a5af2579fd1d1cd5d7df5efe758f00be.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 Practical Financial Management for CSO’s PART II Internal Control Trainer : Alice Azar Date : 13 - May-2016 “This publication is made possible by the support of the American People through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). The content of this publication is the sole responsibility of the contractor and do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID or the United States Government. "
Practical Financial Management for CSO’s PART II Internal Control Trainer : Alice Azar Date : 13 - May-2016 “This publication is made possible by the support of the American People through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). The content of this publication is the sole responsibility of the contractor and do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID or the United States Government. "
 TRAINING MODULES INTRODUCTION TO INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK • INTERNAL CONTROL OBJECTIVES • TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL • • • PHYSICAL CONTROL DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL ADVANCES CONTROL 2/63
TRAINING MODULES INTRODUCTION TO INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK • INTERNAL CONTROL OBJECTIVES • TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL • • • PHYSICAL CONTROL DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL ADVANCES CONTROL 2/63
 TRAINING MODULES INTRODUCTION • INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK TO INTERNAL CONTROL • INTERNAL CONTROL OBJECTIVES • TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL 3/63
TRAINING MODULES INTRODUCTION • INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK TO INTERNAL CONTROL • INTERNAL CONTROL OBJECTIVES • TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL 3/63
 INTERNAL CONTROL Are the policies and procedures adopted by management to ensure that the organization conducts business in an orderly and efficient manner. They provide the framework through which management uses the resources at its disposal to achieve the organization’s goals. It is better to have procedures in place to deter theft and fraud then one to discover it 4/63
INTERNAL CONTROL Are the policies and procedures adopted by management to ensure that the organization conducts business in an orderly and efficient manner. They provide the framework through which management uses the resources at its disposal to achieve the organization’s goals. It is better to have procedures in place to deter theft and fraud then one to discover it 4/63
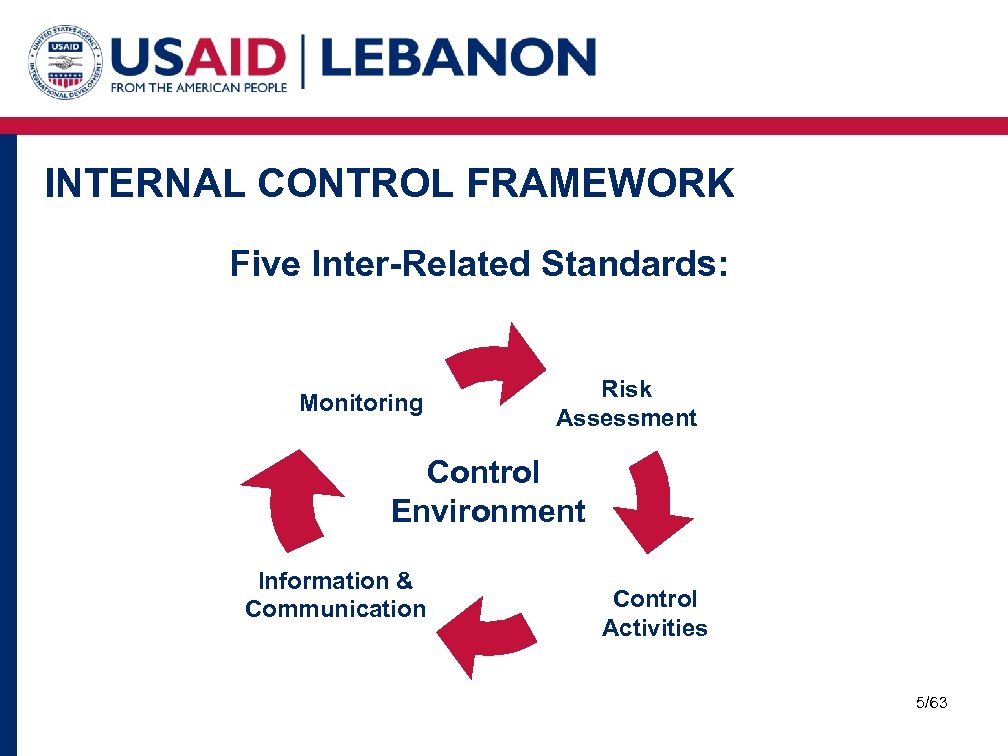 INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK Five Inter-Related Standards: Monitoring Risk Assessment Control Environment Information & Communication Control Activities 5/63
INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK Five Inter-Related Standards: Monitoring Risk Assessment Control Environment Information & Communication Control Activities 5/63
 INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK Embedded in core business processes Control Environment: Attributes of the people conducting the entity’s activities and the environment in which they operate. Control activities: Policies and procedures established and executed that enable management’s directives to be carried out. Information and communication: Systems enabling identification, capture and exchange of information for the conduct and control of operations. Monitoring: Assess performance of internal control over time and make modifications as conditions change. Risk assessment: Establish objectives and mechanisms to identify, analyze and manage risks. 6/63
INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK Embedded in core business processes Control Environment: Attributes of the people conducting the entity’s activities and the environment in which they operate. Control activities: Policies and procedures established and executed that enable management’s directives to be carried out. Information and communication: Systems enabling identification, capture and exchange of information for the conduct and control of operations. Monitoring: Assess performance of internal control over time and make modifications as conditions change. Risk assessment: Establish objectives and mechanisms to identify, analyze and manage risks. 6/63
 “Being a small organization is not an excuse for poor financial controls; it is reason to think carefully about ways to introduce them. ” 7/63
“Being a small organization is not an excuse for poor financial controls; it is reason to think carefully about ways to introduce them. ” 7/63
 TRAINING MODULES INTRODUCTION TO INTERNAL CONTROL • INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK • INTERNAL CONTROL OBJECTIVES • TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL 8/63
TRAINING MODULES INTRODUCTION TO INTERNAL CONTROL • INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK • INTERNAL CONTROL OBJECTIVES • TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL 8/63
 OBJECTIVES OF INTERNAL CONTROL Internal control helps NGOs: Handle everyday risks of mistakes, confusion or fraud Protect staff from any pressure to misuse funds and from the suspicion of wrong-doing Ensure reliability of financial reporting Ensure Compliance with applicable laws and regulations Effectiveness and efficiency of program operations 9/63
OBJECTIVES OF INTERNAL CONTROL Internal control helps NGOs: Handle everyday risks of mistakes, confusion or fraud Protect staff from any pressure to misuse funds and from the suspicion of wrong-doing Ensure reliability of financial reporting Ensure Compliance with applicable laws and regulations Effectiveness and efficiency of program operations 9/63
 ABSENCE OF INTERNAL CONTROL PRESENCE OF THE THREE MAIN FACTORS OF FRAUD AND MISUSE OF RESOURCES 10/63
ABSENCE OF INTERNAL CONTROL PRESENCE OF THE THREE MAIN FACTORS OF FRAUD AND MISUSE OF RESOURCES 10/63
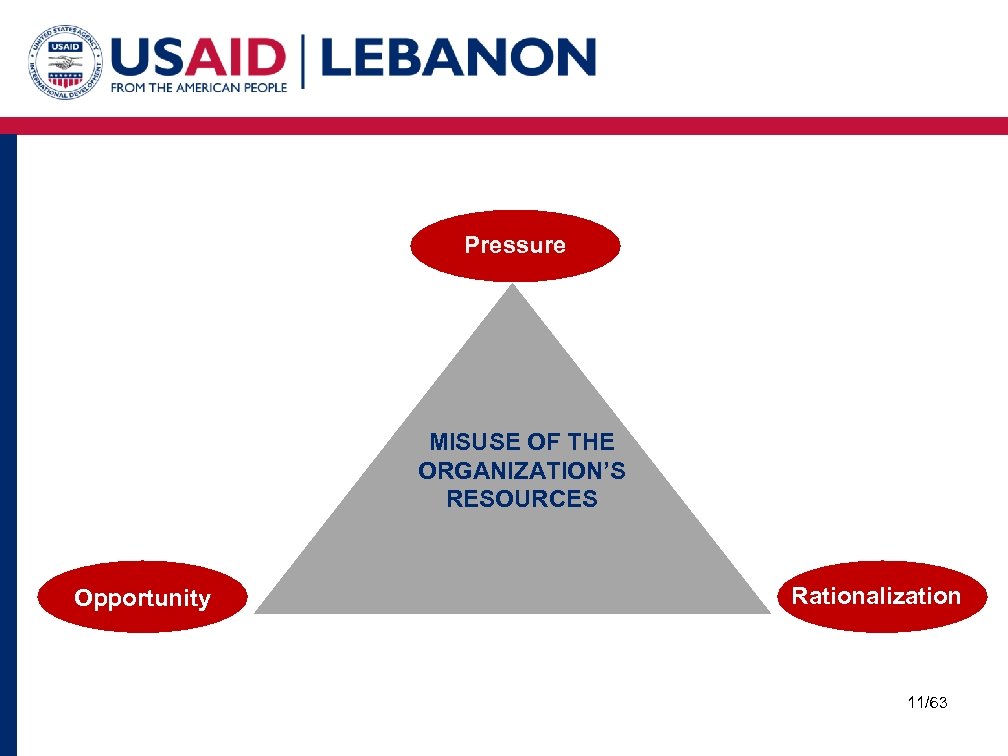 Pressure MISUSE OF THE ORGANIZATION’S RESOURCES Opportunity Rationalization 11/63
Pressure MISUSE OF THE ORGANIZATION’S RESOURCES Opportunity Rationalization 11/63
 MISUSE OF THE ORGANIZATION’S RESOURCES Opportunity occurs when an employee is presented with an occasion to commit fraud, and he or she perceives that there is little or no possibility of being caught. 12/63
MISUSE OF THE ORGANIZATION’S RESOURCES Opportunity occurs when an employee is presented with an occasion to commit fraud, and he or she perceives that there is little or no possibility of being caught. 12/63
 MISUSE OF THE ORGANIZATION’S RESOURCES Rationalization occurs when an employee feels justified in committing fraud. 13/63
MISUSE OF THE ORGANIZATION’S RESOURCES Rationalization occurs when an employee feels justified in committing fraud. 13/63
 MISUSE OF THE ORGANIZATION’S RESOURCES Pressure The strain of a disorganized, crisis-dominated organization and personal problems can put pressure on staff to commit fraud. 14/63
MISUSE OF THE ORGANIZATION’S RESOURCES Pressure The strain of a disorganized, crisis-dominated organization and personal problems can put pressure on staff to commit fraud. 14/63
 TRAINING MODULES INTRODUCTION TO INTERNAL CONTROL • INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK • INTERNAL CONTROL OBJECTIVES • TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL 15/63
TRAINING MODULES INTRODUCTION TO INTERNAL CONTROL • INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK • INTERNAL CONTROL OBJECTIVES • TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL 15/63
 TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL 16/63
TYPE OF INTERNAL CONTROL 16/63
 EXERCISE 1 1. Identify whether the “Misuse of the organization’s resources triangle "factors — opportunity, rationalization, and pressure — are present in your organization. 2. If any of the factors are present, explain how you can reduce or eliminate them. 17/63
EXERCISE 1 1. Identify whether the “Misuse of the organization’s resources triangle "factors — opportunity, rationalization, and pressure — are present in your organization. 2. If any of the factors are present, explain how you can reduce or eliminate them. 17/63
 TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • • • PHYSICAL CONTROL DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL ADVANCES CONTROL 18/63
TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • • • PHYSICAL CONTROL DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL ADVANCES CONTROL 18/63
 INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES Nearly all internal control procedures fall into one of seven categories: 1 - Physical verification – cash counts, asset verification and stock counts 2 - Limited access – locks, passwords and bank signatories 3 - Standard documents – standard formats for receipts, payment vouchers, requisitions, local purchase orders, travel allowance sign sheet etc. … 19/63
INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES Nearly all internal control procedures fall into one of seven categories: 1 - Physical verification – cash counts, asset verification and stock counts 2 - Limited access – locks, passwords and bank signatories 3 - Standard documents – standard formats for receipts, payment vouchers, requisitions, local purchase orders, travel allowance sign sheet etc. … 19/63
 INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES - Continued 4 - Segregation of duties – making sure that not one person carry out a transaction from beginning to end, no self review or self authorization. 5 - Checks and balances – balancing the manual cashbook, double entry controls over accounting records, reviewing the bank reconciliation 6 - Approval and authorization – budget holders approval of payments, board authorization for asset disposal etc. 7 - Reconciliation – Comparing bank statement and cashbook, comparing a statement from 20/63 a supplier to your own records
INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES - Continued 4 - Segregation of duties – making sure that not one person carry out a transaction from beginning to end, no self review or self authorization. 5 - Checks and balances – balancing the manual cashbook, double entry controls over accounting records, reviewing the bank reconciliation 6 - Approval and authorization – budget holders approval of payments, board authorization for asset disposal etc. 7 - Reconciliation – Comparing bank statement and cashbook, comparing a statement from 20/63 a supplier to your own records
 TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • PHYSICAL CONTROL • • • DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL ADVANCES CONTROL 21/63
TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • PHYSICAL CONTROL • • • DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL ADVANCES CONTROL 21/63
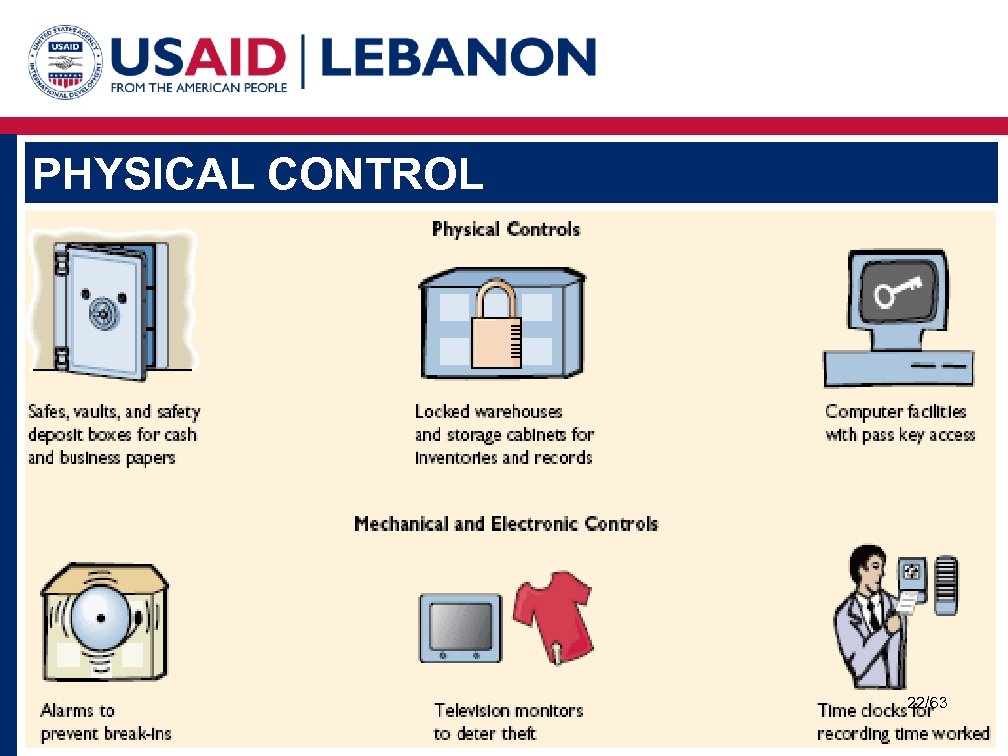 PHYSICAL CONTROL 22/63
PHYSICAL CONTROL 22/63
 PHYSICAL CONTROL Physical controls are additional precautions taken to safeguard the assets of an organization: § Having a Safe § Insurance Cover § Safeguarding Fixed Assets ( Assets Registry, Vehicle and Maintenance Policies) 23/63
PHYSICAL CONTROL Physical controls are additional precautions taken to safeguard the assets of an organization: § Having a Safe § Insurance Cover § Safeguarding Fixed Assets ( Assets Registry, Vehicle and Maintenance Policies) 23/63
 TRAINING MODULES • PHYSICAL CONTROL INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY • • SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL ADVANCES CONTROL 24/63
TRAINING MODULES • PHYSICAL CONTROL INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY • • SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL ADVANCES CONTROL 24/63
 DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY The delegation of authority document should include instructions for such duties as : § Placing and authorizing orders for goods and services § Signing checks § Authorizing staff expenses § Handling cash and checks § Access to the safe and petty cash § Checking and authorizing accounting records § Signing legal documents 25/63
DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY The delegation of authority document should include instructions for such duties as : § Placing and authorizing orders for goods and services § Signing checks § Authorizing staff expenses § Handling cash and checks § Access to the safe and petty cash § Checking and authorizing accounting records § Signing legal documents 25/63
 DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY GUIDELINES Basic guidelines that should be followed when delegating authority include: § Any limits or conditions that apply to delegated authority must be clearly defined. For example, a person may be authorized to commit expenditures up to a specified amount. These limits are usually documented in an authorization table that defines the authority to approve transactions for various levels of management. 26/63
DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY GUIDELINES Basic guidelines that should be followed when delegating authority include: § Any limits or conditions that apply to delegated authority must be clearly defined. For example, a person may be authorized to commit expenditures up to a specified amount. These limits are usually documented in an authorization table that defines the authority to approve transactions for various levels of management. 26/63
 DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY GUIDELINES § No one should authorize any transaction from which they will personally benefit. This exposes the individual to claims of impropriety and calls into question the honesty of management. § Subordinates must not authorize payments to managers; they must be passed to someone who is more senior in the management structure. 27/63
DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY GUIDELINES § No one should authorize any transaction from which they will personally benefit. This exposes the individual to claims of impropriety and calls into question the honesty of management. § Subordinates must not authorize payments to managers; they must be passed to someone who is more senior in the management structure. 27/63
 TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • PHYSICAL CONTROL • DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY • SEGREGATION OF DUTIES • CASH CONTROL • PAYROLL CONTROL • ADVANCES CONTROL 28/63
TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • PHYSICAL CONTROL • DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY • SEGREGATION OF DUTIES • CASH CONTROL • PAYROLL CONTROL • ADVANCES CONTROL 28/63
 SEGREGATION OF ACCOUNTING TASKS The basic requirement is that one employee should not have the responsibility to execute all stages of a transaction, from initiation and processing to recording payment or receipt of funds into the accounting system. Apart from weakening financial control, placing too much responsibility for a particular function on one person creates the risk that if he or she leaves the organization or is absent for long periods, then operation of that function will cease. 29/63
SEGREGATION OF ACCOUNTING TASKS The basic requirement is that one employee should not have the responsibility to execute all stages of a transaction, from initiation and processing to recording payment or receipt of funds into the accounting system. Apart from weakening financial control, placing too much responsibility for a particular function on one person creates the risk that if he or she leaves the organization or is absent for long periods, then operation of that function will cease. 29/63
 SEGREGATION OF ACCOUNTING TASKS In Particular, there are three functions that should be ( ideally) handled by different people when possible Custody : Physical responsibility for cash, stores, vehicle etc…. . Recording: Entry of data in the main accounts/ledger from which reports are made Authorization of purchases and other uses of resources 30/63
SEGREGATION OF ACCOUNTING TASKS In Particular, there are three functions that should be ( ideally) handled by different people when possible Custody : Physical responsibility for cash, stores, vehicle etc…. . Recording: Entry of data in the main accounts/ledger from which reports are made Authorization of purchases and other uses of resources 30/63
 Segregation of Duties: Two Heads are Better than One Authorization • Signature Authority • Approving Transactions • Checks • Record Keeping/Posting • Payments – Petty Cash • Control of computer processing • Physical Possession Reconciliation • Physical Control Prepare Custody • Regular Comparison • Take action on differences Review Recording 31/63
Segregation of Duties: Two Heads are Better than One Authorization • Signature Authority • Approving Transactions • Checks • Record Keeping/Posting • Payments – Petty Cash • Control of computer processing • Physical Possession Reconciliation • Physical Control Prepare Custody • Regular Comparison • Take action on differences Review Recording 31/63
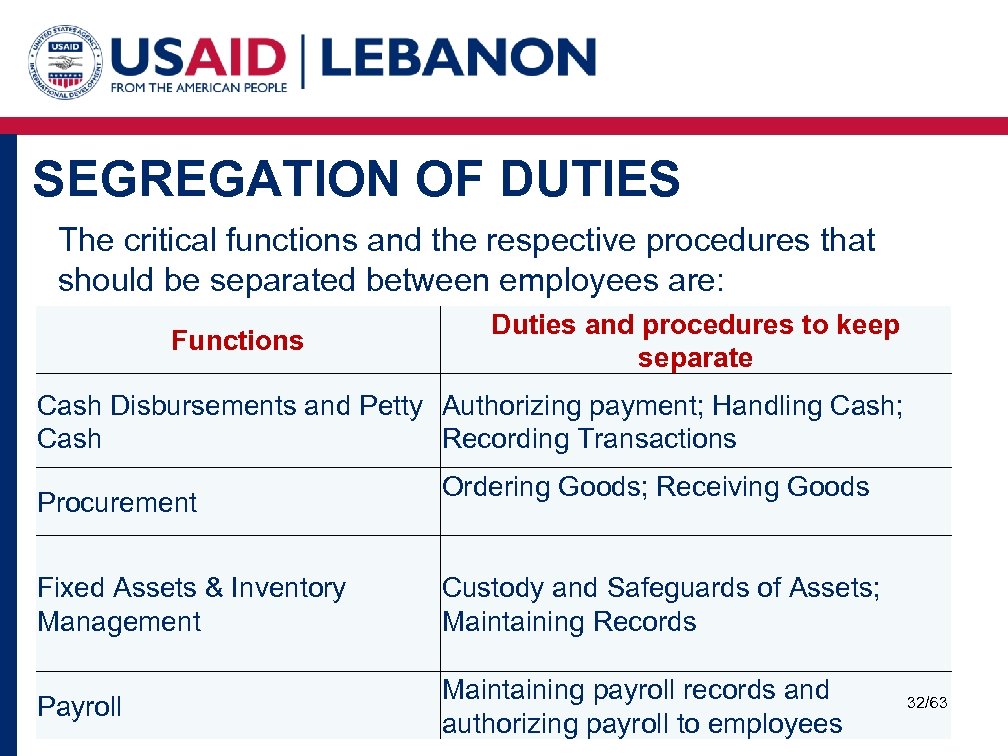 SEGREGATION OF DUTIES The critical functions and the respective procedures that should be separated between employees are: Functions Duties and procedures to keep separate Cash Disbursements and Petty Authorizing payment; Handling Cash; Cash Recording Transactions Ordering Goods; Receiving Goods Procurement Fixed Assets & Inventory Custody and Safeguards of Assets; Management Maintaining Records • Regular Comparison • Take action on differences Maintaining payroll records and Payroll authorizing payroll to employees 32/63
SEGREGATION OF DUTIES The critical functions and the respective procedures that should be separated between employees are: Functions Duties and procedures to keep separate Cash Disbursements and Petty Authorizing payment; Handling Cash; Cash Recording Transactions Ordering Goods; Receiving Goods Procurement Fixed Assets & Inventory Custody and Safeguards of Assets; Management Maintaining Records • Regular Comparison • Take action on differences Maintaining payroll records and Payroll authorizing payroll to employees 32/63
 TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • PHYSICAL CONTROLS • DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY • SEGREGATION OF DUTIES • CASH CONTROL • PAYROLL CONTROL • ADVANCES CONTROL 33/63
TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • PHYSICAL CONTROLS • DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY • SEGREGATION OF DUTIES • CASH CONTROL • PAYROLL CONTROL • ADVANCES CONTROL 33/63
 CASH CONTROL § Bank Reconciliation § Petty Cash Count § Cash Reconciliation 34/63
CASH CONTROL § Bank Reconciliation § Petty Cash Count § Cash Reconciliation 34/63
 CASH CONTROL : BANK RECONCILIATION Bank Reconciliation Definition : It is a method of reconciling the balance shown in the bank statement and the balance at the cash book at any given date Documents Required: 1. Bank Statement: Record kept by the bank of all transactions going through a bank account 2. Cash Book: Record kept in your office to enter all the transactions going through the bank account 35/63
CASH CONTROL : BANK RECONCILIATION Bank Reconciliation Definition : It is a method of reconciling the balance shown in the bank statement and the balance at the cash book at any given date Documents Required: 1. Bank Statement: Record kept by the bank of all transactions going through a bank account 2. Cash Book: Record kept in your office to enter all the transactions going through the bank account 35/63
 CASH CONTROL : BANK RECONCILIATION Adjusted Bank Balance = Adjusted General Ledger Balance 36/63
CASH CONTROL : BANK RECONCILIATION Adjusted Bank Balance = Adjusted General Ledger Balance 36/63
 STEPS FOR BANK RECONCILIATION Step 1. Record the ending Balance for the Bank Statement Step 2. Prepare a detailed list of the deposits still in transit Step 3. Add the total of the deposits in transit to the ending balance from step 1 Step 4. Prepare a detailed list of outstanding checks (sent/written, but not yet cleared) Step 5. Subtract the total outstanding from the ending balance. This is your adjusted bank balance. 37/63
STEPS FOR BANK RECONCILIATION Step 1. Record the ending Balance for the Bank Statement Step 2. Prepare a detailed list of the deposits still in transit Step 3. Add the total of the deposits in transit to the ending balance from step 1 Step 4. Prepare a detailed list of outstanding checks (sent/written, but not yet cleared) Step 5. Subtract the total outstanding from the ending balance. This is your adjusted bank balance. 37/63
 STEPS FOR BANK RECONCILIATION - Continued Step 6. Adjust your ledger balance to add in any interest received from the bank and to subtract any fees incurred. This is your adjusted general ledger balance. Step 7. Compare the adjusted bank balance to the adjusted general ledger balance. These amounts should agree Adjusted Bank Balance = Adjusted General Ledger Balance 38/63
STEPS FOR BANK RECONCILIATION - Continued Step 6. Adjust your ledger balance to add in any interest received from the bank and to subtract any fees incurred. This is your adjusted general ledger balance. Step 7. Compare the adjusted bank balance to the adjusted general ledger balance. These amounts should agree Adjusted Bank Balance = Adjusted General Ledger Balance 38/63
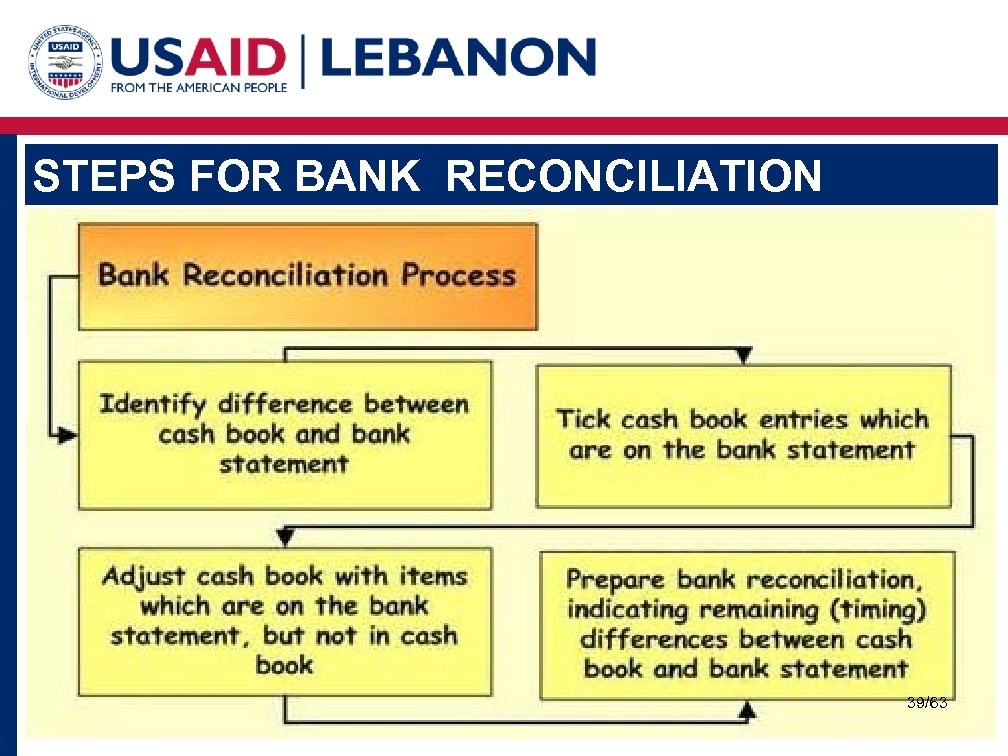 STEPS FOR BANK RECONCILIATION 39/63
STEPS FOR BANK RECONCILIATION 39/63
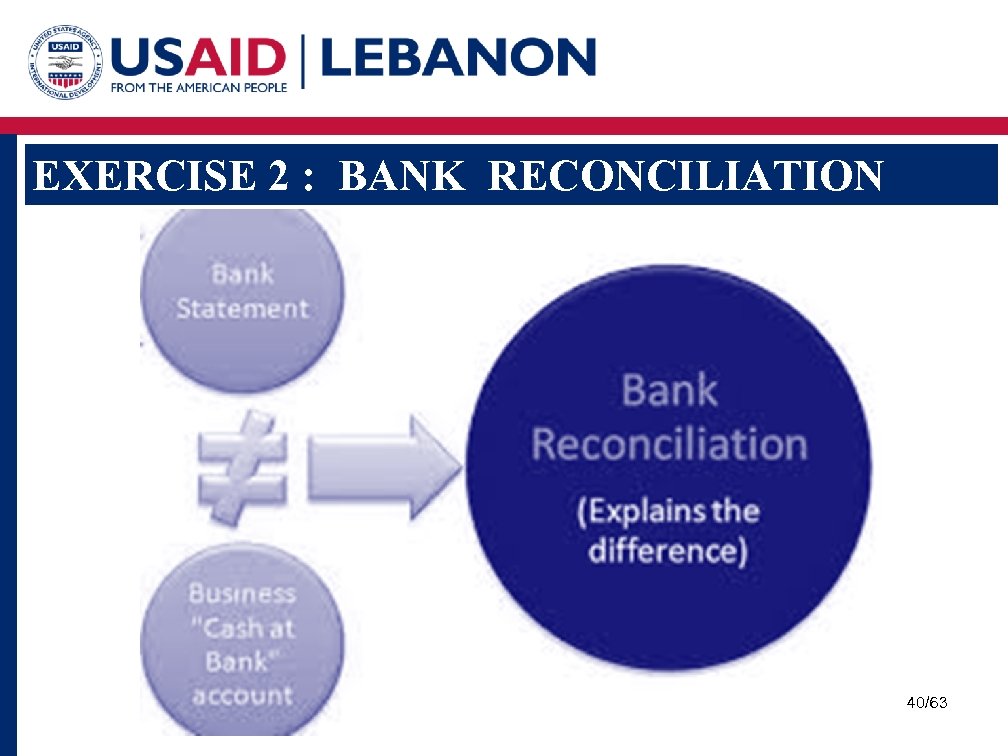 EXERCISE 2 : BANK RECONCILIATION 40/63
EXERCISE 2 : BANK RECONCILIATION 40/63
 PETTY CASH CONTROL Golden Rules for Handling Cash : § Always give receipts for money received § Always obtain receipt for money paid § Deposit extra cash into the bank § Restrict Access to Petty Cash § Keep Cash transactions to absolute Minimum 41/63
PETTY CASH CONTROL Golden Rules for Handling Cash : § Always give receipts for money received § Always obtain receipt for money paid § Deposit extra cash into the bank § Restrict Access to Petty Cash § Keep Cash transactions to absolute Minimum 41/63
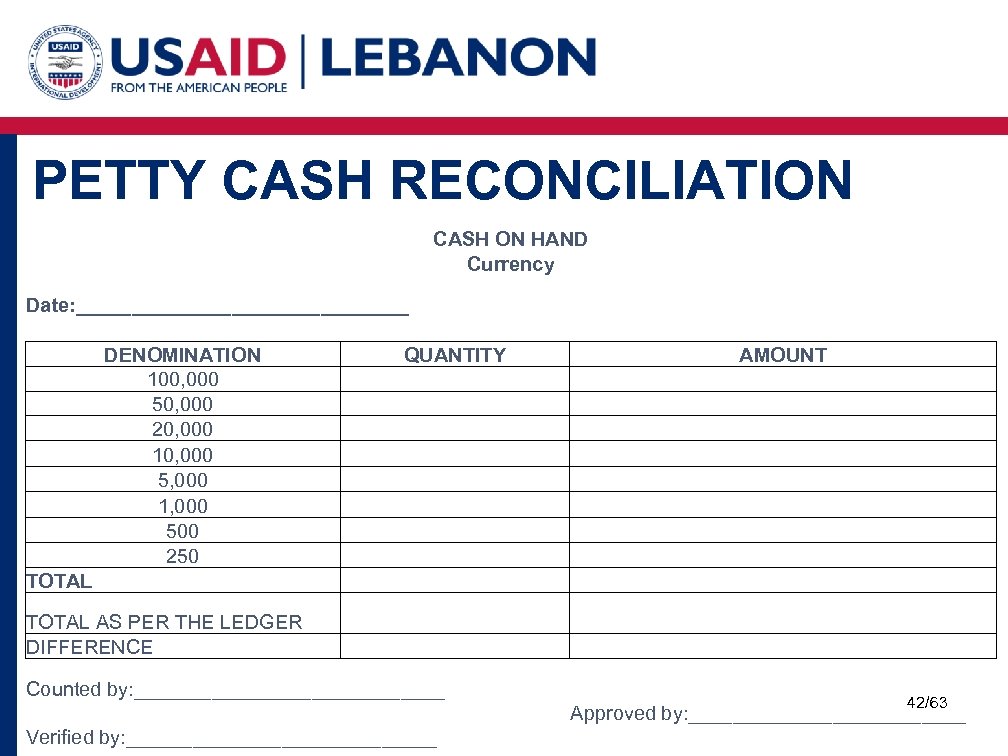 PETTY CASH RECONCILIATION CASH ON HAND Currency Date: _______________ DENOMINATION 100, 000 50, 000 20, 000 10, 000 5, 000 1, 000 500 250 QUANTITY TOTAL AMOUNT TOTAL AS PER THE LEDGER DIFFERENCE Counted by: ______________ 42/63 Approved by: _____________ Verified by: ______________
PETTY CASH RECONCILIATION CASH ON HAND Currency Date: _______________ DENOMINATION 100, 000 50, 000 20, 000 10, 000 5, 000 1, 000 500 250 QUANTITY TOTAL AMOUNT TOTAL AS PER THE LEDGER DIFFERENCE Counted by: ______________ 42/63 Approved by: _____________ Verified by: ______________
 43/63
43/63
 EXERCISE 3 : CASH RECONCILIATION 44/63
EXERCISE 3 : CASH RECONCILIATION 44/63
 TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • • PHYSICAL CONTROLS DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL • PAYROLL CONTROL • ADVANCES CONTROL 45/63
TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • • PHYSICAL CONTROLS DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL • PAYROLL CONTROL • ADVANCES CONTROL 45/63
 PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL § Very confidential information – should be kept under lock and key in a secure location § Finance Policy – Payroll Personnel files maintained in secure location including: • CV • Salary history and amendments • Annual reviews • ID • Qualification certificates 46/63
PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL § Very confidential information – should be kept under lock and key in a secure location § Finance Policy – Payroll Personnel files maintained in secure location including: • CV • Salary history and amendments • Annual reviews • ID • Qualification certificates 46/63
 PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL § Any changes in payroll items (promotions, salary increases, etc. ) must be made with official memo/letter duly approved and authorized by the highest level of authority and filed with payroll in the employee’s file § Advances for travel not reconciled should be deducted from salary at month’s end 47/63
PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL § Any changes in payroll items (promotions, salary increases, etc. ) must be made with official memo/letter duly approved and authorized by the highest level of authority and filed with payroll in the employee’s file § Advances for travel not reconciled should be deducted from salary at month’s end 47/63
 PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL Payroll – Segregation of duties: 1. Preparer – Payroll must be prepared by the treasurer or similar position 2. Reviewed – Payroll should be verified by a person in charge of Human Resources or administration 3. Authorized – Payroll should be approved by the manager 48/63
PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL Payroll – Segregation of duties: 1. Preparer – Payroll must be prepared by the treasurer or similar position 2. Reviewed – Payroll should be verified by a person in charge of Human Resources or administration 3. Authorized – Payroll should be approved by the manager 48/63
 PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL - Continued § The person preparing payroll CANNOT be same person issuing check § Person preparing payroll not same person responsible for recordkeeping § Fines paid on late payment of legal deductions – Unallowable Cost § Pay slips should be issued and signed by employee and the authority authorizing the payment 49/63
PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL - Continued § The person preparing payroll CANNOT be same person issuing check § Person preparing payroll not same person responsible for recordkeeping § Fines paid on late payment of legal deductions – Unallowable Cost § Pay slips should be issued and signed by employee and the authority authorizing the payment 49/63
 PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL - Continued § Preferably – pay into employee’s bank account § If it is not possible to pay directly into employee’s bank account: § Check (advance) written in name of person paying payroll § Advance retired in 3 days with payment evidence confirmed by signature of paid employees § Uncollected salaries returned to bank and deposit slip attached to 50/63
PAYROLL INTERNAL CONTROL - Continued § Preferably – pay into employee’s bank account § If it is not possible to pay directly into employee’s bank account: § Check (advance) written in name of person paying payroll § Advance retired in 3 days with payment evidence confirmed by signature of paid employees § Uncollected salaries returned to bank and deposit slip attached to 50/63
 TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • • • PHYSICAL CONTROLS DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL • ADVANCES CONTROL 51/63
TRAINING MODULES INTERNAL CONTROL PROCEDURES • • • PHYSICAL CONTROLS DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY SEGREGATION OF DUTIES CASH CONTROL PAYROLL CONTROL • ADVANCES CONTROL 51/63
 EXERCISE 4: SCENARIO ADVANCES The program manager returns from a field trip for which he had been given a float of $100. He presents receipts totaling $38 for accommodation from “Shari’s Comfort House. ” He tells his manager that the remaining $62 were spent on food from markets and bus fares, for which no receipts were available. He forgot that he still has an outstanding float of $150 from the last month. What are the issues? 52/63
EXERCISE 4: SCENARIO ADVANCES The program manager returns from a field trip for which he had been given a float of $100. He presents receipts totaling $38 for accommodation from “Shari’s Comfort House. ” He tells his manager that the remaining $62 were spent on food from markets and bus fares, for which no receipts were available. He forgot that he still has an outstanding float of $150 from the last month. What are the issues? 52/63
 ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Advances are “forgotten” by recipients or they deny receiving them or claim they received the incorrect amount • Advances are “forgotten” by the organization or not accounted for or repaid 53/63
ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Advances are “forgotten” by recipients or they deny receiving them or claim they received the incorrect amount • Advances are “forgotten” by the organization or not accounted for or repaid 53/63
 ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Advances are “forgotten” by recipients or they deny receiving them or claim they received the incorrect amount • Advances are “forgotten” by the organization or not accounted for or repaid • COMMON SOLUTIONS All advances are signed for by the recipient and all advances are counted for by the recipient and the person advancing the funds • All advances are recorded in the cash book as an advance (and not as an expense) & also in an advance register • An accounting system can have a control account with 54/63 sub accounts for each staff member
ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Advances are “forgotten” by recipients or they deny receiving them or claim they received the incorrect amount • Advances are “forgotten” by the organization or not accounted for or repaid • COMMON SOLUTIONS All advances are signed for by the recipient and all advances are counted for by the recipient and the person advancing the funds • All advances are recorded in the cash book as an advance (and not as an expense) & also in an advance register • An accounting system can have a control account with 54/63 sub accounts for each staff member
 ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Team members do not understand their responsibilities for accounting for and repaying advances 55/63
ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Team members do not understand their responsibilities for accounting for and repaying advances 55/63
 ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Team members do not understand their responsibilities for accounting for and repaying advances COMMON SOLUTIONS • Develop clear policies & procedures for advances • Only have one advance outstanding at a time – staff must reconcile previous advance before getting new advance 56/63
ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Team members do not understand their responsibilities for accounting for and repaying advances COMMON SOLUTIONS • Develop clear policies & procedures for advances • Only have one advance outstanding at a time – staff must reconcile previous advance before getting new advance 56/63
 ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • A further advance is requested before the previous advance has been repaid and advances then become complicated to track 57/63
ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • A further advance is requested before the previous advance has been repaid and advances then become complicated to track 57/63
 ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • A further advance is • requested before the previous advance has been repaid and advances then become complicated to track • COMMON SOLUTION If staff have not reconciled advance within stipulated period (say 1 month after return) then deduct from salary after notifying staff If due to time constraints the person cannot reconcile – consider giving the advance for all the weeks concerned and then reconcile directly at the end of the trip 58/63
ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • A further advance is • requested before the previous advance has been repaid and advances then become complicated to track • COMMON SOLUTION If staff have not reconciled advance within stipulated period (say 1 month after return) then deduct from salary after notifying staff If due to time constraints the person cannot reconcile – consider giving the advance for all the weeks concerned and then reconcile directly at the end of the trip 58/63
 ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Payments are made without proper receipts 59/63
ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS • Payments are made without proper receipts 59/63
 ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS • COMMON PROBLEMS COMMON SOLUTIONS Payments are made without • Proper receipts are required for all proper receipts payments, and payments without proper receipts will not be accepted, and the cash will have to be refunded by the person • Best policy, no receipt, no expense • Next best policy: • Carry receipt book that person signs to acknowledge receipt • Allow an amount for which no receipts will be required; however, expenses still need to be justified showing date, 60/63 amount, purpose, reviewed and authorized by supervisor
ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS • COMMON PROBLEMS COMMON SOLUTIONS Payments are made without • Proper receipts are required for all proper receipts payments, and payments without proper receipts will not be accepted, and the cash will have to be refunded by the person • Best policy, no receipt, no expense • Next best policy: • Carry receipt book that person signs to acknowledge receipt • Allow an amount for which no receipts will be required; however, expenses still need to be justified showing date, 60/63 amount, purpose, reviewed and authorized by supervisor
 ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS COMMON SOLUTIONS • Cash from an advance is • Missing amount deducted from the lost or stolen person’s salary unless can show a police report • Remember – bad debts or losses cannot be allocated to projects • This should be deducted from the • Money is spent on staff member’s salary activities that have nothing to do with the programs goals and objectives 61/63
ADVANCES : COMMON PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS COMMON PROBLEMS COMMON SOLUTIONS • Cash from an advance is • Missing amount deducted from the lost or stolen person’s salary unless can show a police report • Remember – bad debts or losses cannot be allocated to projects • This should be deducted from the • Money is spent on staff member’s salary activities that have nothing to do with the programs goals and objectives 61/63
 SALARY ADVANCES (OR PERSONAL ADVANCES) Why should they be discouraged? § Organization may be seen as a “Bank” § Salary advances can trap employees in vicious cycle of debt If provided § Advance should not be provided with donor money (use unrestricted funds only) § Organization needs to have very clear policies Other policies that can be considered are • A maximum amount or % of salary advance • All salary advances must be authorised by 62/63 managers
SALARY ADVANCES (OR PERSONAL ADVANCES) Why should they be discouraged? § Organization may be seen as a “Bank” § Salary advances can trap employees in vicious cycle of debt If provided § Advance should not be provided with donor money (use unrestricted funds only) § Organization needs to have very clear policies Other policies that can be considered are • A maximum amount or % of salary advance • All salary advances must be authorised by 62/63 managers
 For More Information Building Alliance for Local Advancement, Development, and Investment – CAP BALADI CAP Follow Us On : http: //baladi-lebanon. org/baladicap/ www. facebook. com/Baladi. cap @BALADICAP https: //baladicap. wordpress. com @BALADICAP 63/63
For More Information Building Alliance for Local Advancement, Development, and Investment – CAP BALADI CAP Follow Us On : http: //baladi-lebanon. org/baladicap/ www. facebook. com/Baladi. cap @BALADICAP https: //baladicap. wordpress. com @BALADICAP 63/63


