Integral estimation_pr1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Practice work № 1: Integral estimation of water quality and water ecosystem state. Generalized index of water ecosystem state building. Determination of “state rate” and “influence rate” to water ecosystem comparison integral index. Dr. Fedorova Irina Viktorovna Department of Hydrology
Practice work № 1: Integral estimation of water quality and water ecosystem state. Generalized index of water ecosystem state building. Determination of “state rate” and “influence rate” to water ecosystem comparison integral index. Dr. Fedorova Irina Viktorovna Department of Hydrology
 Methods of estimation of integral hydro chemical parameters of water quality n V. A. Abakumov – index of water pollution: n n n – number of parameters; Xj – j-th pollution parameter; Aj – exponent of xj; K – exponent , determine of j -th parameter contribution to pollution
Methods of estimation of integral hydro chemical parameters of water quality n V. A. Abakumov – index of water pollution: n n n – number of parameters; Xj – j-th pollution parameter; Aj – exponent of xj; K – exponent , determine of j -th parameter contribution to pollution
 Methods of estimation of integral hydro chemical parameters of water quality T. I. Moiseenko and etc. : two levels of convolution: n the 1 st convolution - three indexes: n n n toxic, physical-chemical, eutrophication n the 2 nd convolution – calculation of the three indexes sum with different number weights: MCL - maximum concentration limit C bg – background level There are not weighting factor for indexes’ estimation scale and not estimated scales
Methods of estimation of integral hydro chemical parameters of water quality T. I. Moiseenko and etc. : two levels of convolution: n the 1 st convolution - three indexes: n n n toxic, physical-chemical, eutrophication n the 2 nd convolution – calculation of the three indexes sum with different number weights: MCL - maximum concentration limit C bg – background level There are not weighting factor for indexes’ estimation scale and not estimated scales
 Modern methods of estimation of integral hydro chemical parameters of water quality V. V. Dmitriev, N. V. Myakisheva, N. V. Hovanov – “Multicryteria estimation of ecological state and stability geosystem based on Aggregates Method. I. Natural water quality”. (1996) n n n Integral estimation of natural water quality Aggregates method
Modern methods of estimation of integral hydro chemical parameters of water quality V. V. Dmitriev, N. V. Myakisheva, N. V. Hovanov – “Multicryteria estimation of ecological state and stability geosystem based on Aggregates Method. I. Natural water quality”. (1996) n n n Integral estimation of natural water quality Aggregates method
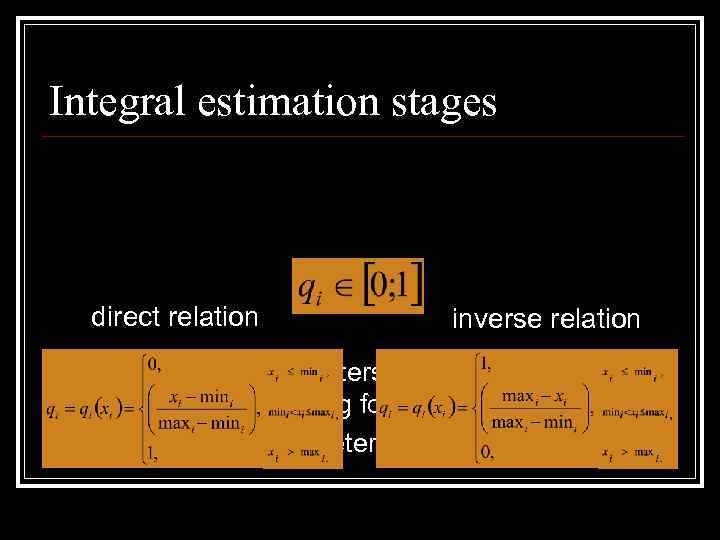 Integral estimation stages direct relation n n inverse relation The 1 st stage: parameters selection qi, quality metering scale building for each class of state The 2 nd stage: parameters normalization
Integral estimation stages direct relation n n inverse relation The 1 st stage: parameters selection qi, quality metering scale building for each class of state The 2 nd stage: parameters normalization
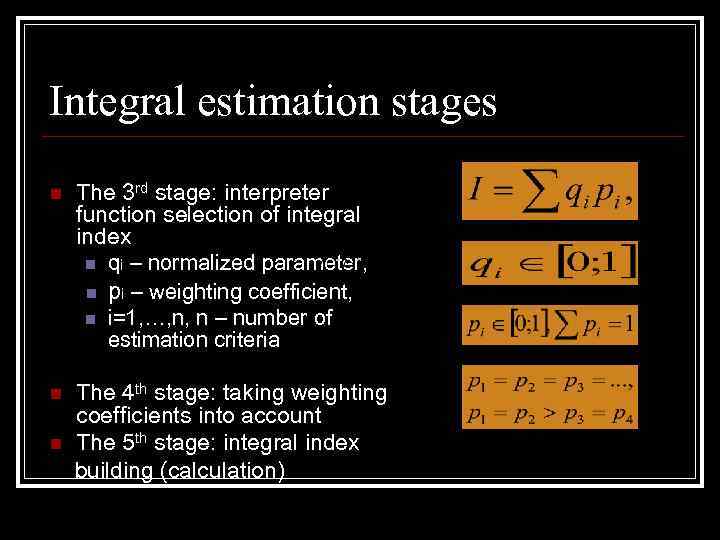 Integral estimation stages n The 3 rd stage: interpreter function selection of integral index n qi – normalized parameter, n pi – weighting coefficient, n i=1, …, n, n – number of estimation criteria n The 4 th stage: taking weighting coefficients into account The 5 th stage: integral index building (calculation) n
Integral estimation stages n The 3 rd stage: interpreter function selection of integral index n qi – normalized parameter, n pi – weighting coefficient, n i=1, …, n, n – number of estimation criteria n The 4 th stage: taking weighting coefficients into account The 5 th stage: integral index building (calculation) n
 Parameters for the practice work #1 n A lot of different kind of parameters can characterize ecosystem state of/and water quality (hydrological, hydrochemical, biological, and etc. ) n Saprobe-toxic index St (сапротоксобности) (Yakovlev, 1988) Biotic index Woodiwiss BI (Вудивисса), (Woodiwiss, 1964) Index of Goodnight-Whitley No/Nc (Гуднайта и Уитлея), (Goodnight, Whitley, 1961) Index of Balushkina Kch (Балушкиной), (Balushkina, 1976) n n n
Parameters for the practice work #1 n A lot of different kind of parameters can characterize ecosystem state of/and water quality (hydrological, hydrochemical, biological, and etc. ) n Saprobe-toxic index St (сапротоксобности) (Yakovlev, 1988) Biotic index Woodiwiss BI (Вудивисса), (Woodiwiss, 1964) Index of Goodnight-Whitley No/Nc (Гуднайта и Уитлея), (Goodnight, Whitley, 1961) Index of Balushkina Kch (Балушкиной), (Balushkina, 1976) n n n
 Biological indication (Bioindication) n The 1 st classical system of biological analyze of water quality was created by R. Kolkwitz and M. Marsson (1902) (Колквитцем и Марссоном). There are two groups of organism-antagonist: n n n Saprobiont (from Greek sapros – rotten). Saprobiont – inhabitant of polluted by organic matter environment. Сапробионт (обитатель загрязнённой органическими веществами среды) Katarobiont (from Greek katharos – clean). Katarobiont inhabitant of exactly clean water. Катаробионт. Saprobe (сапробность) – ability of organism for living in water with high organic matter concentration
Biological indication (Bioindication) n The 1 st classical system of biological analyze of water quality was created by R. Kolkwitz and M. Marsson (1902) (Колквитцем и Марссоном). There are two groups of organism-antagonist: n n n Saprobiont (from Greek sapros – rotten). Saprobiont – inhabitant of polluted by organic matter environment. Сапробионт (обитатель загрязнённой органическими веществами среды) Katarobiont (from Greek katharos – clean). Katarobiont inhabitant of exactly clean water. Катаробионт. Saprobe (сапробность) – ability of organism for living in water with high organic matter concentration
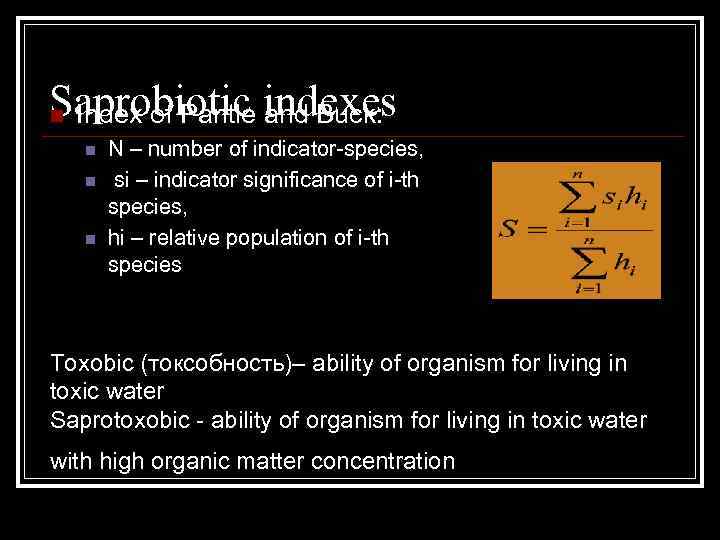 Saprobiotic indexes Index of Pantle and Buck: n n N – number of indicator-species, si – indicator significance of i-th species, hi – relative population of i-th species Toxobic (токсобность)– ability of organism for living in toxic water Saprotoxobic - ability of organism for living in toxic water with high organic matter concentration
Saprobiotic indexes Index of Pantle and Buck: n n N – number of indicator-species, si – indicator significance of i-th species, hi – relative population of i-th species Toxobic (токсобность)– ability of organism for living in toxic water Saprotoxobic - ability of organism for living in toxic water with high organic matter concentration
 Biotic index of Woodiwis n n n Biotic index of Woodiwis was built for estimation of fresh water pollution by zoobenthos for the Trent river in England in 1964. This method based on increasing of indicator groups quintity due to water pollution. There are some indicator-groups of hydrobionts. These are: n n n faverel - веснянка (Erophila) Dayfly - поденка (Ephemeroptera) caddis flies - ручейники (Trichoptera) Amphipods - бокоплавы (Amphipoda) water louse - водяной ослик (Asellus aquaticus) Oligohets – олигохеты
Biotic index of Woodiwis n n n Biotic index of Woodiwis was built for estimation of fresh water pollution by zoobenthos for the Trent river in England in 1964. This method based on increasing of indicator groups quintity due to water pollution. There are some indicator-groups of hydrobionts. These are: n n n faverel - веснянка (Erophila) Dayfly - поденка (Ephemeroptera) caddis flies - ручейники (Trichoptera) Amphipods - бокоплавы (Amphipoda) water louse - водяной ослик (Asellus aquaticus) Oligohets – олигохеты
 Goodhight-Witley index n Goodhight-Witley index – oligohets index n The main point – increasing oligohet population in benthic association on account of water pollution n Clean water – 60 % oligohet from benthic organisms Middle polluted water – 60 -80 % Very polluted water – more 80 % No – oligohet population, NB – benthic population
Goodhight-Witley index n Goodhight-Witley index – oligohets index n The main point – increasing oligohet population in benthic association on account of water pollution n Clean water – 60 % oligohet from benthic organisms Middle polluted water – 60 -80 % Very polluted water – more 80 % No – oligohet population, NB – benthic population
 Index of Balushkina n n Index of Balushkina chironomid index. Ration of chironomids subfamily is an bioindicator of water pollution Chironomids - хирономиды (Chironomidae) – larva of mosquito n n α=N+10 – relevant number of all subfamilies species T- Tanypodinae Ch – Chironominae O - Orthocladiinae
Index of Balushkina n n Index of Balushkina chironomid index. Ration of chironomids subfamily is an bioindicator of water pollution Chironomids - хирономиды (Chironomidae) – larva of mosquito n n α=N+10 – relevant number of all subfamilies species T- Tanypodinae Ch – Chironominae O - Orthocladiinae
 Work execution order 1. Based on Aggregated Method to built a learning classification for water quantity estimation for 6 classes by biological criteria: n n Saprobe index (St) Biotic index (BI) Goodhight-Witley index (No/Nc) Balushkina (Chironomidae) chironomids index (Kch)
Work execution order 1. Based on Aggregated Method to built a learning classification for water quantity estimation for 6 classes by biological criteria: n n Saprobe index (St) Biotic index (BI) Goodhight-Witley index (No/Nc) Balushkina (Chironomidae) chironomids index (Kch)
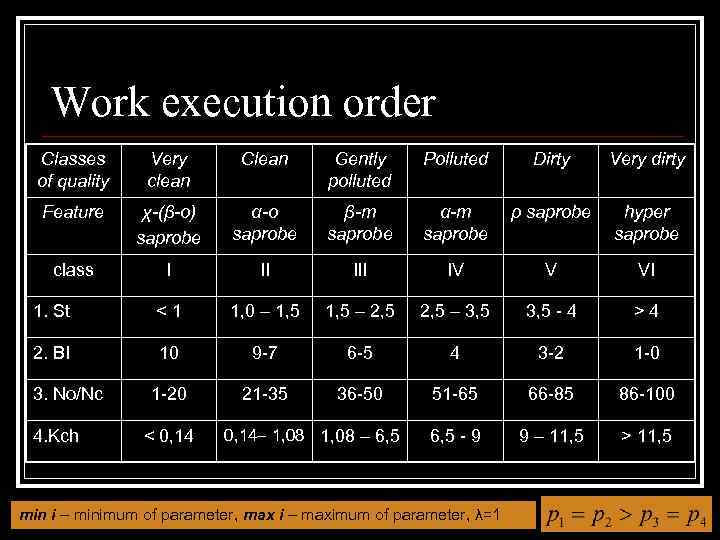 Work execution order Classes of quality Very clean Clean Gently polluted Polluted Dirty Very dirty Feature χ-(β-o) saprobe α-o saprobe β-m saprobe α-m saprobe ρ saprobe hyper saprobe class I II IV V VI 1. St <1 1, 0 – 1, 5 – 2, 5 – 3, 5 - 4 >4 2. BI 10 9 -7 6 -5 4 3 -2 1 -0 1 -20 21 -35 36 -50 51 -65 66 -85 86 -100 6, 5 - 9 9 – 11, 5 > 11, 5 3. No/Nc 4. Kch < 0, 14– 1, 08 – 6, 5 min i – minimum of parameter, max i – maximum of parameter, λ=1
Work execution order Classes of quality Very clean Clean Gently polluted Polluted Dirty Very dirty Feature χ-(β-o) saprobe α-o saprobe β-m saprobe α-m saprobe ρ saprobe hyper saprobe class I II IV V VI 1. St <1 1, 0 – 1, 5 – 2, 5 – 3, 5 - 4 >4 2. BI 10 9 -7 6 -5 4 3 -2 1 -0 1 -20 21 -35 36 -50 51 -65 66 -85 86 -100 6, 5 - 9 9 – 11, 5 > 11, 5 3. No/Nc 4. Kch < 0, 14– 1, 08 – 6, 5 min i – minimum of parameter, max i – maximum of parameter, λ=1
 Work execution order 2. Calculate of integral quality index, St=1, 55; BI=7; No/Nc=51; Kch=5, 0. According to volume to determine of water quality class
Work execution order 2. Calculate of integral quality index, St=1, 55; BI=7; No/Nc=51; Kch=5, 0. According to volume to determine of water quality class
 Work execution order 3. Hypothetical influence to ecosystem causes an ecological situation changing in a water object with indexes volume changing St=2, 25; BI=6; No/Nc=55; Kch=6, 0. Built a new Integral index and determine If such kind of influence to ecosystem is acceptable (tolerant) or not? Use your quality metric scale
Work execution order 3. Hypothetical influence to ecosystem causes an ecological situation changing in a water object with indexes volume changing St=2, 25; BI=6; No/Nc=55; Kch=6, 0. Built a new Integral index and determine If such kind of influence to ecosystem is acceptable (tolerant) or not? Use your quality metric scale
 Thank you for attention
Thank you for attention


