d198ea04d3bb9b3cd0d1b25cc090f680.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank Development in Data and Tools Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Faculty of Philosophy and Arts Charles University in Prague September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools Jan Hajič Otakar Smrž Petr Zemánek Jan Šnaidauf Emanuel Beška
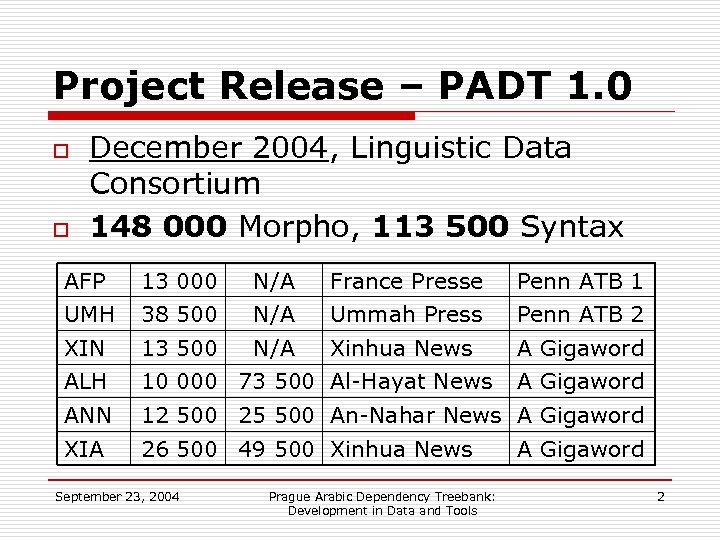
Project Release – PADT 1. 0 o o December 2004, Linguistic Data Consortium 148 000 Morpho, 113 500 Syntax AFP 13 000 N/A France Presse Penn ATB 1 UMH 38 500 N/A Ummah Press Penn ATB 2 XIN 13 500 N/A Xinhua News A Gigaword ALH 10 000 73 500 Al-Hayat News ANN 12 500 25 500 An-Nahar News A Gigaword XIA 26 500 49 500 Xinhua News September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools A Gigaword 2

Open-Source Tools o Tr. Ed Tree Editor n n o Netgraph Search Engine n n o Multi-purpose annotation environment Suite of programming utilities Server/Client system architecture Easy-to-learn query language Encode: : Arabic Perl Module n n Extension for processing of Arabic script Arab. Te. X, Buckwalter, Unicode, … September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 3
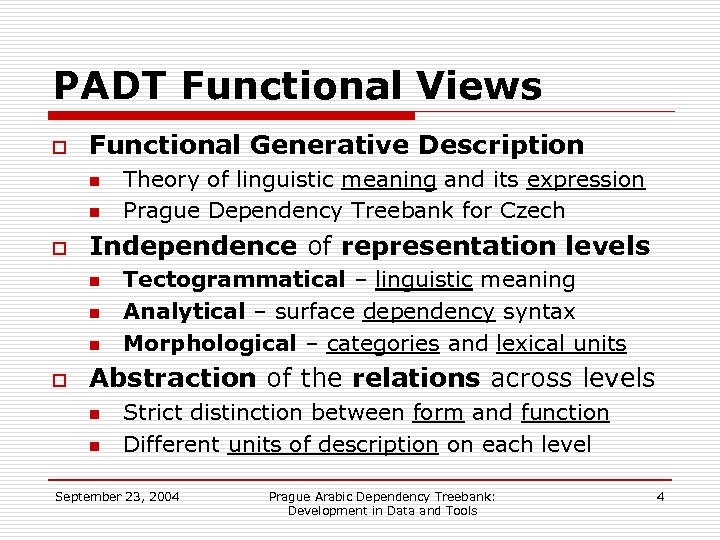
PADT Functional Views o Functional Generative Description n n o Independence of representation levels n n n o Theory of linguistic meaning and its expression Prague Dependency Treebank for Czech Tectogrammatical – linguistic meaning Analytical – surface dependency syntax Morphological – categories and lexical units Abstraction of the relations across levels n n Strict distinction between form and function Different units of description on each level September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 4

Functional Morphology o o o Provides syntax levels with their abstract language, not just giving letters in tokens Revives multiple senses of categories Completeness of generation Strict modeling of grammatical control Morpho. Trees – ‘human tagging’ Successful prototype feature-based tagger September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 5
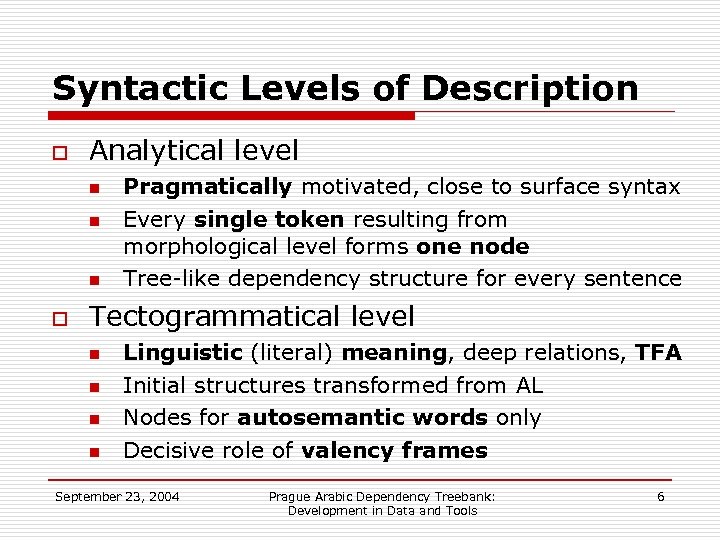
Syntactic Levels of Description o Analytical level n n n o Pragmatically motivated, close to surface syntax Every single token resulting from morphological level forms one node Tree-like dependency structure for every sentence Tectogrammatical level n n Linguistic (literal) meaning, deep relations, TFA Initial structures transformed from AL Nodes for autosemantic words only Decisive role of valency frames September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 6
Logic of Analytical Trees o o Concepts of dependency and valency Reduction: sentence must retain grammatical correctness if leaves (terminal nodes) are chopped off ¨ Trees: clause components clauses sentences paragraphs etc. Subtrees of clauses exchangeable for non-clauses ¨ Nodes: words, tokenized parts of words, punctuation marks – marked by functions ¨ Edges: syntactic relations – governing node dependent node/subtree September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 7

Some Syntax Issues of Arabic o Non-verbal predication of several types o Subordinate non-verbal clauses / modification o Verb-like behavior of many nominal forms o Mostly VSO in verbal sentences, but… n n o o vice-versa in non-verbal clauses different, depending on context boundness Compound verbs, fixed composite prepositions Grammatical co-reference, accusative of inner object, complex referencing, etc. September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 8
Problem I: Predication o Head node of tree: PREDICATE n o o Why? Steady role in sentence, cannot be omitted Verbal predicate: I-go to school Non-verbal predicate n n n Nominal: The-house a-big (=the house is big) Existential: There a-city (=there is a city) Prepositional o o n Possessive: For him a-house (=he has a house) Adverbial: The-mosque in the-city (=…is…) Conjunctional: The-problem that (=…is that) September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 9
![Predication Types in Trees d. Ama [Pred] Nominal lasted kab. Irun [Pnom] a-big [nom. Predication Types in Trees d. Ama [Pred] Nominal lasted kab. Irun [Pnom] a-big [nom.](https://present5.com/presentation/d198ea04d3bb9b3cd0d1b25cc090f680/image-10.jpg)
Predication Types in Trees d. Ama [Pred] Nominal lasted kab. Irun [Pnom] a-big [nom. ] iqtir. AHu [Sb] proposal al-baytu [Sb] Prepositional the-house [nom. ] (possessive) vam~ata [Pred. E] there-is la- [Pred. P] for -hu [Obj] him Existential ‑hu al-Eamal. Iyata [Obj] [Atr] the-operation [acc. ] his Prepositional mad. Inatun [Sb] (adverbial, a-city [nom. ] f. I [Pred. P] locative) Verb-like behavior in (object of noun? ) baytun [Sb] a-house [nom. ] September 23, 2004 Verbal al-j. Ami. Eu [Sb] the-mosque [nom. ] Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools s. AEatayni [Adv] two-hours [acc. ] Eal. A [Aux. P] on zumal. A’i [Obj] colleagues ‑hi [Atr] his al-mad. Inati [Adv] the-city [gen. ] 10
Problem II: Clauses & Co-reference o Recursiveness: subordinate clause is contained as subtree in place of simple element n n n o Head-node of clause gets the same function Problem: non-verbal structures – clauses or not? Compound verbs (m. A z. Ala etc. ) treated equally Grammatical co-reference: Personal pronoun formally required by another element n n n Pronoun must be marked to be treated as such Target of reference is unambiguously identifiable Often in subordinate clauses, mostly attributive Ex. : He-wrote a-book number its-pages hundred September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 11
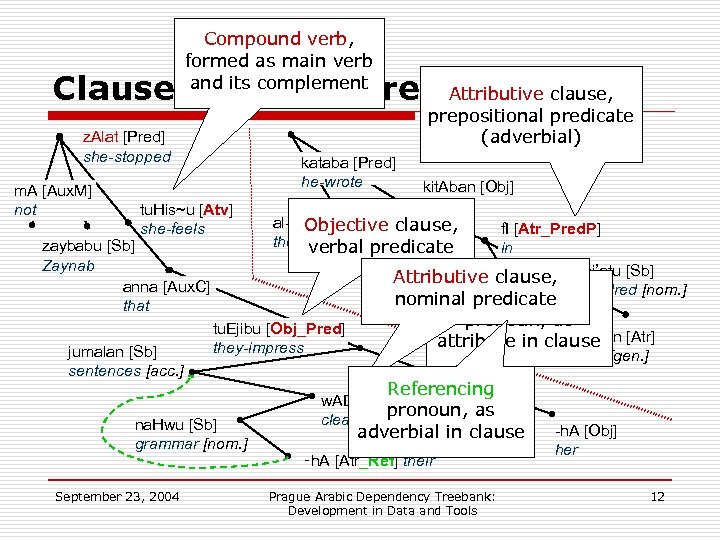
Compound verb, formed as main verb and its complement Attributive clause, Clauses & Co-reference in Trees z. Alat [Pred] she-stopped prepositional predicate (adverbial) kataba [Pred] he-wrote kit. Aban [Obj] a-book tu. His~u [Atv] al-rajulu [Sb] Objective clause, she-feels f. I [Atr_Pred. P] the-man [nom. ] zaybabu [Sb] verbal predicate in Zaynab Attributive clause, mi’atu [Sb] anna [Aux. C] hundred [nom. ] nominal. Referencing predicate that -hi [Adv_Ref] pronoun, as tu. Ejibu [Obj_Pred] it Saf. Hatin [Atr] attribute in clause they-impress jumalan [Sb] pages [gen. ] sentences [acc. ] m. A [Aux. M] not Referencing na. Hwu [Sb] grammar [nom. ] September 23, 2004 w. ADi. Hun [Atr_Pnom] pronoun, as clear [nom. ] adverbial in clause ‑h. A [Atr_Ref] their Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools -h. A [Obj] her 12
Future Prospects o o o Implementation of Functional Morphology Tectogrammatical annotation Lexicons of valency frames Re-training the feature-based tagger on Morpho. Trees Machine-learning on the treebank data for various purposes September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 13

Thank you Questions welcome! http: //ckl. mff. cuni. cz/padt/ September 23, 2004 Prague Arabic Dependency Treebank: Development in Data and Tools 14
d198ea04d3bb9b3cd0d1b25cc090f680.ppt