3d78c7ea8742763fb23bbb424c469c44.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Prenatal infections during pregnancy A possible factor for numerous neurodevelopmental disorders with either infant or adult onset Clinical epidemiological evidence Related to very premature birth, cerebral palsy, PVL… Schizophrenia: higher rates in individuals whose mothers were exposed to an influenza during the 2 nd trimester of pregnancy Other neuropsychotic disorders: autism
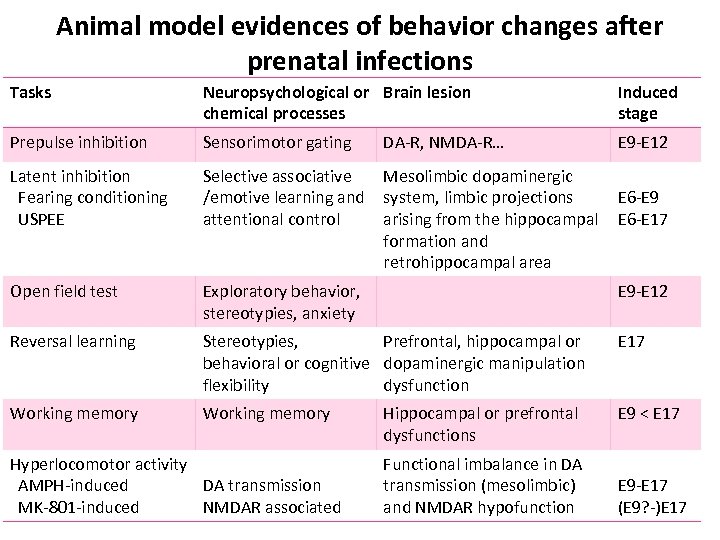
Animal model evidences of behavior changes after prenatal infections Tasks Neuropsychological or Brain lesion chemical processes Induced stage Prepulse inhibition Sensorimotor gating DA-R, NMDA-R… E 9 -E 12 Latent inhibition Fearing conditioning USPEE Selective associative /emotive learning and attentional control Mesolimbic dopaminergic system, limbic projections arising from the hippocampal formation and retrohippocampal area Open field test Exploratory behavior, stereotypies, anxiety E 9 -E 12 Reversal learning Stereotypies, Prefrontal, hippocampal or behavioral or cognitive dopaminergic manipulation flexibility dysfunction E 17 Working memory E 9 < E 17 Hyperlocomotor activity AMPH-induced DA transmission MK-801 -induced NMDAR associated Hippocampal or prefrontal dysfunctions Functional imbalance in DA transmission (mesolimbic) and NMDAR hypofunction E 6 -E 9 E 6 -E 17 E 9 -E 17 (E 9? -)E 17
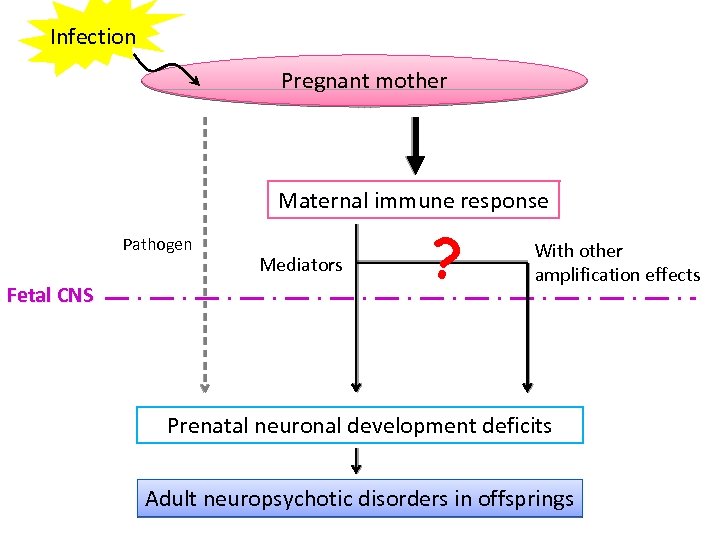
Infection Pregnant mother Maternal immune response Pathogen Fetal CNS Mediators ? With other amplification effects Prenatal neuronal development deficits Adult neuropsychotic disorders in offsprings
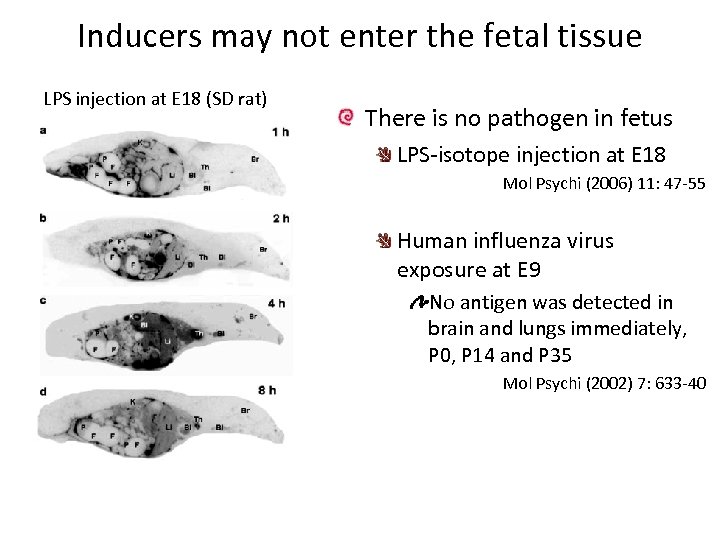
Inducers may not enter the fetal tissue LPS injection at E 18 (SD rat) There is no pathogen in fetus LPS-isotope injection at E 18 Mol Psychi (2006) 11: 47 -55 Human influenza virus exposure at E 9 No antigen was detected in brain and lungs immediately, P 0, P 14 and P 35 Mol Psychi (2002) 7: 633 -40
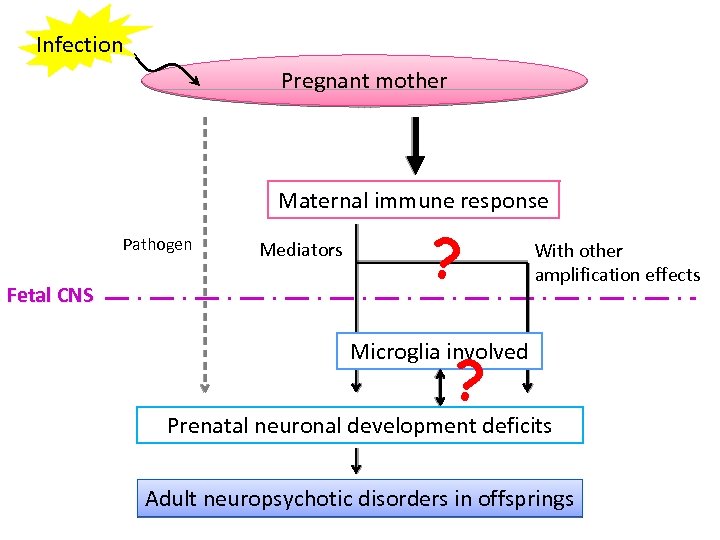
Infection Pregnant mother Maternal immune response Pathogen Fetal CNS Mediators ? With other amplification effects Microglia involved ? Prenatal neuronal development deficits Adult neuropsychotic disorders in offsprings
Microglia during embryonic stage Amoeboid microglia (AMC) Immature form of ramified microglia and present transiently during development From E 10. 5 to P 10 -14 Function as phagocytes A protective barrier which is deemed to be necessary in the early developmental period when the BBB is deficient Regulate the development of CNS Migration Differentiation Apopsotis
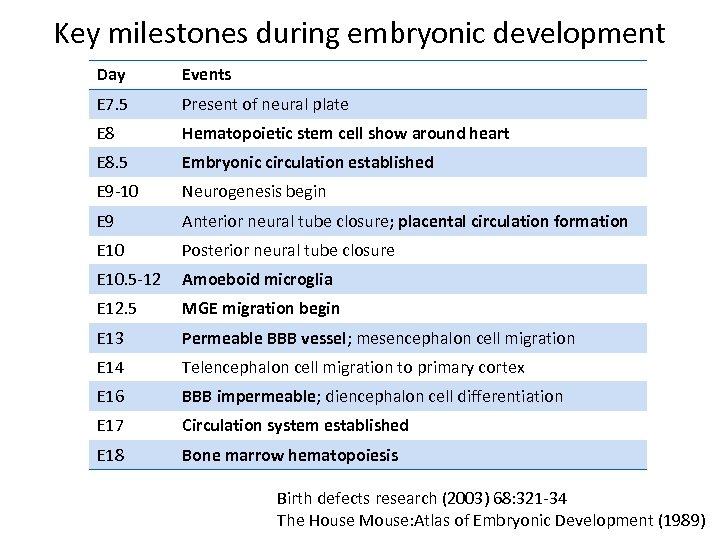
Key milestones during embryonic development Day Events E 7. 5 Present of neural plate E 8 Hematopoietic stem cell show around heart E 8. 5 Embryonic circulation established E 9 -10 Neurogenesis begin E 9 Anterior neural tube closure; placental circulation formation E 10 Posterior neural tube closure E 10. 5 -12 Amoeboid microglia E 12. 5 MGE migration begin E 13 Permeable BBB vessel; mesencephalon cell migration E 14 Telencephalon cell migration to primary cortex E 16 BBB impermeable; diencephalon cell differentiation E 17 Circulation system established E 18 Bone marrow hematopoiesis Birth defects research (2003) 68: 321 -34 The House Mouse: Atlas of Embryonic Development (1989)
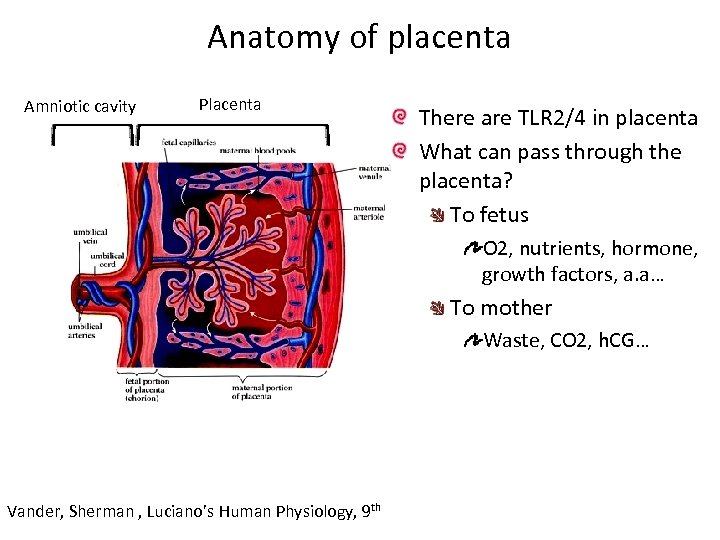
Anatomy of placenta Amniotic cavity Placenta There are TLR 2/4 in placenta What can pass through the placenta? To fetus O 2, nutrients, hormone, growth factors, a. a… To mother Waste, CO 2, h. CG… Vander, Sherman , Luciano’s Human Physiology, 9 th
Cytokines at the maternofetal interface Cytokines can be produced by both fetal and maternal cells in the placenta Beneficial effects: CSF-1, TGF-β, GM-CSF, IL-10 Detrimental effects: TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2 very low levels or absent in normal placenta Actually, beneficial or detrimental effects depends on concentration or stage of pregnancy J Comp Path (2002) 126: 79 -94 Transfer of inflammatory cytokines across the placenta IL-1 α, TNF- α, IL-6 Obstet Gynecol (2004) 103: 546 -50
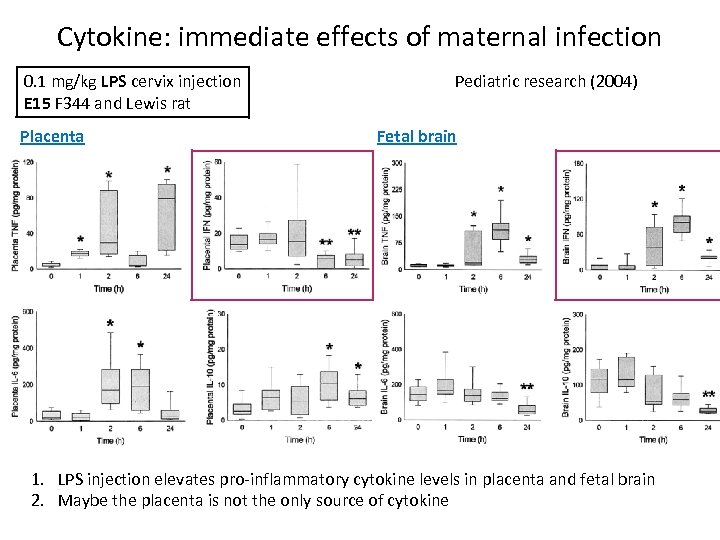
Cytokine: immediate effects of maternal infection 0. 1 mg/kg LPS cervix injection E 15 F 344 and Lewis rat Placenta Pediatric research (2004) Fetal brain 1. LPS injection elevates pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in placenta and fetal brain 2. Maybe the placenta is not the only source of cytokine
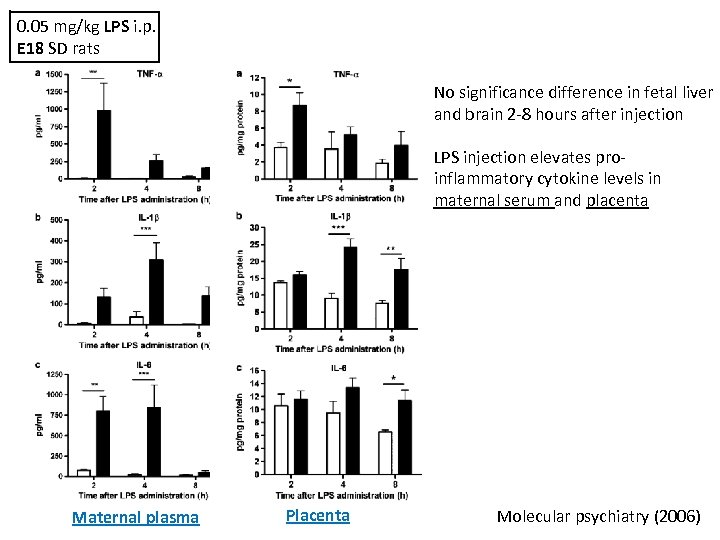
0. 05 mg/kg LPS i. p. E 18 SD rats No significance difference in fetal liver and brain 2 -8 hours after injection LPS injection elevates proinflammatory cytokine levels in maternal serum and placenta Maternal plasma Placenta Molecular psychiatry (2006)
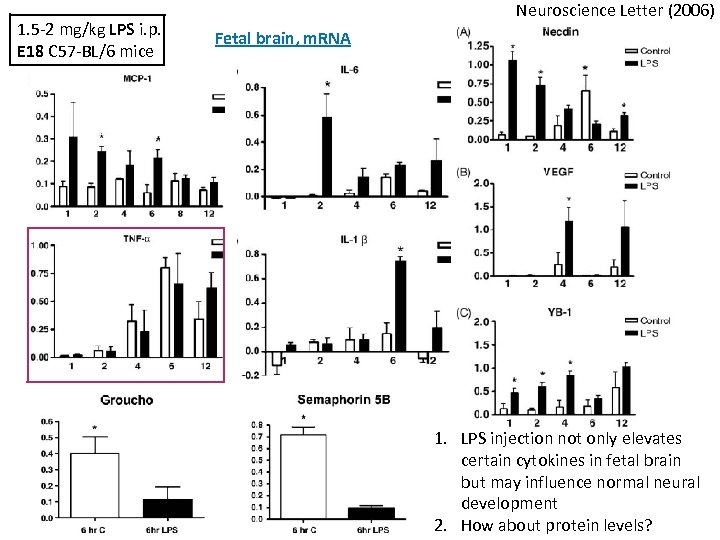
1. 5 -2 mg/kg LPS i. p. E 18 C 57 -BL/6 mice Neuroscience Letter (2006) Fetal brain, m. RNA 1. LPS injection not only elevates certain cytokines in fetal brain but may influence normal neural development 2. How about protein levels?
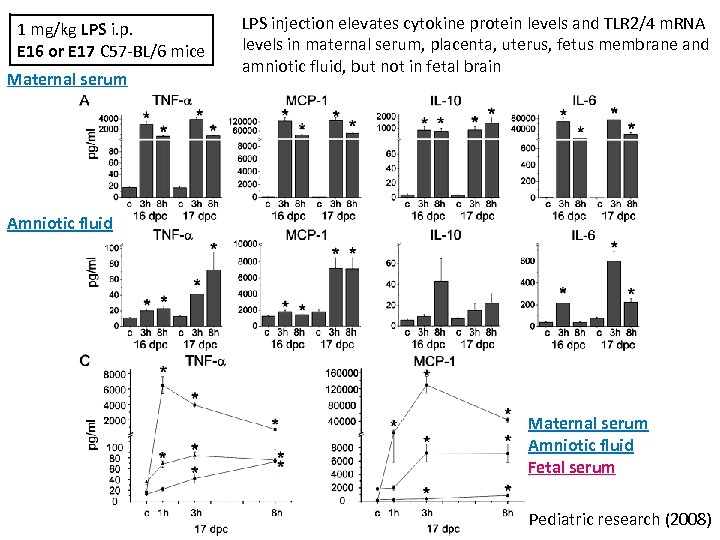
1 mg/kg LPS i. p. E 16 or E 17 C 57 -BL/6 mice Maternal serum LPS injection elevates cytokine protein levels and TLR 2/4 m. RNA levels in maternal serum, placenta, uterus, fetus membrane and amniotic fluid, but not in fetal brain Amniotic fluid Maternal serum Amniotic fluid Fetal serum Pediatric research (2008)
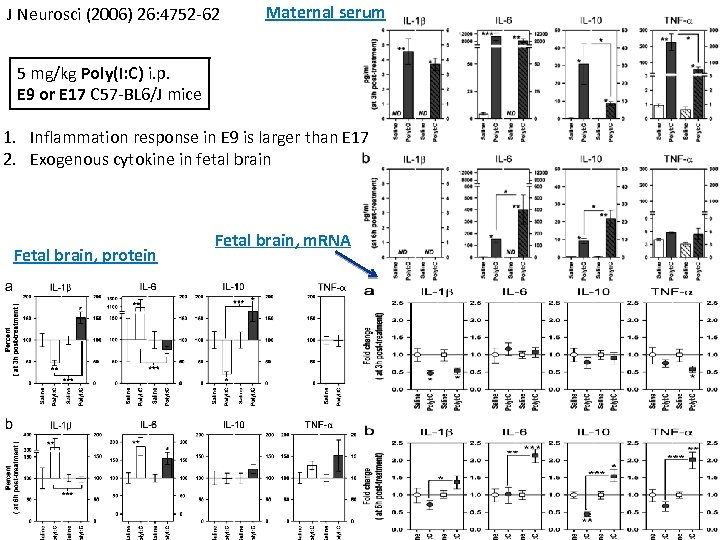
J Neurosci (2006) 26: 4752 -62 Maternal serum 5 mg/kg Poly(I: C) i. p. E 9 or E 17 C 57 -BL 6/J mice 1. Inflammation response in E 9 is larger than E 17 2. Exogenous cytokine in fetal brain Fetal brain, protein Fetal brain, m. RNA
Summary Maternal infection upregulate cytokines in placenta and amniotic fluid immediately Does pathogens pass through maternal fetal interface? No direct evidence Does cytokine pass through maternal fetal interface? Dosage of inducer Gestation day of pregnancy Neuroinflammation/sensitivity Does cytokines play key roles of these complications? IL-2 injection during mid-gestation induce abnormal neurobehavioral pattern like autism IL-6 antibody/KO can reverse the abnormal behaviors in offsprings
3d78c7ea8742763fb23bbb424c469c44.ppt