2eb0a1707556f3d560c198a22f009fe8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

Premature mortality due to tobacco: Counting the dead and saving lives Neil Collishaw Research Director Physicians for a Smoke-Free Canada Ottawa, Ontario June 1, 2007 1

“ 30, 000 die while feds sit on hands” 2
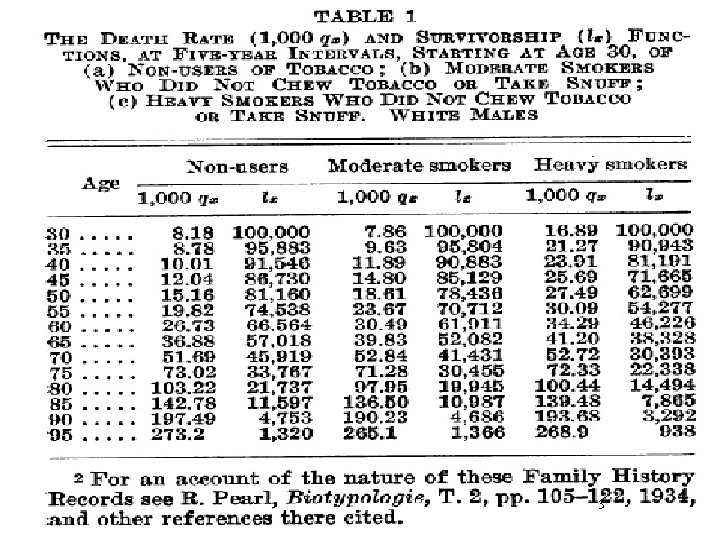
Smokers and nonsmokers life tables: R. Pearl 1938 3
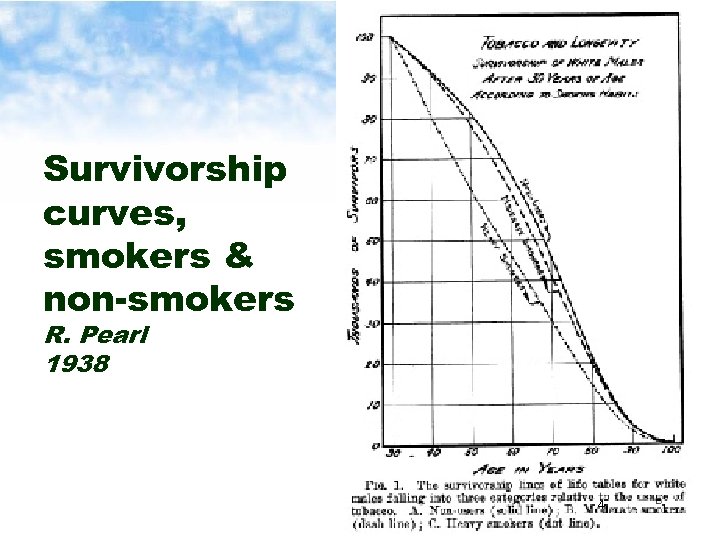
Survivorship curves, smokers & non-smokers R. Pearl 1938 4
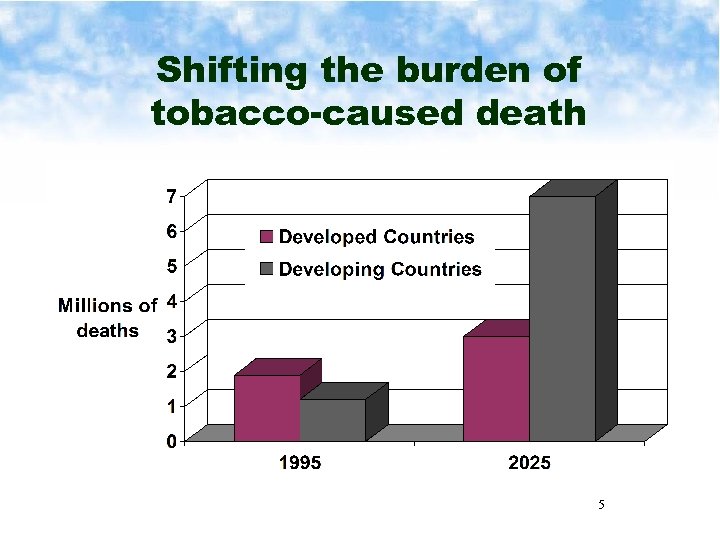
Shifting the burden of tobacco-caused death 5
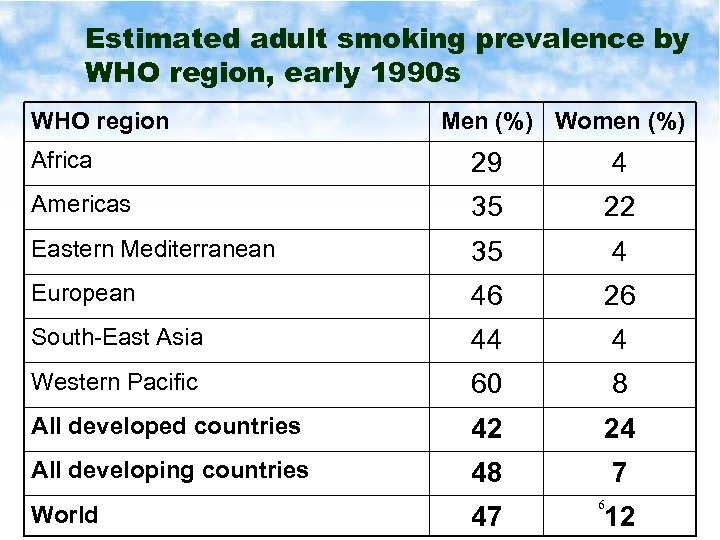
Estimated adult smoking prevalence by WHO region, early 1990 s WHO region Men (%) Women (%) Africa 29 4 Americas 35 22 Eastern Mediterranean 35 4 European 46 26 South-East Asia 44 4 Western Pacific 60 8 All developed countries 42 24 All developing countries 48 7 World 47 6 12
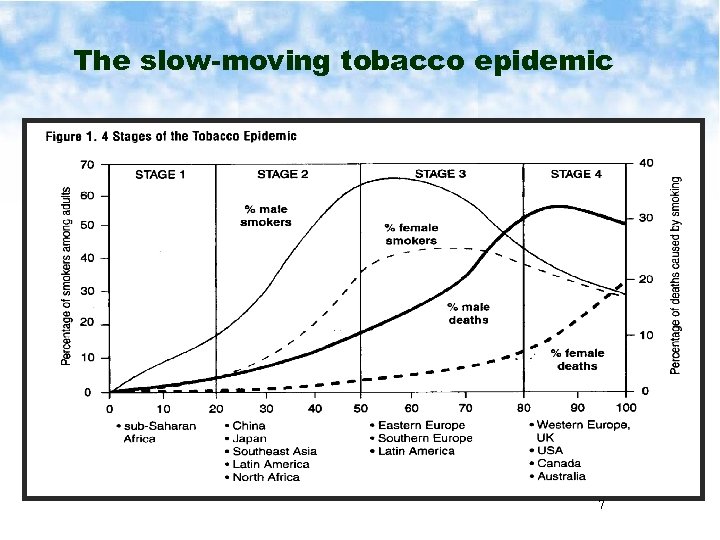
The slow-moving tobacco epidemic 7

FCTC history: 1994: WCTOH calls for convention 1995: WHO asks for feasibility study 1996: WHA accepts framework convention approach 1999– 2000: Working groups 2000 -02: Negotiation sessions 2003: Treaty text agreed to 2004: 40 countries ratify (including Canada) 2005: Came into force on Feb. 27 2006: 1 st Conference of Parties in Feb. , 2006 2007: 2 nd Co. P in July, 2007: 147 parties 10

Ten key obligations are in Articles… 5: general obligations 6: prices and taxes 8: protection from second-hand smoke 11: health warnings on packages 12: health promotion and education 13: tobacco advertising 14: smoking cessation 15: smuggling 20: surveillance and research 22: international cooperation 11

In the future the FCTC could: Protect non-smokers End tobacco advertising Control cigarette smuggling Protect from unfair trade challenges Help developing countries put measures in place Hold tobacco companies accountable Monitor global tobacco use Improve warnings on packages Increase research 12

Cooperate…cooperation…cooperate…c ooperation…cooperate …cooperative… cooperation…cooperate …cooperation…cooperate…cooperation…cooper ate…cooperation…cooperate…cooperation…coop erate…cooperation…cooperate…cooperation…co operate…cooperation…cooperate…cooperation… 13 cooperate…cooperation…cooperate…

We have a plan… Organize regional training seminars to trainers Send trained workers to help in selected developing countries Fund local personnel and projects Ongoing monitoring and encouragement, including follow-up visits to target countries Attract additional partners With participation of additional partners, expand project beyond original target countries, eventually to all countries 14

1969: External Statements Brief to Commons Health Committee (Isabelle Committee), 1969. ITL head Paul Pare presents for industry 15

1969: internal research § du Maurier § Players § Matinee Minutes of BAT Research & Development Meeting, July 1969. R. S. Wade from Imperial Tobacco Canada participated. 16

Dr. S. J. “Jim” Green Senior Scientist, BAT UK, 1976 17

The dissembly continues in 1987… “It is not the position of the industry that tobacco causes any disease … The role, if any, that tobacco or smoking plays in the initiation and development of any these diseases is still very uncertain. ” Jean-Louis Mercier President, Imperial Tobacco House of Commons Parliamentary Committee on Bill C-204 and C-51. November 24, 1987 18

Before TPCA After TA 19

Are tobacco companies evil? Are they pscyhopaths? 20

Imperative to maximize profits which restricts corporations from acting in ways that protect public health if the result is a reduction in short and long term profits. 122. (1) Every director and officer of a corporation in exercising their powers and discharging their duties shall (a) act honestly and in good faith with a view to the best interests of the corporation; 21

"The cigarette company is to the lung cancer epidemic what the mosquito is to malaria. It is the vector of disease. " 22
The anatomy of a mosquito 23
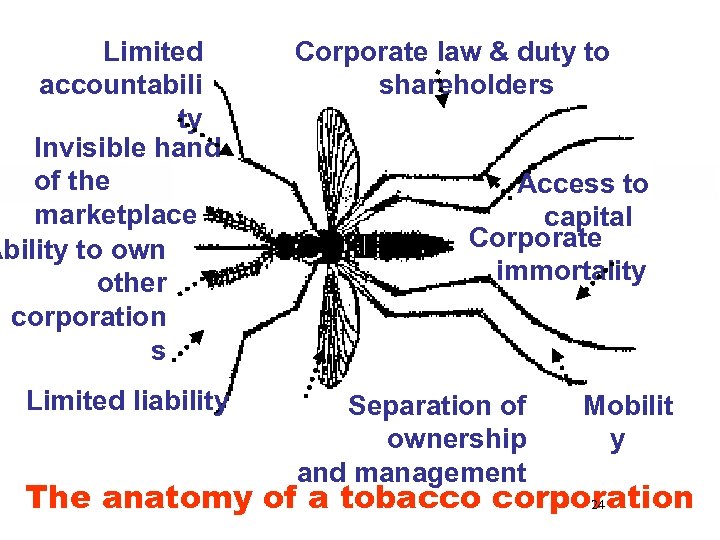
Limited accountabili ty Invisible hand of the marketplace Ability to own other corporation s Limited liability Corporate law & duty to shareholders Access to capital Corporate immortality Separation of ownership and management Mobilit y The anatomy of a tobacco corporation 24
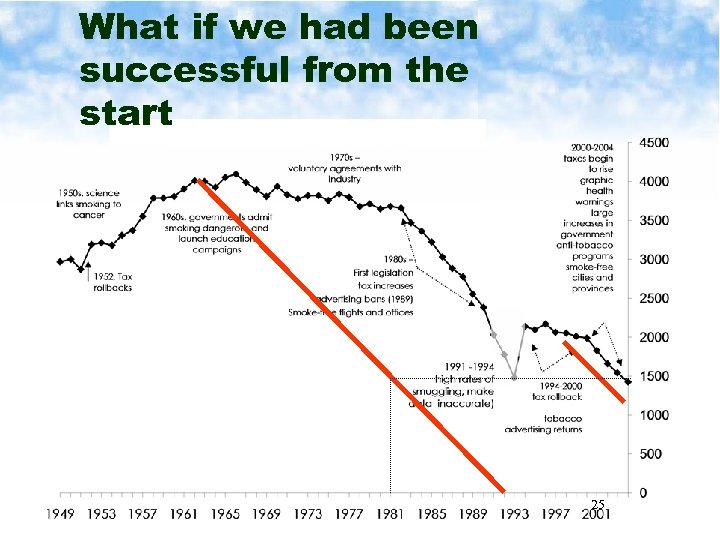
What if we had been successful from the start 25
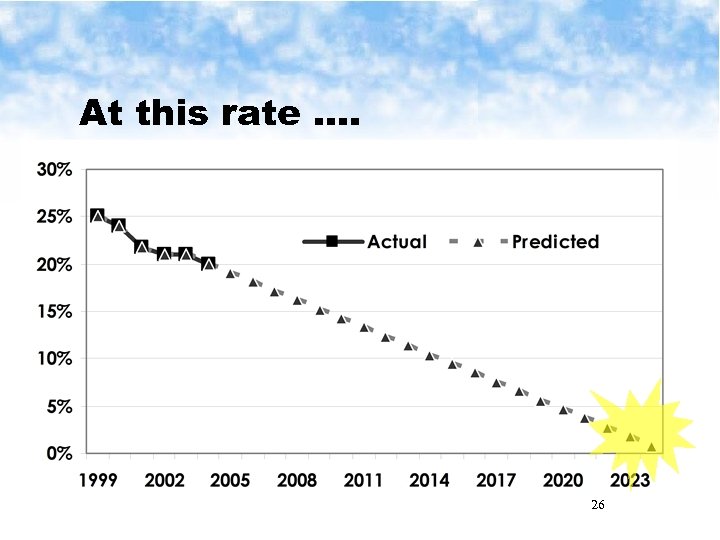
At this rate …. 26

27

28

29

30

Long-term solution: Tobacco can be supplied by publicinterest enterprises 31
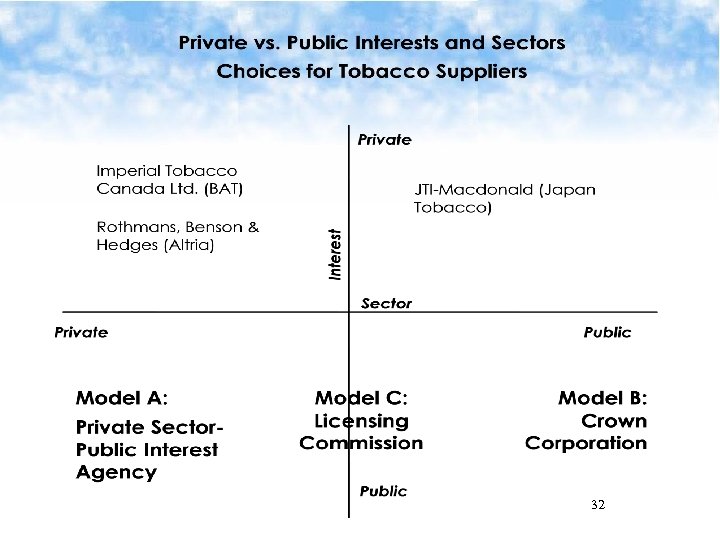
32

New potential Tap the secret knowledge of tobacco experts § Tobacco marketers become tobacco demarketers § R&D department stops designing cigarettes that will sell more, and starts designing cigarettes that will sell less Increase innovation Meet the needs of smokers End the war between Big Tobacco and public health Resolve the ambiguity of government’s intentions Create a more cohesive society 33

Revolution? Evolution? 34

Bolder goal-setting and tobacco control actions by governments 35

Tobacco retailing in Canada 60, 000 retailers get $80 million per year in promotional allowances from Big Tobacco. Advertising banned; power walls being banned. Sale to minors prohibited and enforced. Smoker buys cigarettes once a day but only visits his doctor once a year. 36

Power walls Blank walls 37

Transformed walls 38

Transforming tobacco retailers from Big Tobacco lackeys to public health agents and community centres. § § § Create incentives for transformation. Train clerks in brief counselling and smoking cessation referral, and other health promotion techniques. Transform stores into meeting places, neighbourhhood watch and community information centres. 39
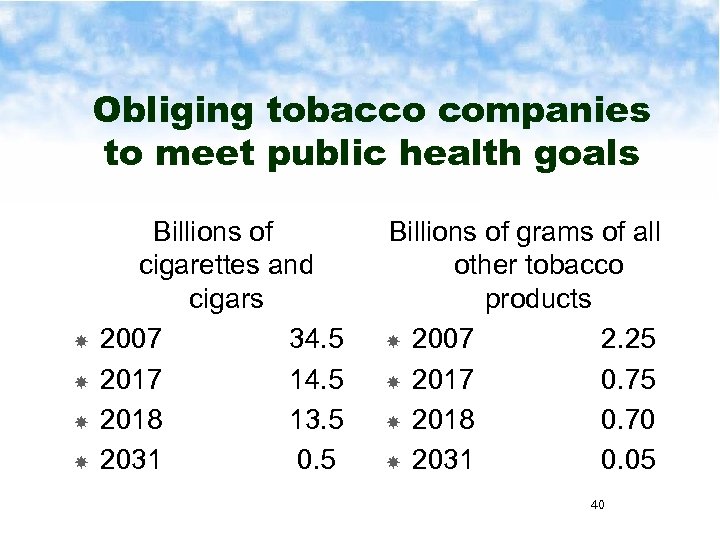
Obliging tobacco companies to meet public health goals Billions of cigarettes and cigars 2007 34. 5 2017 14. 5 2018 13. 5 2031 0. 5 Billions of grams of all other tobacco products 2007 2. 25 2017 0. 75 2018 0. 70 2031 0. 05 40

Lesson # 1: We can change the world Lesson # 2: Tobacco companies adapt to overcome public health measures Lesson #3: Tobacco corporations are compelled to maximize profits. 41
2eb0a1707556f3d560c198a22f009fe8.ppt