8bf137be53d43d0c26313aba51a4faf6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Predictor of Customer Perceived Software Quality By Haroon Malik

Introduction • Predict the customer’s experience within first three months • Quantifying the relative importance of various processes and product factors on customer experience • Deployment issues – Usage patterns, – Software platforms & – Hardware platform.

Introduction • Come up with a model that can be easily adapted and used at other organization with little or more tailoring.

Driving force • Techniques already exists to predict how many faults remains in unchanging software system, changes or module will have defect and even how much effort defect repairs will require. • Many researches examined the effect of software contents and development process on measure of customer perceived quality.

Driving force • Most of which ignore the – – Hardware configurations, Software platform, Usage patterns & Deployment issues • End users experience the software typically experience the quality of the entire “Solution”. • Past researches do consider the importance of these factors but no solid work is done to validate the claim or quantify these factors.

The Software project • Call processing software for AVYA telephony systems – Established product – Seven million lines of code mostly in C and C++ • Multiple releases are in field and are being used by tens of thousands of customers. • Used by clients whose business depend on the high availability of the product.
Capturing Interaction • Four database are considered for capturing customer interaction measures -1 atabase D Da tab – Customer issue tracking system as e-2 • Trouble ticket database – The equipment database – Change management • Sablime database
The Process • Avaya uses a tiered support process. • Trouble Ticket • Half of the over 4 million tickets created in 2003 are related to product analyzed in this project. • Equipment Database – Software release – Number of licensed ports – 4 million systems listen in equipment databases.
Customer perceived quality models M M odell e el od od M M Model • Business activity distraction ---Negative effect • To major aspect of customer perceived quality: – Impact of problem occurrence – Frequency of problem occurrence • Interest – Rare high-impact problems • Equipment services outages • Malfunction resulting in software modification
Customer perceived quality models M M odell e el od od M M – Frequent low impact problems Model • Technician dispatches • Customer calls • Alarm reports
Factors to predict • Factors – – lack empirical Deployment issues validation Usage patterns Software platform Hardware configurations • Prior work examines – Software product – Development process They are not good predictors (Static. do not vary for a single release)

Predictor Measures ? • Value Predictors – System size. – – Operating system Ports Total Deployment time Software Upgrades • Nuisance Predictors – US of international installation – Service contracts – Missing configuration information

System size • This predictor measures – Hardware configuration factors – Software platform factors and – Usage patterns factor. • Introduced “LARGE” variable indicator in the model • Small and medium systems have: – – Fewer customer interactions Few settings to configure Fewer systems to interface with Likely not to be involved in business critical application requiring 7 x 24 uptime. – Less likely to experience and report issues.
Operating System • Operating system predictor measures: – Software platform factor & – Hardware configuration factor • Considered – An open Linux – proprietary – Commercial windows • Very small number Os systems used NT/Win 2000 • Off-the-shelf operating system introduce unnecessary complexity and configuration issue.
Ports • The port predictor measures – Usage pattern factor & – Hardware configuration factors • The number of ports indicates how many licensed end points are supported by the system. • Model encoded the log number of ports with log(n. Port) variable
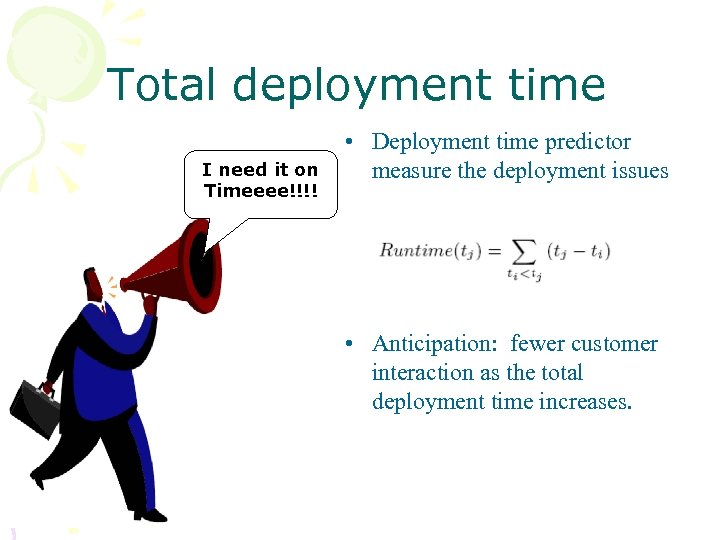
Total deployment time I need it on Timeeee!!!! • Deployment time predictor measure the deployment issues • Anticipation: fewer customer interaction as the total deployment time increases.

Software upgrades • The software upgrades predictor measures the deployment issues factor. • Encoded the existence of upgrade using an indictor variable called “Upgr”. • Upgrade serves to keep the machine running properly by incorporating the latest fixes and refinements to the system • Upgrades have clearly defined purpose of making the system more stable, so expect to have that effect.

Nuisance Factors • These factors are likely to identify peculiarities of data reporting and collection process, but not necessarily differences in underlying customer perceived quality. – US of International installation – Service contracts – Missing configuration information
Factors Vs Predictors • Predict for each customer (outputs): – – – Software defects System outages Technician dispatches Calls Automated alarms • Using Logistic regression and Linear regression • Using predictors (inputs): – – – Total deployment time Operating system System size Ports Software upgrades • For a real world software system

Results • First fit the models to test the relationships hypothesized previously. • Use the models to predict customer interaction for the next major releases. • Present full results only for two measures.
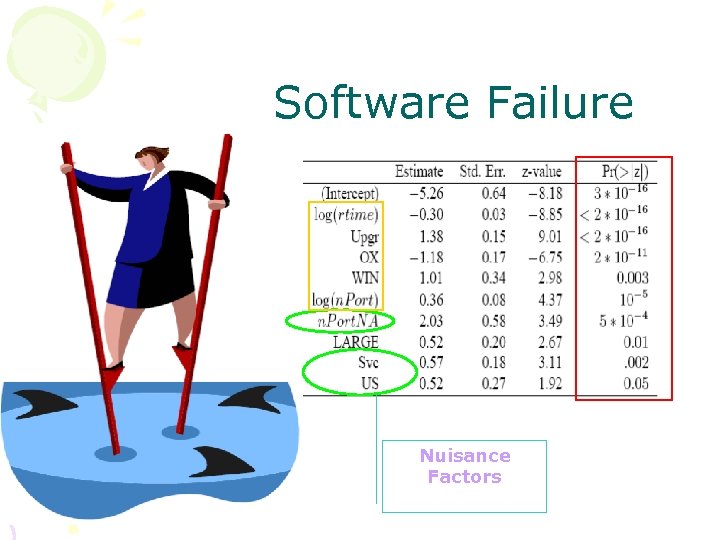
Software Failure Nuisance Factors
Most important predictor • Total Deployment time: – Customers who installed the application early may have detected malfunctions that are fixed by the time later customers install their systems – The individuals performing the installation and configuration may have acquired more experience, have access to improved documentation – The lesson from this relationship is that customers that are less tolerant of availability issues should not be the first to install a major software release “never upgrade to dot zero release. ”

Another Important Predictor • Operating system (software platform, hardware configurations) – Systems running on the proprietary OS are 3 times less likely to experience a software defect compared with systems on running the open OS (Linux) – Systems running on the commercial OS (Windows) are 3 times more likely to experience a software defect compared with systems running on the open OS (Linux)
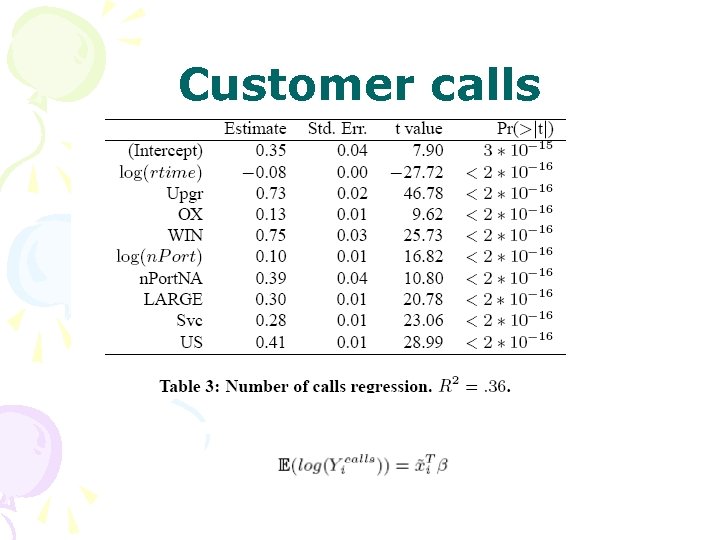
Customer calls

Predicting customer call traffic • Ports and NAPorts are not available • know from talking to the customer call center that they have estimates of how many calls a call representative can handle so our prediction of the number of calls in a month can be used to plan staffing. • The take away is that they the predictions are accurate and can be used to plan various activities
Validations • Accounted for data reporting differences – Included indicator variables in the models to identify populations (e. g. US or international customers) • Independently validated the data collection process – Independently extracted data and performed analyses • Interviewed personnel to validate findings – Programmers – Field technicians
Best Contributions • Identified and quantified characteristics, like time of deployment, that can affect customer perceived quality by more than an order of magnitude • created models that can predict various customer interactions and found that predictors have consistent effect across interactions • We learned that controlled deployment may be the key for high reliability systems
8bf137be53d43d0c26313aba51a4faf6.ppt