c23839f53308cb3e1584061b63f5d79b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 Pre Class n. List 5 things that you know (or think you know) about the religion of Islam, Islamic culture and history.
Pre Class n. List 5 things that you know (or think you know) about the religion of Islam, Islamic culture and history.
 Arab? Islam? Muslim? Islamic? Arab – someone who speaks Arabic n Islam – the faith founded by Muhammad n Muslim – someone who practices the religion of Islam n Islamic – describing an object (ie. Islamic country, Islamic calendar, Islamic law) n
Arab? Islam? Muslim? Islamic? Arab – someone who speaks Arabic n Islam – the faith founded by Muhammad n Muslim – someone who practices the religion of Islam n Islamic – describing an object (ie. Islamic country, Islamic calendar, Islamic law) n
 The Arab World
The Arab World
 Islam - religion started by Muhammad and his teachings/revelations from Allah n. Means “submission” –people must throw themselves upon the mercy of God (submit) in order to be saved n“Muslim” – people who practice the religion of Islam
Islam - religion started by Muhammad and his teachings/revelations from Allah n. Means “submission” –people must throw themselves upon the mercy of God (submit) in order to be saved n“Muslim” – people who practice the religion of Islam
 Arabia Before Muhammad n n Bedouin tribes – nomadic animal herders – Worshipped pagan gods – Constantly at war (scarcity of water, resources) Mecca – Popular because of the Kaaba (tribes worshipped pagan gods) – Prosperous – Kaaba made it a center of trade
Arabia Before Muhammad n n Bedouin tribes – nomadic animal herders – Worshipped pagan gods – Constantly at war (scarcity of water, resources) Mecca – Popular because of the Kaaba (tribes worshipped pagan gods) – Prosperous – Kaaba made it a center of trade
 Muhammad n born in Mecca 570 A. D. (Arabian Peninsula) n “revelation” from God in a cave n set out to preach the idea of MONOTHEISM (one God) and social justice
Muhammad n born in Mecca 570 A. D. (Arabian Peninsula) n “revelation” from God in a cave n set out to preach the idea of MONOTHEISM (one God) and social justice
 Why didn’t Arabs like Muhammad's message? n Threatened their gods/way of life – monotheism, non-violence n Threatened their power and wealth – Kaaba brought trade and prosperity – Rich had to give to poor
Why didn’t Arabs like Muhammad's message? n Threatened their gods/way of life – monotheism, non-violence n Threatened their power and wealth – Kaaba brought trade and prosperity – Rich had to give to poor

 622 -The Hijra n Muhammad forced out of Mecca and went to Yathrib (Medina - city of the prophet) n began the religion of Islam in Medina n Year 1 on Muslim calendar
622 -The Hijra n Muhammad forced out of Mecca and went to Yathrib (Medina - city of the prophet) n began the religion of Islam in Medina n Year 1 on Muslim calendar

 Prophet’s Mosque-Medina
Prophet’s Mosque-Medina
 630 Muhammad returns to Mecca n Battle of Badr n captures the city of Mecca n Died in 632
630 Muhammad returns to Mecca n Battle of Badr n captures the city of Mecca n Died in 632
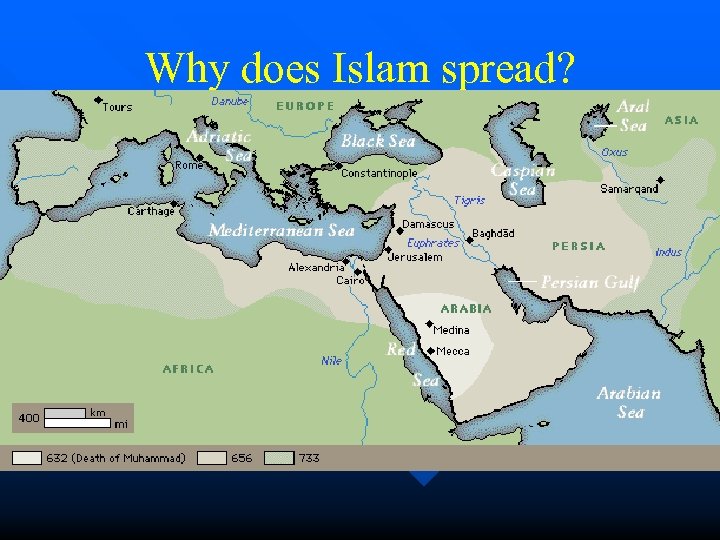 Why does Islam spread? Social justice message – non-violence, equality n Strength of Muhammad’s forces n – New power in Arabia – People converted to Islam
Why does Islam spread? Social justice message – non-violence, equality n Strength of Muhammad’s forces n – New power in Arabia – People converted to Islam
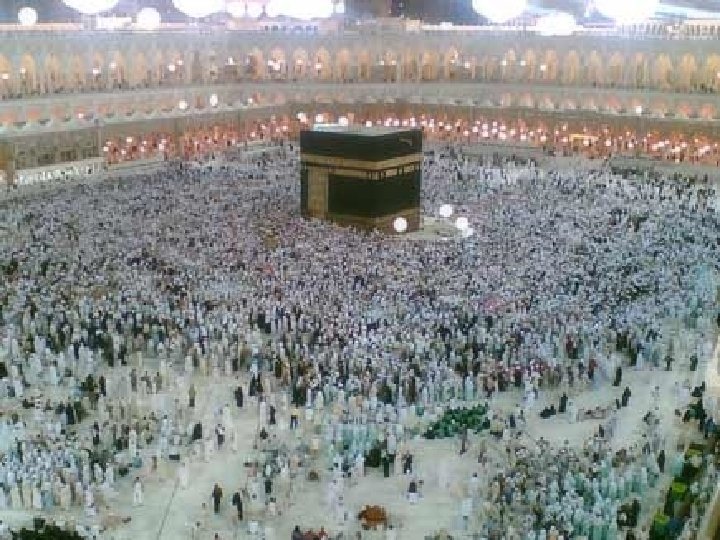
 Kaaba Before Muhammad: After Muhammad: “black stone” worshipped, along with pagan gods • • • re-dedicated to one God (Allah) 1 st mosque (Muslim house of worship) Sight of the hajj
Kaaba Before Muhammad: After Muhammad: “black stone” worshipped, along with pagan gods • • • re-dedicated to one God (Allah) 1 st mosque (Muslim house of worship) Sight of the hajj

 Islam Splits – Writing assignment n Using SEVEN of the vocab terms that you defined for homework, write a paragraph that responds to the following questions: - What are the major differences between Shiite and Sunni Muslims? - Which difference, do you think, is the most significant? Why? YOU MUST UNDERLINE EACH WORD n THIS WILL BE GRADED! n
Islam Splits – Writing assignment n Using SEVEN of the vocab terms that you defined for homework, write a paragraph that responds to the following questions: - What are the major differences between Shiite and Sunni Muslims? - Which difference, do you think, is the most significant? Why? YOU MUST UNDERLINE EACH WORD n THIS WILL BE GRADED! n
 Pre Class Which difference between Sunnis and Shiites do you believe is the most significant? Why?
Pre Class Which difference between Sunnis and Shiites do you believe is the most significant? Why?
 Islam: After Muhammad's Death AD 632 – Muhammad dies n Abu Bakr takes over as caliph (successor to the prophet; political leader of Islam) n AD 661 – Ali, the 4 th caliph (relative of Muhammad) is murdered n Dispute over who will be the next successor erupts!!! n
Islam: After Muhammad's Death AD 632 – Muhammad dies n Abu Bakr takes over as caliph (successor to the prophet; political leader of Islam) n AD 661 – Ali, the 4 th caliph (relative of Muhammad) is murdered n Dispute over who will be the next successor erupts!!! n
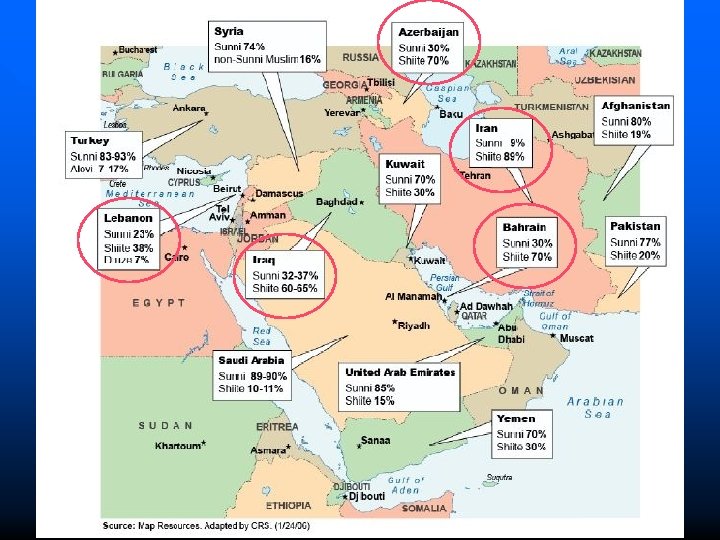
 Sunnis/Shiites: SIMILARITIES n Monotheistic (believe in one God = Allah) n Muhammad = prophet n Koran – unchanging EXACT word of God n Hadith/Sunnah n Sharia (Islamic law) n Worship in mosques n Mecca = holy city n 5 Pillars = responsibilities as Muslims
Sunnis/Shiites: SIMILARITIES n Monotheistic (believe in one God = Allah) n Muhammad = prophet n Koran – unchanging EXACT word of God n Hadith/Sunnah n Sharia (Islamic law) n Worship in mosques n Mecca = holy city n 5 Pillars = responsibilities as Muslims
 Islam Splits SHIISM SUNNISM n Traditional Islam n Any devout Muslim can be caliph Emphasis on Koran, Hadith and Sunnah Scholars interpret Koran Don’t recognize imams/ayatollahs No clergymen 85 -90% n n n “Ali’s Party” Caliph must be direct descendant of Muhammad Believe Muhammad chose first imam (Ali) Imam – leader – interprets Koran/Hadith Ayatollahs issue decrees on Islamic law 10 -15%
Islam Splits SHIISM SUNNISM n Traditional Islam n Any devout Muslim can be caliph Emphasis on Koran, Hadith and Sunnah Scholars interpret Koran Don’t recognize imams/ayatollahs No clergymen 85 -90% n n n “Ali’s Party” Caliph must be direct descendant of Muhammad Believe Muhammad chose first imam (Ali) Imam – leader – interprets Koran/Hadith Ayatollahs issue decrees on Islamic law 10 -15%
 Muhammad’s Teachings § Allah was the one and only God and all should submit and be thankful to Him § All believers in Allah were equal under Him (SOCIAL JUSTICE) § rich should share wealth with the poor § Allah knows people’s destiny, but they should strive to live good lives
Muhammad’s Teachings § Allah was the one and only God and all should submit and be thankful to Him § All believers in Allah were equal under Him (SOCIAL JUSTICE) § rich should share wealth with the poor § Allah knows people’s destiny, but they should strive to live good lives
 n Christians and Jews “people of the book” n required to treat them with tolerance
n Christians and Jews “people of the book” n required to treat them with tolerance
 Five Pillars of Islam n Faith n Daily prayer n Almsgiving n Fast n Pilgrimage to Mecca (hajj)
Five Pillars of Islam n Faith n Daily prayer n Almsgiving n Fast n Pilgrimage to Mecca (hajj)
 Testament of Faith n There is ONE God, Allah, and Muhammad is his prophet
Testament of Faith n There is ONE God, Allah, and Muhammad is his prophet
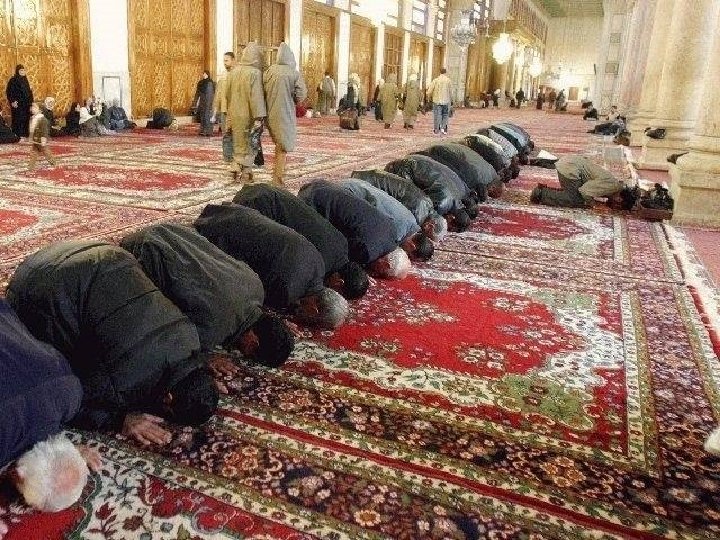
 Daily Prayer n Pray five times a day n facing Mecca n In Arabic
Daily Prayer n Pray five times a day n facing Mecca n In Arabic

 Almsgiving n Charity to the poor and aged n 2. 5% of possessions
Almsgiving n Charity to the poor and aged n 2. 5% of possessions
 Fast n during the month of Ramadan n NO food – sunrise to sunset n Refrain from violence, harsh language, gossip, etc.
Fast n during the month of Ramadan n NO food – sunrise to sunset n Refrain from violence, harsh language, gossip, etc.
 Dates – used to break fasts by many Muslims (Kuwait)
Dates – used to break fasts by many Muslims (Kuwait)
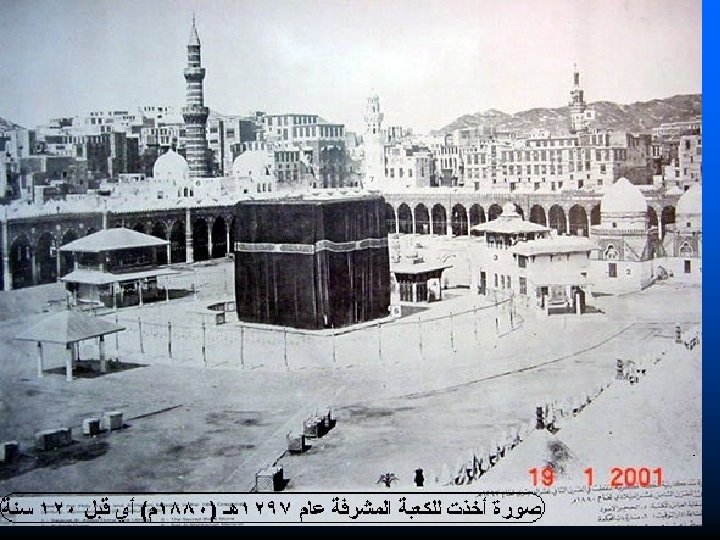
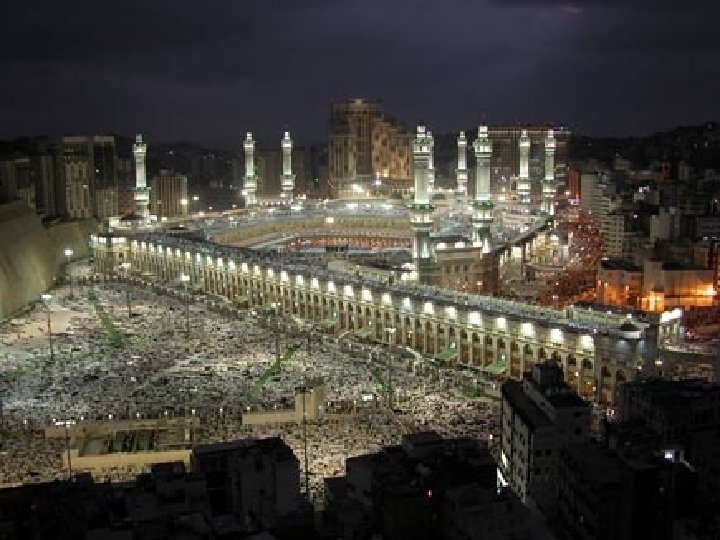
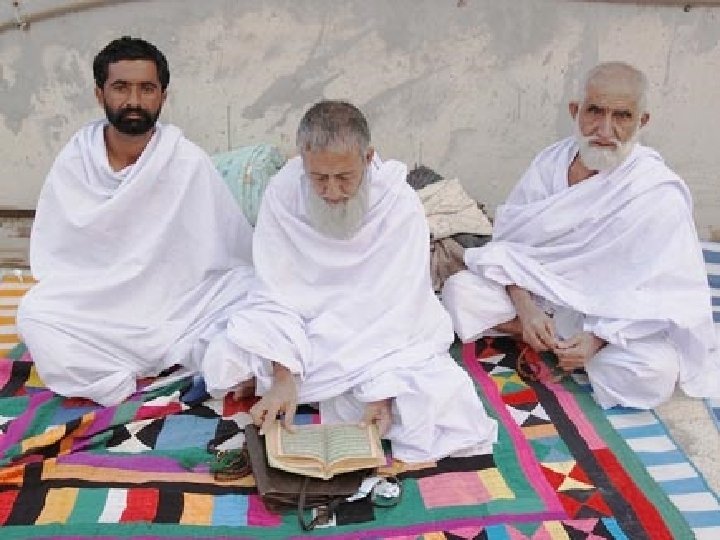
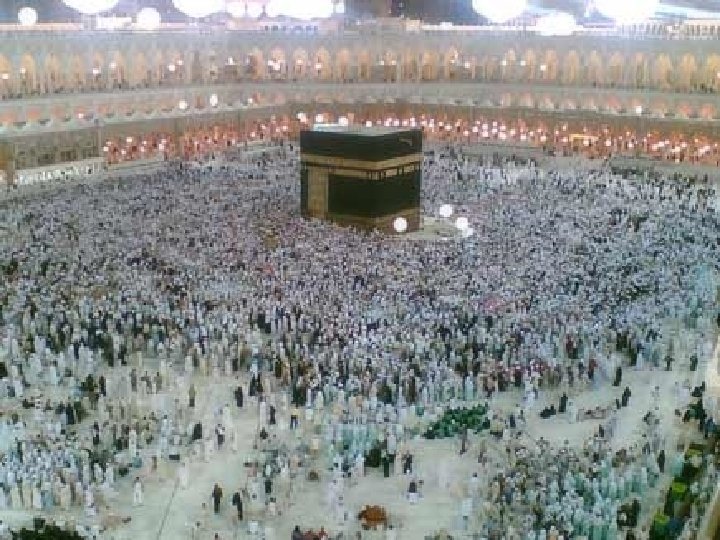
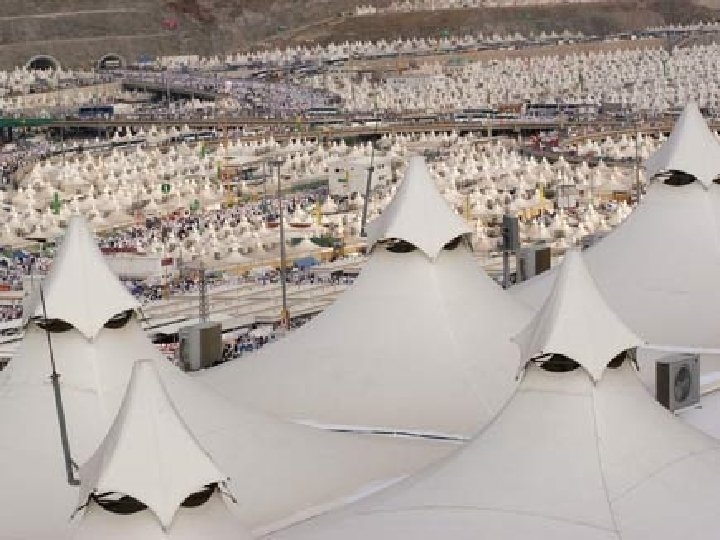
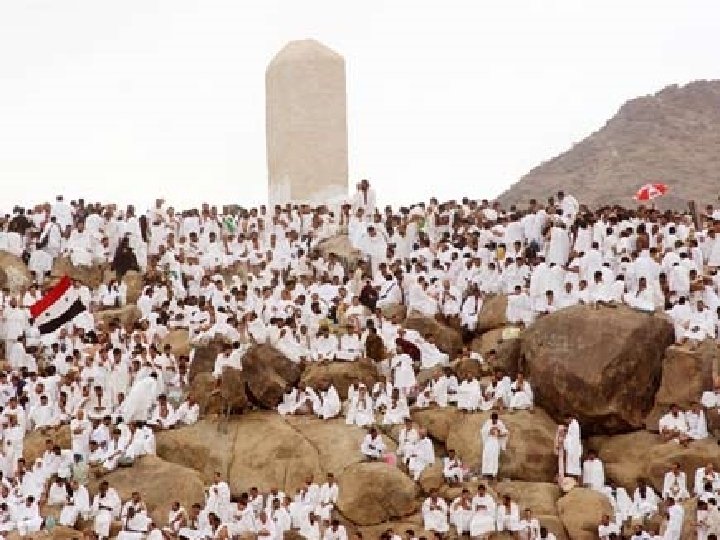
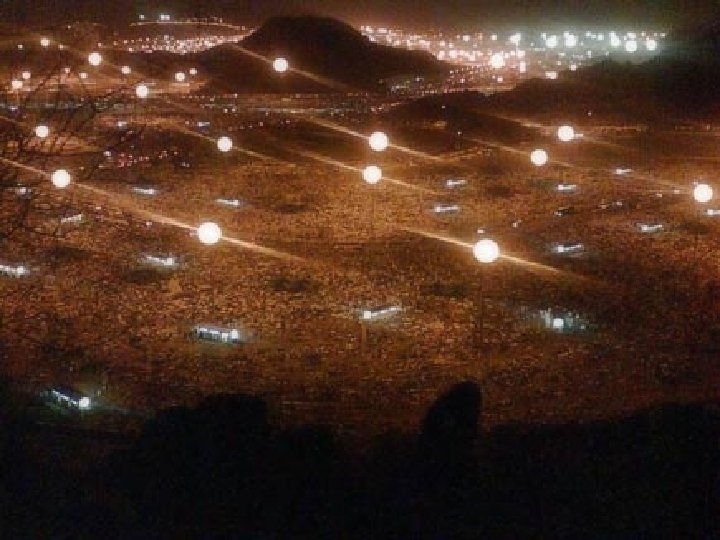
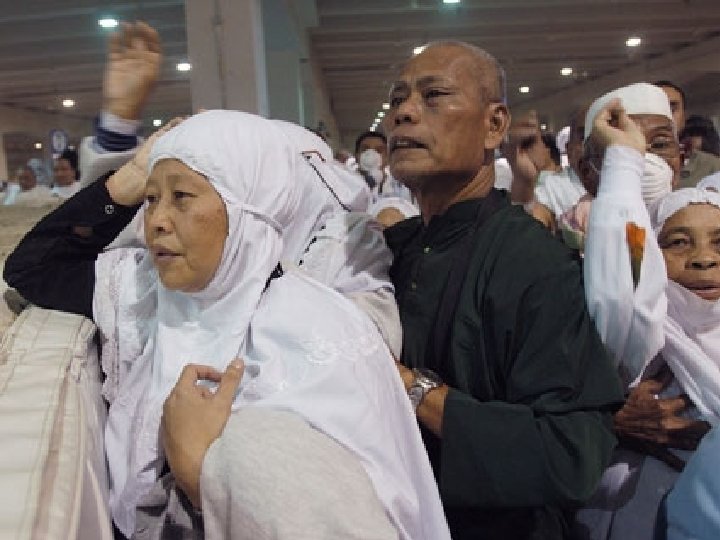
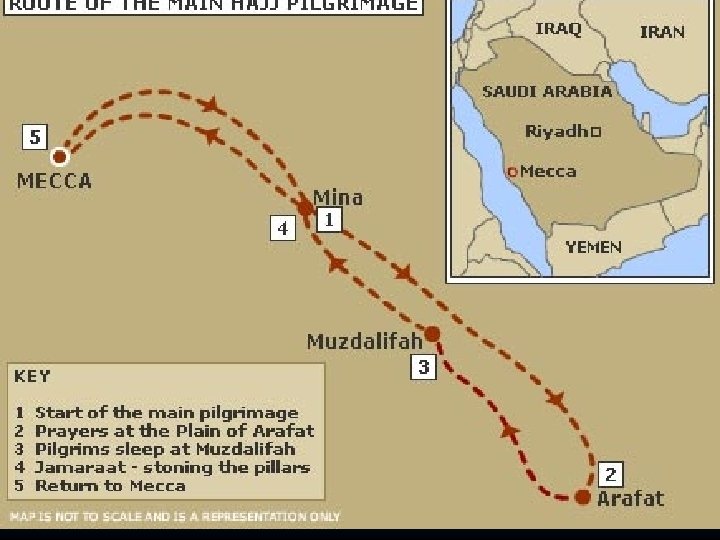
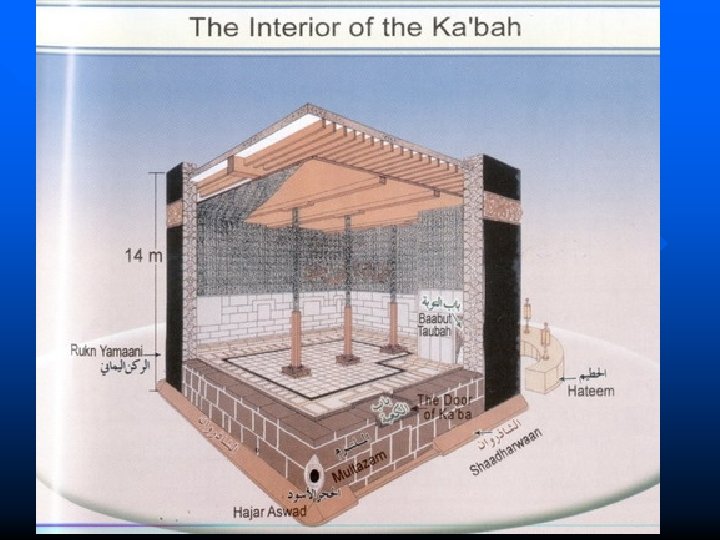
 Kabba Hajj An American Muslim n “pilgrimage” to Mecca n All Muslims who are able must make the journey Stoning
Kabba Hajj An American Muslim n “pilgrimage” to Mecca n All Muslims who are able must make the journey Stoning










 The Koran n Sacred book n Muhammad’s miracle n God’s final message to his people n Final authority for Muslims, on: religion, politics, law, economic, and social life n Islamic Law – Sharia
The Koran n Sacred book n Muhammad’s miracle n God’s final message to his people n Final authority for Muslims, on: religion, politics, law, economic, and social life n Islamic Law – Sharia
 Pre Class Look at your Christianity/Judaism/Islam chart n Identify 5 similarities between these three major religions n
Pre Class Look at your Christianity/Judaism/Islam chart n Identify 5 similarities between these three major religions n
 How have religions spread? ?
How have religions spread? ?
 Elements of Islamic Life n Dietary Laws (Halal) - no pork, alcohol (article) n Honor Parents n Women cannot wear clothes that bring attention to their body n Traditional colors of the prophet = green and white
Elements of Islamic Life n Dietary Laws (Halal) - no pork, alcohol (article) n Honor Parents n Women cannot wear clothes that bring attention to their body n Traditional colors of the prophet = green and white
 Traditional Clothing n men = taqiyah (Hadith) n Women = Hijab/veiling According to the Hadith, "My Lord agreed with me ('Umar) in three things. . . (2) And as regards the veiling of women, I said 'O Allah's Apostle! I wish you ordered your wives to cover themselves from the men because good and bad ones talk to them. ' So the verse of the veiling of the women was revealled" (Bukhari, v 1, bk 8, sunnah 395). (http: //www. english. emory. edu/Bah ri/Veil. html)
Traditional Clothing n men = taqiyah (Hadith) n Women = Hijab/veiling According to the Hadith, "My Lord agreed with me ('Umar) in three things. . . (2) And as regards the veiling of women, I said 'O Allah's Apostle! I wish you ordered your wives to cover themselves from the men because good and bad ones talk to them. ' So the verse of the veiling of the women was revealled" (Bukhari, v 1, bk 8, sunnah 395). (http: //www. english. emory. edu/Bah ri/Veil. html)
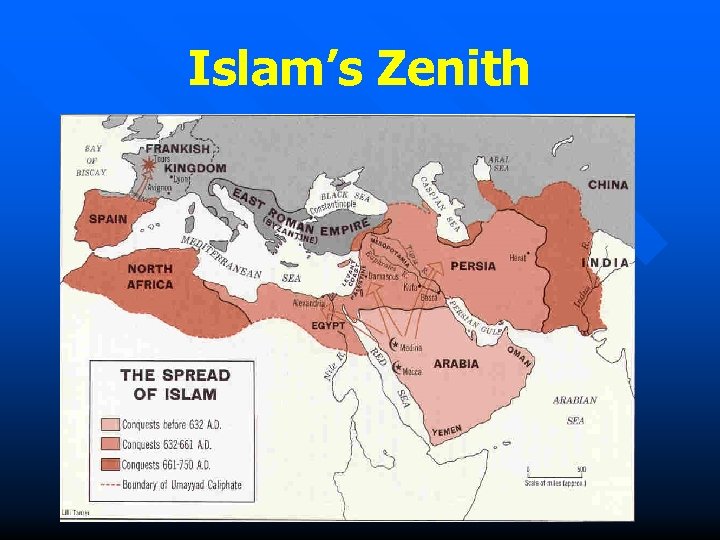 Islam’s Zenith
Islam’s Zenith
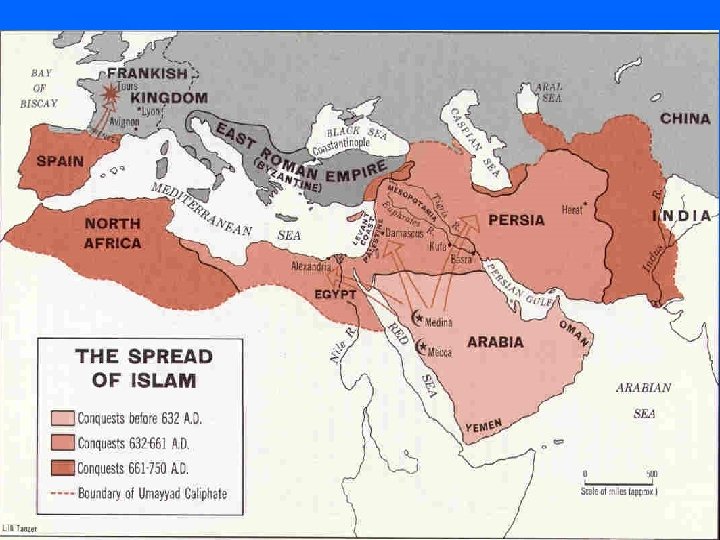
 Expansion of Islam Spread beliefs and gain riches n Arab armies launched Jihad (holy war) – To defend Islam – “Struggle within” n 732 Arabs conquer empire from Indus river, to Atlantic Ocean n Tolerance/ taxes on non-believers n
Expansion of Islam Spread beliefs and gain riches n Arab armies launched Jihad (holy war) – To defend Islam – “Struggle within” n 732 Arabs conquer empire from Indus river, to Atlantic Ocean n Tolerance/ taxes on non-believers n