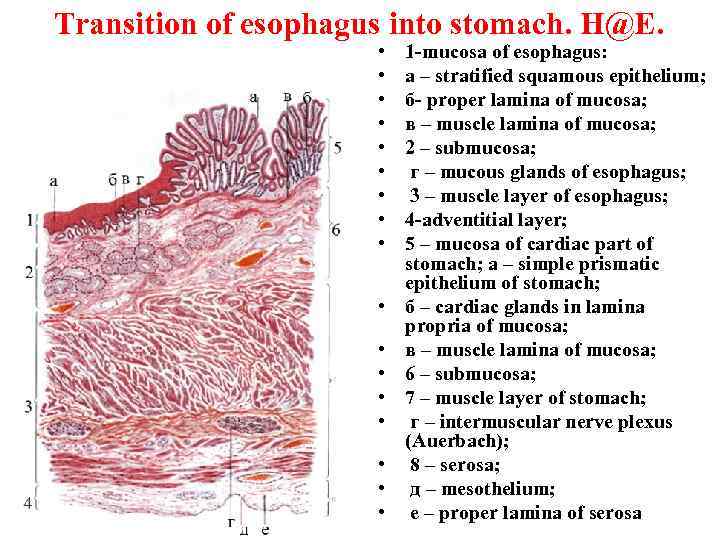 Transition of esophagus into stomach. H@E. • • • • • 1 -mucosa of esophagus: а – stratified squamous epithelium; б- proper lamina of mucosa; в – muscle lamina of mucosa; 2 – submucosa; г – mucous glands of esophagus; 3 – muscle layer of esophagus; 4 -adventitial layer; 5 – mucosa of cardiac part of stomach; а – simple prismatic epithelium of stomach; б – cardiac glands in lamina propria of mucosa; в – muscle lamina of mucosa; 6 – submucosa; 7 – muscle layer of stomach; г – intermuscular nerve plexus (Аuerbach); 8 – serosa; д – mesothelium; е – proper lamina of serosa
Transition of esophagus into stomach. H@E. • • • • • 1 -mucosa of esophagus: а – stratified squamous epithelium; б- proper lamina of mucosa; в – muscle lamina of mucosa; 2 – submucosa; г – mucous glands of esophagus; 3 – muscle layer of esophagus; 4 -adventitial layer; 5 – mucosa of cardiac part of stomach; а – simple prismatic epithelium of stomach; б – cardiac glands in lamina propria of mucosa; в – muscle lamina of mucosa; 6 – submucosa; 7 – muscle layer of stomach; г – intermuscular nerve plexus (Аuerbach); 8 – serosa; д – mesothelium; е – proper lamina of serosa
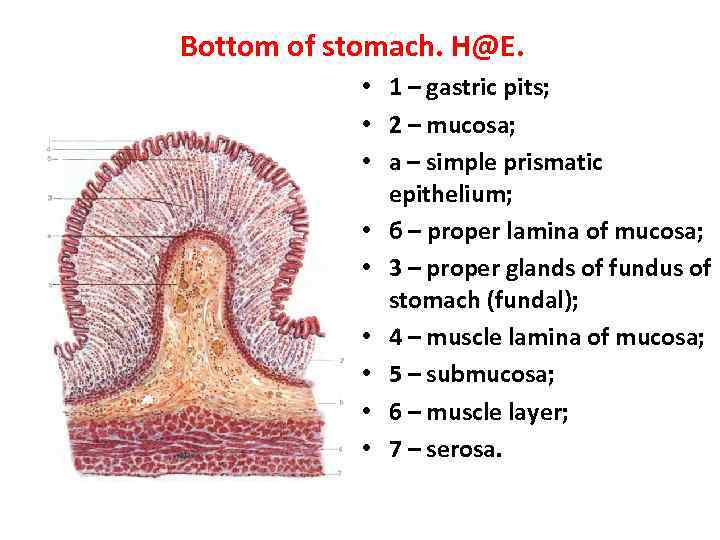 Bottom of stomach. H@E. • 1 – gastric pits; • 2 – mucosa; • a – simple prismatic epithelium; • б – proper lamina of mucosa; • 3 – proper glands of fundus of stomach (fundal); • 4 – muscle lamina of mucosa; • 5 – submucosa; • 6 – muscle layer; • 7 – serosa.
Bottom of stomach. H@E. • 1 – gastric pits; • 2 – mucosa; • a – simple prismatic epithelium; • б – proper lamina of mucosa; • 3 – proper glands of fundus of stomach (fundal); • 4 – muscle lamina of mucosa; • 5 – submucosa; • 6 – muscle layer; • 7 – serosa.
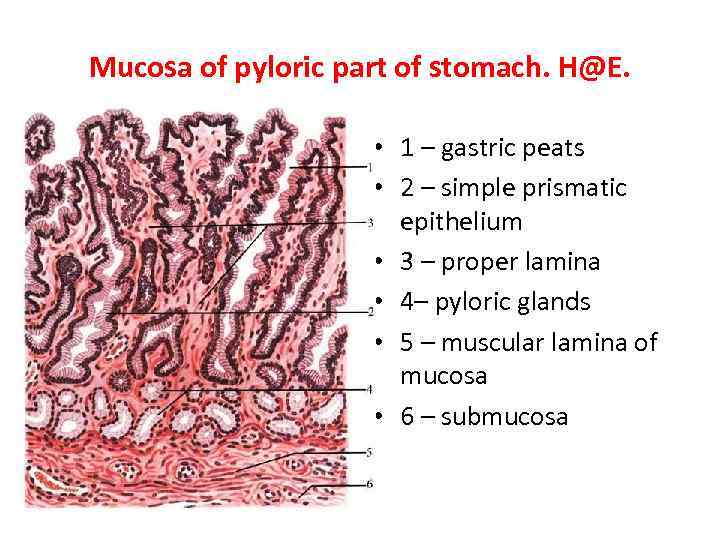 Mucosa of pyloric part of stomach. H@E. • 1 – gastric peats • 2 – simple prismatic epithelium • 3 – proper lamina • 4– pyloric glands • 5 – muscular lamina of mucosa • 6 – submucosa
Mucosa of pyloric part of stomach. H@E. • 1 – gastric peats • 2 – simple prismatic epithelium • 3 – proper lamina • 4– pyloric glands • 5 – muscular lamina of mucosa • 6 – submucosa
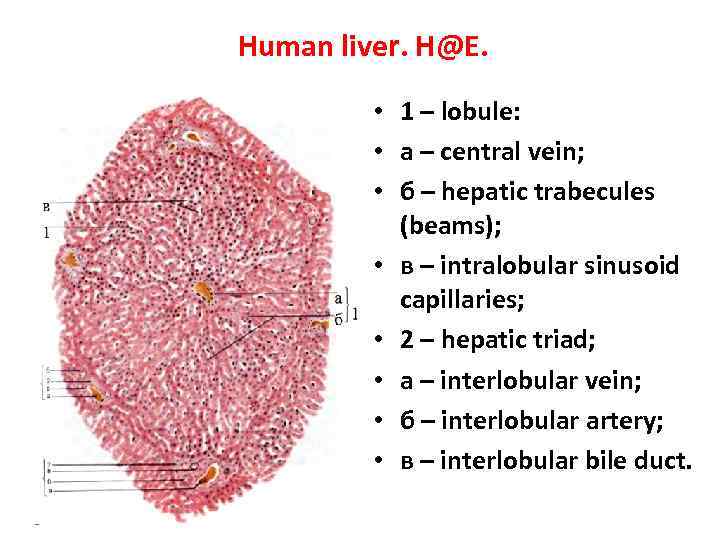 Human liver. H@E. • 1 – lobule: • a – central vein; • б – hepatic trabecules (beams); • в – intralobular sinusoid capillaries; • 2 – hepatic triad; • a – interlobular vein; • б – interlobular artery; • в – interlobular bile duct.
Human liver. H@E. • 1 – lobule: • a – central vein; • б – hepatic trabecules (beams); • в – intralobular sinusoid capillaries; • 2 – hepatic triad; • a – interlobular vein; • б – interlobular artery; • в – interlobular bile duct.
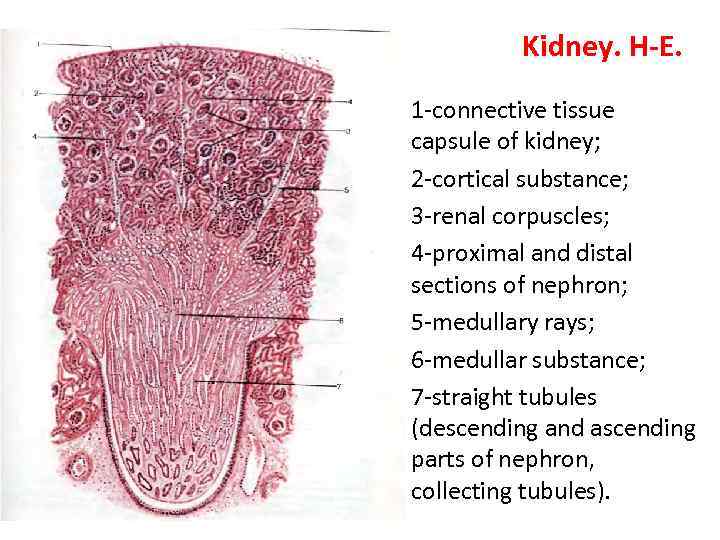 Kidney. H-E. • 1 -connective tissue capsule of kidney; • 2 -cortical substance; • 3 -renal corpuscles; • 4 -proximal and distal sections of nephron; • 5 -medullary rays; • 6 -medullar substance; • 7 -straight tubules (descending and ascending parts of nephron, collecting tubules).
Kidney. H-E. • 1 -connective tissue capsule of kidney; • 2 -cortical substance; • 3 -renal corpuscles; • 4 -proximal and distal sections of nephron; • 5 -medullary rays; • 6 -medullar substance; • 7 -straight tubules (descending and ascending parts of nephron, collecting tubules).
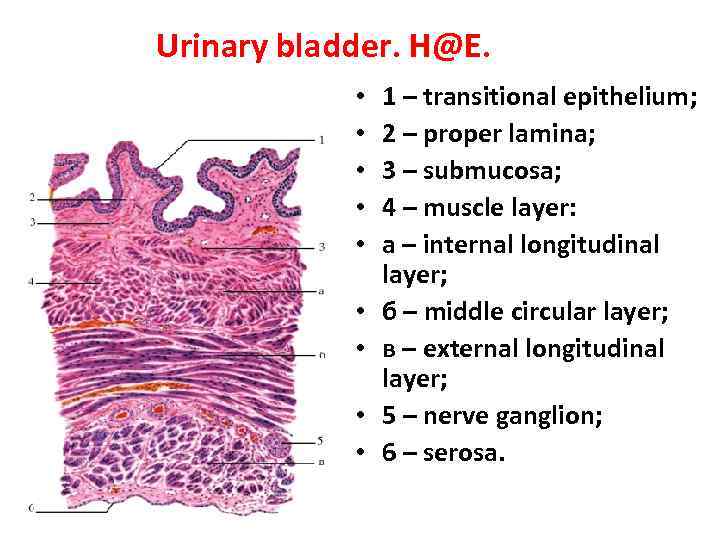 Urinary bladder. H@E. • • • 1 – transitional epithelium; 2 – proper lamina; 3 – submucosa; 4 – muscle layer: а – internal longitudinal layer; б – middle circular layer; в – external longitudinal layer; 5 – nerve ganglion; 6 – serosa.
Urinary bladder. H@E. • • • 1 – transitional epithelium; 2 – proper lamina; 3 – submucosa; 4 – muscle layer: а – internal longitudinal layer; б – middle circular layer; в – external longitudinal layer; 5 – nerve ganglion; 6 – serosa.
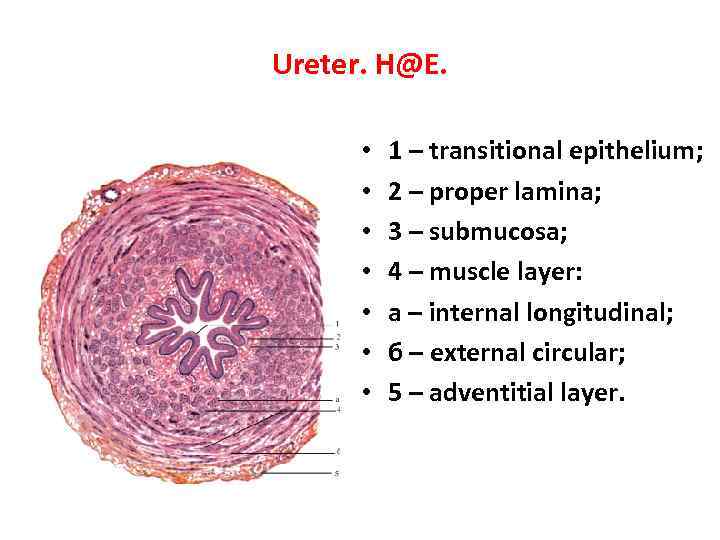 Ureter. H@E. • • 1 – transitional epithelium; 2 – proper lamina; 3 – submucosa; 4 – muscle layer: а – internal longitudinal; б – external circular; 5 – adventitial layer.
Ureter. H@E. • • 1 – transitional epithelium; 2 – proper lamina; 3 – submucosa; 4 – muscle layer: а – internal longitudinal; б – external circular; 5 – adventitial layer.
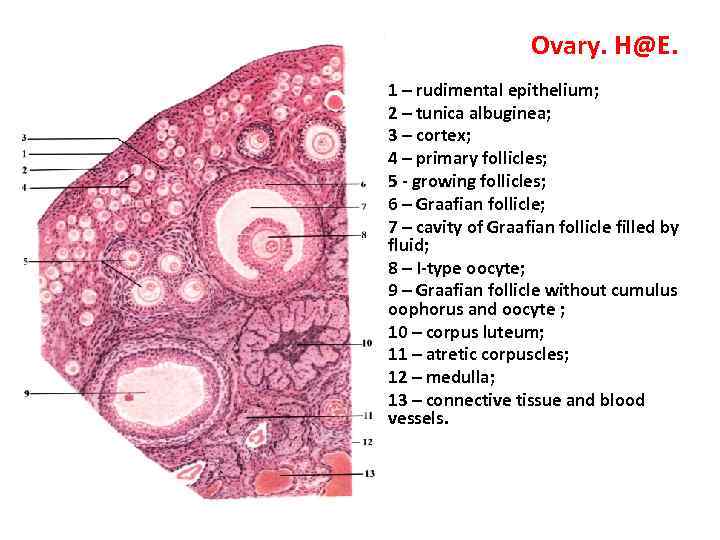 Ovary. H@E. • • • • 1 – rudimental epithelium; 2 – tunica albuginea; 3 – cortex; 4 – primary follicles; 5 - growing follicles; 6 – Graafian follicle; 7 – cavity of Graafian follicle filled by fluid; 8 – I-type oocyte; 9 – Graafian follicle without cumulus oophorus and oocyte ; 10 – corpus luteum; 11 – atretic corpuscles; 12 – medulla; 13 – connective tissue and blood vessels.
Ovary. H@E. • • • • 1 – rudimental epithelium; 2 – tunica albuginea; 3 – cortex; 4 – primary follicles; 5 - growing follicles; 6 – Graafian follicle; 7 – cavity of Graafian follicle filled by fluid; 8 – I-type oocyte; 9 – Graafian follicle without cumulus oophorus and oocyte ; 10 – corpus luteum; 11 – atretic corpuscles; 12 – medulla; 13 – connective tissue and blood vessels.
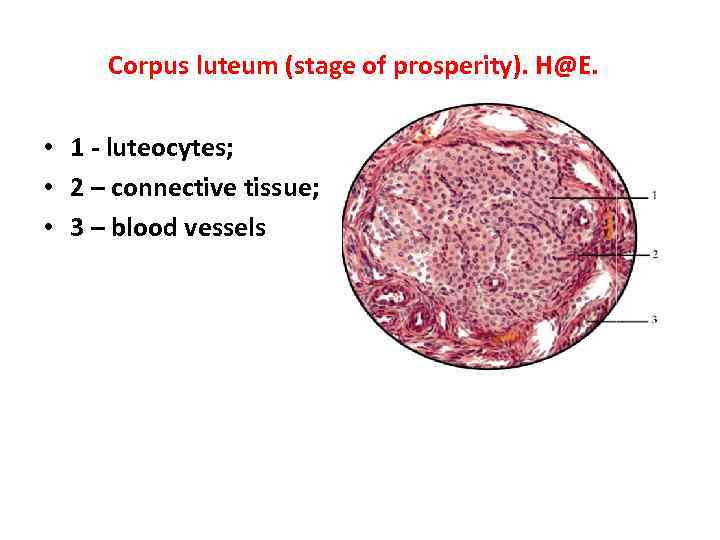 Corpus luteum (stage of prosperity). H@E. • 1 - luteocytes; • 2 – connective tissue; • 3 – blood vessels
Corpus luteum (stage of prosperity). H@E. • 1 - luteocytes; • 2 – connective tissue; • 3 – blood vessels
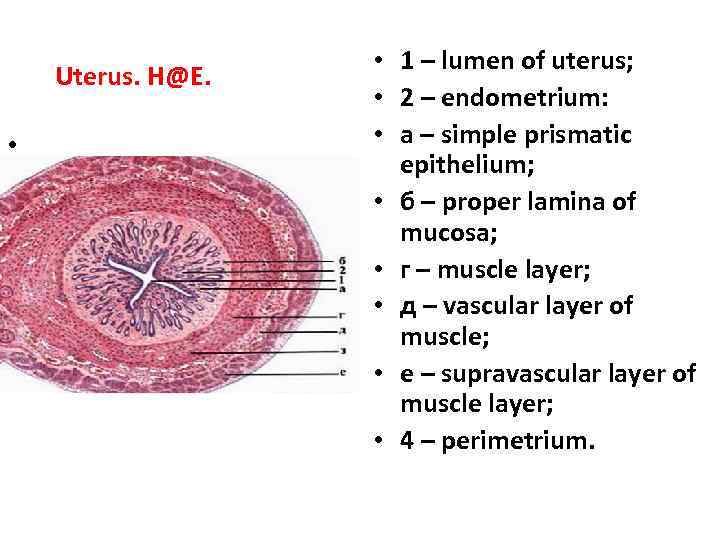 Uterus. H@E. • • 1 – lumen of uterus; • 2 – endometrium: • а – simple prismatic epithelium; • б – proper lamina of mucosa; • г – muscle layer; • д – vascular layer of muscle; • е – supravascular layer of muscle layer; • 4 – perimetrium.
Uterus. H@E. • • 1 – lumen of uterus; • 2 – endometrium: • а – simple prismatic epithelium; • б – proper lamina of mucosa; • г – muscle layer; • д – vascular layer of muscle; • е – supravascular layer of muscle layer; • 4 – perimetrium.
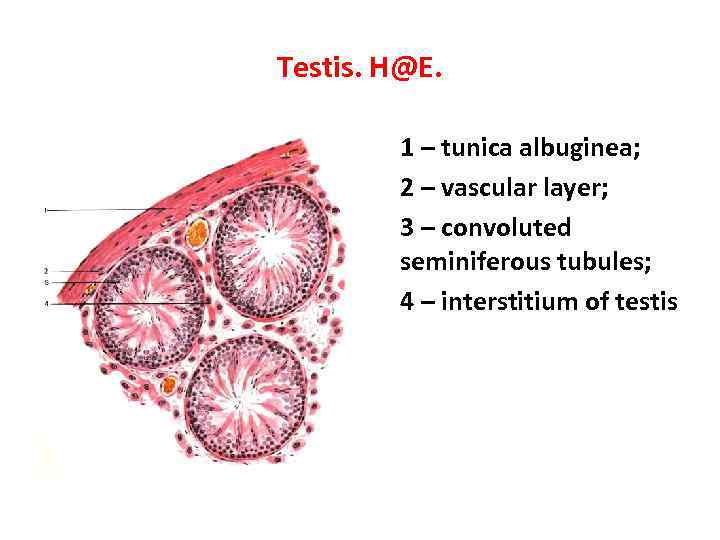 Testis. H@E. 1 – tunica albuginea; 2 – vascular layer; 3 – convoluted seminiferous tubules; 4 – interstitium of testis
Testis. H@E. 1 – tunica albuginea; 2 – vascular layer; 3 – convoluted seminiferous tubules; 4 – interstitium of testis
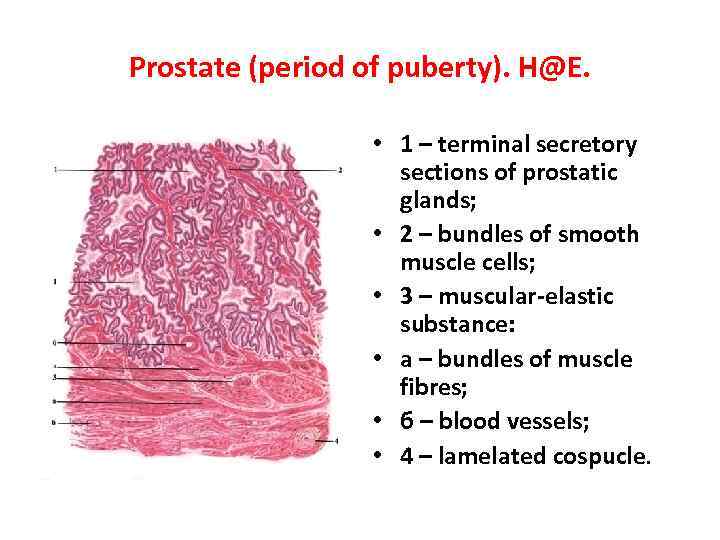 Prostate (period of puberty). H@E. • 1 – terminal secretory sections of prostatic glands; • 2 – bundles of smooth muscle cells; • 3 – muscular-elastic substance: • а – bundles of muscle fibres; • б – blood vessels; • 4 – lamelated cospucle.
Prostate (period of puberty). H@E. • 1 – terminal secretory sections of prostatic glands; • 2 – bundles of smooth muscle cells; • 3 – muscular-elastic substance: • а – bundles of muscle fibres; • б – blood vessels; • 4 – lamelated cospucle.
 Transversal section of tendon. H-E.
Transversal section of tendon. H-E.
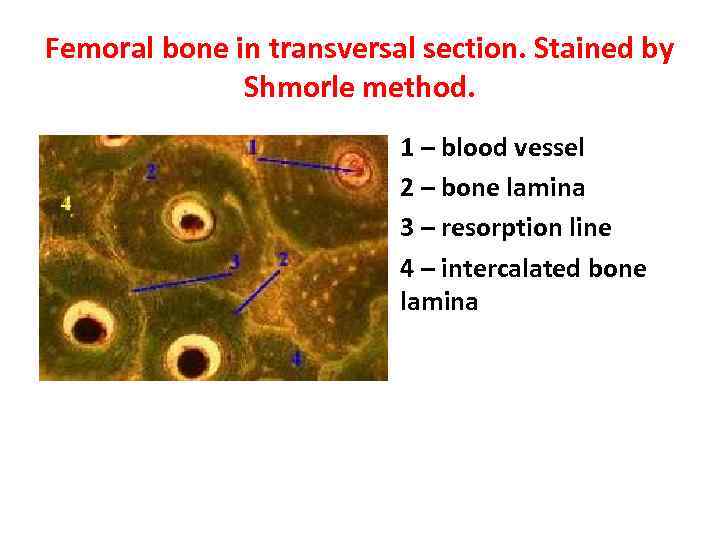 Femoral bone in transversal section. Stained by Shmorle method. 1 – blood vessel 2 – bone lamina 3 – resorption line 4 – intercalated bone lamina
Femoral bone in transversal section. Stained by Shmorle method. 1 – blood vessel 2 – bone lamina 3 – resorption line 4 – intercalated bone lamina
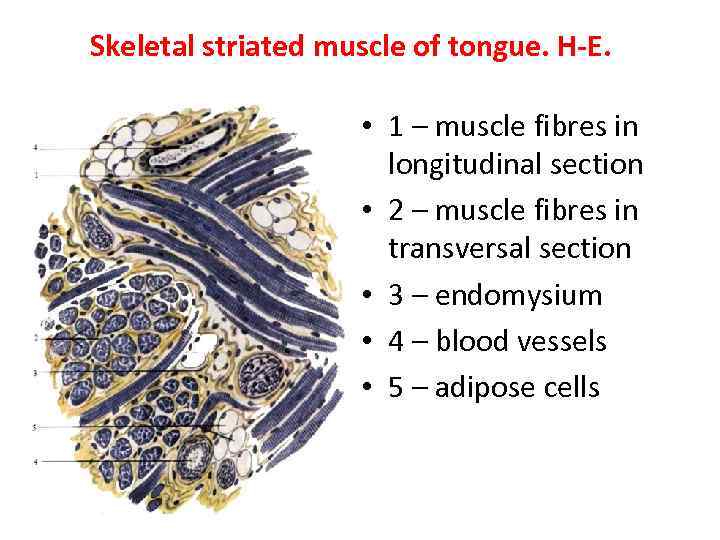 Skeletal striated muscle of tongue. H-E. • 1 – muscle fibres in longitudinal section • 2 – muscle fibres in transversal section • 3 – endomysium • 4 – blood vessels • 5 – adipose cells
Skeletal striated muscle of tongue. H-E. • 1 – muscle fibres in longitudinal section • 2 – muscle fibres in transversal section • 3 – endomysium • 4 – blood vessels • 5 – adipose cells
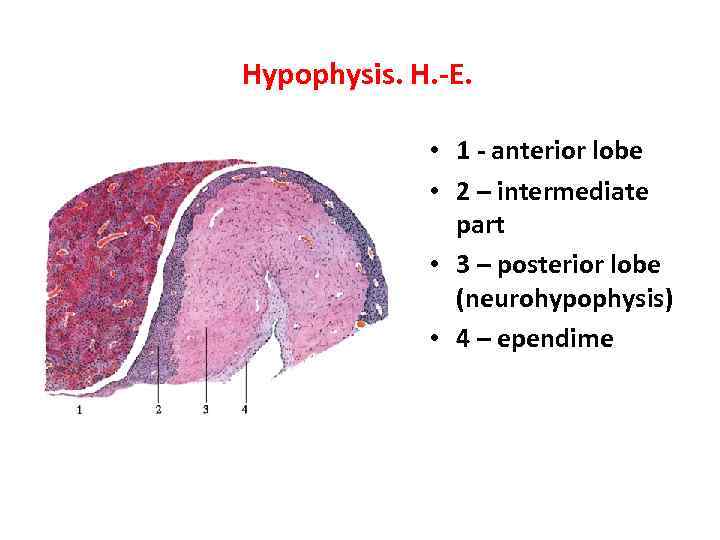 Hypophysis. H. -E. • 1 - anterior lobe • 2 – intermediate part • 3 – posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) • 4 – ependime
Hypophysis. H. -E. • 1 - anterior lobe • 2 – intermediate part • 3 – posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) • 4 – ependime
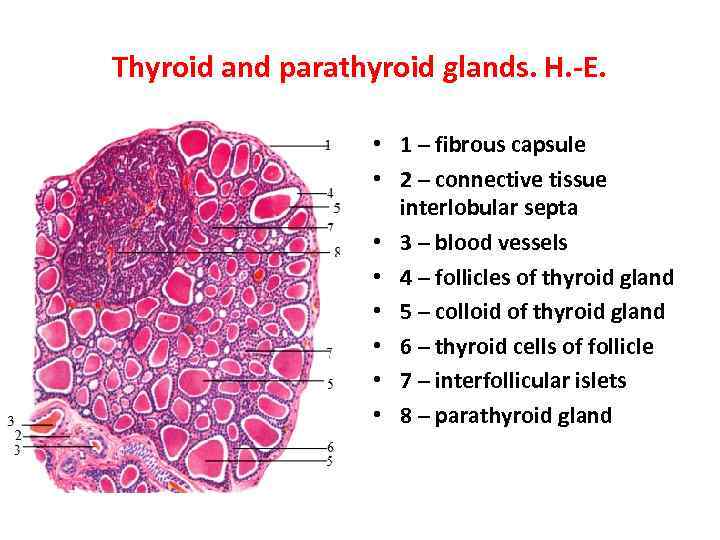 Thyroid and parathyroid glands. H. -E. • 1 – fibrous capsule • 2 – connective tissue interlobular septa • 3 – blood vessels • 4 – follicles of thyroid gland • 5 – colloid of thyroid gland • 6 – thyroid cells of follicle • 7 – interfollicular islets • 8 – parathyroid gland
Thyroid and parathyroid glands. H. -E. • 1 – fibrous capsule • 2 – connective tissue interlobular septa • 3 – blood vessels • 4 – follicles of thyroid gland • 5 – colloid of thyroid gland • 6 – thyroid cells of follicle • 7 – interfollicular islets • 8 – parathyroid gland
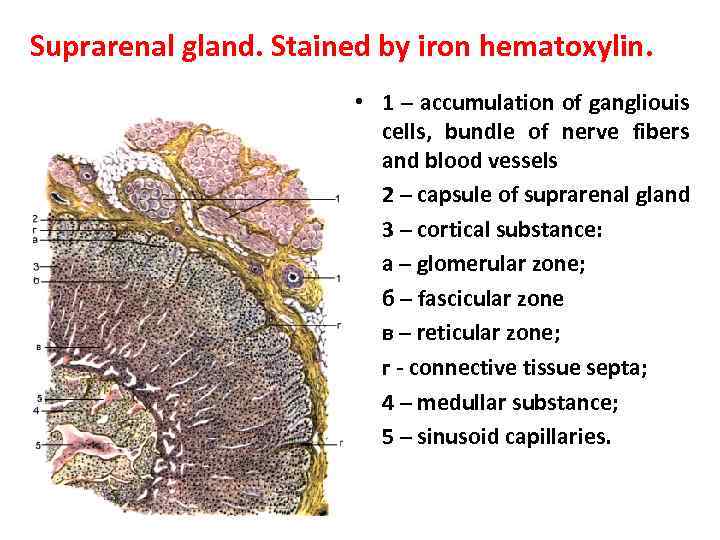 Suprarenal gland. Stained by iron hematoxylin. • 1 – accumulation of gangliouis cells, bundle of nerve fibers and blood vessels • 2 – capsule of suprarenal gland • 3 – cortical substance: • a – glomerular zone; • б – fascicular zone • в – reticular zone; • г - connective tissue septa; • 4 – medullar substance; • 5 – sinusoid capillaries.
Suprarenal gland. Stained by iron hematoxylin. • 1 – accumulation of gangliouis cells, bundle of nerve fibers and blood vessels • 2 – capsule of suprarenal gland • 3 – cortical substance: • a – glomerular zone; • б – fascicular zone • в – reticular zone; • г - connective tissue septa; • 4 – medullar substance; • 5 – sinusoid capillaries.


