Risk. Is it in you.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Practical risk management Stuart Lawson April 2013
Practical risk management Stuart Lawson April 2013
 Contact Stuart Lawson, Executive Director Tel. : +7 (495) 662 -9312 E-mail: Stuart. Lawson@ru. ey. com ► 35 years in banking in EM and OECD. ► 25 years in Citibank in 11 countries including 10 as crisis manager. ► 15 years in Russia as CEO/Chairman Citibank, Deltabank, Banks Soyuz, HSBC, director Trust, Menatep. ► Chairman AEB Finance and Investment, Deputy Chairman The. City. UK Russia stream, Supervisory Board IDA. Page 2 Practical risk management
Contact Stuart Lawson, Executive Director Tel. : +7 (495) 662 -9312 E-mail: Stuart. Lawson@ru. ey. com ► 35 years in banking in EM and OECD. ► 25 years in Citibank in 11 countries including 10 as crisis manager. ► 15 years in Russia as CEO/Chairman Citibank, Deltabank, Banks Soyuz, HSBC, director Trust, Menatep. ► Chairman AEB Finance and Investment, Deputy Chairman The. City. UK Russia stream, Supervisory Board IDA. Page 2 Practical risk management
 How to take risk?
How to take risk?
 A practitioner’s course ► What is risk? A vocabulary. ► Risk management, how to maximise appropriate returns. ► Black swans can get in the way. ► Risk tools, the quadrants and heat map. Page 4 Practical risk management
A practitioner’s course ► What is risk? A vocabulary. ► Risk management, how to maximise appropriate returns. ► Black swans can get in the way. ► Risk tools, the quadrants and heat map. Page 4 Practical risk management
 Heads or Tails?
Heads or Tails?
 What is risk? ► Flip a coin, no financial outcome, does it have risk? (flipped coins have no memory) ► Interest in outcome creates concept of financial risk. ► Risk must deal with concept of loss but is inherent in the concept of profitability. Page 6 Practical risk management
What is risk? ► Flip a coin, no financial outcome, does it have risk? (flipped coins have no memory) ► Interest in outcome creates concept of financial risk. ► Risk must deal with concept of loss but is inherent in the concept of profitability. Page 6 Practical risk management
 What types of risk? ► Across a broad spectrum. ► External, outside your control. ► Within your control. ► The element of context and time. ► Types of risks. ► The constituents. ► The role of the board. Page 7 Practical risk management
What types of risk? ► Across a broad spectrum. ► External, outside your control. ► Within your control. ► The element of context and time. ► Types of risks. ► The constituents. ► The role of the board. Page 7 Practical risk management
 Risks you don’t control ► Macroeconomic, financial markets, domestic, international. ► Political, cross border. ► Industrial, cyclical, paradigm. ► Technological progress ► Business environment, local customs. ► Legal and regulatory. ► Acts of nature. Page 8 Practical risk management
Risks you don’t control ► Macroeconomic, financial markets, domestic, international. ► Political, cross border. ► Industrial, cyclical, paradigm. ► Technological progress ► Business environment, local customs. ► Legal and regulatory. ► Acts of nature. Page 8 Practical risk management
 Risks you do control ► Financial within company. ► Company strategy and tactics. ► Technology, systems, IT security. ► Operational, across all processes. ► Management, key man and team. ► Reputational and PR. ► Legal (not environmental). Page 9 Practical risk management
Risks you do control ► Financial within company. ► Company strategy and tactics. ► Technology, systems, IT security. ► Operational, across all processes. ► Management, key man and team. ► Reputational and PR. ► Legal (not environmental). Page 9 Practical risk management
 Industrial ► Innovations can create new paradigm. ► Market dominance and impact on price led or followed. ► Supply chain changes and flexibility. ► Cyclical or not, correlated to what factors (input prices, within without control). Page 10 Practical risk management
Industrial ► Innovations can create new paradigm. ► Market dominance and impact on price led or followed. ► Supply chain changes and flexibility. ► Cyclical or not, correlated to what factors (input prices, within without control). Page 10 Practical risk management
 Political ► Socio economic factors, short term elections, long term demographics. ► Can have broad repercussions across all industries and trading profiles. ► Impacts demand foreign direct investment. ► Cross border concepts and pricing. Impact of aggressive market positioning. Page 11 Practical risk management
Political ► Socio economic factors, short term elections, long term demographics. ► Can have broad repercussions across all industries and trading profiles. ► Impacts demand foreign direct investment. ► Cross border concepts and pricing. Impact of aggressive market positioning. Page 11 Practical risk management
 Company ► Dependent on corporate organisation, might be single entity, group or part of group. ► Driven by company specific tactics or strategy. ► Internal risk management failure. ► Relationships with employees. ► Impact of counterparty, suppliers, tax, banks. ► Risk profile of specific corporate. Page 12 Practical risk management
Company ► Dependent on corporate organisation, might be single entity, group or part of group. ► Driven by company specific tactics or strategy. ► Internal risk management failure. ► Relationships with employees. ► Impact of counterparty, suppliers, tax, banks. ► Risk profile of specific corporate. Page 12 Practical risk management
 Finance ► Balance between risk and return on capital, leverage ► Availability of liquidity resources during period of risk. ► Ability to extend trade creditors etc ► Crisis management and restructuring protocols. ► Shareholder support. Page 13 Practical risk management
Finance ► Balance between risk and return on capital, leverage ► Availability of liquidity resources during period of risk. ► Ability to extend trade creditors etc ► Crisis management and restructuring protocols. ► Shareholder support. Page 13 Practical risk management
 Technology ► Differing profiles of vulnerability to technology but always essential. Correct infrastructure regularly reviewed, properly documented ► Importance of appropriate MIS, training. ► Information security, vulnerability to internet and vendors. business continuity. ► Competitive map, what developments are needed to keep up? IT implementation ► Danger of the techies not understood by board, management. Competence to understand. Page 14 Practical risk management
Technology ► Differing profiles of vulnerability to technology but always essential. Correct infrastructure regularly reviewed, properly documented ► Importance of appropriate MIS, training. ► Information security, vulnerability to internet and vendors. business continuity. ► Competitive map, what developments are needed to keep up? IT implementation ► Danger of the techies not understood by board, management. Competence to understand. Page 14 Practical risk management
 Operational risk ► Holistic view of all aspects of the environment, what could go wrong? ► Protocols in place to govern intersection of entity with external events. ► A ‘what if’ set of action plans to address development of differing levels of risk. ► Physical risk to plant and employees. ► Intersection with technology, importance of processes. Page 15 Practical risk management
Operational risk ► Holistic view of all aspects of the environment, what could go wrong? ► Protocols in place to govern intersection of entity with external events. ► A ‘what if’ set of action plans to address development of differing levels of risk. ► Physical risk to plant and employees. ► Intersection with technology, importance of processes. Page 15 Practical risk management
 Management risk ► Misaligned organisational structures. ► Role of KPI’s. ► Key man risk, role of succession planning. ► Importance of corporate culture to bridge ‘gaps’. Page 16 Practical risk management
Management risk ► Misaligned organisational structures. ► Role of KPI’s. ► Key man risk, role of succession planning. ► Importance of corporate culture to bridge ‘gaps’. Page 16 Practical risk management
 Legal risk ► Enforceability of ownership rights fundamental to entrepreneurship. ► Regulation of rights between constituents. ► Trademarks, IP. ► Overly strong creditor rights enabling banks to seize assets. ► Unclear legal environment with changing laws. ► Corruption. Page 17 Practical risk management
Legal risk ► Enforceability of ownership rights fundamental to entrepreneurship. ► Regulation of rights between constituents. ► Trademarks, IP. ► Overly strong creditor rights enabling banks to seize assets. ► Unclear legal environment with changing laws. ► Corruption. Page 17 Practical risk management
 Reputational ► Enhances or diminishes brand value and ability to super price. ► Cuts across all business lines. ► Subject to event risk, importance of tight public relations. ► Requires clearly delineated ‘rules of road’ for interaction with media. ► Once broken, extremely difficult, costly and time consuming to repair. Page 18 Practical risk management
Reputational ► Enhances or diminishes brand value and ability to super price. ► Cuts across all business lines. ► Subject to event risk, importance of tight public relations. ► Requires clearly delineated ‘rules of road’ for interaction with media. ► Once broken, extremely difficult, costly and time consuming to repair. Page 18 Practical risk management
 PR ► Once out, particularly on internet, you can’t put it back ► It develops a momentum of its own ► Can be controlled by competitors ► Impact on brand value ► Who controls the ‘storyline’ Page 19 Practical risk management
PR ► Once out, particularly on internet, you can’t put it back ► It develops a momentum of its own ► Can be controlled by competitors ► Impact on brand value ► Who controls the ‘storyline’ Page 19 Practical risk management
 Perspective, context and time ► Experience is memory based and we have selective memories. ► History will influence the view of risk (eg been lucky in the past). ► Representative bias, that things should make sense. ► Risk does not take place in a vacuum (competitors, macro, industry). Page 20 Practical risk management
Perspective, context and time ► Experience is memory based and we have selective memories. ► History will influence the view of risk (eg been lucky in the past). ► Representative bias, that things should make sense. ► Risk does not take place in a vacuum (competitors, macro, industry). Page 20 Practical risk management
 Types of risk ► Market versus firm specific. ► Continuous versus event risk. ► Catastrophic versus smaller risk. ► Risks don’t have same rankings over time. ► ‘Chemistry’ of risks, not predictable. Page 21 Practical risk management
Types of risk ► Market versus firm specific. ► Continuous versus event risk. ► Catastrophic versus smaller risk. ► Risks don’t have same rankings over time. ► ‘Chemistry’ of risks, not predictable. Page 21 Practical risk management
 Who are the constituents? ► The management ► The customers ► The regulators ► The employees ► The shareholders Page 22 Practical risk management
Who are the constituents? ► The management ► The customers ► The regulators ► The employees ► The shareholders Page 22 Practical risk management
 Role of board in risk ► Management board ► Set up the vocabulary of risk. ► Dialogue with the supervisory board to set return parameters. ► Create and enforce control environment ► Supervisory board ► Represents the interests of the shareholders. ► Approves the overall risk and reward appetite. Page 23 Practical risk management 23
Role of board in risk ► Management board ► Set up the vocabulary of risk. ► Dialogue with the supervisory board to set return parameters. ► Create and enforce control environment ► Supervisory board ► Represents the interests of the shareholders. ► Approves the overall risk and reward appetite. Page 23 Practical risk management 23
 Risk management, a balancing act….
Risk management, a balancing act….
 What to do with risk? ► Avoid, strategic or tactical repositioning. ► Transfer, economically, to customers, banks, insurance companies. ► Mitigate, operational controls, redundancy systems. ► Keep. ► Maximise. An appropriate return for risk taken Page 25 Practical risk management
What to do with risk? ► Avoid, strategic or tactical repositioning. ► Transfer, economically, to customers, banks, insurance companies. ► Mitigate, operational controls, redundancy systems. ► Keep. ► Maximise. An appropriate return for risk taken Page 25 Practical risk management
 Dangers of risk management ► Wrong risk culture means faster to wrong conclusions, the herd mentality. ► Wrong input, wrong output (credit scoring Russia). ► Enables increased risks to systemic level. ► Can be used to disguise underlying risks. ► By changing shape of cash flow, may benefit one constituent at expense of another (compensation and career path). Page 26 Practical risk management 26
Dangers of risk management ► Wrong risk culture means faster to wrong conclusions, the herd mentality. ► Wrong input, wrong output (credit scoring Russia). ► Enables increased risks to systemic level. ► Can be used to disguise underlying risks. ► By changing shape of cash flow, may benefit one constituent at expense of another (compensation and career path). Page 26 Practical risk management 26
 …if you get it right ► Grow faster at more efficient rate of capital. ► Lengthens growth period. ► Impacts the default rate and therefore cost of debt. ► Creates a greater upside opportunity where the firm focuses on areas where it has competitive advantage. ► Allows stability of earnings that may be reflected in market valuation. ► Tax impact of earnings smoothing, reduces tax on excessive profit. Page 27 Practical risk management
…if you get it right ► Grow faster at more efficient rate of capital. ► Lengthens growth period. ► Impacts the default rate and therefore cost of debt. ► Creates a greater upside opportunity where the firm focuses on areas where it has competitive advantage. ► Allows stability of earnings that may be reflected in market valuation. ► Tax impact of earnings smoothing, reduces tax on excessive profit. Page 27 Practical risk management
 Black swan risk
Black swan risk
 Black swan, what is it? ► An outlier, outside normal expectations, rarity (the fat tail). ► Carries an extreme impact. ► Human nature causes us to explain why it occurred AFTER the event. ► Non occurance of the probable. ► Differing timeframes (earthquakes and internet). ► Unknown unknowns. Page 29 Practical risk management
Black swan, what is it? ► An outlier, outside normal expectations, rarity (the fat tail). ► Carries an extreme impact. ► Human nature causes us to explain why it occurred AFTER the event. ► Non occurance of the probable. ► Differing timeframes (earthquakes and internet). ► Unknown unknowns. Page 29 Practical risk management
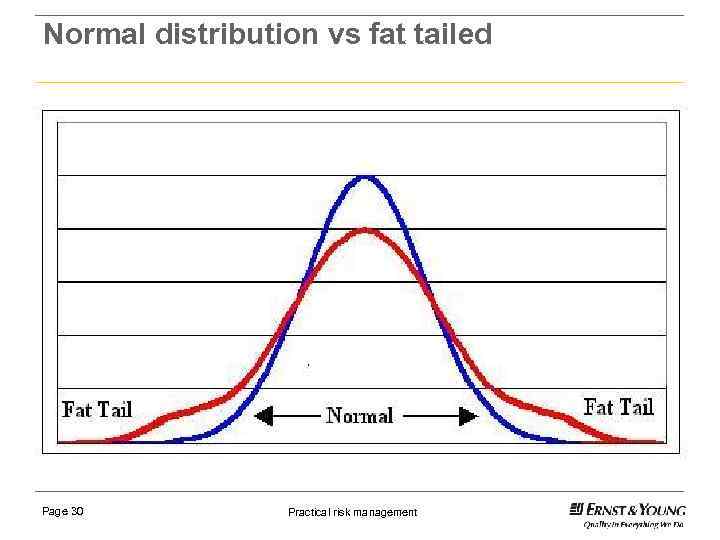 Normal distribution vs fat tailed Page 30 Practical risk management
Normal distribution vs fat tailed Page 30 Practical risk management
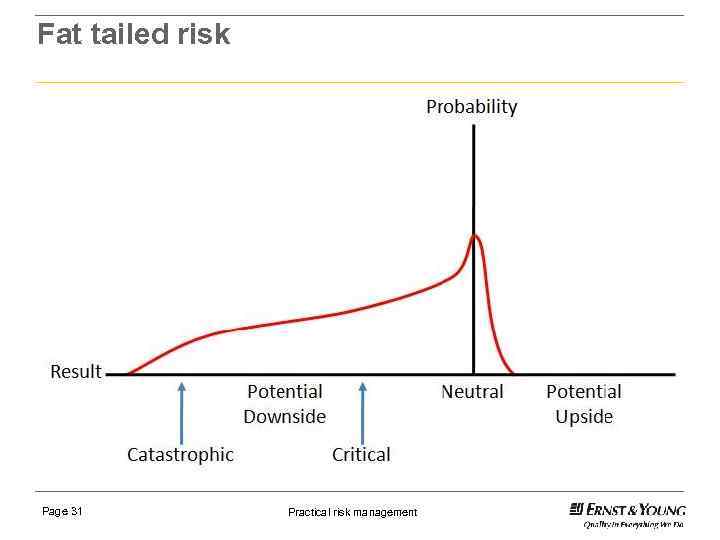 Fat tailed risk Page 31 Practical risk management
Fat tailed risk Page 31 Practical risk management
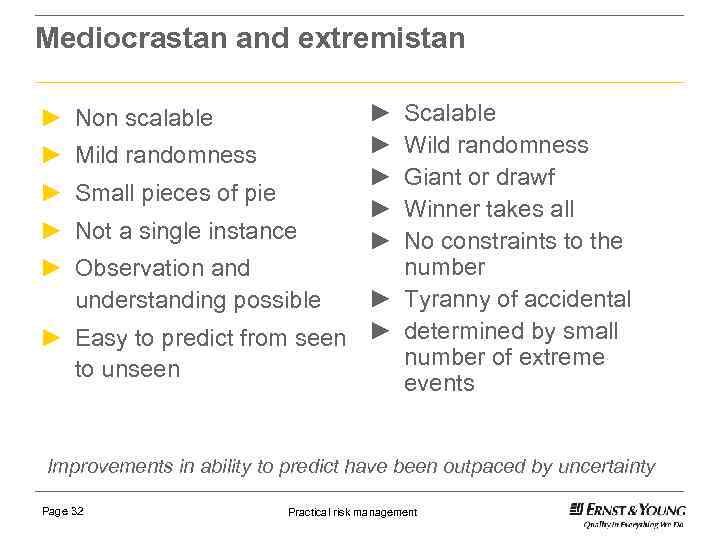 Mediocrastan and extremistan ► ► ► ► ► Scalable Wild randomness Mild randomness Giant or drawf Small pieces of pie Winner takes all Not a single instance No constraints to the number Observation and ► Tyranny of accidental understanding possible Easy to predict from seen ► determined by small number of extreme to unseen events ► Non scalable Improvements in ability to predict have been outpaced by uncertainty Page 32 Practical risk management
Mediocrastan and extremistan ► ► ► ► ► Scalable Wild randomness Mild randomness Giant or drawf Small pieces of pie Winner takes all Not a single instance No constraints to the number Observation and ► Tyranny of accidental understanding possible Easy to predict from seen ► determined by small number of extreme to unseen events ► Non scalable Improvements in ability to predict have been outpaced by uncertainty Page 32 Practical risk management
 And so? ? ? ► Allowing unexpected to happen key to success. ► Importance of trial and error, be as exposed as possible to chance encounters. ► Key to success is not always skills doesn’t mean skills not relevant. ► Can deliver black swans after thousands of white swans (the past does not predict the future, as a turkey around Thanksgiving). ► BS unpredictable consequences, retrospective explainability. ► Won’t know the unknown but maximise upside exposure to it. ► Preparedness not prediction, chance favours the prepared. Focus on consequences not probability Page 33 Practical risk management
And so? ? ? ► Allowing unexpected to happen key to success. ► Importance of trial and error, be as exposed as possible to chance encounters. ► Key to success is not always skills doesn’t mean skills not relevant. ► Can deliver black swans after thousands of white swans (the past does not predict the future, as a turkey around Thanksgiving). ► BS unpredictable consequences, retrospective explainability. ► Won’t know the unknown but maximise upside exposure to it. ► Preparedness not prediction, chance favours the prepared. Focus on consequences not probability Page 33 Practical risk management
 Four quadrants of risk
Four quadrants of risk
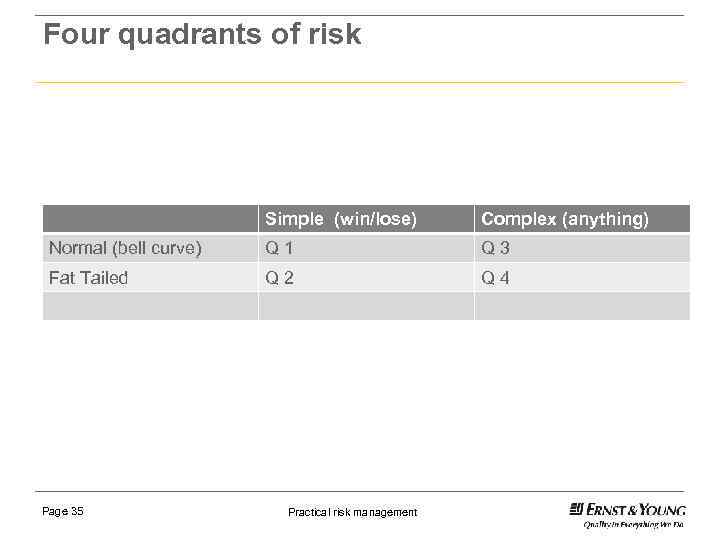 Four quadrants of risk Simple (win/lose) Complex (anything) Normal (bell curve) Q 1 Q 3 Fat Tailed Q 2 Q 4 Page 35 Practical risk management
Four quadrants of risk Simple (win/lose) Complex (anything) Normal (bell curve) Q 1 Q 3 Fat Tailed Q 2 Q 4 Page 35 Practical risk management
 Quadrant 1, simple, normal ► Heads or tails. ► No single outcome can dramatically change mean (height not wealth. ) ► Time of movie. ► Elections, win or lose. ► No leverage exists. . Page 36 Practical risk management
Quadrant 1, simple, normal ► Heads or tails. ► No single outcome can dramatically change mean (height not wealth. ) ► Time of movie. ► Elections, win or lose. ► No leverage exists. . Page 36 Practical risk management
 Quadrant 1 tools ► Probabilities from historical data work well. ► No outlier, surprises. ► At risk type models work well (VAR). Page 37 Practical risk management
Quadrant 1 tools ► Probabilities from historical data work well. ► No outlier, surprises. ► At risk type models work well (VAR). Page 37 Practical risk management
 Quadrant 2, simple, fat tailed ► Payoff simple (happens or not). ► Able to understand the outcomes of events that might happen. ► Manageable risks. ► Apple (Q 1) coconut (Q 2) trees. ► Shark attack. ► Oil spills. ► Define risks. Page 38 Practical risk management
Quadrant 2, simple, fat tailed ► Payoff simple (happens or not). ► Able to understand the outcomes of events that might happen. ► Manageable risks. ► Apple (Q 1) coconut (Q 2) trees. ► Shark attack. ► Oil spills. ► Define risks. Page 38 Practical risk management
 Quadrant 2 tools ► Do not understand the distribution of risks well. ► Do not know when a dramatic event may occur. ► But we do know the consequences. ► Don’t know timing or how bad. . ► If size matters and timing everything, we have a problem. ► Generally the risks can be managed, rules based, reduce, cap, mitigate. Page 39 Practical risk management
Quadrant 2 tools ► Do not understand the distribution of risks well. ► Do not know when a dramatic event may occur. ► But we do know the consequences. ► Don’t know timing or how bad. . ► If size matters and timing everything, we have a problem. ► Generally the risks can be managed, rules based, reduce, cap, mitigate. Page 39 Practical risk management
 Q 3, complex, normal distribution ► No leverage. ► Outcome predictable with high level of certainty. ► Errors mostly human not physical ► O rings on challenger. ► Auto parts, complex machinery. ► Lunar expedition. ► Are historical statistics reliable guide? Page 40 Practical risk management
Q 3, complex, normal distribution ► No leverage. ► Outcome predictable with high level of certainty. ► Errors mostly human not physical ► O rings on challenger. ► Auto parts, complex machinery. ► Lunar expedition. ► Are historical statistics reliable guide? Page 40 Practical risk management
 Quadrant 3 tools ► Resilient, redundancy, fail safe systems. ► Are the tails really thin or is it a lack of historical data (ie are we fooling ourselves). ► True Quadrant 3 risks can be managed around. Page 41 Practical risk management
Quadrant 3 tools ► Resilient, redundancy, fail safe systems. ► Are the tails really thin or is it a lack of historical data (ie are we fooling ourselves). ► True Quadrant 3 risks can be managed around. Page 41 Practical risk management
 Q 4 complex, fat tailed ► Black swan territory. ► Infrequent but massive impact. ► Leverage is often excessive. ► Risk models dont work. ► Extremistan. ► Social impact high (job loss, government fail). ► Dont rely on statistics or models. Page 42 Practical risk management
Q 4 complex, fat tailed ► Black swan territory. ► Infrequent but massive impact. ► Leverage is often excessive. ► Risk models dont work. ► Extremistan. ► Social impact high (job loss, government fail). ► Dont rely on statistics or models. Page 42 Practical risk management
 Quadrant 4 tools ► We cannot manage or model the unknown risks of Q 4. ► Limit the downside risk contractually. ► Reduce the impact of relationships and complexities we do not understand. ► Build in redundancies, train. Page 43 Practical risk management 43
Quadrant 4 tools ► We cannot manage or model the unknown risks of Q 4. ► Limit the downside risk contractually. ► Reduce the impact of relationships and complexities we do not understand. ► Build in redundancies, train. Page 43 Practical risk management 43
 Risk tools
Risk tools
 Over the horizon, strategic ► Longer the horizon, more strategic needs more discussion and challenge to historical bias. ► Challenge the output with independent experts. ► Small cross functional risk team that collates silo’s information and looks for patterns etc. ► Maps of potential risk and response. Page 45 Practical risk management
Over the horizon, strategic ► Longer the horizon, more strategic needs more discussion and challenge to historical bias. ► Challenge the output with independent experts. ► Small cross functional risk team that collates silo’s information and looks for patterns etc. ► Maps of potential risk and response. Page 45 Practical risk management
 External ► External, uncontrollable risks (black swans excluded). ► Stress testing, but watch out for recent history (eg USA real estate) causing myopia ► Scenario planning, define time horizon, which events will have maximum impact on company (watch out for over optimism). ► War gaming, teams develop what competitors (actual and potential) could do to disrupt plan. Page 46 Practical risk management
External ► External, uncontrollable risks (black swans excluded). ► Stress testing, but watch out for recent history (eg USA real estate) causing myopia ► Scenario planning, define time horizon, which events will have maximum impact on company (watch out for over optimism). ► War gaming, teams develop what competitors (actual and potential) could do to disrupt plan. Page 46 Practical risk management
 Preventable, predictable risks ► Compliance, rules based systems with appropriate exceptions (important to know who can make the call). ► Standard operating procedure and clear internal culture around strong mission statement ► Integrated risk management alongside line, but beware of ‘going local’ ► Checked with internal audit, line reviews Page 47 Practical risk management
Preventable, predictable risks ► Compliance, rules based systems with appropriate exceptions (important to know who can make the call). ► Standard operating procedure and clear internal culture around strong mission statement ► Integrated risk management alongside line, but beware of ‘going local’ ► Checked with internal audit, line reviews Page 47 Practical risk management
 Some tools ► Scenarios, separate risks, three outcomes ► Decision trees, separate risks, many outcomes ► Scenario planning, continuous risk, correlated, built into each simulation Page 48 Practical risk management
Some tools ► Scenarios, separate risks, three outcomes ► Decision trees, separate risks, many outcomes ► Scenario planning, continuous risk, correlated, built into each simulation Page 48 Practical risk management
 Practical approach to risk management ► Make inventory of all risks, categorise them ► Quantify risk for entity, high, medium, low ► Manage the downside whilst maximising the upside. Decide which risks to hedge, which to pass through to investors. Cost versus impact. ► What risk hedging products are available, correlation? ► Which risks can be handled better than competition? ► Create strategies to maximise exposure to risks which entity can better handle Page 49 Practical risk management 49
Practical approach to risk management ► Make inventory of all risks, categorise them ► Quantify risk for entity, high, medium, low ► Manage the downside whilst maximising the upside. Decide which risks to hedge, which to pass through to investors. Cost versus impact. ► What risk hedging products are available, correlation? ► Which risks can be handled better than competition? ► Create strategies to maximise exposure to risks which entity can better handle Page 49 Practical risk management 49
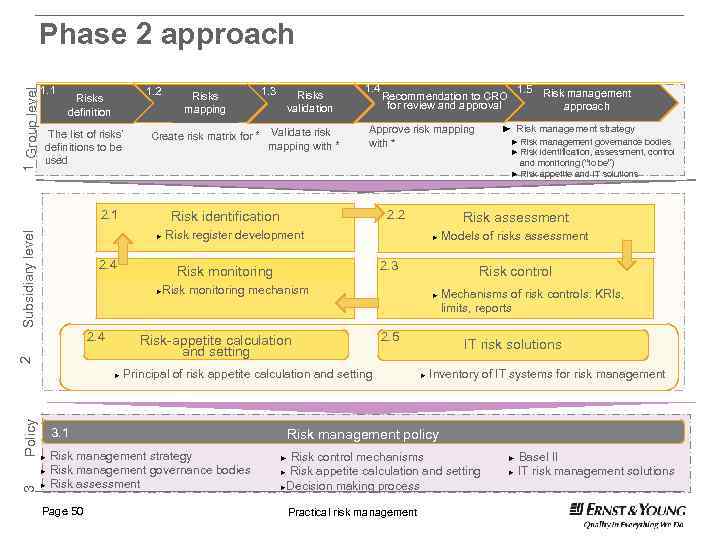 1 Group level Phase 2 approach 1. 1 1. 2 Risks definition The list of risks’ definitions to be used Risks mapping 1. 4 1. 5 Risk management approach Recommendation to CRO for review and approval ► Risk management strategy Approve risk mapping with * ► Risk management governance bodies ► Risk identification, assessment, control and monitoring (“to be”) ► Risk appetite and IT solutions Subsidiary level 2. 2 Risk identification ► 2. 4 Risk assessment Risk register development ► 2. 3 Risk monitoring mechanism 2 Risk-appetite calculation and setting ► 3. 1 Risk management strategy ► Risk management governance bodies ► Risk assessment ► Page 50 ► 2. 5 Principal of risk appetite calculation and setting Models of risks assessment Risk control ► 2. 4 Policy Risks validation Create risk matrix for * Validate risk mapping with * 2. 1 3 1. 3 Mechanisms of risk controls: KRIs, limits, reports IT risk solutions ► Inventory of IT systems for risk management Risk management policy Risk control mechanisms Risk appetite calculation and setting ►Decision making process ► ► Practical risk management Basel II IT risk management solutions
1 Group level Phase 2 approach 1. 1 1. 2 Risks definition The list of risks’ definitions to be used Risks mapping 1. 4 1. 5 Risk management approach Recommendation to CRO for review and approval ► Risk management strategy Approve risk mapping with * ► Risk management governance bodies ► Risk identification, assessment, control and monitoring (“to be”) ► Risk appetite and IT solutions Subsidiary level 2. 2 Risk identification ► 2. 4 Risk assessment Risk register development ► 2. 3 Risk monitoring mechanism 2 Risk-appetite calculation and setting ► 3. 1 Risk management strategy ► Risk management governance bodies ► Risk assessment ► Page 50 ► 2. 5 Principal of risk appetite calculation and setting Models of risks assessment Risk control ► 2. 4 Policy Risks validation Create risk matrix for * Validate risk mapping with * 2. 1 3 1. 3 Mechanisms of risk controls: KRIs, limits, reports IT risk solutions ► Inventory of IT systems for risk management Risk management policy Risk control mechanisms Risk appetite calculation and setting ►Decision making process ► ► Practical risk management Basel II IT risk management solutions
 1 Risk management design process 1. 1 Risks’ definition Page 51 Practical risk management
1 Risk management design process 1. 1 Risks’ definition Page 51 Practical risk management
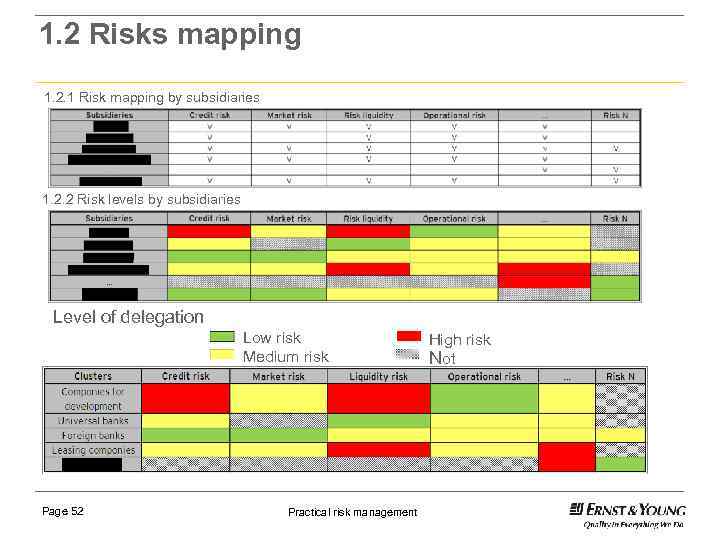 1. 2 Risks mapping 1. 2. 1 Risk mapping by subsidiaries 1. 2. 2 Risk levels by subsidiaries Level of delegation Low risk Medium risk 1. 2. 3 Risk levels by clusters Page 52 Practical risk management High risk Not applicable
1. 2 Risks mapping 1. 2. 1 Risk mapping by subsidiaries 1. 2. 2 Risk levels by subsidiaries Level of delegation Low risk Medium risk 1. 2. 3 Risk levels by clusters Page 52 Practical risk management High risk Not applicable
 Conclusion ► Before you have the discussion, create the vocabulary. ► Create a broad log of all risks. ► Ensure that all constituents participate. ► Map risks against quadrants. ► Review appropriate actions against each set of risks. ► Schedule regular reviews, risks change over time. Page 53 Practical risk management
Conclusion ► Before you have the discussion, create the vocabulary. ► Create a broad log of all risks. ► Ensure that all constituents participate. ► Map risks against quadrants. ► Review appropriate actions against each set of risks. ► Schedule regular reviews, risks change over time. Page 53 Practical risk management
 Thank you !
Thank you !


