28856a74af19cf637ccfb8b8a0467a4e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Preferred Stock Valuation • No ownership as with common stock • Give higher return than bonds (debt) VPS : Value of Preferred Stock, $100/sh DPS : Preferred Stock Dividend, $10/sh KPS : Return On Investment or Required Return of Preferred Stock investors, eg. 10% (Risk Free Return + Risk)
Preferred Stock Valuation • No ownership as with common stock • Give higher return than bonds (debt) VPS : Value of Preferred Stock, $100/sh DPS : Preferred Stock Dividend, $10/sh KPS : Return On Investment or Required Return of Preferred Stock investors, eg. 10% (Risk Free Return + Risk)
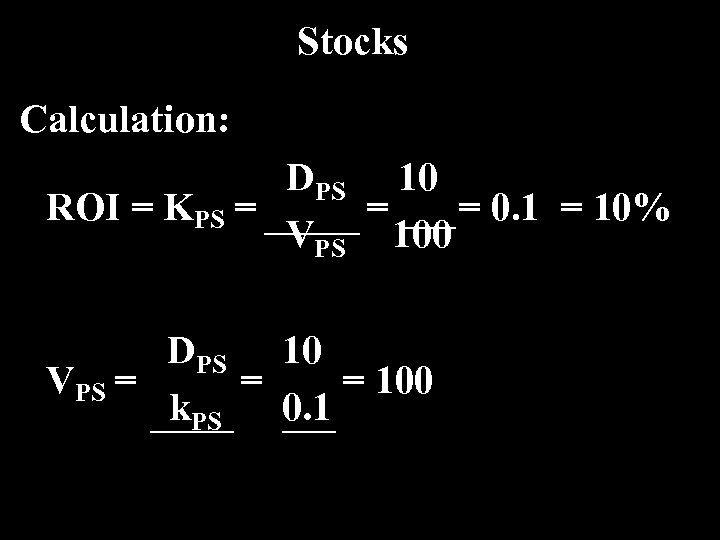 Stocks Calculation: DPS 10 ROI = KPS = = = 0. 1 = 10% VPS 100 DPS 10 VPS = = = 100 k. PS 0. 1
Stocks Calculation: DPS 10 ROI = KPS = = = 0. 1 = 10% VPS 100 DPS 10 VPS = = = 100 k. PS 0. 1
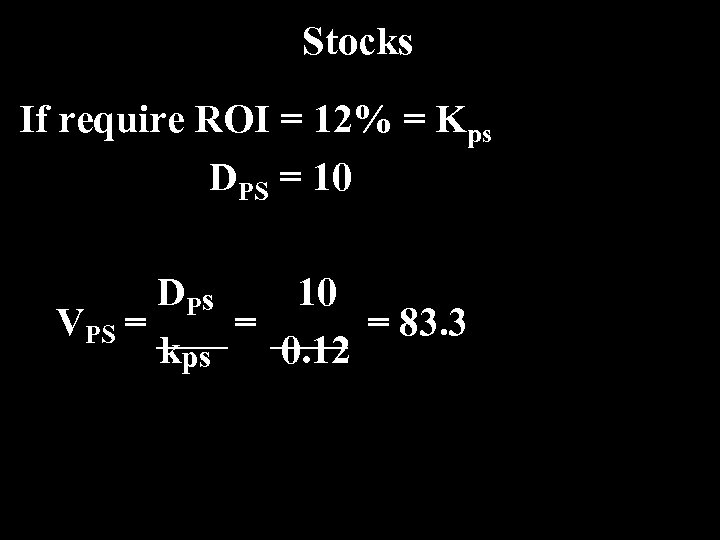 Stocks If require ROI = 12% = Kps DPS = 10 DP s 10 VPS = = = 83. 3 kps 0. 12
Stocks If require ROI = 12% = Kps DPS = 10 DP s 10 VPS = = = 83. 3 kps 0. 12
 Common Stock Valuation Pt = Stock price at time t Dt = Dividend at time t D 0 = Dividend at time t = 0 (just paid) D 1 = Dividend at time t = 1 (1 year from today) KS = Return on Investment on Common Stock
Common Stock Valuation Pt = Stock price at time t Dt = Dividend at time t D 0 = Dividend at time t = 0 (just paid) D 1 = Dividend at time t = 1 (1 year from today) KS = Return on Investment on Common Stock
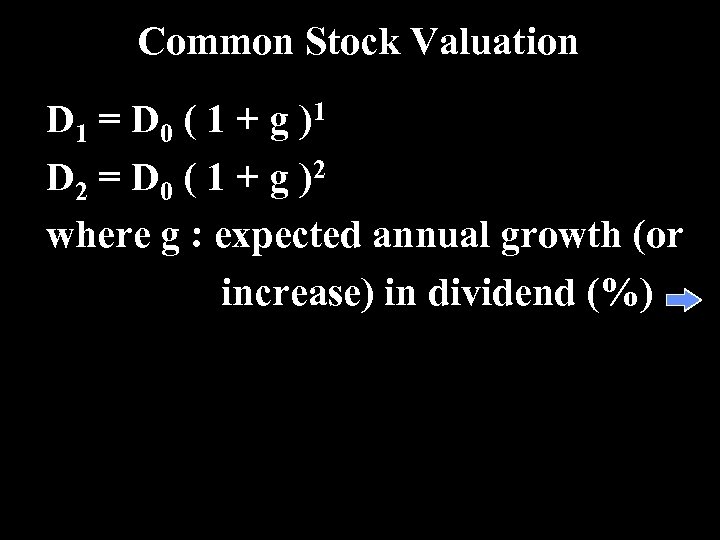 Common Stock Valuation D 1 = D 0 ( 1 + g ) 1 D 2 = D 0 ( 1 + g ) 2 where g : expected annual growth (or increase) in dividend (%)
Common Stock Valuation D 1 = D 0 ( 1 + g ) 1 D 2 = D 0 ( 1 + g ) 2 where g : expected annual growth (or increase) in dividend (%)
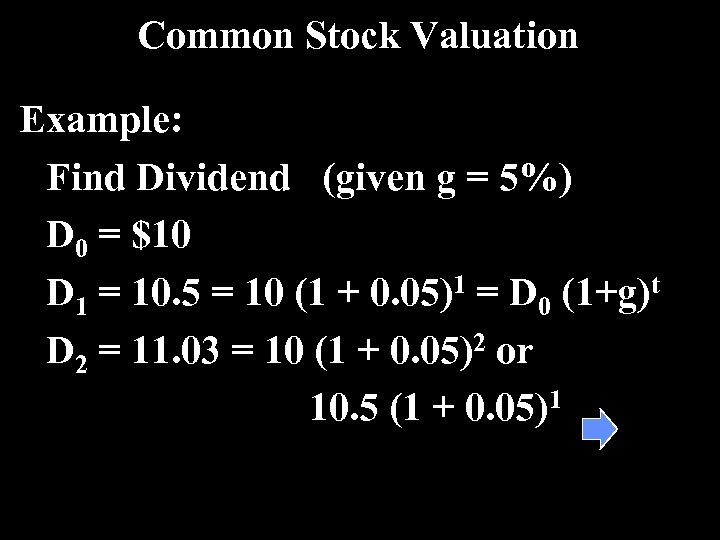 Common Stock Valuation Example: Find Dividend (given g = 5%) D 0 = $10 D 1 = 10. 5 = 10 (1 + 0. 05)1 = D 0 (1+g)t D 2 = 11. 03 = 10 (1 + 0. 05)2 or 10. 5 (1 + 0. 05)1
Common Stock Valuation Example: Find Dividend (given g = 5%) D 0 = $10 D 1 = 10. 5 = 10 (1 + 0. 05)1 = D 0 (1+g)t D 2 = 11. 03 = 10 (1 + 0. 05)2 or 10. 5 (1 + 0. 05)1
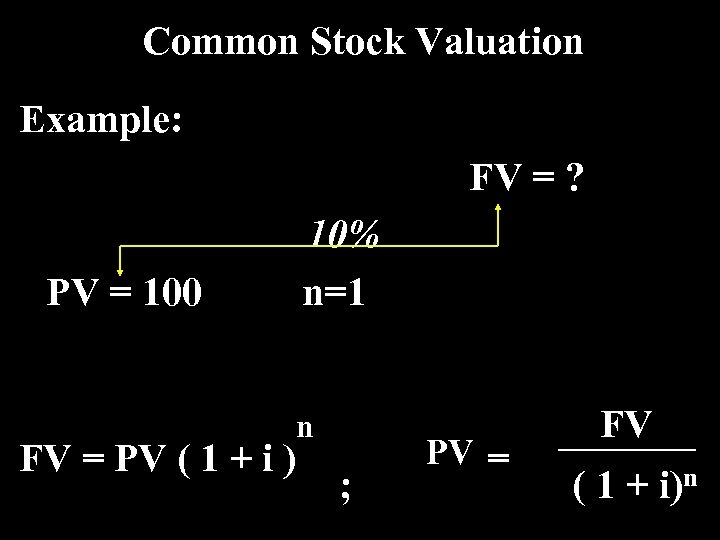 Common Stock Valuation Example: FV = ? PV = 100 FV = PV ( 1 + i ) 10% n=1 n ; PV = FV ( 1 + i)n
Common Stock Valuation Example: FV = ? PV = 100 FV = PV ( 1 + i ) 10% n=1 n ; PV = FV ( 1 + i)n
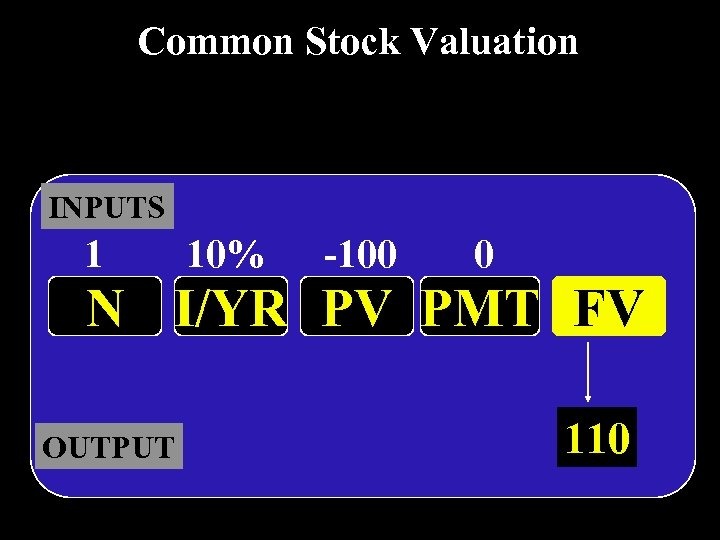 Common Stock Valuation INPUTS 1 10% -100 0 N I/YR PV PMT FV OUTPUT 110
Common Stock Valuation INPUTS 1 10% -100 0 N I/YR PV PMT FV OUTPUT 110
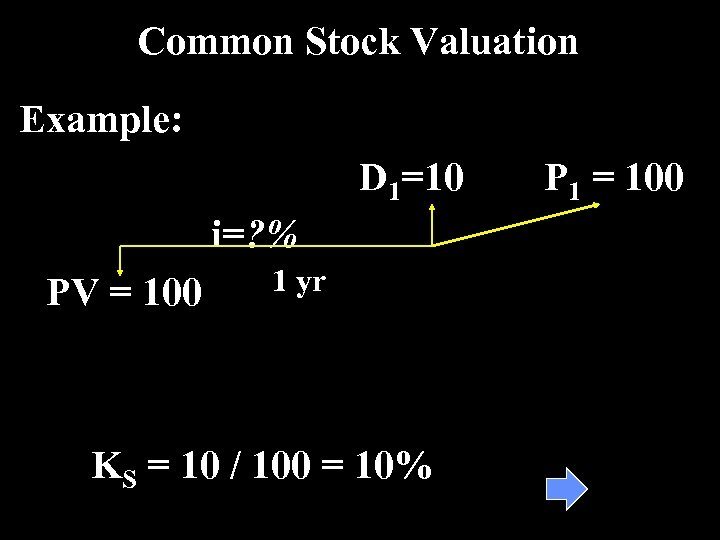 Common Stock Valuation Example: D 1=10 i=? % PV = 100 1 yr KS = 10 / 100 = 10% P 1 = 100
Common Stock Valuation Example: D 1=10 i=? % PV = 100 1 yr KS = 10 / 100 = 10% P 1 = 100
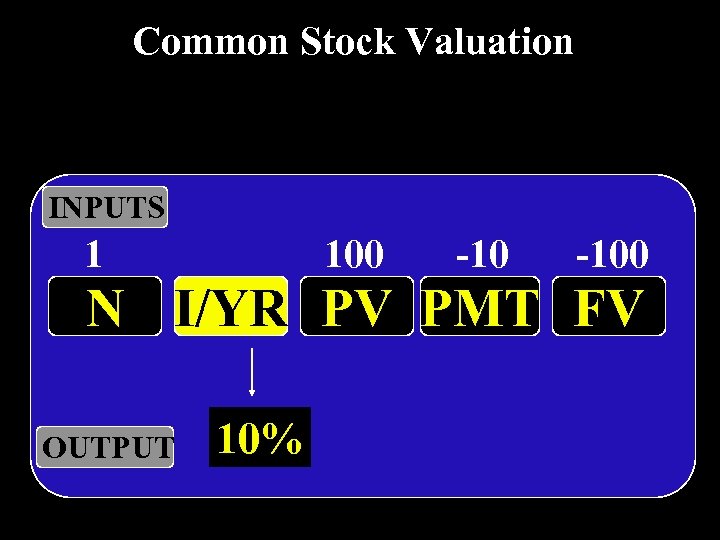 Common Stock Valuation INPUTS 1 100 -100 N I/YR PV PMT FV OUTPUT 10%
Common Stock Valuation INPUTS 1 100 -100 N I/YR PV PMT FV OUTPUT 10%
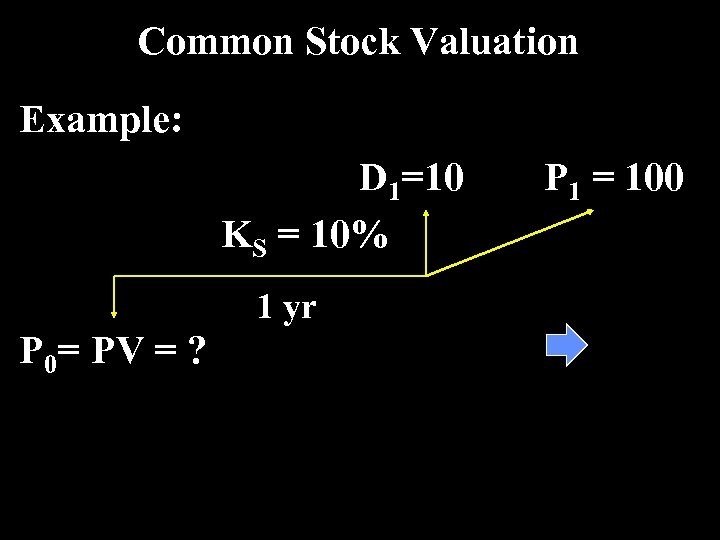 Common Stock Valuation Example: D 1=10 KS = 10% 1 yr P 0= PV = ? P 1 = 100
Common Stock Valuation Example: D 1=10 KS = 10% 1 yr P 0= PV = ? P 1 = 100
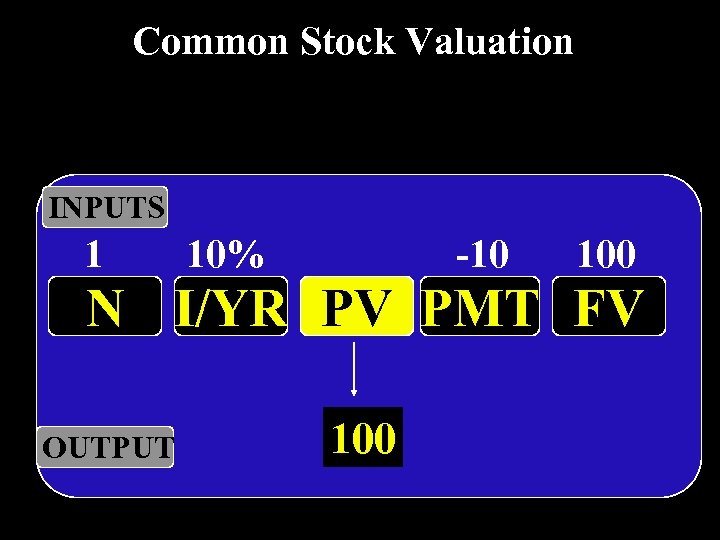 Common Stock Valuation INPUTS 1 10% -10 100 N I/YR PV PMT FV OUTPUT 100
Common Stock Valuation INPUTS 1 10% -10 100 N I/YR PV PMT FV OUTPUT 100
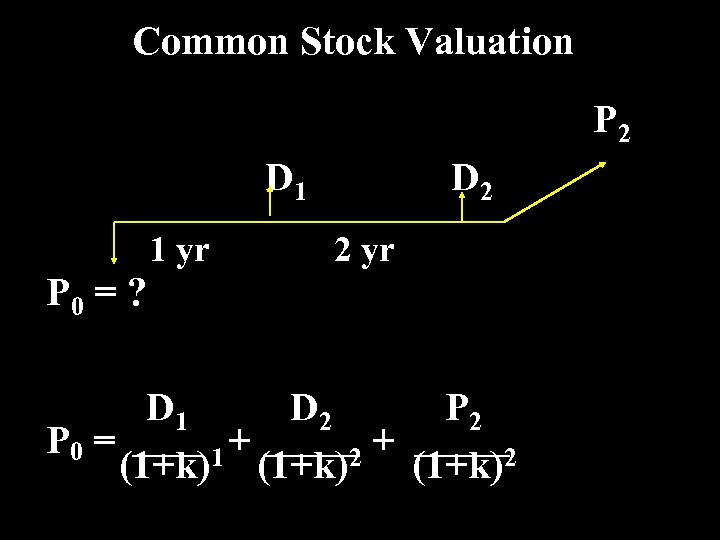 Common Stock Valuation P 2 D 1 1 yr D 2 2 yr P 0 = ? D 1 D 2 P 0 = + + 1 (1+k)2
Common Stock Valuation P 2 D 1 1 yr D 2 2 yr P 0 = ? D 1 D 2 P 0 = + + 1 (1+k)2
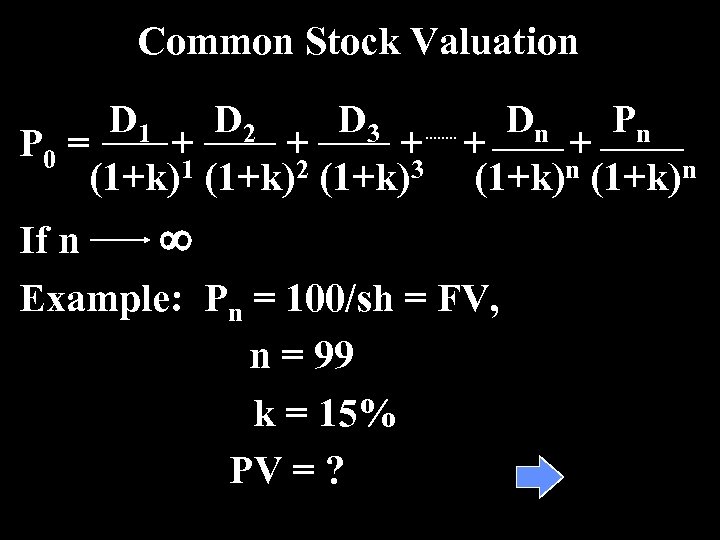 Common Stock Valuation D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn Pn P 0 = + + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n If n ¥ Example: Pn = 100/sh = FV, n = 99 k = 15% PV = ?
Common Stock Valuation D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn Pn P 0 = + + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n If n ¥ Example: Pn = 100/sh = FV, n = 99 k = 15% PV = ?
 Common Stock Valuation INPUTS 99 15% 0 -100 N I/YR PV PMT FV OUTPUT 0. 00009793
Common Stock Valuation INPUTS 99 15% 0 -100 N I/YR PV PMT FV OUTPUT 0. 00009793
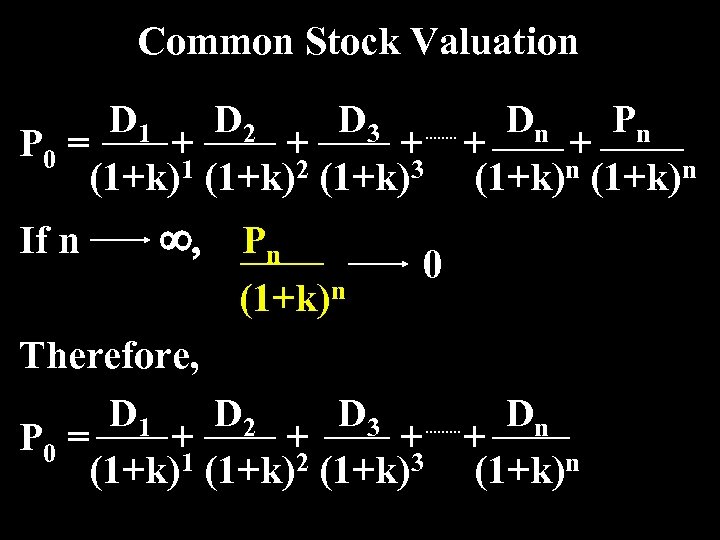 Common Stock Valuation D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn Pn P 0 = + + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n If n ¥, Pn (1+k)n 0 Therefore, D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn P 0 = + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n
Common Stock Valuation D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn Pn P 0 = + + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n If n ¥, Pn (1+k)n 0 Therefore, D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn P 0 = + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n
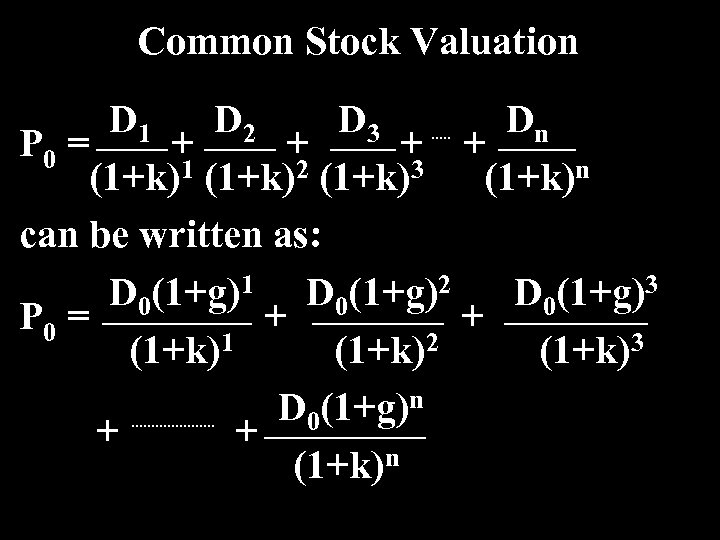 Common Stock Valuation D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn P 0 = + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n can be written as: D 0(1+g)1 D 0(1+g)2 D 0(1+g)3 P 0 = + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 D 0(1+g)n + + (1+k)n
Common Stock Valuation D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn P 0 = + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n can be written as: D 0(1+g)1 D 0(1+g)2 D 0(1+g)3 P 0 = + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 D 0(1+g)n + + (1+k)n
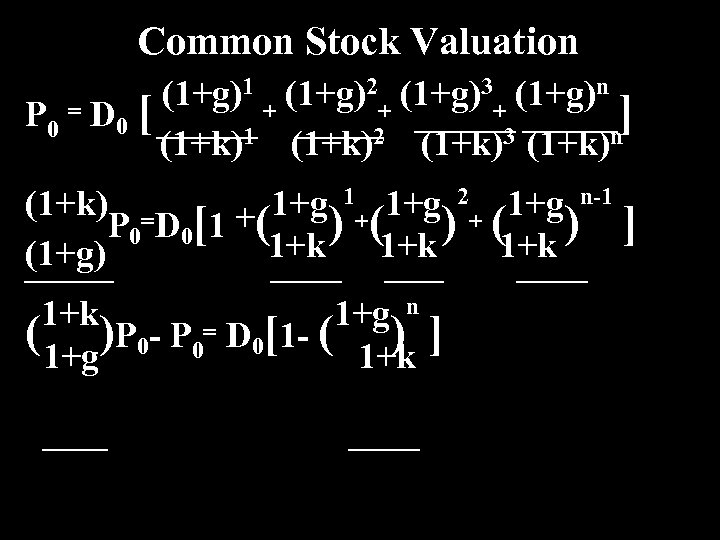 Common Stock Valuation (1+g)1 + (1+g)2+ (1+g)3+ (1+g)n P 0 = D 0 [ ] (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n (1+k) = 1+g 1+ 1+g 2+ 1+g n-1 P 0 D 0[ 1 + ( ) (1+k ) ] 1+k (1+g) 1+k 1+g n ( 1+g)P 0 - P 0= D 0[1 - ( 1+k ] )
Common Stock Valuation (1+g)1 + (1+g)2+ (1+g)3+ (1+g)n P 0 = D 0 [ ] (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n (1+k) = 1+g 1+ 1+g 2+ 1+g n-1 P 0 D 0[ 1 + ( ) (1+k ) ] 1+k (1+g) 1+k 1+g n ( 1+g)P 0 - P 0= D 0[1 - ( 1+k ] )
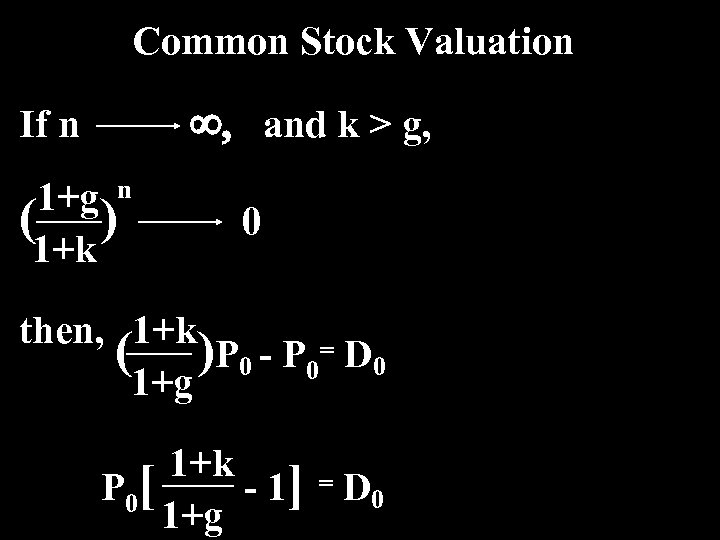 Common Stock Valuation ¥, and k > g, If n 1+g n ( ) 1+k 0 then, 1+k ( ) P 0 - P 0= D 0 1+g 1+k P 0[ - 1] = D 0 1+g
Common Stock Valuation ¥, and k > g, If n 1+g n ( ) 1+k 0 then, 1+k ( ) P 0 - P 0= D 0 1+g 1+k P 0[ - 1] = D 0 1+g
![Common Stock Valuation P 0[ 1+k-1 -g 1+g ] = D 0 k-g = Common Stock Valuation P 0[ 1+k-1 -g 1+g ] = D 0 k-g =](https://present5.com/presentation/28856a74af19cf637ccfb8b8a0467a4e/image-20.jpg) Common Stock Valuation P 0[ 1+k-1 -g 1+g ] = D 0 k-g = P 0[ ] D 0 1+g P 0 D 0 (1+g) = k-g = D 1 k-g
Common Stock Valuation P 0[ 1+k-1 -g 1+g ] = D 0 k-g = P 0[ ] D 0 1+g P 0 D 0 (1+g) = k-g = D 1 k-g
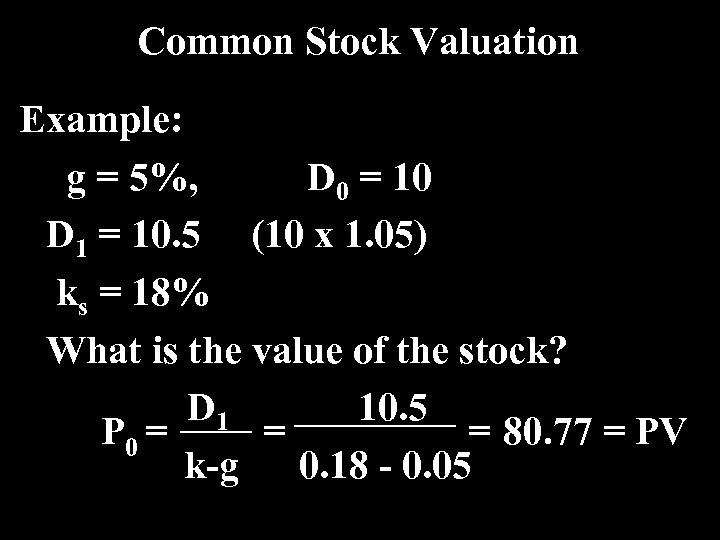 Common Stock Valuation Example: g = 5%, D 0 = 10 D 1 = 10. 5 (10 x 1. 05) ks = 18% What is the value of the stock? D 1 10. 5 P 0 = = = 80. 77 = PV k-g 0. 18 - 0. 05
Common Stock Valuation Example: g = 5%, D 0 = 10 D 1 = 10. 5 (10 x 1. 05) ks = 18% What is the value of the stock? D 1 10. 5 P 0 = = = 80. 77 = PV k-g 0. 18 - 0. 05
 Common Stock Valuation If the stock is purchased at $90, K=? 10. 5 D 1 90 = P 0 = k-g P 0 k - 0. 05 D 1 k= +g P 0 k = 17% Dividend/Stock Price = Dividend Yield
Common Stock Valuation If the stock is purchased at $90, K=? 10. 5 D 1 90 = P 0 = k-g P 0 k - 0. 05 D 1 k= +g P 0 k = 17% Dividend/Stock Price = Dividend Yield
 I. Stock Markets and Stock Reporting A. New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) B. American Stock Exchange (AMEX) C. Over-the-counter (OTC) markets D. Smaller regional markets II. Stock Market Reporting 52 Weeks Yld. P-E Sales Net High Low Stock Div. % Ratio 100 s High Low Close Chg. 1757/8 102 IBM 4. 40 3. 8 16 27989 1181/4 1151/4 1171/4 +13/4 Dividend yield = D/P = $4. 40 / $117. 25 = 3. 8%
I. Stock Markets and Stock Reporting A. New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) B. American Stock Exchange (AMEX) C. Over-the-counter (OTC) markets D. Smaller regional markets II. Stock Market Reporting 52 Weeks Yld. P-E Sales Net High Low Stock Div. % Ratio 100 s High Low Close Chg. 1757/8 102 IBM 4. 40 3. 8 16 27989 1181/4 1151/4 1171/4 +13/4 Dividend yield = D/P = $4. 40 / $117. 25 = 3. 8%
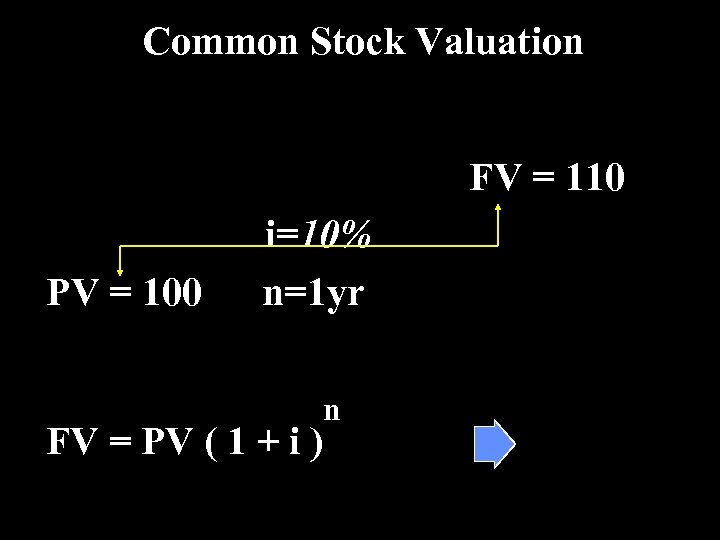 Common Stock Valuation FV = 110 PV = 100 i=10% n=1 yr FV = PV ( 1 + i ) n
Common Stock Valuation FV = 110 PV = 100 i=10% n=1 yr FV = PV ( 1 + i ) n
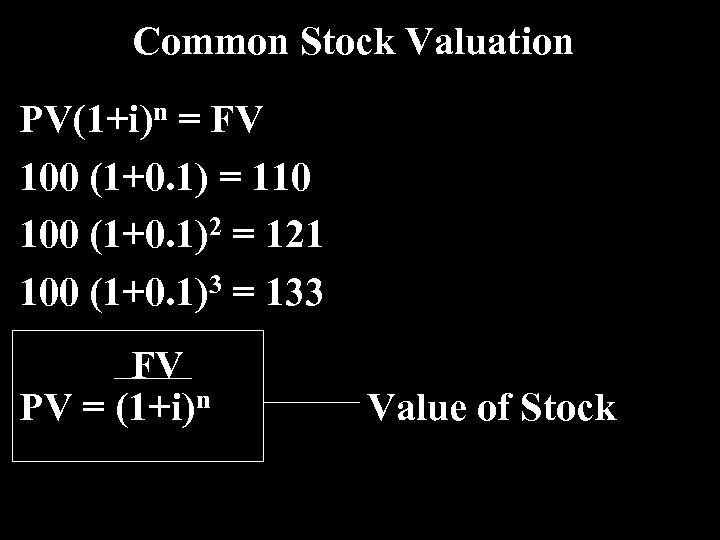 Common Stock Valuation PV(1+i)n = FV 100 (1+0. 1) = 110 100 (1+0. 1)2 = 121 100 (1+0. 1)3 = 133 FV PV = (1+i)n Value of Stock
Common Stock Valuation PV(1+i)n = FV 100 (1+0. 1) = 110 100 (1+0. 1)2 = 121 100 (1+0. 1)3 = 133 FV PV = (1+i)n Value of Stock
 Common Stock Valuation • • Discounted Valuation Approach Know FV Calculate PV (price you have to pay now) or (value of stock or bond) Bond debt - interest Stock - dividend
Common Stock Valuation • • Discounted Valuation Approach Know FV Calculate PV (price you have to pay now) or (value of stock or bond) Bond debt - interest Stock - dividend
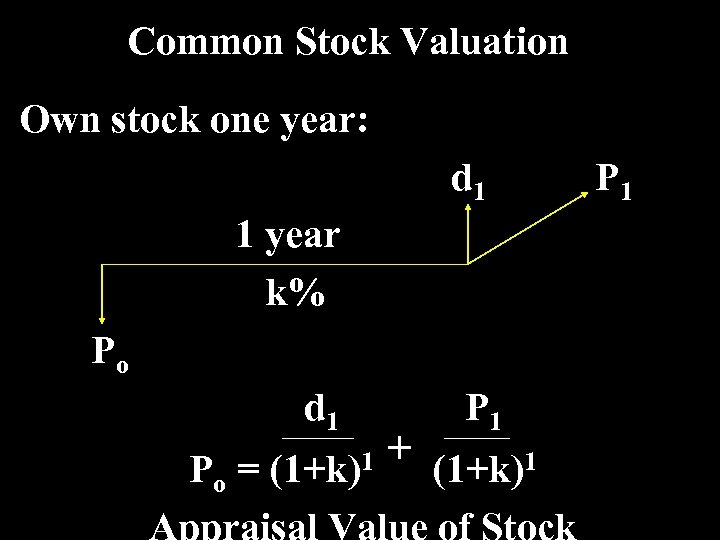 Common Stock Valuation Own stock one year: d 1 1 year k% Po d 1 Po = (1+k)1 P 1 + (1+k)1 P 1
Common Stock Valuation Own stock one year: d 1 1 year k% Po d 1 Po = (1+k)1 P 1 + (1+k)1 P 1
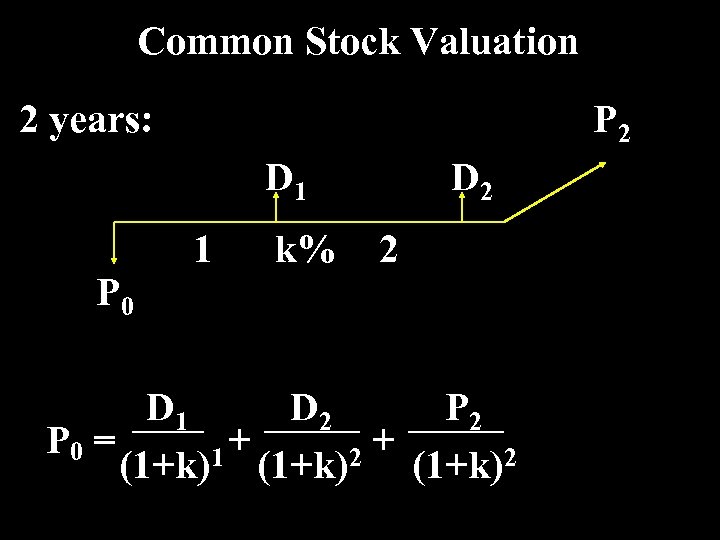 Common Stock Valuation 2 years: P 2 D 1 P 0 1 k% D 2 2 D 1 D 2 P 0 = + + 1 (1+k)2
Common Stock Valuation 2 years: P 2 D 1 P 0 1 k% D 2 2 D 1 D 2 P 0 = + + 1 (1+k)2
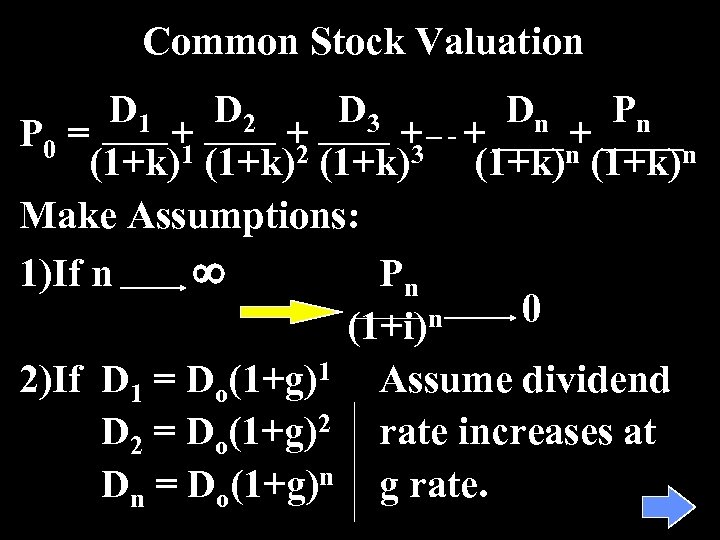 Common Stock Valuation D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn Pn P 0 = + + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n Make Assumptions: 1)If n ¥ Pn 0 n (1+i) 2)If D 1 = Do(1+g)1 Assume dividend D 2 = Do(1+g)2 rate increases at Dn = Do(1+g)n g rate.
Common Stock Valuation D 1 D 2 D 3 Dn Pn P 0 = + + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k)n Make Assumptions: 1)If n ¥ Pn 0 n (1+i) 2)If D 1 = Do(1+g)1 Assume dividend D 2 = Do(1+g)2 rate increases at Dn = Do(1+g)n g rate.
 Common Stock Valuation Example: Do = $10 g = 5% D 1 =10 (1+0. 05) D 1 = $10. 5
Common Stock Valuation Example: Do = $10 g = 5% D 1 =10 (1+0. 05) D 1 = $10. 5
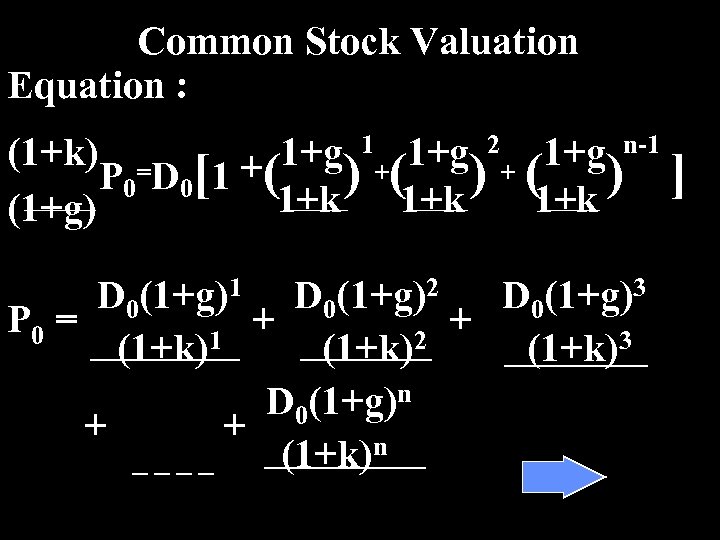 Common Stock Valuation Equation : (1+k) = 1+g 1+ 1+g 2+ 1+g n-1 P 0 D 0[1 +( ) (1+k ) ] 1+k (1+g) D 0(1+g)1 D 0(1+g)2 D 0(1+g)3 P 0 = + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 D 0(1+g)n + + (1+k)n
Common Stock Valuation Equation : (1+k) = 1+g 1+ 1+g 2+ 1+g n-1 P 0 D 0[1 +( ) (1+k ) ] 1+k (1+g) D 0(1+g)1 D 0(1+g)2 D 0(1+g)3 P 0 = + + (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 D 0(1+g)n + + (1+k)n
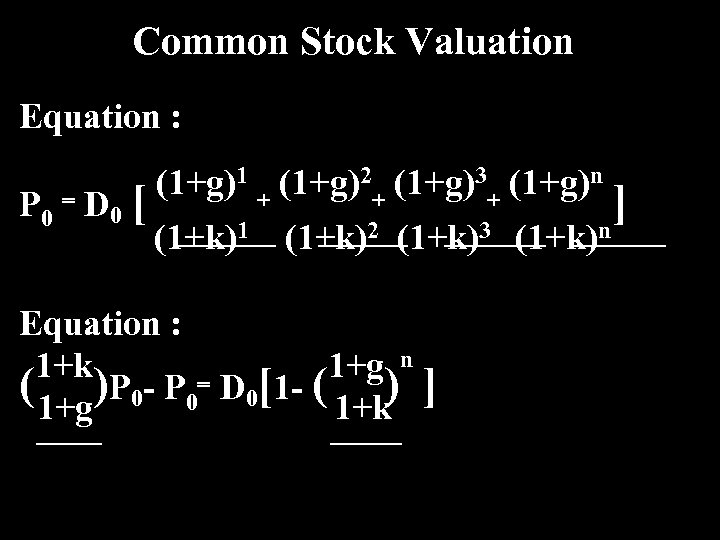 Common Stock Valuation Equation : P 0 = D 0 [ (1+g)1 + (1+g)2+ (1+g)3+ (1+g)n (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k) Equation : 1+k 1+g n ( 1+g)P 0 - P 0= D 0[1 - ( 1+k) ] ] n
Common Stock Valuation Equation : P 0 = D 0 [ (1+g)1 + (1+g)2+ (1+g)3+ (1+g)n (1+k)1 (1+k)2 (1+k)3 (1+k) Equation : 1+k 1+g n ( 1+g)P 0 - P 0= D 0[1 - ( 1+k) ] ] n
 Don’t Forget. . . k = ROI (%) = Required Return on Investment g = Dividend Growth
Don’t Forget. . . k = ROI (%) = Required Return on Investment g = Dividend Growth
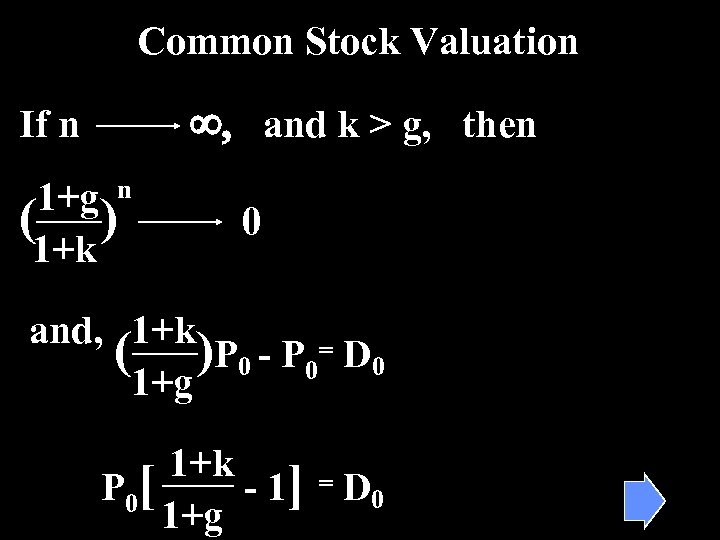 Common Stock Valuation ¥, and k > g, then If n 1+g n ( ) 1+k 0 and, 1+k ( ) P 0 - P 0= D 0 1+g 1+k P 0[ - 1] = D 0 1+g
Common Stock Valuation ¥, and k > g, then If n 1+g n ( ) 1+k 0 and, 1+k ( ) P 0 - P 0= D 0 1+g 1+k P 0[ - 1] = D 0 1+g
![Common Stock Valuation P 0[ 1+k-(1+g) 1+g ] = D 0 k-g = P Common Stock Valuation P 0[ 1+k-(1+g) 1+g ] = D 0 k-g = P](https://present5.com/presentation/28856a74af19cf637ccfb8b8a0467a4e/image-35.jpg) Common Stock Valuation P 0[ 1+k-(1+g) 1+g ] = D 0 k-g = P 0[ ] D 0 1+g P 0 D 0 (1+g) = k-g = D 1 k-g
Common Stock Valuation P 0[ 1+k-(1+g) 1+g ] = D 0 k-g = P 0[ ] D 0 1+g P 0 D 0 (1+g) = k-g = D 1 k-g
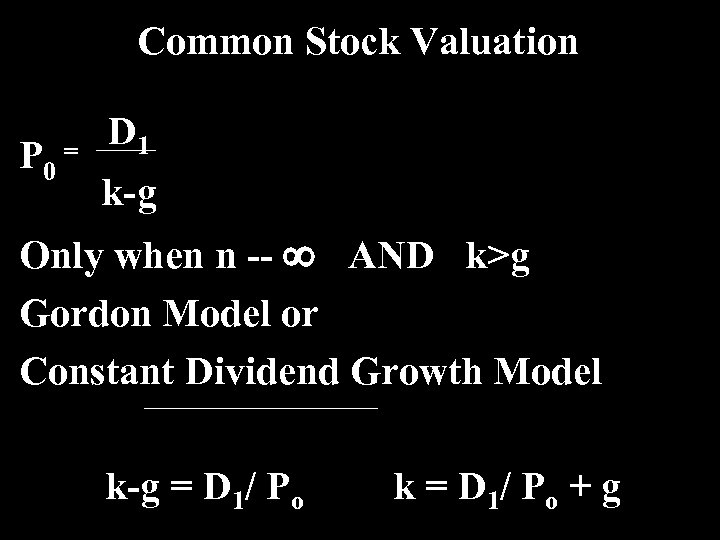 Common Stock Valuation P 0 = D 1 k-g Only when n -- ¥ AND k>g Gordon Model or Constant Dividend Growth Model k-g = D 1/ Po k = D 1/ P o + g
Common Stock Valuation P 0 = D 1 k-g Only when n -- ¥ AND k>g Gordon Model or Constant Dividend Growth Model k-g = D 1/ Po k = D 1/ P o + g
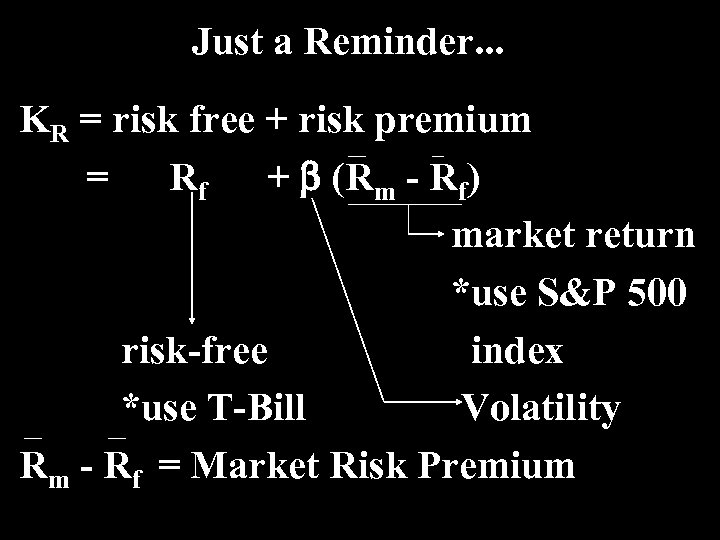 Just a Reminder. . . KR = risk free + risk premium = Rf + b (Rm - Rf) market return *use S&P 500 risk-free index *use T-Bill Volatility Rm - Rf = Market Risk Premium
Just a Reminder. . . KR = risk free + risk premium = Rf + b (Rm - Rf) market return *use S&P 500 risk-free index *use T-Bill Volatility Rm - Rf = Market Risk Premium
 Common Stock Valuation Example: Do=Paid Dividend=$5/share g=Dividend Growth=5% KR=Required Return=10% pay for stock now Do(1+g) $5(1+0. 05) Po = K - g = 0. 1 - 0. 05 = $105 R
Common Stock Valuation Example: Do=Paid Dividend=$5/share g=Dividend Growth=5% KR=Required Return=10% pay for stock now Do(1+g) $5(1+0. 05) Po = K - g = 0. 1 - 0. 05 = $105 R
 Common Stock Valuation Value of Stock = $105 (appraisal value) Stock Price = $110 *Don’t buy the stock because the stock is over valued. (too expensive)
Common Stock Valuation Value of Stock = $105 (appraisal value) Stock Price = $110 *Don’t buy the stock because the stock is over valued. (too expensive)
 Common Stock Valuation KE = D 1/ Po + g = Expected Return (Po = Stock Price = $110) Do (1+g) $5(1+0. 05) KE = +g = +0. 05 $110 Po KE = 9. 7% (Expected Return) KR = 10% (Required Return) Therefore, do not purchase
Common Stock Valuation KE = D 1/ Po + g = Expected Return (Po = Stock Price = $110) Do (1+g) $5(1+0. 05) KE = +g = +0. 05 $110 Po KE = 9. 7% (Expected Return) KR = 10% (Required Return) Therefore, do not purchase


