Prehistory.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
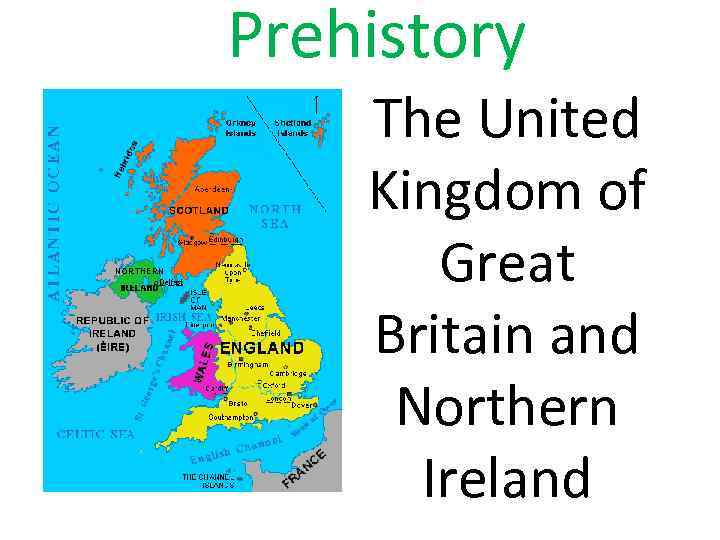
Prehistory The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
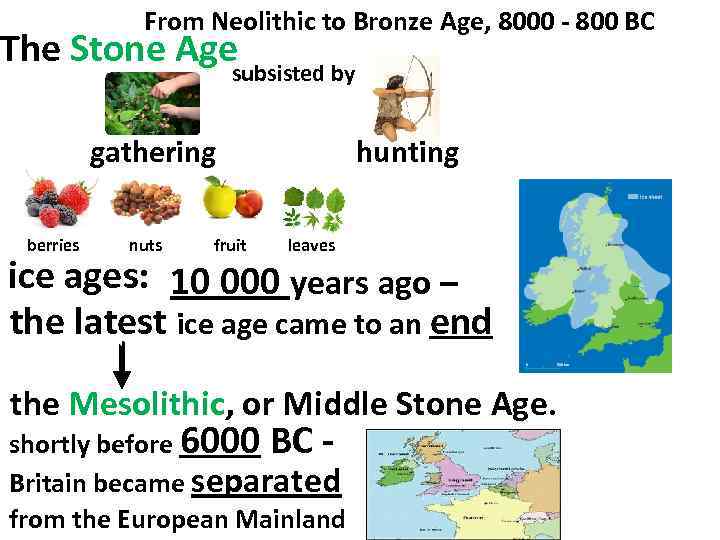
From Neolithic to Bronze Age, 8000 - 800 BC The Stone Agesubsisted by gathering berries nuts fruit hunting leaves ice ages: 10 000 years ago – the latest ice age came to an end the Mesolithic, or Middle Stone Age. shortly before 6000 BC - Britain became separated from the European Mainland

one of the biggest changes in human history - the introduction of farming 5000 BC - 4500 BC The spreading took 2000 years the Neolithic or New Stone Age sheep goat pig dog settled way of life wheat barley (ячмень)
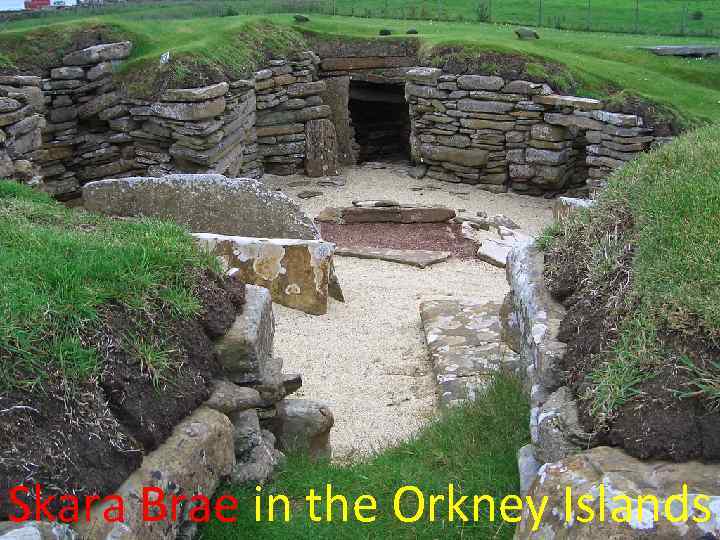

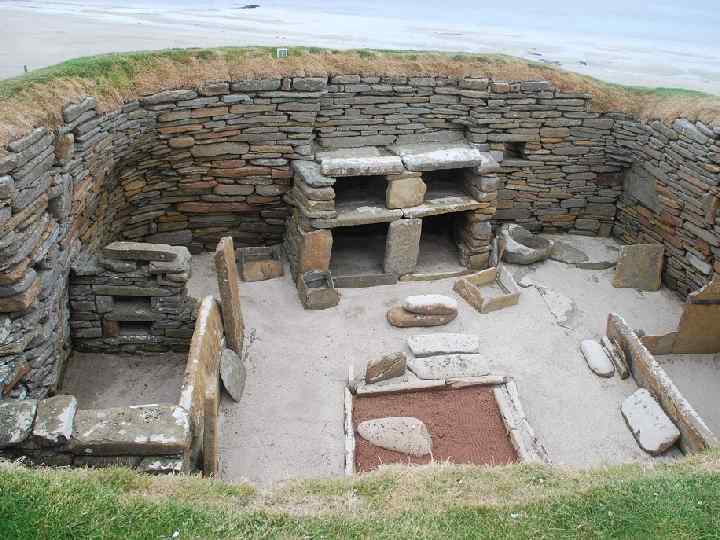
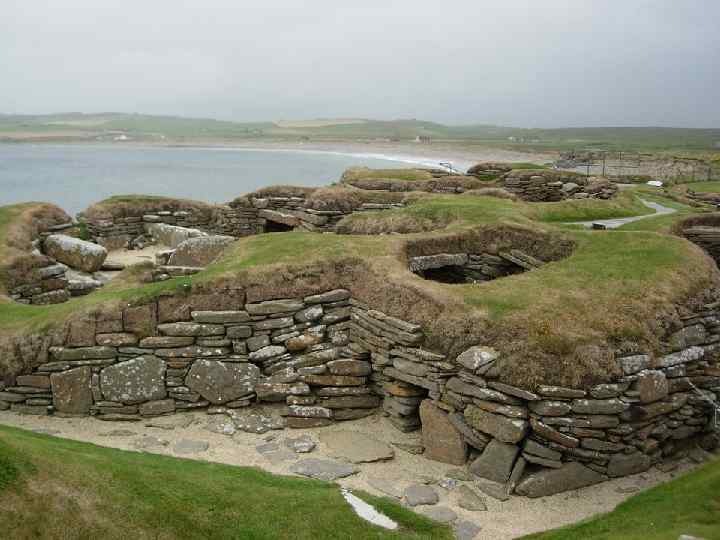
Skara Brae in the Orkney Islands

rectangular thatched buildings made from timber with walls of wattle (woven hazel rods) smeared with a plaster-like 'daub' (made from clay, straw and cow dung)
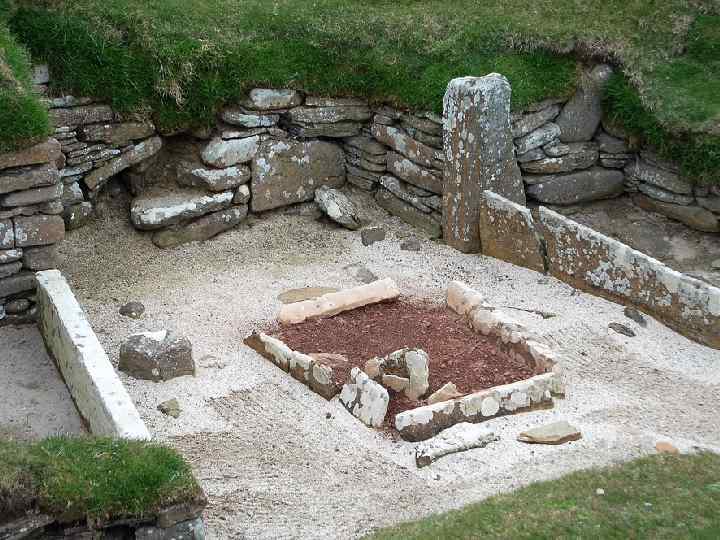
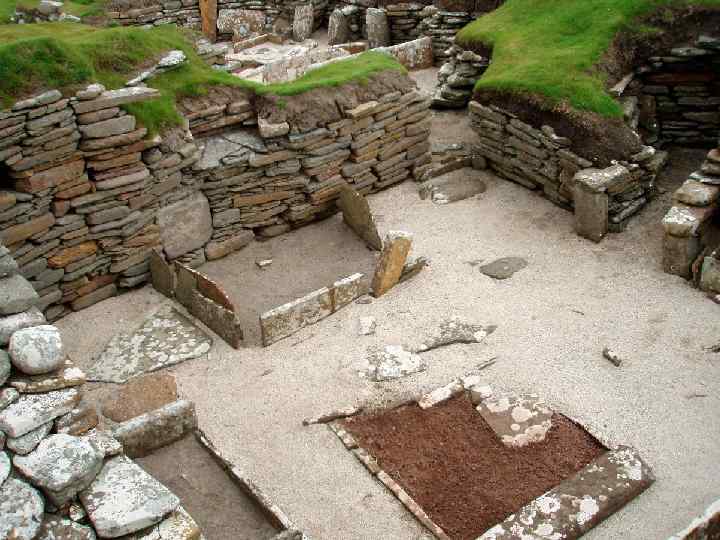





≈3800 BC the Middle Neolithic the first large communal tombs long barrows/ mounds the earliest ceremonial monuments to socialise to meet new partners to acquire fresh livestock to exchange ceremonial gifts to perform rituals pottery human to bury significant items axe head vessels skull

passage graves aligned according to the position of the sun during the winter or summer solstice. the central burial chamber

≈3000 BC 'henge' monuments incorporate lunar and solar alignments to unite the physical and social structures of human societies with the powers of the natural world ≈ calendars

2500 BC The Bronze Age tools bronze copper tin
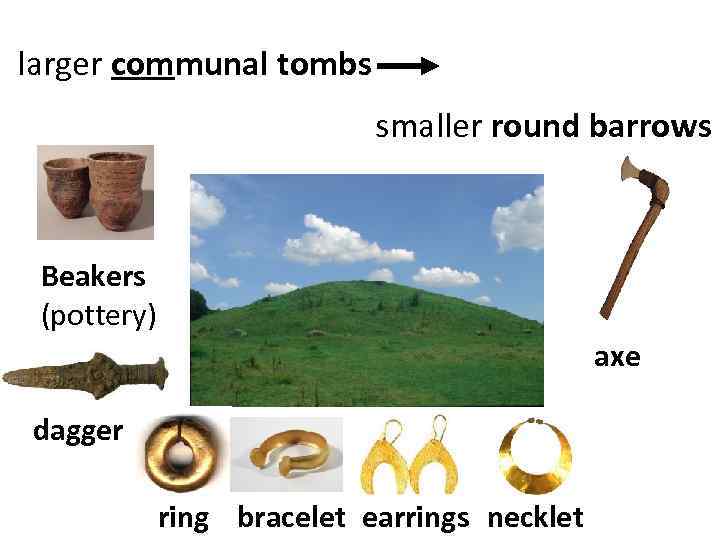
larger communal tombs smaller round barrows Beakers (pottery) axe dagger ring bracelet earrings necklet

Houses : round a conical roof a single entrance.

The Middle Bronze Age (1500 - 1250 BC) important period of change: cremation in large open cemeteries urn round houses were grouped together increasing number of metalwork hoards the first field systems in Britain

The Late Bronze Age (1250 -800 BC) new styles of metalwork and pottery horse-riding the first construction of a few hillforts the start of the so-called 'Celtic' way of life

The Iron Age, 800 BC - AD 43 the gradual introduction of iron working technology 500 -400 BC widespread strong regional groupings By 1 BC 'tribal' states and kingdoms the potter's wheel the lathe (shale objects) the rotary quern for grinding grain new crops, including improved varieties of barley and wheat increased farming of peas, beans, flax and other crops the iron-tipped ploughshare at the end of 2 BC coinage flax – лен

hill forts ≈3000 Maiden Castle in Dorset a major, planned settlement with zones for food storage, crop processing, domestic habitation, religious buildings Old Oswestry in Shropshire Danebury in Hampshire the emergence of more centralised tribal states ≈100 BC hill forts were abandoned

the roundhouse made of timber or stone with a roof covering of thatch or turf low circular walls with clear entrances Crannogs artificial islands stone and timber

‘Brochs’ (Scotland) large stone structures tall tower structures often surrounded by smaller roundhouses

‘Oppida’ in southern Britain political, economic and religious centres production centres for Iron Age coins,

http: //www. bgs. ac. uk http: //www. prehistoric. org. uk/ http: //www. bbc. co. uk/history/ancient/british_prehistory http: //www. phenomenica. com/2008/10/skara-brae. html http: //www. sacred-destinations. com/england/prehistoric-england. htm http: //www. english-heritage. org. uk/professional/research/strategies/researchstrategies/prehistoric/ http: //www. britainexpress. com/wales/az/ancient/index. htm http: //www. bbc. co. uk/wales/history/sites/themes/guide/ch 1_prehistoric_wales. shtml http: //www. ancient-wisdom. co. uk/wales. htm http: //www. scotland. org/culture/history-and-tradition/ancient-times/ http: //www. historic-scotland. gov. uk http: //www. sacred-destinations. com/ireland/prehistoric-ireland. htm http: //www. wesleyjohnston. com/users/ireland/past/ pre_norman_history/neolithic_age. html http: //www. megalithomania. com/
Prehistory.ppt