 Practical Phonetics Week 2 Classifying sounds: place and manner of articulation Where and how sounds are made
Practical Phonetics Week 2 Classifying sounds: place and manner of articulation Where and how sounds are made
 Thinking about sounds • Say ‘mmmm’ – where is the ‘m’ sound produced? It’s a bilabial consonant (this is the place of articulation) • Pinch your nose – what happens? It stops: it’s a nasal (not an oral) consonant • Put your fingers in your ears – what do you hear? The vibrations of the vocal cords: it’s a voiced consonant
Thinking about sounds • Say ‘mmmm’ – where is the ‘m’ sound produced? It’s a bilabial consonant (this is the place of articulation) • Pinch your nose – what happens? It stops: it’s a nasal (not an oral) consonant • Put your fingers in your ears – what do you hear? The vibrations of the vocal cords: it’s a voiced consonant
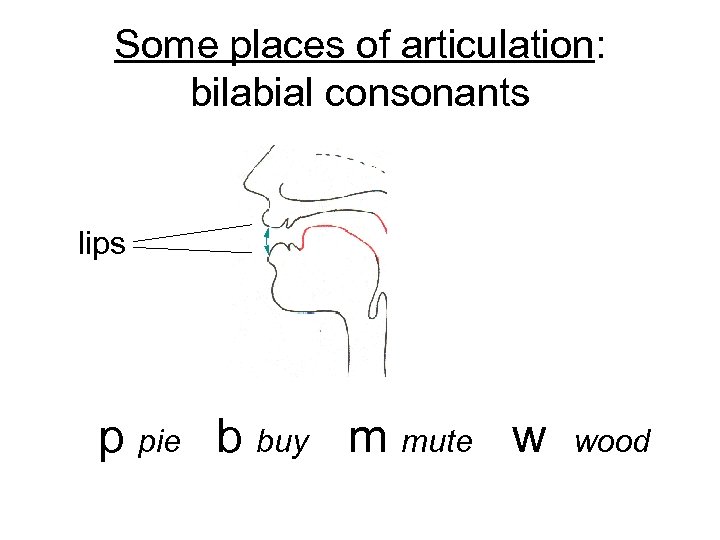 Some places of articulation: bilabial consonants lips p pie b buy m mute w wood
Some places of articulation: bilabial consonants lips p pie b buy m mute w wood
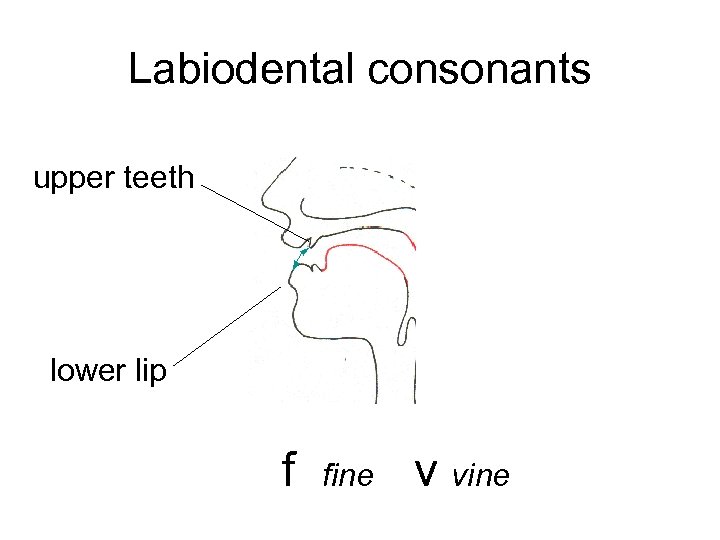 Labiodental consonants upper teeth lower lip f fine v vine
Labiodental consonants upper teeth lower lip f fine v vine
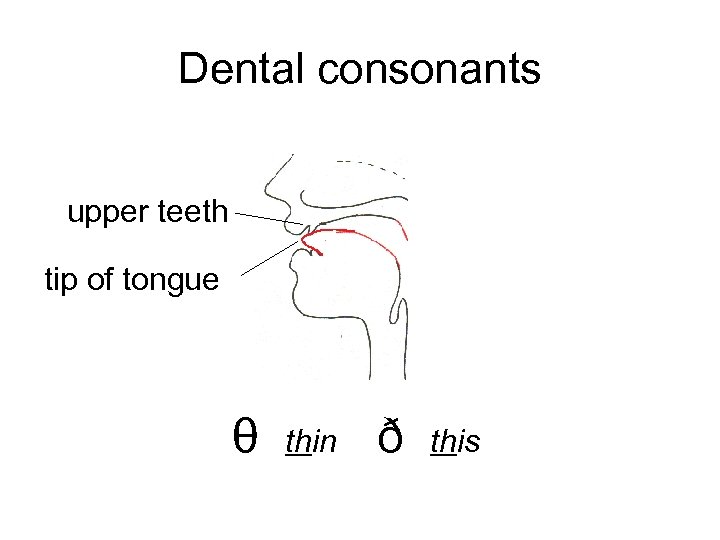 Dental consonants upper teeth tip of tongue θ thin ð this
Dental consonants upper teeth tip of tongue θ thin ð this
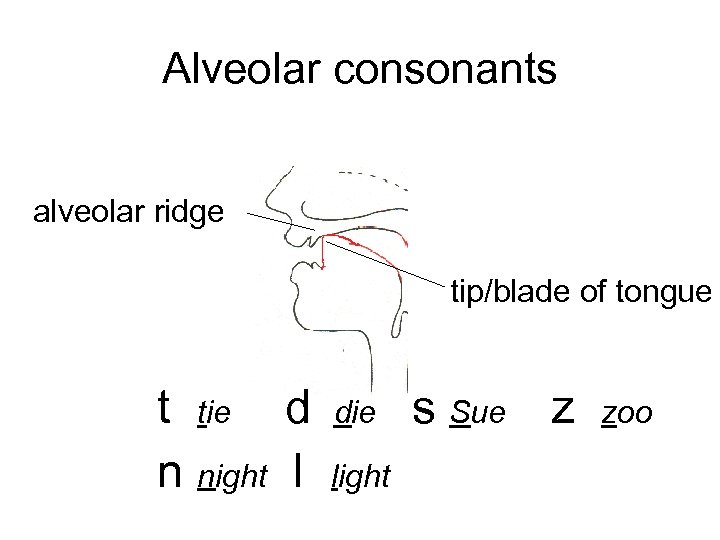 Alveolar consonants alveolar ridge tip/blade of tongue t tie d n night l die light s Sue z zoo
Alveolar consonants alveolar ridge tip/blade of tongue t tie d n night l die light s Sue z zoo
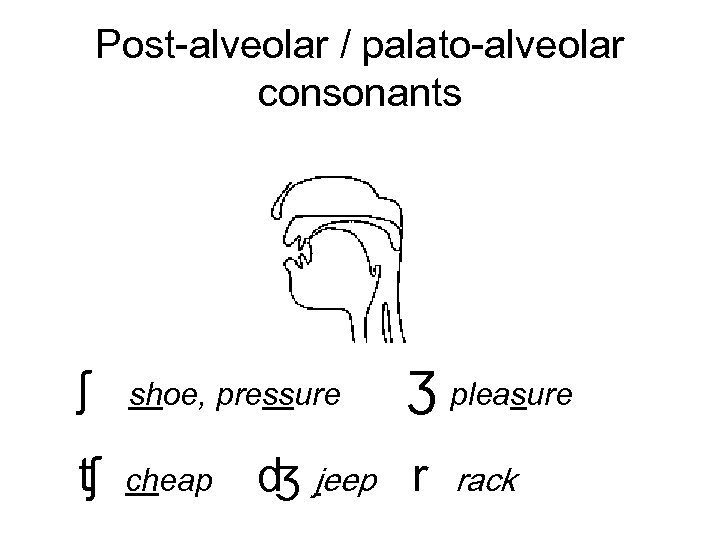 Post-alveolar / palato-alveolar consonants ʃ shoe, pressure ʧ cheap Ʒ pleasure ʤ jeep r rack
Post-alveolar / palato-alveolar consonants ʃ shoe, pressure ʧ cheap Ʒ pleasure ʤ jeep r rack
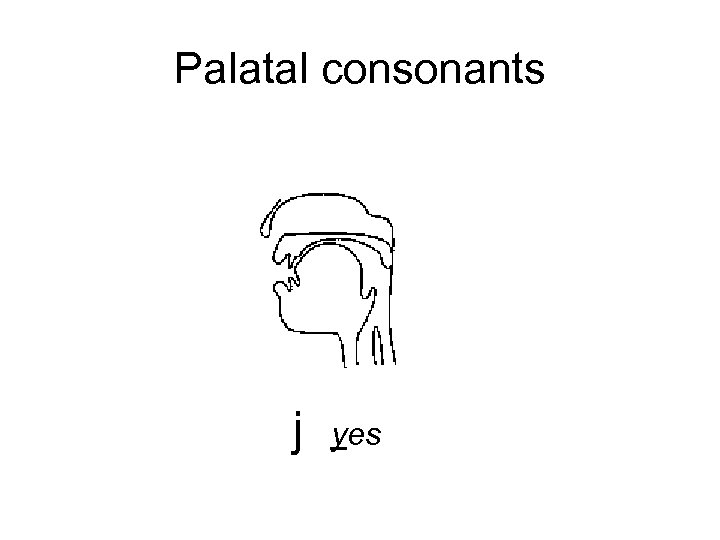 Palatal consonants j yes
Palatal consonants j yes
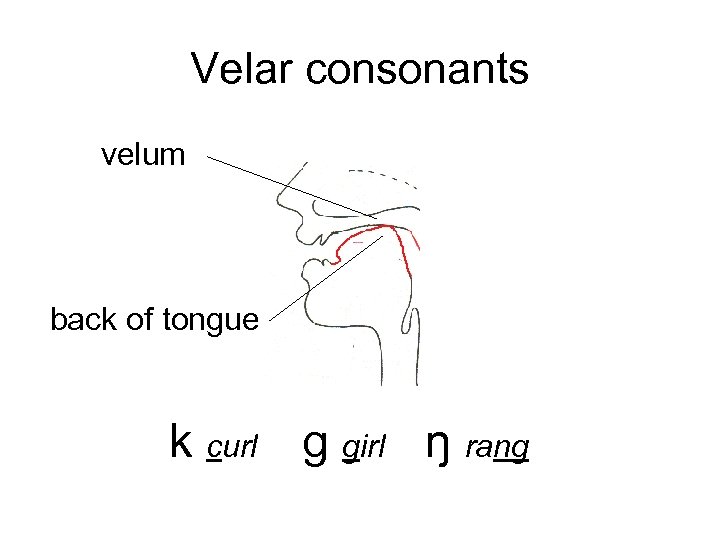 Velar consonants velum back of tongue k curl g girl ŋ rang
Velar consonants velum back of tongue k curl g girl ŋ rang
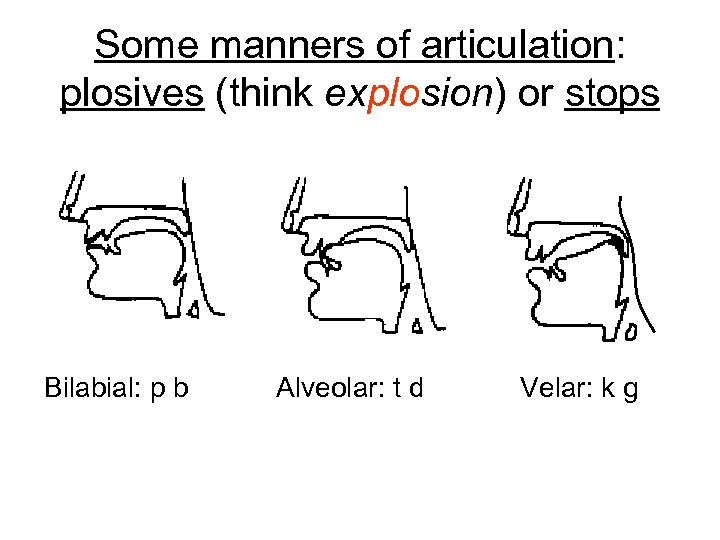 Some manners of articulation: plosives (think explosion) or stops Bilabial: p b Alveolar: t d Velar: k g
Some manners of articulation: plosives (think explosion) or stops Bilabial: p b Alveolar: t d Velar: k g
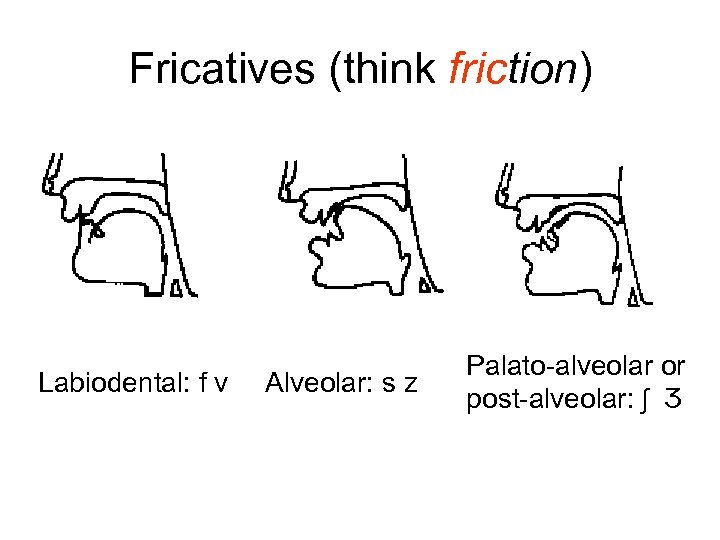 Fricatives (think friction) Labiodental: f v Alveolar: s z Palato-alveolar or post-alveolar: ʃ Ʒ
Fricatives (think friction) Labiodental: f v Alveolar: s z Palato-alveolar or post-alveolar: ʃ Ʒ
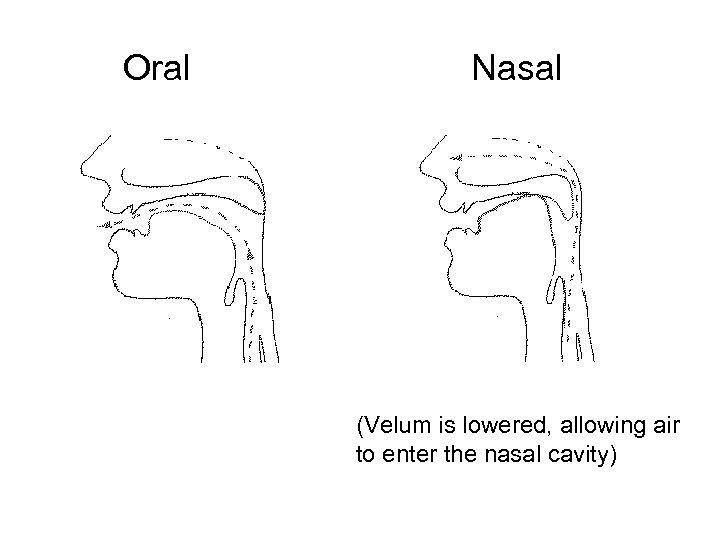 Oral Nasal (Velum is lowered, allowing air to enter the nasal cavity)
Oral Nasal (Velum is lowered, allowing air to enter the nasal cavity)
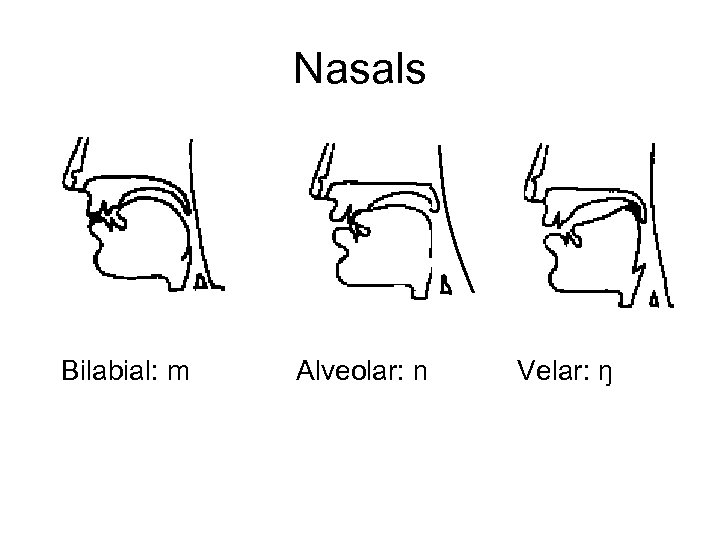 Nasals Bilabial: m Alveolar: n Velar: ŋ
Nasals Bilabial: m Alveolar: n Velar: ŋ
 Other consonants • Affricates (a combination of stop + fricative): ʧ = voiceless post-alveolar affricate ʤ = voiced post-alveolar affricate • Approximant (articulators approach each other but do not touch): w r j • Lateral (also called lateral approximant; air flows over sides of tongue): l
Other consonants • Affricates (a combination of stop + fricative): ʧ = voiceless post-alveolar affricate ʤ = voiced post-alveolar affricate • Approximant (articulators approach each other but do not touch): w r j • Lateral (also called lateral approximant; air flows over sides of tongue): l
 Summary of Places of Articulation Bilabial (lips) p b m w • Labiodental (lips and teeth) f fine v vine • Dental (tongue and teeth) θ thin ð then • Alveolar (tongue and alveolar ridge) tdsznl • Palato-alveolar (tongue and front part of hard palate) ʃ shoe ʒ measure ʧ cheap ʤ jeep r • Palatal (tongue and hard palate) j yes • Velar (tongue and velum) k g ŋ running • Glottal (glottis) h •
Summary of Places of Articulation Bilabial (lips) p b m w • Labiodental (lips and teeth) f fine v vine • Dental (tongue and teeth) θ thin ð then • Alveolar (tongue and alveolar ridge) tdsznl • Palato-alveolar (tongue and front part of hard palate) ʃ shoe ʒ measure ʧ cheap ʤ jeep r • Palatal (tongue and hard palate) j yes • Velar (tongue and velum) k g ŋ running • Glottal (glottis) h •
 Summary of manners of articulation • • • Plosive / Stop p b t d k g Fricative f v θ ð s z ʃ ʒ h Affricate (stop + fricative) ʧ ʤ Nasal m n ŋ Approximants w r j (central) l (lateral)
Summary of manners of articulation • • • Plosive / Stop p b t d k g Fricative f v θ ð s z ʃ ʒ h Affricate (stop + fricative) ʧ ʤ Nasal m n ŋ Approximants w r j (central) l (lateral)
 Classifying consonants • Voiced or voiceless • Place of articulation • (Central or lateral) • (Oral or nasal) • Manner of articulation Example 1 : s (sing): - A voiceless, alveolar, (central), (oral) fricative - A voiceless, alveolar plosive/stop = ? /t/ What is /k/? - A voiceless, velar plosive/stop
Classifying consonants • Voiced or voiceless • Place of articulation • (Central or lateral) • (Oral or nasal) • Manner of articulation Example 1 : s (sing): - A voiceless, alveolar, (central), (oral) fricative - A voiceless, alveolar plosive/stop = ? /t/ What is /k/? - A voiceless, velar plosive/stop
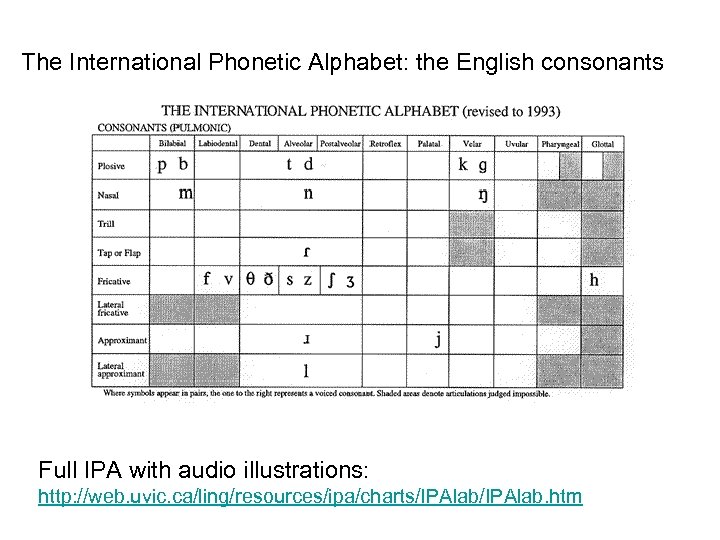 The International Phonetic Alphabet: the English consonants Full IPA with audio illustrations: http: //web. uvic. ca/ling/resources/ipa/charts/IPAlab. htm
The International Phonetic Alphabet: the English consonants Full IPA with audio illustrations: http: //web. uvic. ca/ling/resources/ipa/charts/IPAlab. htm
 And finally…an x-ray (not x-rated) movie: http: //www. practicalphonetics. com/seeing%20 through%20 speech. htm Review activities • Complete the “Classifying Consonants” chart • Labels practice: http: //www. phon. ucl. ac. uk/home/johnm/flash/phonflashrp. htm • Symbols practice: http: //www. phon. ucl. ac. uk/home/johnm/flash/findrp. htm
And finally…an x-ray (not x-rated) movie: http: //www. practicalphonetics. com/seeing%20 through%20 speech. htm Review activities • Complete the “Classifying Consonants” chart • Labels practice: http: //www. phon. ucl. ac. uk/home/johnm/flash/phonflashrp. htm • Symbols practice: http: //www. phon. ucl. ac. uk/home/johnm/flash/findrp. htm