Lesson #6 Деф.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Practical lesson #6 Education of children with speech impairments • Warm-up: Quiz • Key special words • Questions • Speech organs • Speech and language disorders • Speech therapist • Present Continuous • Famous people with speech impairments
Practical lesson #6 Education of children with speech impairments • Warm-up: Quiz • Key special words • Questions • Speech organs • Speech and language disorders • Speech therapist • Present Continuous • Famous people with speech impairments
 Who developed theories on human development? • Sigmund Freud • John Watson • B. F. Skinner • Lev Vygotsky • Erikson • Jean Piaget
Who developed theories on human development? • Sigmund Freud • John Watson • B. F. Skinner • Lev Vygotsky • Erikson • Jean Piaget
 Who is the father of psychoanalysis?
Who is the father of psychoanalysis?
 Who is the father of behaviorism?
Who is the father of behaviorism?
 Who is the father of operant conditioning?
Who is the father of operant conditioning?
 Who developed stages of cognitive development?
Who developed stages of cognitive development?
 Who developed sociocultural theory of human development?
Who developed sociocultural theory of human development?
 Who developed stages of psychosocial development?
Who developed stages of psychosocial development?
 What areas of human development? • Physical development • Cognitive development • Emotional and social development
What areas of human development? • Physical development • Cognitive development • Emotional and social development
 What are stages of human development? • Infancy • Childhood • Adolescence • Adulthood
What are stages of human development? • Infancy • Childhood • Adolescence • Adulthood
 Scientist Sigmund Freud Erikson John Watson B. F. Skinner Jean Piaget Name of theory (-ies) Main achievements Psychoanalysis or • Development is a conflictual process psychosexual theory • 3 components of personality • Free association method • Defense mechanisms Psychosocial • 8 stages of psychosocial development • Childhood and Society (1950) Behaviorism: classical • Applying the mechanisms of classical conditioning to children • 1928: Psychological Care of Infant and Child Behaviorism: operant • Advocated behavioral engineering by means of conditioning different schedules of reinforcement and punishment Cognitive • Four stages of cognitive development Developmental Theory • The Origins of Intelligence in Children (1952) (cognitive constructivism) Lev Vygotsky Sociocultural theory • Studies on the cultural context of children’s lives (social constructivism) • Zone of proximal development • Scaffolding Who developed different theories on human development?
Scientist Sigmund Freud Erikson John Watson B. F. Skinner Jean Piaget Name of theory (-ies) Main achievements Psychoanalysis or • Development is a conflictual process psychosexual theory • 3 components of personality • Free association method • Defense mechanisms Psychosocial • 8 stages of psychosocial development • Childhood and Society (1950) Behaviorism: classical • Applying the mechanisms of classical conditioning to children • 1928: Psychological Care of Infant and Child Behaviorism: operant • Advocated behavioral engineering by means of conditioning different schedules of reinforcement and punishment Cognitive • Four stages of cognitive development Developmental Theory • The Origins of Intelligence in Children (1952) (cognitive constructivism) Lev Vygotsky Sociocultural theory • Studies on the cultural context of children’s lives (social constructivism) • Zone of proximal development • Scaffolding Who developed different theories on human development?
 What is special pedagogy divided into? • Special pedagogy is divided into: • Surdopedagogy • Typhlopedagogy • Logopedics or Speech therapy • Oligophrenopedagogy • Orthopedagogy
What is special pedagogy divided into? • Special pedagogy is divided into: • Surdopedagogy • Typhlopedagogy • Logopedics or Speech therapy • Oligophrenopedagogy • Orthopedagogy
 What is special psychology divided into? • Special psychology is divided into: • Surdopsychology • Typhlopsychology • Logopsychology • Oligophrenopsychology
What is special psychology divided into? • Special psychology is divided into: • Surdopsychology • Typhlopsychology • Logopsychology • Oligophrenopsychology
 What sciences are related to Special education (Defectology)? • • Special psychology Special pedagogy Pathology Neology Psychopathology Neuropathology Medicine Anatomy • • Linguistics Neurolinguistics Immunology Physiology Psychiatry Children psychiatry Orthopedics Ophthalmology
What sciences are related to Special education (Defectology)? • • Special psychology Special pedagogy Pathology Neology Psychopathology Neuropathology Medicine Anatomy • • Linguistics Neurolinguistics Immunology Physiology Psychiatry Children psychiatry Orthopedics Ophthalmology
 What are types of impairments? • Visual impairments • Hearing impairments • Intellectual disorders • Speech impairments • Behaviour disorders • Locomotor impairments • Multiple disorders
What are types of impairments? • Visual impairments • Hearing impairments • Intellectual disorders • Speech impairments • Behaviour disorders • Locomotor impairments • Multiple disorders
 What are types of disabilities? • physical disabilities (locomotor impairments, spinal injury, amputation, etc. ) • sensory disabilities (visual impairments, hearing impairments, olfactory and gustatory impairment, somatosensory impairment, balance disorder) • cognitive or developmental disabilities (intellectual disability, cerebral palsy) • mental health and emotional disabilities • non-visible disabilities ( diabetes, asthma, epilepsy, narcolepsy, etc. )
What are types of disabilities? • physical disabilities (locomotor impairments, spinal injury, amputation, etc. ) • sensory disabilities (visual impairments, hearing impairments, olfactory and gustatory impairment, somatosensory impairment, balance disorder) • cognitive or developmental disabilities (intellectual disability, cerebral palsy) • mental health and emotional disabilities • non-visible disabilities ( diabetes, asthma, epilepsy, narcolepsy, etc. )
 What are categories of disabled people? • • • The disabled/ handicapped The deaf The hearing impaired The blind The visually impaired The dumb/ mute The speech impaired The intellectually impaired The mentally retarded Individuals with behaviour disorders Individuals with locomotor impairments Individuals with multiple impairments/ disorders
What are categories of disabled people? • • • The disabled/ handicapped The deaf The hearing impaired The blind The visually impaired The dumb/ mute The speech impaired The intellectually impaired The mentally retarded Individuals with behaviour disorders Individuals with locomotor impairments Individuals with multiple impairments/ disorders
 What mental functions do you know? • • • Sensation Perception Attention Thinking Memory Speech Imagination Emotion Volition Consciousness
What mental functions do you know? • • • Sensation Perception Attention Thinking Memory Speech Imagination Emotion Volition Consciousness

 True or false?
True or false?
 Match: • • Albert Einstein Pablo Picasso Rudolf Nureyev Wolfgang Mozart Siberia, 1938 Austria, 1756 Spain, 1881 Germany, 1879 • • artist composer scientist ballet dancer • Theory of relativity • Requiem • Cubism • Swan Lake
Match: • • Albert Einstein Pablo Picasso Rudolf Nureyev Wolfgang Mozart Siberia, 1938 Austria, 1756 Spain, 1881 Germany, 1879 • • artist composer scientist ballet dancer • Theory of relativity • Requiem • Cubism • Swan Lake
 Human Psychology: Match • Sigmund Freud • Erikson • Lev Vygotsky behaviorism operant conditioning stages of psychosocial development psychoanalysis • B. F. Skinner stages of cognitive development • John Watson zone of proximal development • Jean Piaget
Human Psychology: Match • Sigmund Freud • Erikson • Lev Vygotsky behaviorism operant conditioning stages of psychosocial development psychoanalysis • B. F. Skinner stages of cognitive development • John Watson zone of proximal development • Jean Piaget
 Education of children with speech impairments • Aim: to train students to define and understand psychological and pedagogical peculiarities of teaching children with speech impairments. • Key special words: speech impairment, speech therapy, speech therapist, aphasia, alalia, dyslalia, rhinolalia, dyslexia, alexia, dysarthria, general speech underdevelopment, apraxia of speech, verbal dyspraxia, voice disorders (aphonia, dysphonia), speech sound disorders, stuttering, dumb/mute children, selective mutism, language-based learning disabilities, fluency of speech, vocal cords, aphonia, dysphonia, articulation, phonation, lisp.
Education of children with speech impairments • Aim: to train students to define and understand psychological and pedagogical peculiarities of teaching children with speech impairments. • Key special words: speech impairment, speech therapy, speech therapist, aphasia, alalia, dyslalia, rhinolalia, dyslexia, alexia, dysarthria, general speech underdevelopment, apraxia of speech, verbal dyspraxia, voice disorders (aphonia, dysphonia), speech sound disorders, stuttering, dumb/mute children, selective mutism, language-based learning disabilities, fluency of speech, vocal cords, aphonia, dysphonia, articulation, phonation, lisp.
 Key special words • • • • speech impairment – нарушение речи speech therapy - логопедия speech therapist - логопед aphasia - афазия, афразия (нарушение речи, характеризующееся утратой способности понимать чужую речь) alalia - алалия (неспособность говорить вследствие патологии мышц речевого аппарата) dyslalia - дислалия, косноязычие (расстройство артикуляции, обусловленное структурными аномалиями соответствующих органов или связанное с нарушением слуха) rhinolalia - ринолалия, ринофония, гнусавость dyslexia - дислексия, неспособность к чтению alexia - алексия, вербальная слепота, словесная слепота, полная неспособность к чтению dysarthria - дизартрия (расстройство артикуляции, замедленность речи) general speech underdevelopment – общее недоразвитие речи apraxia of speech - апраксия (расстройство произвольных движений) речи verbal dyspraxia – вербальная диспраксия (нарушение функций речевых органов)
Key special words • • • • speech impairment – нарушение речи speech therapy - логопедия speech therapist - логопед aphasia - афазия, афразия (нарушение речи, характеризующееся утратой способности понимать чужую речь) alalia - алалия (неспособность говорить вследствие патологии мышц речевого аппарата) dyslalia - дислалия, косноязычие (расстройство артикуляции, обусловленное структурными аномалиями соответствующих органов или связанное с нарушением слуха) rhinolalia - ринолалия, ринофония, гнусавость dyslexia - дислексия, неспособность к чтению alexia - алексия, вербальная слепота, словесная слепота, полная неспособность к чтению dysarthria - дизартрия (расстройство артикуляции, замедленность речи) general speech underdevelopment – общее недоразвитие речи apraxia of speech - апраксия (расстройство произвольных движений) речи verbal dyspraxia – вербальная диспраксия (нарушение функций речевых органов)
 Key special words • voice disorders (aphonia, dysphonia) – расстройства голоса • aphonia - афония (полная утрата голоса, безголосье) • dysphonia – дисфония (затруднение или болезненность, возникающие при разговоре) • speech sound disorders – расстройство звуков речи • stuttering - заикание • dumb/mute children – немые дети • selective mutism – селективная немота • muteness - немота • language-based learning disabilities – нарушения в обучении, связанные с языком • fluency of speech – беглость речи • accuracy of speech - точность речи • coherence of speech – связность речи • vocal cords – голосовые связки • articulation - артикуляция • phonation – фонация (голосообразование) • lisp - шепелявость
Key special words • voice disorders (aphonia, dysphonia) – расстройства голоса • aphonia - афония (полная утрата голоса, безголосье) • dysphonia – дисфония (затруднение или болезненность, возникающие при разговоре) • speech sound disorders – расстройство звуков речи • stuttering - заикание • dumb/mute children – немые дети • selective mutism – селективная немота • muteness - немота • language-based learning disabilities – нарушения в обучении, связанные с языком • fluency of speech – беглость речи • accuracy of speech - точность речи • coherence of speech – связность речи • vocal cords – голосовые связки • articulation - артикуляция • phonation – фонация (голосообразование) • lisp - шепелявость
 Questions: • What is speech impairment? • What are the main causes and symptoms of speech impairments? • What are types of speech impairment? • What is aphasia? • What is stuttering? • What are peculiarities of teaching children with speech impairments? • What are ways / methods of teaching children with speech impairment?
Questions: • What is speech impairment? • What are the main causes and symptoms of speech impairments? • What are types of speech impairment? • What is aphasia? • What is stuttering? • What are peculiarities of teaching children with speech impairments? • What are ways / methods of teaching children with speech impairment?
 What is speech impairment? • Speech disorders are a type of communication disorders where 'normal' speech is disrupted. • Speech and language disorders refer to problems in communication and related areas such as oral motor function.
What is speech impairment? • Speech disorders are a type of communication disorders where 'normal' speech is disrupted. • Speech and language disorders refer to problems in communication and related areas such as oral motor function.
 Speech organs
Speech organs
 Speech disorders • Apraxia of speech may result from stroke or progressive illness, and involves inconsistent production of speech sounds and rearranging of sounds in a word ("potato" may become "topato" and next "totapo"). • Cluttering, a speech and fluency disorder characterized primarily by a rapid rate of speech, which makes speech difficult to understand. • Developmental verbal dyspraxia also known as childhood apraxia of speech. • Dysarthria is a weakness or paralysis of speech muscles caused by damage to the nerves and/or brain. Dysarthria is often caused by strokes, parkinsons disease, ALS, head or neck injuries, surgical accident, or cerebral palsy. • Dysprosody is the rarest neurological speech disorder. It is characterized by alterations in intensity, in the timing of utterance segments, and in rhythm, cadence, and intonation of words. • Muteness is complete inability to speak. • Speech sound disorders involve difficulty in producing specific speech sounds (most often certain consonants, such as /s/ or /r/), and are subdivided into articulation disorders (also called phonetic disorders) and phonemic disorders. • Stuttering affects approximately 90% of the adult population. • Voice disorders are impairments, often physical, that involve the function of the larynx or vocal resonance.
Speech disorders • Apraxia of speech may result from stroke or progressive illness, and involves inconsistent production of speech sounds and rearranging of sounds in a word ("potato" may become "topato" and next "totapo"). • Cluttering, a speech and fluency disorder characterized primarily by a rapid rate of speech, which makes speech difficult to understand. • Developmental verbal dyspraxia also known as childhood apraxia of speech. • Dysarthria is a weakness or paralysis of speech muscles caused by damage to the nerves and/or brain. Dysarthria is often caused by strokes, parkinsons disease, ALS, head or neck injuries, surgical accident, or cerebral palsy. • Dysprosody is the rarest neurological speech disorder. It is characterized by alterations in intensity, in the timing of utterance segments, and in rhythm, cadence, and intonation of words. • Muteness is complete inability to speak. • Speech sound disorders involve difficulty in producing specific speech sounds (most often certain consonants, such as /s/ or /r/), and are subdivided into articulation disorders (also called phonetic disorders) and phonemic disorders. • Stuttering affects approximately 90% of the adult population. • Voice disorders are impairments, often physical, that involve the function of the larynx or vocal resonance.
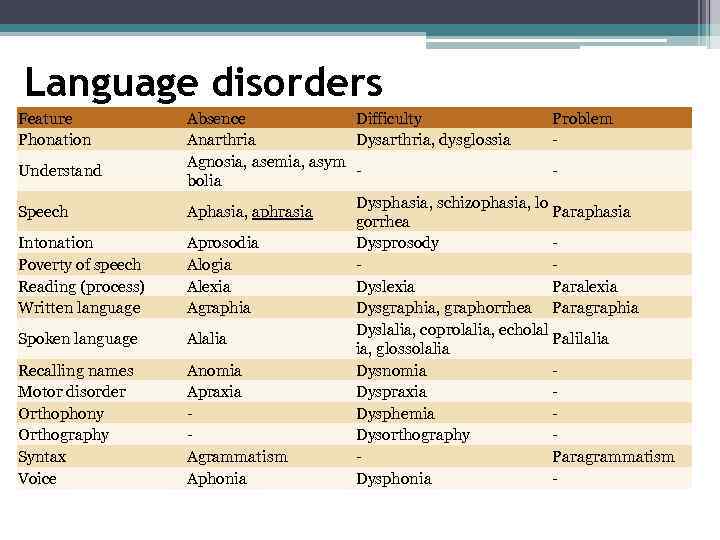 Language disorders Feature Phonation Understand Speech Intonation Poverty of speech Reading (process) Written language Spoken language Recalling names Motor disorder Orthophony Orthography Syntax Voice Absence Difficulty Problem Anarthria Dysarthria, dysglossia Agnosia, asemia, asym bolia Dysphasia, schizophasia, lo Aphasia, aphrasia Paraphasia gorrhea Aprosodia Dysprosody Alogia Alexia Dyslexia Paralexia Agraphia Dysgraphia, graphorrhea Paragraphia Dyslalia, coprolalia, echolal Alalia Palilalia ia, glossolalia Anomia Dysnomia Apraxia Dysphemia Dysorthography Agrammatism Paragrammatism Aphonia Dysphonia -
Language disorders Feature Phonation Understand Speech Intonation Poverty of speech Reading (process) Written language Spoken language Recalling names Motor disorder Orthophony Orthography Syntax Voice Absence Difficulty Problem Anarthria Dysarthria, dysglossia Agnosia, asemia, asym bolia Dysphasia, schizophasia, lo Aphasia, aphrasia Paraphasia gorrhea Aprosodia Dysprosody Alogia Alexia Dyslexia Paralexia Agraphia Dysgraphia, graphorrhea Paragraphia Dyslalia, coprolalia, echolal Alalia Palilalia ia, glossolalia Anomia Dysnomia Apraxia Dysphemia Dysorthography Agrammatism Paragrammatism Aphonia Dysphonia -
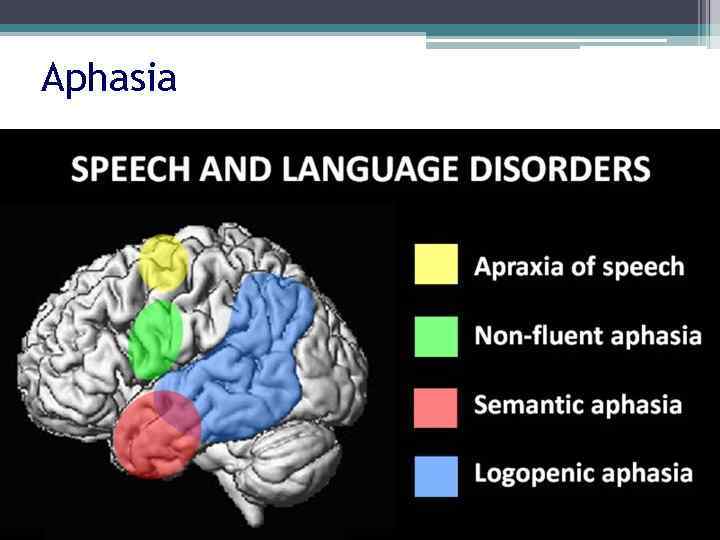 Aphasia
Aphasia
 Complete a) __________ is a form of therapy which is designed to address language and speech disorders. b) Speech therapy is typically provided by a __________. c) _______________ involve an inability to use language. d) ___________ involve physical obstacles to speech which create speech impediments or difficulty speaking, such as disorders of the vocal cords. e) _________ is a motor speech disorder that results from a neurological injury. Some stem from central damage, while other stem from peripheral nerve damage. f) ______________ may be of two varieties: articulation (the production of sounds) or phonological processes (sound patterns) disorders. g) ___________ a disruption in the fluency of an individual’s speech, which begins in childhood and may persist over a lifetime. h) ___________ range from aphonia (loss of phonation) to dysphonia. i) __________ is a collection of language disorders caused by damage to the brain. j) ________________ refer to difficulties with reading, spelling, and/or writing that are evidenced in a significant lag behind the individual’s same-age peers.
Complete a) __________ is a form of therapy which is designed to address language and speech disorders. b) Speech therapy is typically provided by a __________. c) _______________ involve an inability to use language. d) ___________ involve physical obstacles to speech which create speech impediments or difficulty speaking, such as disorders of the vocal cords. e) _________ is a motor speech disorder that results from a neurological injury. Some stem from central damage, while other stem from peripheral nerve damage. f) ______________ may be of two varieties: articulation (the production of sounds) or phonological processes (sound patterns) disorders. g) ___________ a disruption in the fluency of an individual’s speech, which begins in childhood and may persist over a lifetime. h) ___________ range from aphonia (loss of phonation) to dysphonia. i) __________ is a collection of language disorders caused by damage to the brain. j) ________________ refer to difficulties with reading, spelling, and/or writing that are evidenced in a significant lag behind the individual’s same-age peers.
 Speech/language pathologist (SLP) or Speech therapist • A specialist who diagnoses and treats or remediates communication disorders in children. • The SLP provides individual therapy for children, consults with the child’s teachers about the most effective ways to facilitate the child’s communication in the class setting, and works closely with the family to develop goals and techniques for effective therapy in class and at home.
Speech/language pathologist (SLP) or Speech therapist • A specialist who diagnoses and treats or remediates communication disorders in children. • The SLP provides individual therapy for children, consults with the child’s teachers about the most effective ways to facilitate the child’s communication in the class setting, and works closely with the family to develop goals and techniques for effective therapy in class and at home.
 Speech therapist • Your duties as a speech therapist in a public school may include the following tasks: • Working with children one-on-one or in groups to treat voice disorders, stuttering problems or learning disabilities • Conducting school-wide hearing tests to identify and diagnose auditory problems among young children and promote early intervention • Teaching students with hearing or speech conditions to use sign language • Teaming with special education teachers to create comprehensive treatment plans for special needs children • Counseling parents on how to cope with speech and language disorders • Collaborating with teachers, administrators and parents to implement speech therapy programs • • Questions: What are main public school speech therapist’s tasks? What kinds of special tests to identify speech impairments do you know? What other duties should a speech therapist execute?
Speech therapist • Your duties as a speech therapist in a public school may include the following tasks: • Working with children one-on-one or in groups to treat voice disorders, stuttering problems or learning disabilities • Conducting school-wide hearing tests to identify and diagnose auditory problems among young children and promote early intervention • Teaching students with hearing or speech conditions to use sign language • Teaming with special education teachers to create comprehensive treatment plans for special needs children • Counseling parents on how to cope with speech and language disorders • Collaborating with teachers, administrators and parents to implement speech therapy programs • • Questions: What are main public school speech therapist’s tasks? What kinds of special tests to identify speech impairments do you know? What other duties should a speech therapist execute?
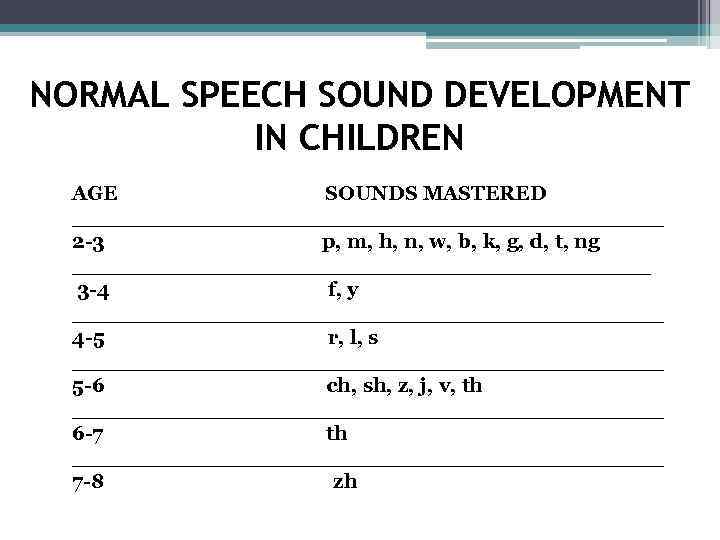 NORMAL SPEECH SOUND DEVELOPMENT IN CHILDREN AGE SOUNDS MASTERED _______________________ 2 -3 p, m, h, n, w, b, k, g, d, t, ng _______________________ 3 -4 f, y _______________________ 4 -5 r, l, s _______________________ 5 -6 ch, sh, z, j, v, th _______________________ 6 -7 th _______________________ 7 -8 zh
NORMAL SPEECH SOUND DEVELOPMENT IN CHILDREN AGE SOUNDS MASTERED _______________________ 2 -3 p, m, h, n, w, b, k, g, d, t, ng _______________________ 3 -4 f, y _______________________ 4 -5 r, l, s _______________________ 5 -6 ch, sh, z, j, v, th _______________________ 6 -7 th _______________________ 7 -8 zh
 Famous people with speech impairments
Famous people with speech impairments
 • BRUCE WILLIS is a famous Hollywood actor. • He is best known for his role of John Mc. Clane in the Die Hard series, Pulp Fiction, The Fifth Element. • Willis is left handed. • He and Demi Moore have three daughters. • He used to stutter in his youth. However, he overcame the impairment without therapy. He said that he lost his stutter because of acting.
• BRUCE WILLIS is a famous Hollywood actor. • He is best known for his role of John Mc. Clane in the Die Hard series, Pulp Fiction, The Fifth Element. • Willis is left handed. • He and Demi Moore have three daughters. • He used to stutter in his youth. However, he overcame the impairment without therapy. He said that he lost his stutter because of acting.
 • Nicole Kidman is an Oscar awardwinning actress from Australia. • She is known for her performances in The Hours, To Die For, Batman Forever, Rabbit Hole and Moulin Rouge! • She suffered from stuttering as a child and ultimately overcame her stammer with hard work and speech therapy. • Her first husband was Tom Cruise, current husband is Keith Urban.
• Nicole Kidman is an Oscar awardwinning actress from Australia. • She is known for her performances in The Hours, To Die For, Batman Forever, Rabbit Hole and Moulin Rouge! • She suffered from stuttering as a child and ultimately overcame her stammer with hard work and speech therapy. • Her first husband was Tom Cruise, current husband is Keith Urban.
 • JULIA ROBERTS is a famous Academy Awardwinning actress and producer. • She used to stutter when she was younger. However, she does not talk too much about it. • She became a Hollywood star after headlining the romantic comedy Pretty Woman (1990). • She practices Hinduism.
• JULIA ROBERTS is a famous Academy Awardwinning actress and producer. • She used to stutter when she was younger. However, she does not talk too much about it. • She became a Hollywood star after headlining the romantic comedy Pretty Woman (1990). • She practices Hinduism.
 • Tiger Woods is American professional golfer. • Woods used to stutter as a child. • However, he overcame the problem with therapy, which included talking to his dog until he fell asleep. • Woods is the only player to have won all four professional major championships in a row, accomplishing the feat in the 2000– 2001 seasons.
• Tiger Woods is American professional golfer. • Woods used to stutter as a child. • However, he overcame the problem with therapy, which included talking to his dog until he fell asleep. • Woods is the only player to have won all four professional major championships in a row, accomplishing the feat in the 2000– 2001 seasons.
 • MARILYN MONROE was an American actress, singer and model. • She took parts in the films: Gentlemen Prefer Blondes and Some Like It Hot • Her famous romance was with John Kennedy. • Marilyn Monroe died on 5 August in Brentwood (California) because of fatal overdose of soporific. • She developed her trademark breathy style of speech as a way to combat her stutter.
• MARILYN MONROE was an American actress, singer and model. • She took parts in the films: Gentlemen Prefer Blondes and Some Like It Hot • Her famous romance was with John Kennedy. • Marilyn Monroe died on 5 August in Brentwood (California) because of fatal overdose of soporific. • She developed her trademark breathy style of speech as a way to combat her stutter.
 • WINSTON CHURCHILL was the British prime minister from 1940 to 1945 and again from 1951 until 1955. • A noted statesman and orator. • He described himself as having a speech impediment, which he consistently worked to overcome. • Churchill suffered from stuttering and lisp. • He won the Nobel Prize in Literature. • He made popular V-sign (V for victory) during the World War II.
• WINSTON CHURCHILL was the British prime minister from 1940 to 1945 and again from 1951 until 1955. • A noted statesman and orator. • He described himself as having a speech impediment, which he consistently worked to overcome. • Churchill suffered from stuttering and lisp. • He won the Nobel Prize in Literature. • He made popular V-sign (V for victory) during the World War II.
 ELVIS PRESLEY was an American singer and actor He was called “The King of Rock'n'roll”. Elvis started singing as a method of speech therapy to help with his stutter. Presley's first single, "Heartbreak Hotel", released in January 1956, was a number one hit. He starred in 33 films. Elvis brought together the musical sounds of the black in America and of country people. He died at the age of 42 in his house because of cordial arrest.
ELVIS PRESLEY was an American singer and actor He was called “The King of Rock'n'roll”. Elvis started singing as a method of speech therapy to help with his stutter. Presley's first single, "Heartbreak Hotel", released in January 1956, was a number one hit. He starred in 33 films. Elvis brought together the musical sounds of the black in America and of country people. He died at the age of 42 in his house because of cordial arrest.
 • KING GEORGE VI was King of the United Kingdom. • He was so embarrassed by his stutter that he hired speechlanguage pathologist, Lionel Logue, and greatly improved his public speaking. • This training and its results are the featured in the 2010 film, The King’s Speech.
• KING GEORGE VI was King of the United Kingdom. • He was so embarrassed by his stutter that he hired speechlanguage pathologist, Lionel Logue, and greatly improved his public speaking. • This training and its results are the featured in the 2010 film, The King’s Speech.


