77bf334ec872bffabed3a64e7efd1852.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

 Prehistory • What is “history”? • Documentation – Written records – Archaeological discovery
Prehistory • What is “history”? • Documentation – Written records – Archaeological discovery
 Development of Hominids • Animals adapt themselves to environment • Hominids adapt environment to themselves – Use of tools – Language – Complex cooperative social structures
Development of Hominids • Animals adapt themselves to environment • Hominids adapt environment to themselves – Use of tools – Language – Complex cooperative social structures
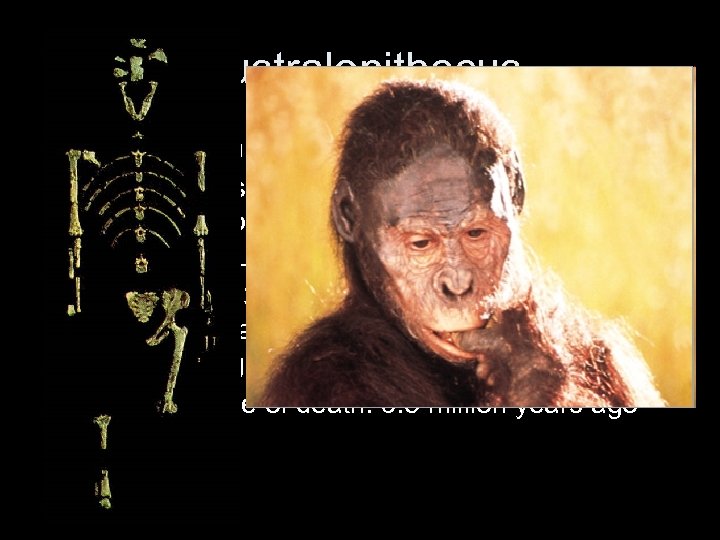 Australopithecus • “The southern ape” – Despite name a hominid • Discovery of skeleton AL-288 -1, north of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia – Nicknamed “Lucy” • 40% of SWF, 3’ 5”, 55 lb. , bipedal, Brain 500 cc (modern human: 1400 cc), limited speech but opposable digit • Estimated date of death: 3. 5 million years ago
Australopithecus • “The southern ape” – Despite name a hominid • Discovery of skeleton AL-288 -1, north of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia – Nicknamed “Lucy” • 40% of SWF, 3’ 5”, 55 lb. , bipedal, Brain 500 cc (modern human: 1400 cc), limited speech but opposable digit • Estimated date of death: 3. 5 million years ago
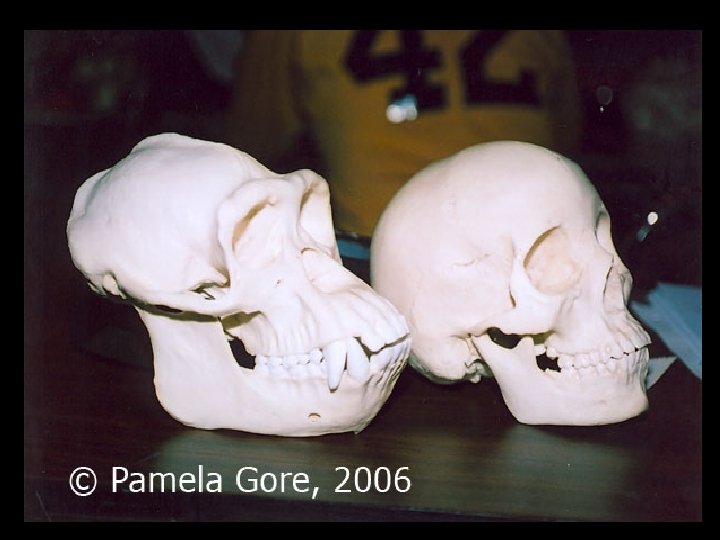
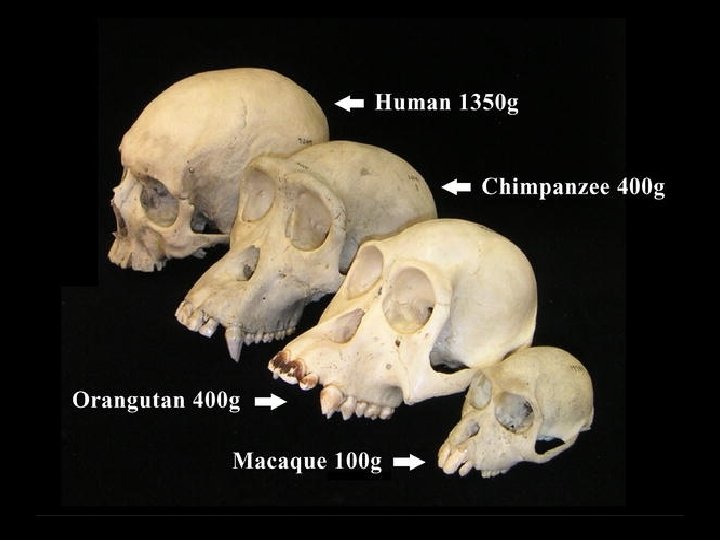
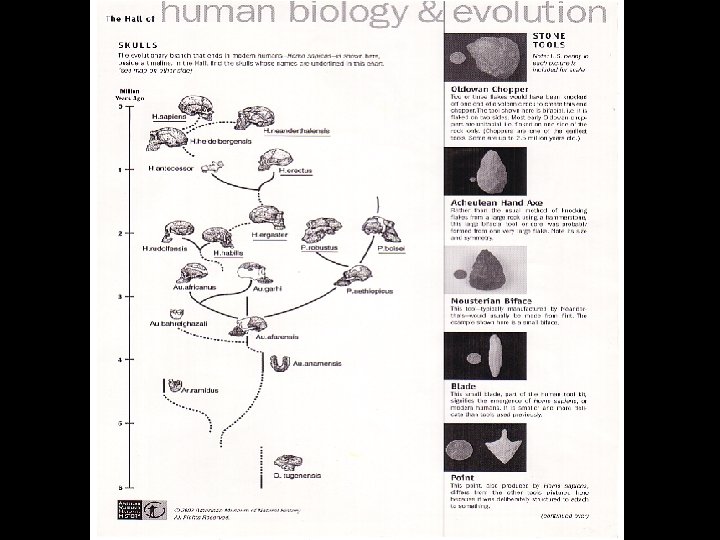
 Later Hominids • Homo Erectus, “upright man” • Larger brain capacity (1000 cc), improved tool use, control of fire • Homo Sapiens, “consciously thinking human” • Largest brain, esp. frontal regions • Most sophisticated tools and social organization • Migrations of Homo Erectus and Homo Sapiens
Later Hominids • Homo Erectus, “upright man” • Larger brain capacity (1000 cc), improved tool use, control of fire • Homo Sapiens, “consciously thinking human” • Largest brain, esp. frontal regions • Most sophisticated tools and social organization • Migrations of Homo Erectus and Homo Sapiens
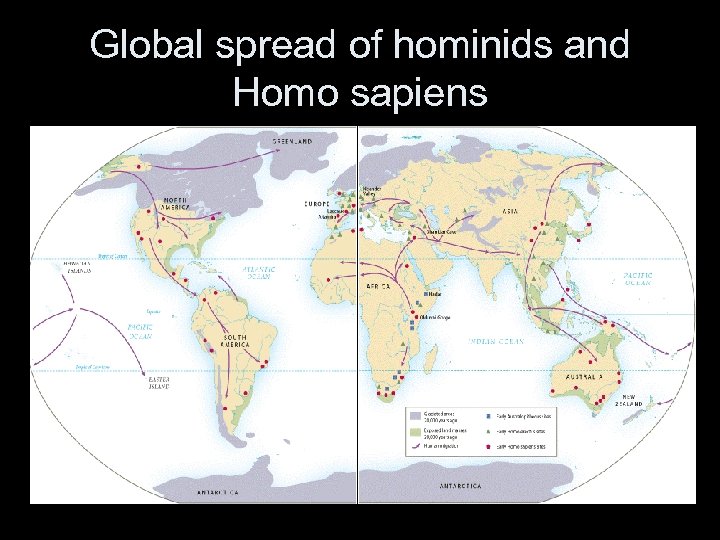 Global spread of hominids and Homo sapiens
Global spread of hominids and Homo sapiens
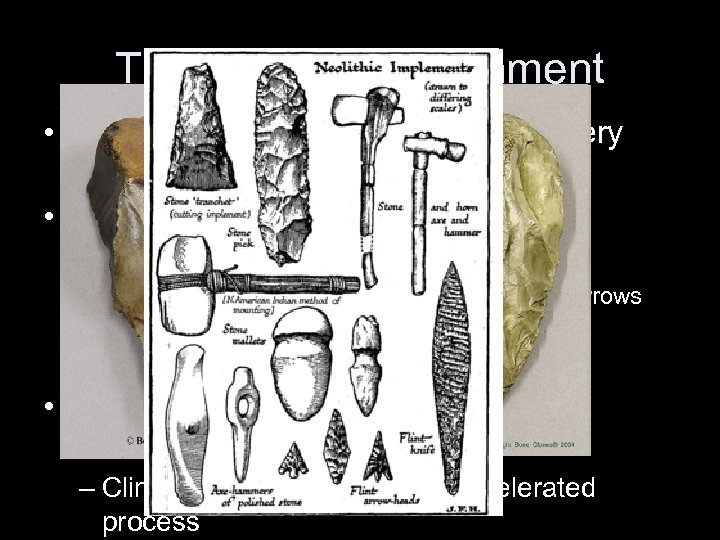 The Natural Environment • By 13, 000 BCE Homo sapiens in every inhabitable part of the world • Archaeological finds: – Sophisticated tools • Choppers, scrapers, axes, knives, bows, arrows • Cave and hut like dwellings • Use of fire, animal skins • Hunted several mammal species to extinction – Climactic change may have accelerated process
The Natural Environment • By 13, 000 BCE Homo sapiens in every inhabitable part of the world • Archaeological finds: – Sophisticated tools • Choppers, scrapers, axes, knives, bows, arrows • Cave and hut like dwellings • Use of fire, animal skins • Hunted several mammal species to extinction – Climactic change may have accelerated process
 Relative Social Equality • Nomadic culture precludes accumulation of land-based wealth – More likely determinants of status: age, hunting skill, fertility, personality – Possible gender equality related to food production – Men: protein from hunting – Women: plant gathering
Relative Social Equality • Nomadic culture precludes accumulation of land-based wealth – More likely determinants of status: age, hunting skill, fertility, personality – Possible gender equality related to food production – Men: protein from hunting – Women: plant gathering
 Paleolithic Era (“Old Stone Age”) • Evidence: – Archaeological finds – Extrapolation from modern hunter-gatherer societies • Nomadic existence precludes advanced civilization – Groups of 30 -50 – Division of labor along gender lines
Paleolithic Era (“Old Stone Age”) • Evidence: – Archaeological finds – Extrapolation from modern hunter-gatherer societies • Nomadic existence precludes advanced civilization – Groups of 30 -50 – Division of labor along gender lines
 Big Game Hunting • Evidence of intelligent coordination of hunting expeditions – Development of weaponry – Animal-skin disguises – Stampeding tactics • Lighting of fires, etc. to drive game into kill zones • Requires planning, communication
Big Game Hunting • Evidence of intelligent coordination of hunting expeditions – Development of weaponry – Animal-skin disguises – Stampeding tactics • Lighting of fires, etc. to drive game into kill zones • Requires planning, communication
 Paleolithic Settlements • Natufian society – Modern Israel and Jordan – Wild wheat, herding • Jomon society – Japan – Wild buckwheat, fishing • Chinook society – Pacific Northwest – Berries, acorns, salmon runs • Groups of 1000 or more
Paleolithic Settlements • Natufian society – Modern Israel and Jordan – Wild wheat, herding • Jomon society – Japan – Wild buckwheat, fishing • Chinook society – Pacific Northwest – Berries, acorns, salmon runs • Groups of 1000 or more
 Neandertal Peoples • Neander valley, western Germany • Flourished in Europe & SW Asia, 200, 000 – 35, 000 years ago • Also found in Africa, east Asia • Evidence of spirituality: ritual burial • Inhabited some of the same areas as Homo sapiens
Neandertal Peoples • Neander valley, western Germany • Flourished in Europe & SW Asia, 200, 000 – 35, 000 years ago • Also found in Africa, east Asia • Evidence of spirituality: ritual burial • Inhabited some of the same areas as Homo sapiens
 Creativity of Homo sapiens • Constructed flexible languages for communication of complex ideas • Increased variety of tools – stone blades, spear throwers, sewing needles, barbed harpoons • Fabricated ornamental beads, necklaces and bracelets • The bow and arrow – a dramatic improvement in humans power over nature • “Venus” figurines • Cave paintings
Creativity of Homo sapiens • Constructed flexible languages for communication of complex ideas • Increased variety of tools – stone blades, spear throwers, sewing needles, barbed harpoons • Fabricated ornamental beads, necklaces and bracelets • The bow and arrow – a dramatic improvement in humans power over nature • “Venus” figurines • Cave paintings
 Neolithic Era (“New Stone Age”) • Corresponds with the end of the last Ice Age • Distinction in tool production – Chipped vs. polished • Men: herding animals rather than hunting • Women: nurtured vegetation rather than foraging • Spread of Agriculture – Slash-and burn techniques – Exhaustion of soil promotes migration – Transport of crops from one region to another
Neolithic Era (“New Stone Age”) • Corresponds with the end of the last Ice Age • Distinction in tool production – Chipped vs. polished • Men: herding animals rather than hunting • Women: nurtured vegetation rather than foraging • Spread of Agriculture – Slash-and burn techniques – Exhaustion of soil promotes migration – Transport of crops from one region to another
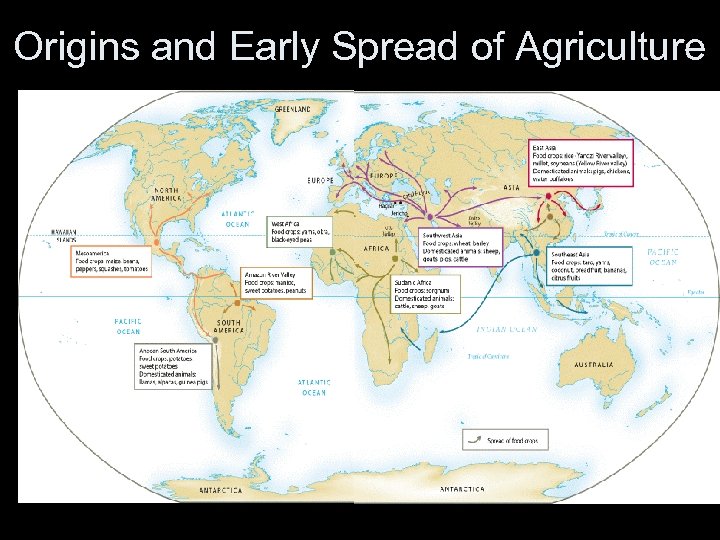 Origins and Early Spread of Agriculture
Origins and Early Spread of Agriculture
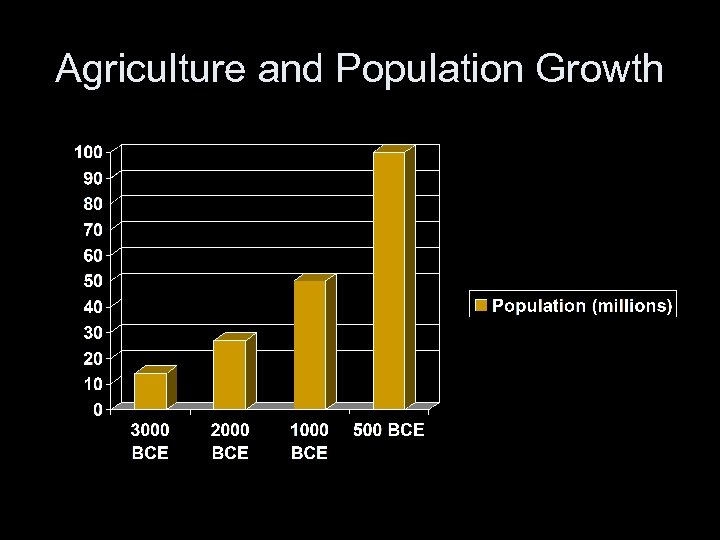 Agriculture and Population Growth
Agriculture and Population Growth
 Forming the Complex Society • Basic development: – Hunting and Foraging – Agriculture – Complex Society • Key issue: surplus capital • Major development of first complex societies 3500 BCE – 500 BCE
Forming the Complex Society • Basic development: – Hunting and Foraging – Agriculture – Complex Society • Key issue: surplus capital • Major development of first complex societies 3500 BCE – 500 BCE
 Early Agricultural Society • Emergence of villages and towns • Discoveries at Çatal Hüyük – a prominent village located in Turkey, occupied 72505400 BCE – Pots, baskets, textiles, leather, stone, metal tools, wood carvings, carpets, beads, and jewelry • Development of crafts –pottery, metallurgy, and textile production
Early Agricultural Society • Emergence of villages and towns • Discoveries at Çatal Hüyük – a prominent village located in Turkey, occupied 72505400 BCE – Pots, baskets, textiles, leather, stone, metal tools, wood carvings, carpets, beads, and jewelry • Development of crafts –pottery, metallurgy, and textile production
 Social Distinctions • Accumulation of landed wealth initiates development of social classes • Individuals could trade surplus food for valuable items • Archaeological evidence in variety of household decorations, goods buried with deceased members of society at Çatal Hüyük
Social Distinctions • Accumulation of landed wealth initiates development of social classes • Individuals could trade surplus food for valuable items • Archaeological evidence in variety of household decorations, goods buried with deceased members of society at Çatal Hüyük
 Neolithic Culture • Farmers closely observed the natural world – an early kind of applied science • Elements of natural environment essential for functioning • Archaeological evidence of religious worship: thousands of clay figurines, drawings on pots, tool decorations, other ritual objects – Fertility: Venus figurines
Neolithic Culture • Farmers closely observed the natural world – an early kind of applied science • Elements of natural environment essential for functioning • Archaeological evidence of religious worship: thousands of clay figurines, drawings on pots, tool decorations, other ritual objects – Fertility: Venus figurines
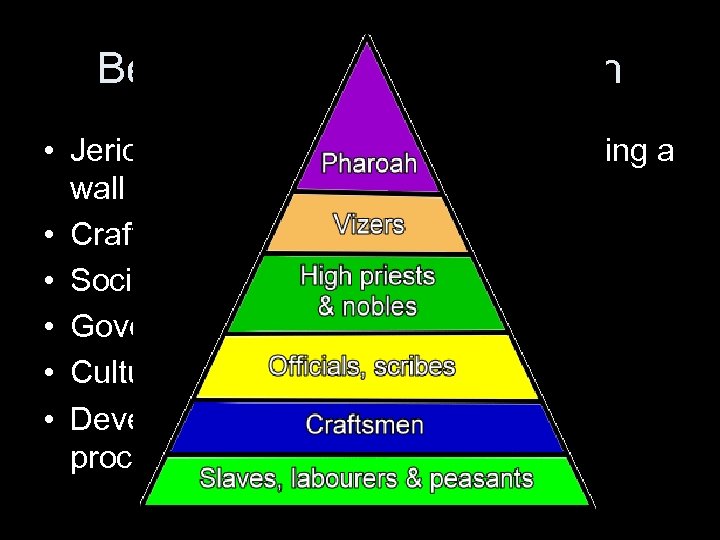 Beginnings of Urbanization • Jericho: concentration of wealth, building a wall • Craft specialization • Social stratification • Governance • Cultural workers • Development of the city – a gradual process
Beginnings of Urbanization • Jericho: concentration of wealth, building a wall • Craft specialization • Social stratification • Governance • Cultural workers • Development of the city – a gradual process
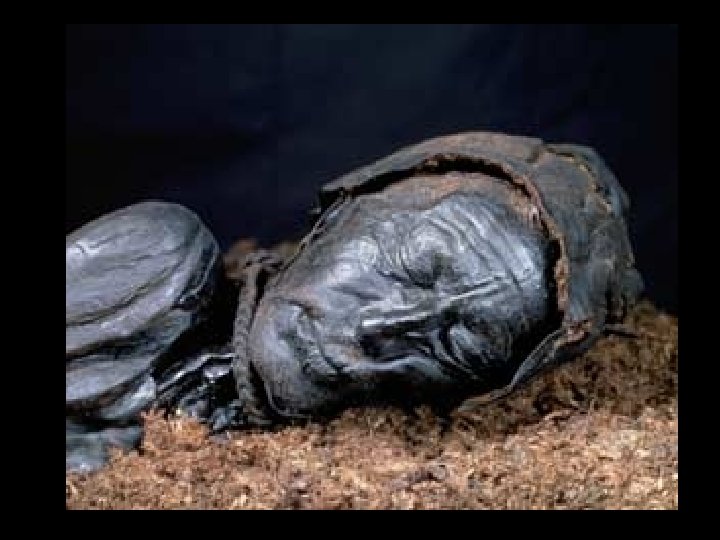
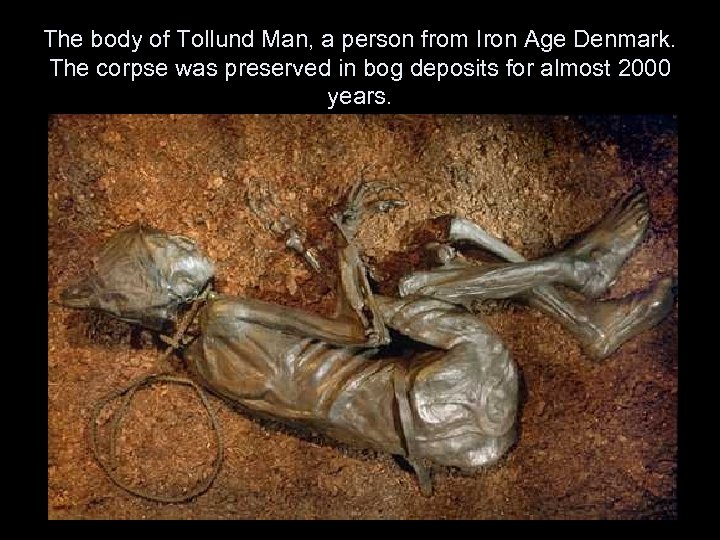 The body of Tollund Man, a person from Iron Age Denmark. The corpse was preserved in bog deposits for almost 2000 years.
The body of Tollund Man, a person from Iron Age Denmark. The corpse was preserved in bog deposits for almost 2000 years.

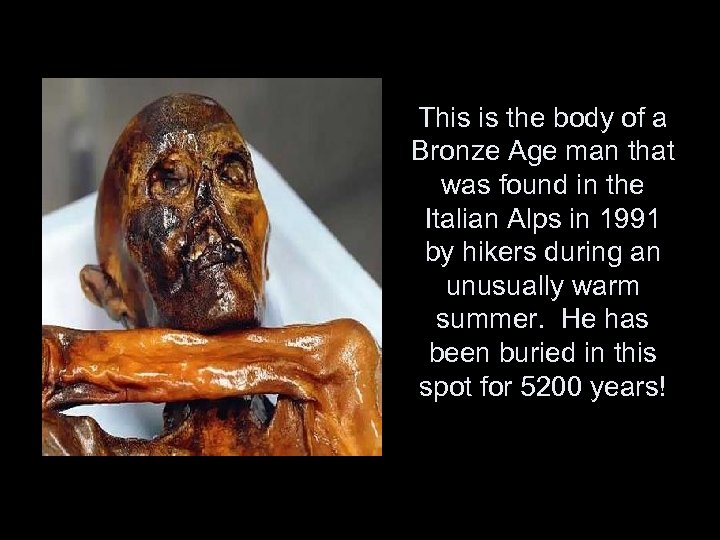 This is the body of a Bronze Age man that was found in the Italian Alps in 1991 by hikers during an unusually warm summer. He has been buried in this spot for 5200 years!
This is the body of a Bronze Age man that was found in the Italian Alps in 1991 by hikers during an unusually warm summer. He has been buried in this spot for 5200 years!


