lecture_3.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Practical Data Mining Lecture 3. Supervised learning (part 2) + short intro to dimension reduction. Victor Kantor MIPT 2014
Practical Data Mining Lecture 3. Supervised learning (part 2) + short intro to dimension reduction. Victor Kantor MIPT 2014
 Plan 1. Bayesian methods 2. Linear methods introduction 3. Principal component and SVD introduction 4. Python, scikit-learn and kaggle. com
Plan 1. Bayesian methods 2. Linear methods introduction 3. Principal component and SVD introduction 4. Python, scikit-learn and kaggle. com
 Bayesian methods 1. Spam classification with Naïve Bayes classifier 2. Probabilities estimation 3. Loss function and risk function
Bayesian methods 1. Spam classification with Naïve Bayes classifier 2. Probabilities estimation 3. Loss function and risk function
 Intro: simple idea of spam detection Spam message examples: • “Hi! : ) Purchase Exclusive Tabs Online http: //. . . ” • “We Offer Loan At A Very Low Rate Of 3%. If Interested, Kindly Contact Us, Reply by this email …. @hotmail. com”
Intro: simple idea of spam detection Spam message examples: • “Hi! : ) Purchase Exclusive Tabs Online http: //. . . ” • “We Offer Loan At A Very Low Rate Of 3%. If Interested, Kindly Contact Us, Reply by this email …. @hotmail. com”
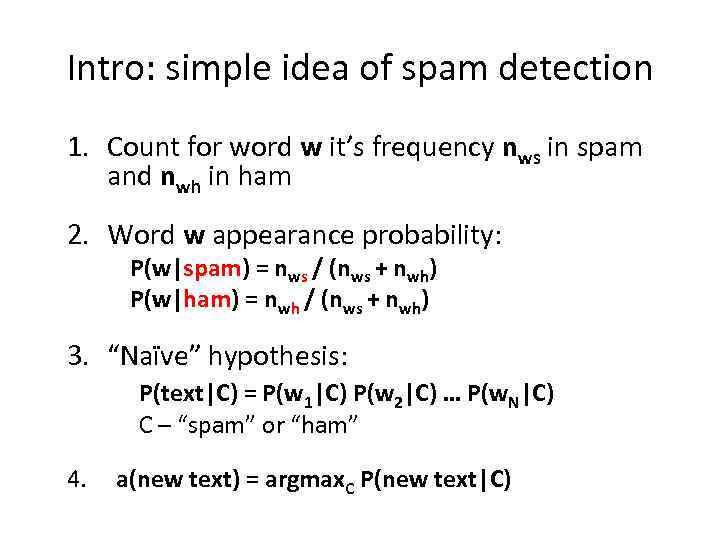 Intro: simple idea of spam detection 1. Count for word w it’s frequency nws in spam and nwh in ham 2. Word w appearance probability: P(w|spam) = nws / (nws + nwh) P(w|ham) = nwh / (nws + nwh) 3. “Naïve” hypothesis: P(text|C) = P(w 1|C) P(w 2|C) … P(w. N|C) C – “spam” or “ham” 4. a(new text) = argmax. C P(new text|C)
Intro: simple idea of spam detection 1. Count for word w it’s frequency nws in spam and nwh in ham 2. Word w appearance probability: P(w|spam) = nws / (nws + nwh) P(w|ham) = nwh / (nws + nwh) 3. “Naïve” hypothesis: P(text|C) = P(w 1|C) P(w 2|C) … P(w. N|C) C – “spam” or “ham” 4. a(new text) = argmax. C P(new text|C)
 Intro: simple idea of spam detection Wait, it’s wrong! a(new text) = argmax. C P(new text|C) We already know new text, so we need probability P(C|new text) and a(new text) = argmax. C P(C|new text) But one can show (using Bayes theorem) that argmax. C P(C|new text) = argmax. C P(new text|C) if P(spam) = P(ham)
Intro: simple idea of spam detection Wait, it’s wrong! a(new text) = argmax. C P(new text|C) We already know new text, so we need probability P(C|new text) and a(new text) = argmax. C P(C|new text) But one can show (using Bayes theorem) that argmax. C P(C|new text) = argmax. C P(new text|C) if P(spam) = P(ham)
 Naïve Bayes Classifier 1. Bayes classifier: a(x) = argmax. C P(C|x) = argmax. C P(x|C) P(C) (Bayes theorem: P(C|x) = P(x|C) P(C) / P(x) ) 2. with Naïve hypothesis: P(x|C) = P(f 1(x)|C) P(f 2(x)|C) … P(f. N(x)|C) fi(x) – i-th feature of object x
Naïve Bayes Classifier 1. Bayes classifier: a(x) = argmax. C P(C|x) = argmax. C P(x|C) P(C) (Bayes theorem: P(C|x) = P(x|C) P(C) / P(x) ) 2. with Naïve hypothesis: P(x|C) = P(f 1(x)|C) P(f 2(x)|C) … P(f. N(x)|C) fi(x) – i-th feature of object x
 Smoothing probabilities estimates If nws = nwh = 0, P(w|C) = 0 ? When we have no information about word, we can ignore it, but more realistic model is to suppose that it can be spam and ham word with equal probabilities: P(w|spam) = (nws +1)/ (nws + nwh+2) P(w|ham) = (nws +1)/ (nws + nwh+2) This is a robust estimation called Laplas smoothing. General formula: P(f|c) = (1 + nfc )/ (|C| + ∑ynfy)
Smoothing probabilities estimates If nws = nwh = 0, P(w|C) = 0 ? When we have no information about word, we can ignore it, but more realistic model is to suppose that it can be spam and ham word with equal probabilities: P(w|spam) = (nws +1)/ (nws + nwh+2) P(w|ham) = (nws +1)/ (nws + nwh+2) This is a robust estimation called Laplas smoothing. General formula: P(f|c) = (1 + nfc )/ (|C| + ∑ynfy)
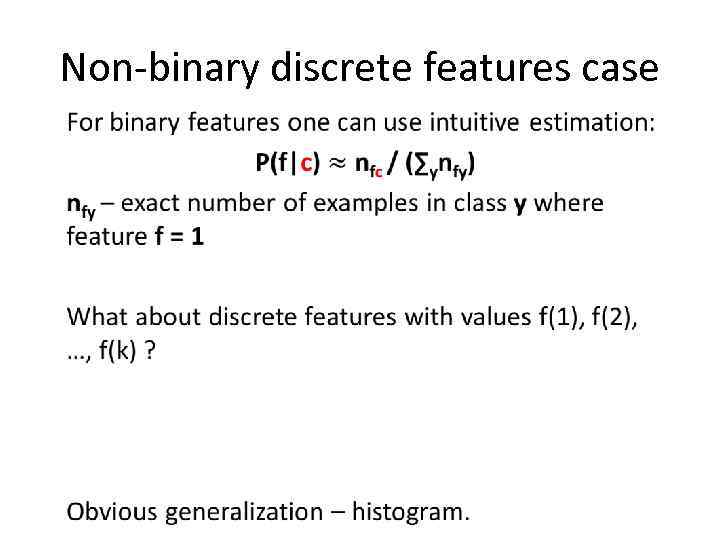 Non-binary discrete features case •
Non-binary discrete features case •
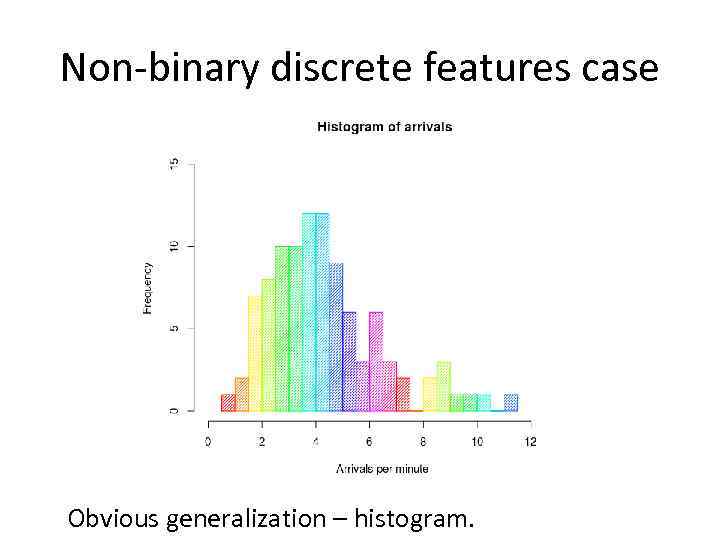 Non-binary discrete features case Obvious generalization – histogram.
Non-binary discrete features case Obvious generalization – histogram.
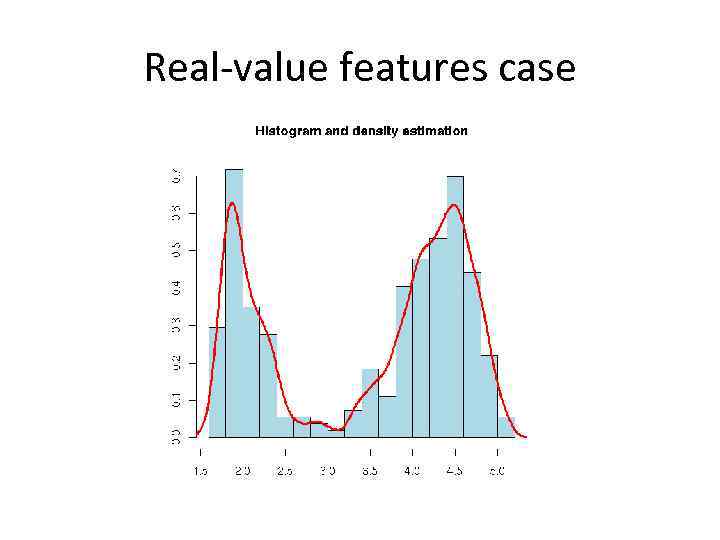
 Real-value features case X: What about real-value features? Y: Make it discrete! Z: And smooth!
Real-value features case X: What about real-value features? Y: Make it discrete! Z: And smooth!
 Real-value features case
Real-value features case
 Parametric probabilities estimation The other method is to choose probability distribution class (f. ex. normal distribution or multinomial distribution) and estimate ϴci : P(fi(x) = t|c) = ϕ(ϴci; t) For ϴc estimation we could use maximum likehood: ϴc = argmaxϴ ϕ(ϴ; fi(xc 1)) ϕ(ϴ; fi(xc 2)) … ϕ(ϴ; fi(xcm)) xck - k-th example from class c in training set
Parametric probabilities estimation The other method is to choose probability distribution class (f. ex. normal distribution or multinomial distribution) and estimate ϴci : P(fi(x) = t|c) = ϕ(ϴci; t) For ϴc estimation we could use maximum likehood: ϴc = argmaxϴ ϕ(ϴ; fi(xc 1)) ϕ(ϴ; fi(xc 2)) … ϕ(ϴ; fi(xcm)) xck - k-th example from class c in training set
 Distribution class choice recommendations • Text features/other sparse discrete features – multinomial distribution • Continuous features with low scatter – normal distribution • Continuous features with outliers – distributions with “heavy tail”
Distribution class choice recommendations • Text features/other sparse discrete features – multinomial distribution • Continuous features with low scatter – normal distribution • Continuous features with outliers – distributions with “heavy tail”
 Bayes classification without naïve hypothesis • Generalization of density estimation methods – parametric and non-parametric estimation of highdimensional densities • Parametric estimation: – formula P(fi(x) = t|c) = ϕ(ϴci; t) changes to P(f (x) = t|c) = ϕ(ϴc; t), f(x) – feature vector • Non-parametric estimation: – Generalization of histogram smoothing technique:
Bayes classification without naïve hypothesis • Generalization of density estimation methods – parametric and non-parametric estimation of highdimensional densities • Parametric estimation: – formula P(fi(x) = t|c) = ϕ(ϴci; t) changes to P(f (x) = t|c) = ϕ(ϴc; t), f(x) – feature vector • Non-parametric estimation: – Generalization of histogram smoothing technique:
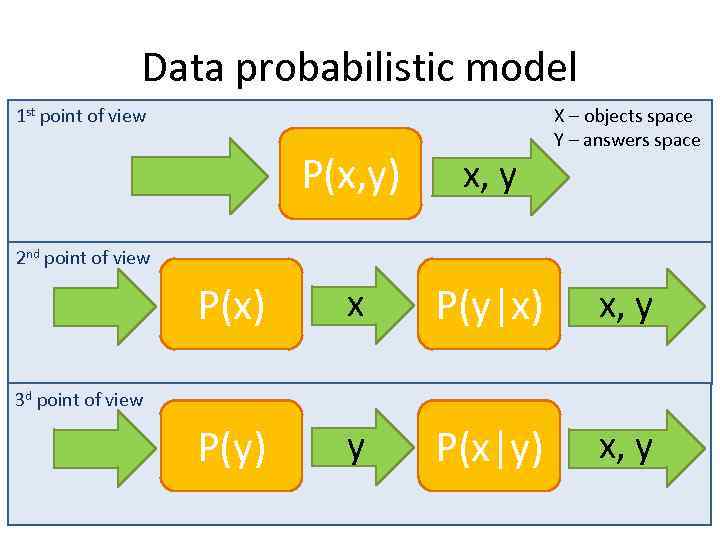 Data probabilistic model 1 st point of view X – objects space Y – answers space P(x, y) x, y P(x) x P(y|x) x, y P(y) y P(x|y) x, y 2 nd point of view 3 d point of view
Data probabilistic model 1 st point of view X – objects space Y – answers space P(x, y) x, y P(x) x P(y|x) x, y P(y) y P(x|y) x, y 2 nd point of view 3 d point of view
 Generalization: loss function •
Generalization: loss function •
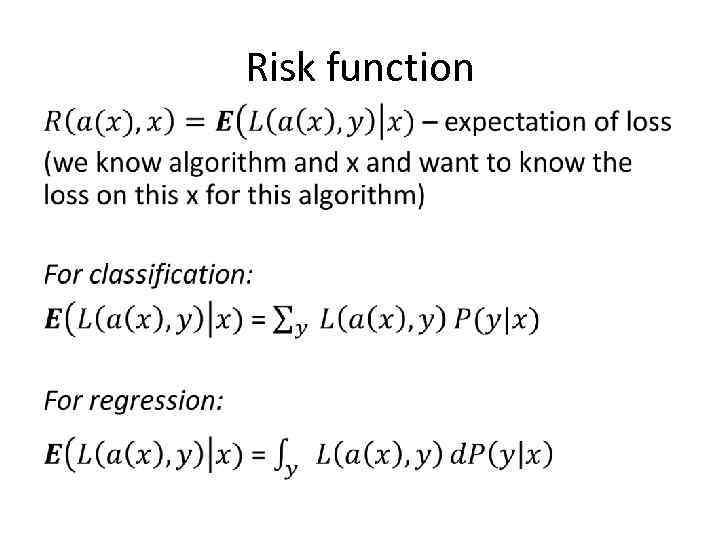 Risk function •
Risk function •
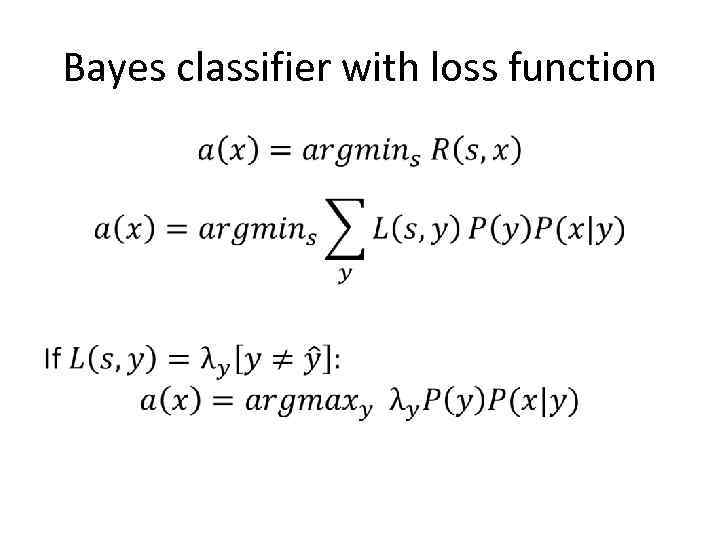 Bayes classifier with loss function •
Bayes classifier with loss function •
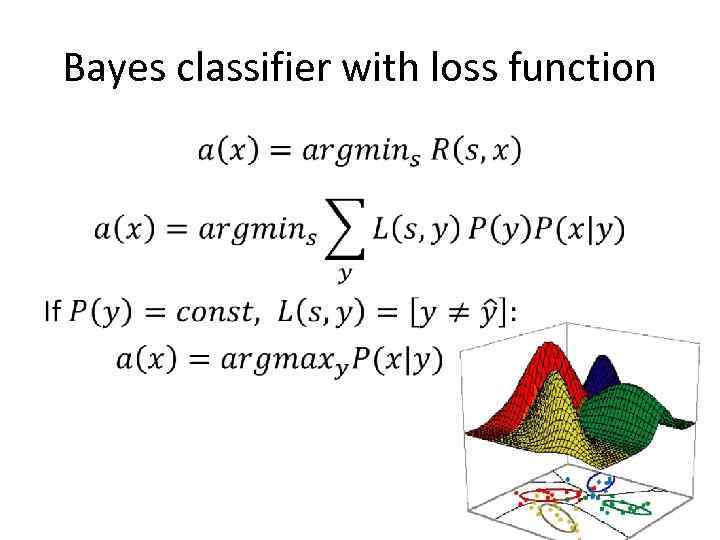 Bayes classifier with loss function •
Bayes classifier with loss function •
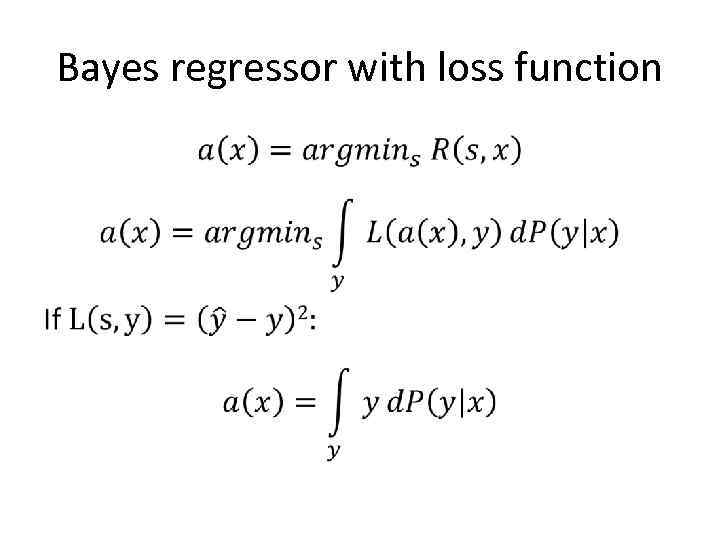 Bayes regressor with loss function •
Bayes regressor with loss function •
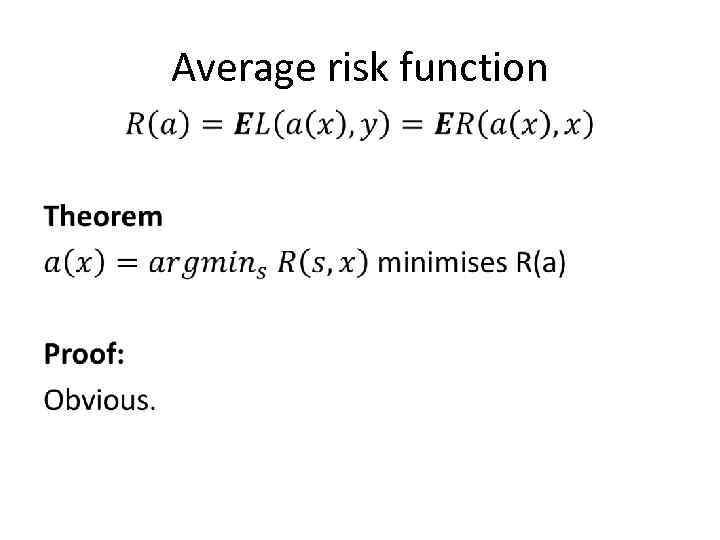 Average risk function •
Average risk function •


