Lesson 1 Academic-prefixes.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Prefixes & Suffixes
Prefixes & Suffixes
 Prefixes A prefix goes at the beginning of a word. A suffix goes at the end of a word. A prefix is placed at the beginning of a word to modify or change its meaning. This is a list of the most common prefixes in English, together with their basic meaning and some examples. You can find more detail or precision for each prefix in any good dictionary. The origins of words are extremely complicated. You should use this list as a guide only, to help you understand possible meanings. But be very careful, because often what appears to be a prefix is not a prefix at all. Note also that this list does not include elements like "auto-" or " bio-", because these are "combining forms", not prefixes.
Prefixes A prefix goes at the beginning of a word. A suffix goes at the end of a word. A prefix is placed at the beginning of a word to modify or change its meaning. This is a list of the most common prefixes in English, together with their basic meaning and some examples. You can find more detail or precision for each prefix in any good dictionary. The origins of words are extremely complicated. You should use this list as a guide only, to help you understand possible meanings. But be very careful, because often what appears to be a prefix is not a prefix at all. Note also that this list does not include elements like "auto-" or " bio-", because these are "combining forms", not prefixes.
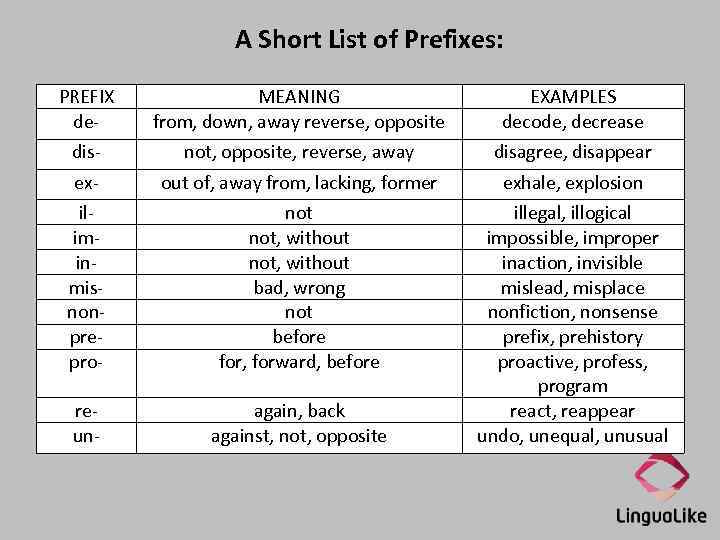 A Short List of Prefixes: PREFIX de- MEANING from, down, away reverse, opposite EXAMPLES decode, decrease dis- not, opposite, reverse, away disagree, disappear ex- out of, away from, lacking, former exhale, explosion iliminmisnonprepro- not, without bad, wrong not before for, forward, before reun- again, back against, not, opposite illegal, illogical impossible, improper inaction, invisible mislead, misplace nonfiction, nonsense prefix, prehistory proactive, profess, program react, reappear undo, unequal, unusual
A Short List of Prefixes: PREFIX de- MEANING from, down, away reverse, opposite EXAMPLES decode, decrease dis- not, opposite, reverse, away disagree, disappear ex- out of, away from, lacking, former exhale, explosion iliminmisnonprepro- not, without bad, wrong not before for, forward, before reun- again, back against, not, opposite illegal, illogical impossible, improper inaction, invisible mislead, misplace nonfiction, nonsense prefix, prehistory proactive, profess, program react, reappear undo, unequal, unusual
 Learning the prefixes, suffixes and roots found in this site will help you with your knowledge of the English Language. Why? How? Many words -- though not a majority it's still a large percentage -- are made up of prefixes or suffixes added to a root, or root word. And most of the prefixes, suffixes and roots come from either the Greek or Latin Languages. It's a fact. Learning Greek prefixes will help you in your knowledge of English so really spend some time and do learn the following!
Learning the prefixes, suffixes and roots found in this site will help you with your knowledge of the English Language. Why? How? Many words -- though not a majority it's still a large percentage -- are made up of prefixes or suffixes added to a root, or root word. And most of the prefixes, suffixes and roots come from either the Greek or Latin Languages. It's a fact. Learning Greek prefixes will help you in your knowledge of English so really spend some time and do learn the following!
 Latin & Greek Roots Resource Pack http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6825041/la-roots-resource-pack-pdf 354 k? da=y This has some good information that can be used to help. Complete list of Prefixes & Suffixes http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6823093/complete-list-of-prefixes-docx 64 k? da=y Greek Prefixes & Meanings http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6823094/greek-prefixes-meanings-usagedocx-13 k? da=y Latin Prefixes & Meanings http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6823095/latin-prefixes-meanings-usagedocx-13 k? da=y Latin Suffixes http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6825040/suffixes-docx-17 k? da=y
Latin & Greek Roots Resource Pack http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6825041/la-roots-resource-pack-pdf 354 k? da=y This has some good information that can be used to help. Complete list of Prefixes & Suffixes http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6823093/complete-list-of-prefixes-docx 64 k? da=y Greek Prefixes & Meanings http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6823094/greek-prefixes-meanings-usagedocx-13 k? da=y Latin Prefixes & Meanings http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6823095/latin-prefixes-meanings-usagedocx-13 k? da=y Latin Suffixes http: //www. keepandshare. com/doc/6825040/suffixes-docx-17 k? da=y
 What is a suffix? Answering the 'what is a suffix' question, it's probably best to keep it short and sweet. A suffix, in short, is a word ending. It is a letter, or group of letters, added to the end of a word or word root. When you add a suffix to a word root you often change the meaning of the word. The examples that follow should clear up any confusion about this question.
What is a suffix? Answering the 'what is a suffix' question, it's probably best to keep it short and sweet. A suffix, in short, is a word ending. It is a letter, or group of letters, added to the end of a word or word root. When you add a suffix to a word root you often change the meaning of the word. The examples that follow should clear up any confusion about this question.
 Example: talk - talking where 'ing' is an inflectional suffix added to the word 'talk. ‘ talk - talkative where 'ative' is a derivational suffix added to the word 'talk. ' Now, as seen in the example above, there are two basic types, or kinds, of suffixes that answer the 'what is a suffix' question. Inflectional suffixes basically change the word within its syntactic category. From present to past and from singular to plural. Derivational suffixes change the word from one part of speech into another. From verbs to nouns or from adjectives to adverbs thereby making 'derivatives. '
Example: talk - talking where 'ing' is an inflectional suffix added to the word 'talk. ‘ talk - talkative where 'ative' is a derivational suffix added to the word 'talk. ' Now, as seen in the example above, there are two basic types, or kinds, of suffixes that answer the 'what is a suffix' question. Inflectional suffixes basically change the word within its syntactic category. From present to past and from singular to plural. Derivational suffixes change the word from one part of speech into another. From verbs to nouns or from adjectives to adverbs thereby making 'derivatives. '
 Inflectional suffixes do not change the meaning of the original word. So in "Every day I walk to school" and "Yesterday I walked to school", the words walk and walked have the same basic meaning. In "I have one car" and "I have two cars", the basic meaning of the words car and cars is exactly the same. In these cases, the suffix is added simply for grammatical "correctness". Look at these examples:
Inflectional suffixes do not change the meaning of the original word. So in "Every day I walk to school" and "Yesterday I walked to school", the words walk and walked have the same basic meaning. In "I have one car" and "I have two cars", the basic meaning of the words car and cars is exactly the same. In these cases, the suffix is added simply for grammatical "correctness". Look at these examples:
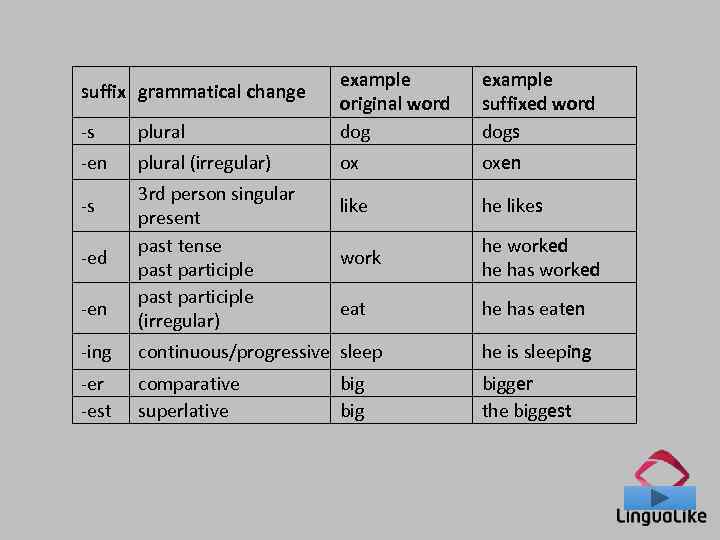 -s plural example original word dog -en plural (irregular) ox oxen like he likes work he worked he has worked eat he has eaten suffix grammatical change -s -ed -en 3 rd person singular present past tense past participle (irregular) example suffixed word dogs -ing continuous/progressive sleep he is sleeping -er -est comparative superlative bigger the biggest big
-s plural example original word dog -en plural (irregular) ox oxen like he likes work he worked he has worked eat he has eaten suffix grammatical change -s -ed -en 3 rd person singular present past tense past participle (irregular) example suffixed word dogs -ing continuous/progressive sleep he is sleeping -er -est comparative superlative bigger the biggest big
 Derivational suffixes With derivational suffixes, the new word has a new meaning, and is usually a different part of speech. But the new meaning is related to the old meaning - it is "derived" from the old meaning. We can add more than one suffix, as in this example: derive (verb) + tion = derivation (noun) + al = derivational (adjective)
Derivational suffixes With derivational suffixes, the new word has a new meaning, and is usually a different part of speech. But the new meaning is related to the old meaning - it is "derived" from the old meaning. We can add more than one suffix, as in this example: derive (verb) + tion = derivation (noun) + al = derivational (adjective)
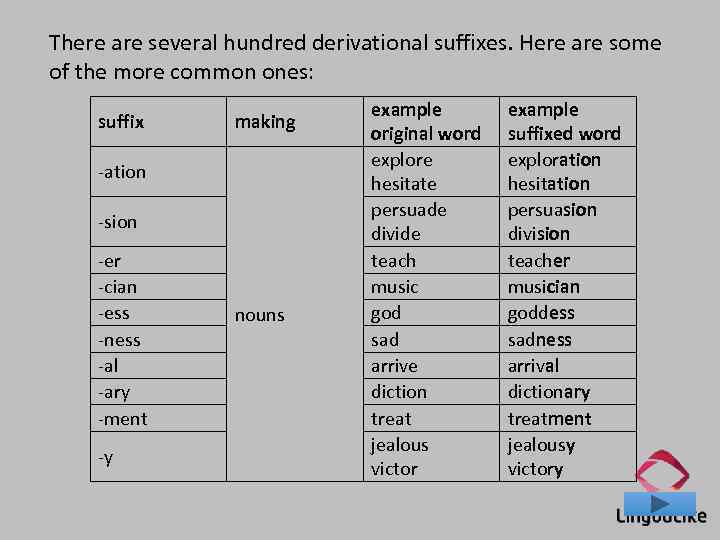 There are several hundred derivational suffixes. Here are some of the more common ones: suffix making -ation -sion -er -cian -ess -ness -al -ary -ment -y nouns example original word explore hesitate persuade divide teach music god sad arrive diction treat jealous victor example suffixed word exploration hesitation persuasion division teacher musician goddess sadness arrival dictionary treatment jealousy victory
There are several hundred derivational suffixes. Here are some of the more common ones: suffix making -ation -sion -er -cian -ess -ness -al -ary -ment -y nouns example original word explore hesitate persuade divide teach music god sad arrive diction treat jealous victor example suffixed word exploration hesitation persuasion division teacher musician goddess sadness arrival dictionary treatment jealousy victory
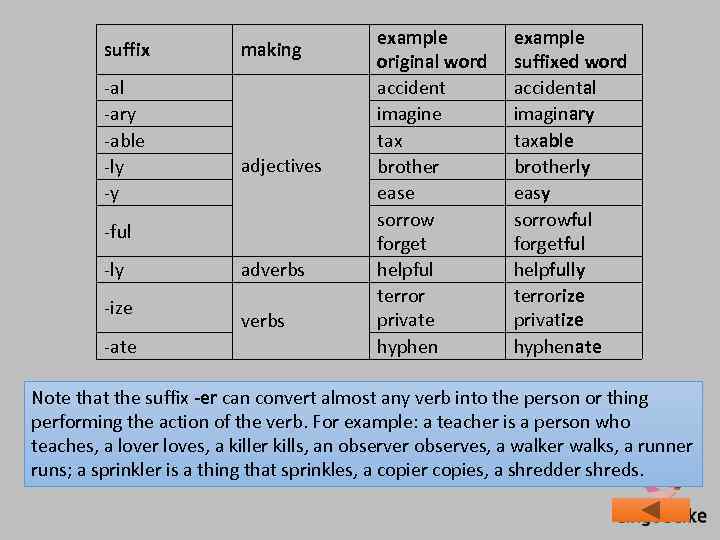 suffix -al -ary -able -ly -y making adjectives -ful -ly -ize -ate adverbs example original word accident imagine tax brother ease sorrow forget helpful terror private hyphen example suffixed word accidental imaginary taxable brotherly easy sorrowful forgetful helpfully terrorize privatize hyphenate Note that the suffix -er can convert almost any verb into the person or thing performing the action of the verb. For example: a teacher is a person who teaches, a lover loves, a killer kills, an observer observes, a walker walks, a runner runs; a sprinkler is a thing that sprinkles, a copier copies, a shredder shreds.
suffix -al -ary -able -ly -y making adjectives -ful -ly -ize -ate adverbs example original word accident imagine tax brother ease sorrow forget helpful terror private hyphen example suffixed word accidental imaginary taxable brotherly easy sorrowful forgetful helpfully terrorize privatize hyphenate Note that the suffix -er can convert almost any verb into the person or thing performing the action of the verb. For example: a teacher is a person who teaches, a lover loves, a killer kills, an observer observes, a walker walks, a runner runs; a sprinkler is a thing that sprinkles, a copier copies, a shredder shreds.
 Determining a Root Word Many of the words we use come from a root word. Once you pull off any prefixes or suffixes, the root will be normally at the front or the back of the remaining word. A little digging will uncover just what the root word really means. For example, in a word such as scissors, the root word is sciss, which means cut. Some examples of root words can be found in everyday language. The root word for bicycle would be cycle and the root word for transactions would be action. Words can even have two root words, such as schoolhouse
Determining a Root Word Many of the words we use come from a root word. Once you pull off any prefixes or suffixes, the root will be normally at the front or the back of the remaining word. A little digging will uncover just what the root word really means. For example, in a word such as scissors, the root word is sciss, which means cut. Some examples of root words can be found in everyday language. The root word for bicycle would be cycle and the root word for transactions would be action. Words can even have two root words, such as schoolhouse
 Root Words Can Have Their Own Meaning There are many root words that are frequently used as parts of common words in the English language. For example, the following root words are provided with their meaning and, in italics, with an example of the root word as part of a word Aqua - means water. Aquamarine Arbor - means tree. Arboreal Audio - means sound or hearing. Audible Bell - means war. Bellicism Dict - means say. Dictation Geo - means earth. Geography Graph - means write. Graphics Hydra - means water. Hydrofoil Man - means hand. Manual Min - means small. Minimal Nov - means new. Novice Path - means feeling or suffering. Pathetic and Apathy Sol - means sun. Solar Therm - means heat. Thermometer Vac - means empty. Vacuum Vent - means opening to let air in. Ventilate Vit - means life. Vitamin Liter, glyph, cap, morph, crypt, plan, ego, scent, and zoo are also root words. For example, animal is the actual meaning of the root word zoo, so when they named the zoo, they were right.
Root Words Can Have Their Own Meaning There are many root words that are frequently used as parts of common words in the English language. For example, the following root words are provided with their meaning and, in italics, with an example of the root word as part of a word Aqua - means water. Aquamarine Arbor - means tree. Arboreal Audio - means sound or hearing. Audible Bell - means war. Bellicism Dict - means say. Dictation Geo - means earth. Geography Graph - means write. Graphics Hydra - means water. Hydrofoil Man - means hand. Manual Min - means small. Minimal Nov - means new. Novice Path - means feeling or suffering. Pathetic and Apathy Sol - means sun. Solar Therm - means heat. Thermometer Vac - means empty. Vacuum Vent - means opening to let air in. Ventilate Vit - means life. Vitamin Liter, glyph, cap, morph, crypt, plan, ego, scent, and zoo are also root words. For example, animal is the actual meaning of the root word zoo, so when they named the zoo, they were right.
 Root Words Can Be Partial Words Some root words aren’t even fully words, such as bio. Bio is the root word for biography or biology. Bio means life. Here a few more examples: Acri - means bitter. Acrimony Carn - means flesh. Carnivorous Corp - means body. Corporal punishment Deca - means ten. Decade Erg - means work. Energy Gen - means birth. Genesis Lum - means light. Luminary Sen - means old. Senior Tele - means far. Telephone Vor - means eat greedily. Devour By knowing different root words, you can understand what a word means even if you don’t know the word, since the meaning can be derived from a combination of the root words.
Root Words Can Be Partial Words Some root words aren’t even fully words, such as bio. Bio is the root word for biography or biology. Bio means life. Here a few more examples: Acri - means bitter. Acrimony Carn - means flesh. Carnivorous Corp - means body. Corporal punishment Deca - means ten. Decade Erg - means work. Energy Gen - means birth. Genesis Lum - means light. Luminary Sen - means old. Senior Tele - means far. Telephone Vor - means eat greedily. Devour By knowing different root words, you can understand what a word means even if you don’t know the word, since the meaning can be derived from a combination of the root words.
 Meaning Does Not Always Equal the Definition Some root words make less sense. For example, take the word apology. The root word "logy" is the study of something, and apo is from or away from. So, if you interpret the meaning of apology based on root words alone, you would see that it means "away from the study of something? " Not a very good explanation. When we see apology we think sorry or sad about something. So, although many words have root words, knowing the meaning of the roots won't always provide you with a clear definition. The web’s largest root words site https: //www. learnthat. org/pages/view/roots. html
Meaning Does Not Always Equal the Definition Some root words make less sense. For example, take the word apology. The root word "logy" is the study of something, and apo is from or away from. So, if you interpret the meaning of apology based on root words alone, you would see that it means "away from the study of something? " Not a very good explanation. When we see apology we think sorry or sad about something. So, although many words have root words, knowing the meaning of the roots won't always provide you with a clear definition. The web’s largest root words site https: //www. learnthat. org/pages/view/roots. html
 Exercises Choose the best available answer for each of the following words: 1) telescope a) device for looking at stars b) a deep sea animal with eight arms c) device for looking at tiny objects d) device for making sound louder(bigger) 2) microphone a) device for making sound louder(bigger) b) remove from the centre to surrounding areas c) device for looking at stars d) device for looking at tiny objects
Exercises Choose the best available answer for each of the following words: 1) telescope a) device for looking at stars b) a deep sea animal with eight arms c) device for looking at tiny objects d) device for making sound louder(bigger) 2) microphone a) device for making sound louder(bigger) b) remove from the centre to surrounding areas c) device for looking at stars d) device for looking at tiny objects
 3) microscope a) device for looking at tiny objects b) ship that travels under the ocean c) device for looking at stars d) a deep sea animal with eight arms 4) submarine a) device for looking at stars b) a deep sea animal with eight arms c) device for making sound louder(bigger) d) ship that travels under the ocean
3) microscope a) device for looking at tiny objects b) ship that travels under the ocean c) device for looking at stars d) a deep sea animal with eight arms 4) submarine a) device for looking at stars b) a deep sea animal with eight arms c) device for making sound louder(bigger) d) ship that travels under the ocean
 5) decentralize a) device for looking at tiny objects b) a deep sea animal with eight arms c) device for looking at stars d) remove from the centre to surrounding areas 6) octopus a) device for looking at tiny objects b) device for looking at stars c) a deep sea animal with eight arms d) ship that travels under the ocean
5) decentralize a) device for looking at tiny objects b) a deep sea animal with eight arms c) device for looking at stars d) remove from the centre to surrounding areas 6) octopus a) device for looking at tiny objects b) device for looking at stars c) a deep sea animal with eight arms d) ship that travels under the ocean
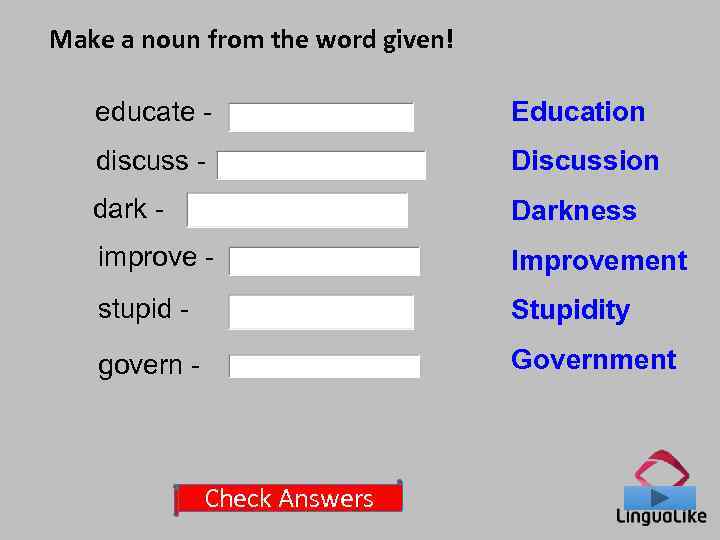 Make a noun from the word given! educate - Education discuss - Discussion dark - Darkness improve - Improvement stupid - Stupidity govern - Government Check Answers
Make a noun from the word given! educate - Education discuss - Discussion dark - Darkness improve - Improvement stupid - Stupidity govern - Government Check Answers
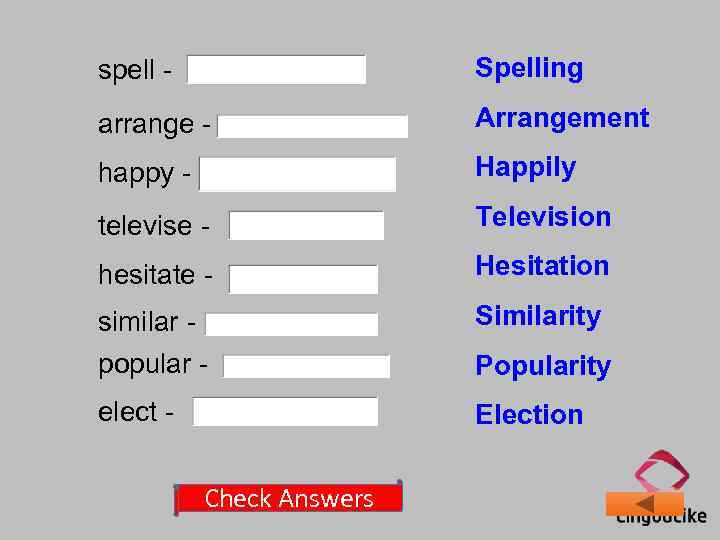 spell - Spelling arrange - Arrangement happy - Happily televise - Television hesitate - Hesitation similar popular - Similarity elect - Election Check Answers Popularity
spell - Spelling arrange - Arrangement happy - Happily televise - Television hesitate - Hesitation similar popular - Similarity elect - Election Check Answers Popularity


