lecture_2.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Practical Data Mining Lecture 2. Supervised learning (part 1). Victor Kantor MIPT 2014
Practical Data Mining Lecture 2. Supervised learning (part 1). Victor Kantor MIPT 2014
 Plan 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Course tasks and practice Previous lecture reminder Supervised learning: quality measures Distance (metric) based methods Bayesian methods (introduction)
Plan 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Course tasks and practice Previous lecture reminder Supervised learning: quality measures Distance (metric) based methods Bayesian methods (introduction)
 Course tasks • First deadline – 22 November: – Theoretical task – Intro Python task – Intro R task – 4 Contests • Second deadline – 13 December: – Team Data Mining Project – 2 -3 practical tasks on real data • Without deadlines: – “toys” – simple task on standard datasets or tasks “try to use package X in language Y and write a short report”
Course tasks • First deadline – 22 November: – Theoretical task – Intro Python task – Intro R task – 4 Contests • Second deadline – 13 December: – Team Data Mining Project – 2 -3 practical tasks on real data • Without deadlines: – “toys” – simple task on standard datasets or tasks “try to use package X in language Y and write a short report”
 Previous lecture reminder Supervised learning • What is machine learning? • Classification, regression, clustering • Overfitting
Previous lecture reminder Supervised learning • What is machine learning? • Classification, regression, clustering • Overfitting
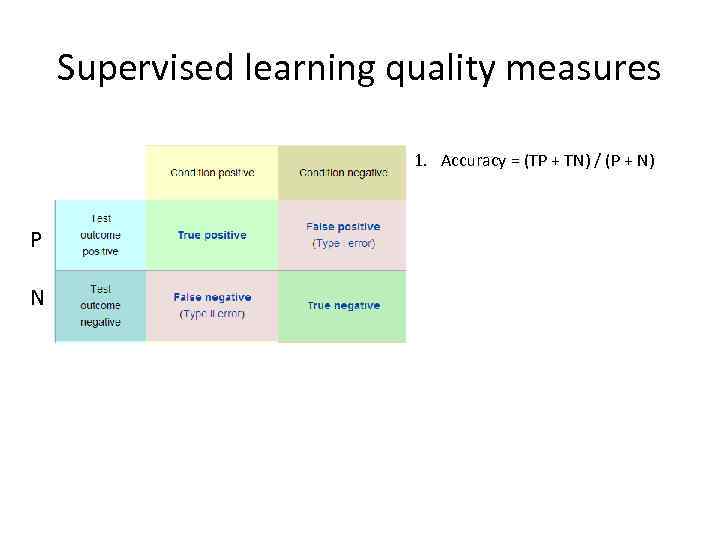 Supervised learning quality measures 1. Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (P + N) P N
Supervised learning quality measures 1. Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (P + N) P N
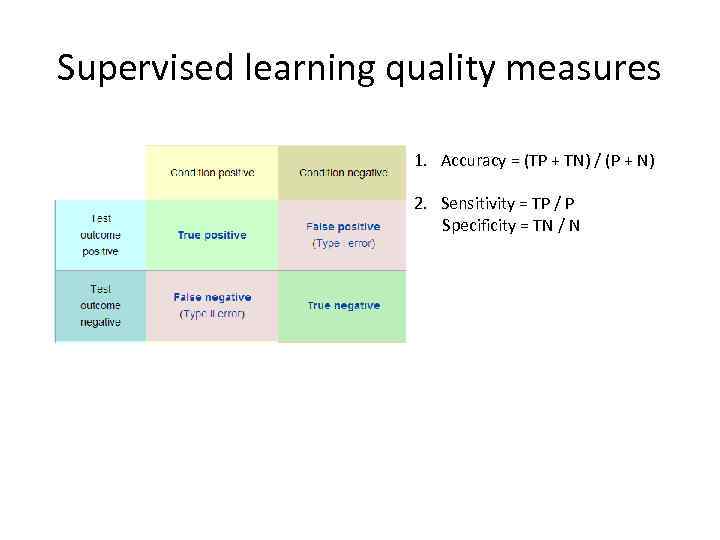 Supervised learning quality measures 1. Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (P + N) 2. Sensitivity = TP / P Specificity = TN / N
Supervised learning quality measures 1. Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (P + N) 2. Sensitivity = TP / P Specificity = TN / N
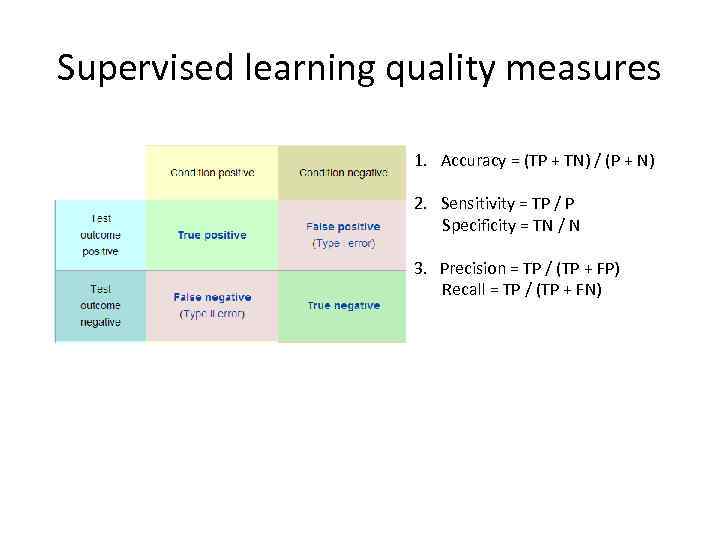 Supervised learning quality measures 1. Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (P + N) 2. Sensitivity = TP / P Specificity = TN / N 3. Precision = TP / (TP + FP) Recall = TP / (TP + FN)
Supervised learning quality measures 1. Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (P + N) 2. Sensitivity = TP / P Specificity = TN / N 3. Precision = TP / (TP + FP) Recall = TP / (TP + FN)
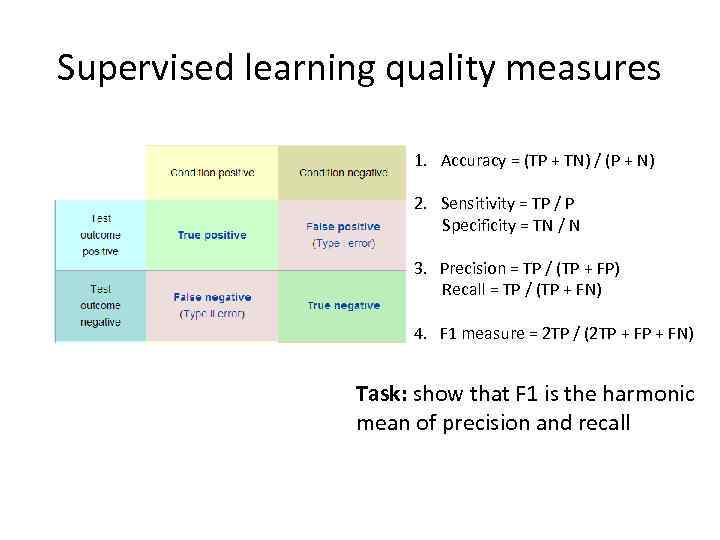 Supervised learning quality measures 1. Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (P + N) 2. Sensitivity = TP / P Specificity = TN / N 3. Precision = TP / (TP + FP) Recall = TP / (TP + FN) 4. F 1 measure = 2 TP / (2 TP + FN) Task: show that F 1 is the harmonic mean of precision and recall
Supervised learning quality measures 1. Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (P + N) 2. Sensitivity = TP / P Specificity = TN / N 3. Precision = TP / (TP + FP) Recall = TP / (TP + FN) 4. F 1 measure = 2 TP / (2 TP + FN) Task: show that F 1 is the harmonic mean of precision and recall
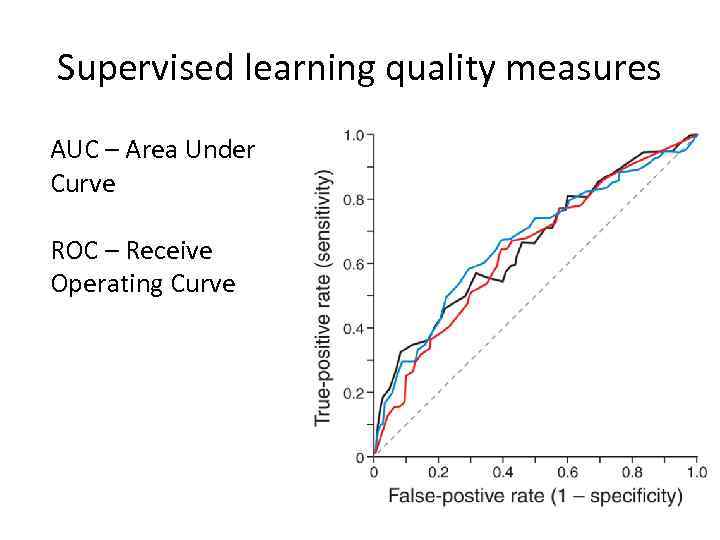 Supervised learning quality measures AUC – Area Under Curve ROC – Receive Operating Curve ROC curve
Supervised learning quality measures AUC – Area Under Curve ROC – Receive Operating Curve ROC curve
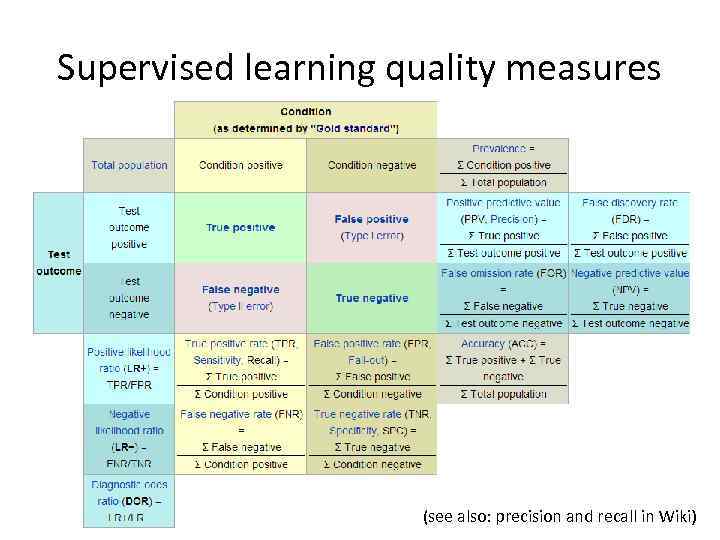 Supervised learning quality measures (see also: precision and recall in Wiki)
Supervised learning quality measures (see also: precision and recall in Wiki)
 Distance based methods 1. 2. 3. 4. k. NN – k Nearest Neighbors Weighted k. NN CNN – condensed nearest neighbors Nearest Centroid Classifier
Distance based methods 1. 2. 3. 4. k. NN – k Nearest Neighbors Weighted k. NN CNN – condensed nearest neighbors Nearest Centroid Classifier
 k. NN Weighted k. NN with w(x(i)) = const(x(i))
k. NN Weighted k. NN with w(x(i)) = const(x(i))
 Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): ?
Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): ?
 Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): ?
Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): ?
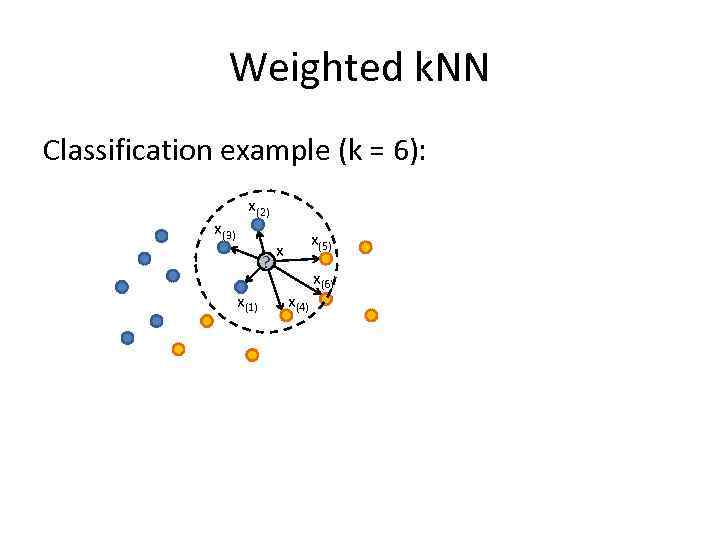 Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6)
Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6)
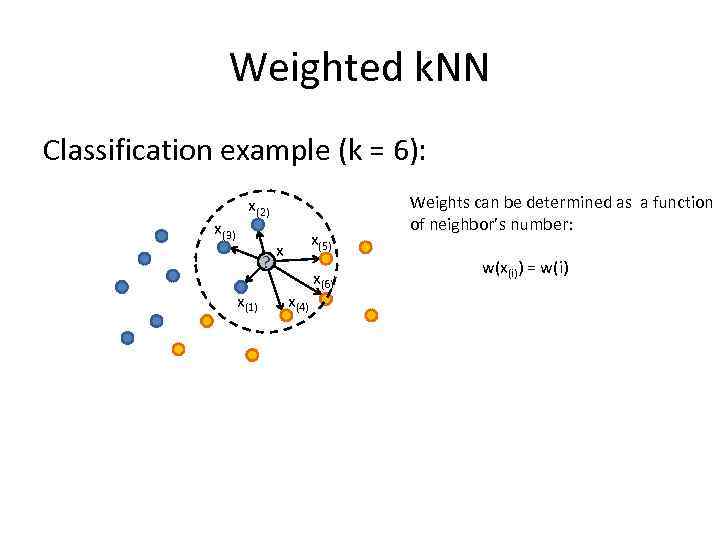 Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i)
Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i)
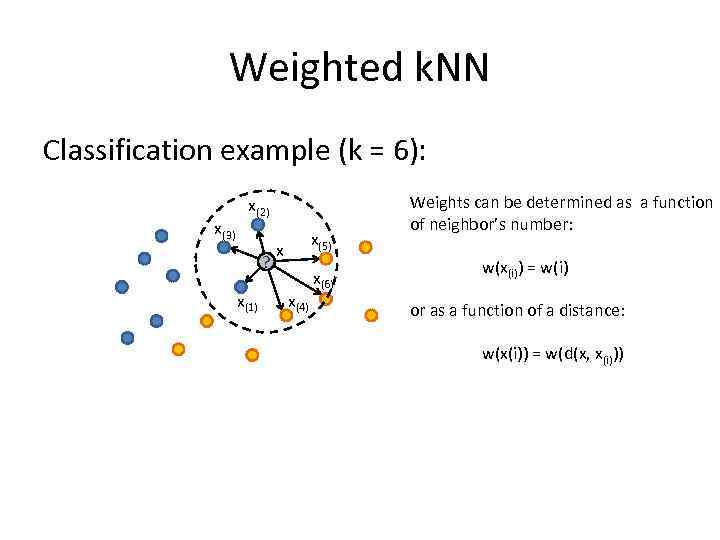 Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
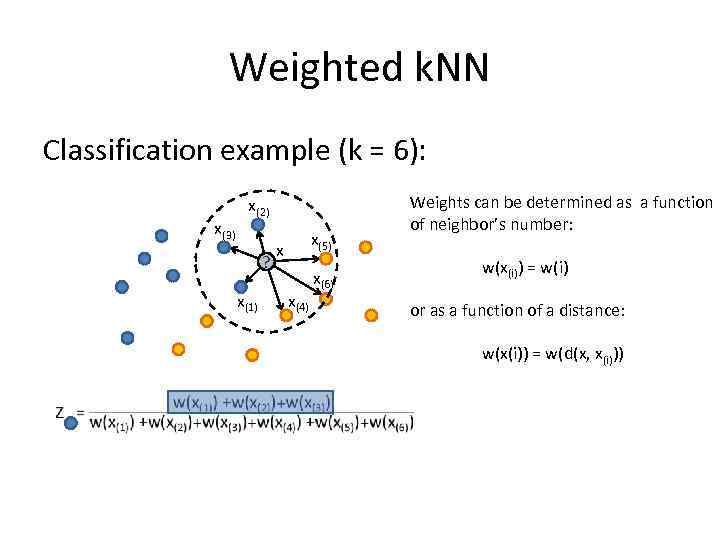 Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
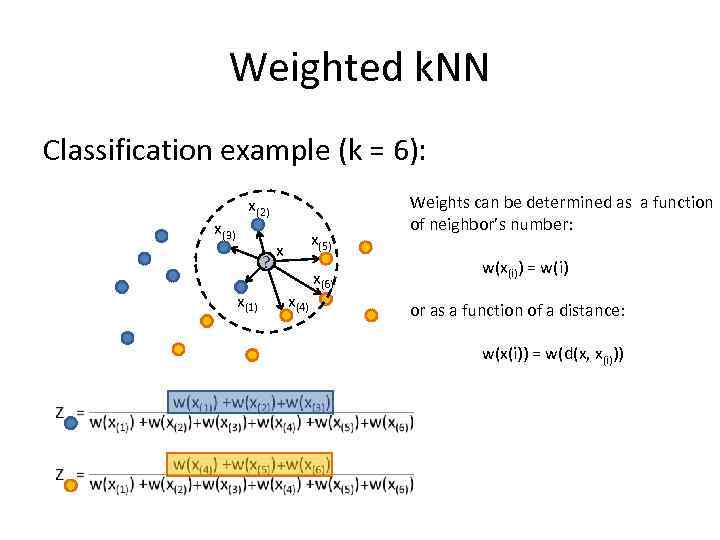 Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
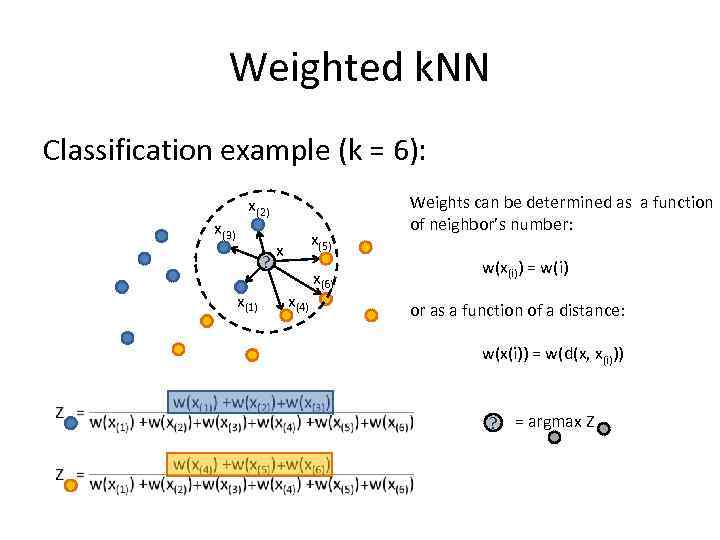 Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i))) ? = argmax Z
Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i))) ? = argmax Z
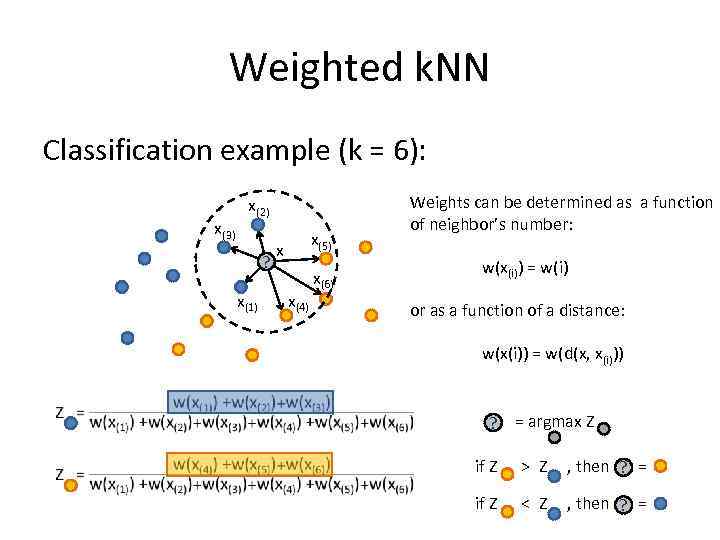 Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i))) ? = argmax Z if Z > Z , then = ? if Z < Z , then = ?
Weighted k. NN Classification example (k = 6): x(3) x(2) ? x(1) x(5) x x(4) x(6) Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i))) ? = argmax Z if Z > Z , then = ? if Z < Z , then = ?
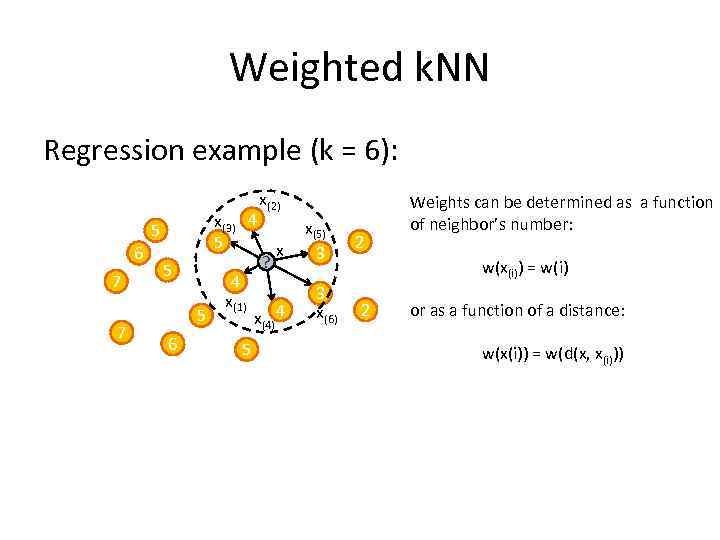 Weighted k. NN Regression example (k = 6): x(3) 4 5 5 6 7 7 5 5 6 4 x(1) 5 x(2) ? x x(4) 4 x(5) 3 3 x(6) 2 Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) 2 or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
Weighted k. NN Regression example (k = 6): x(3) 4 5 5 6 7 7 5 5 6 4 x(1) 5 x(2) ? x x(4) 4 x(5) 3 3 x(6) 2 Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) 2 or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
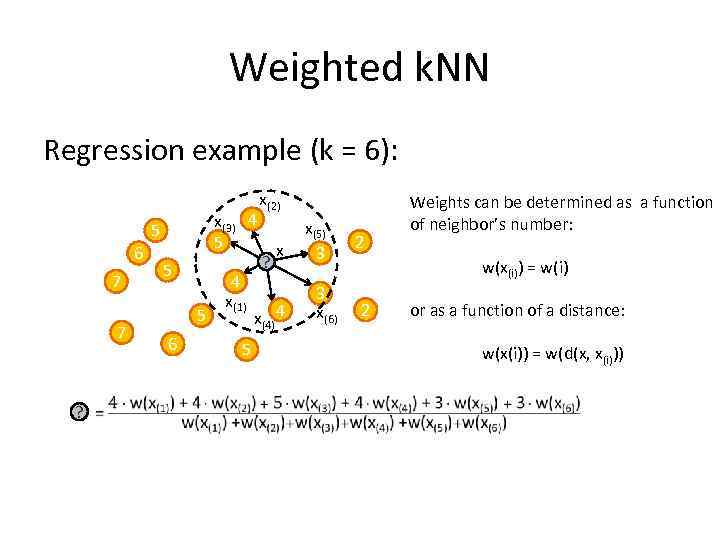 Weighted k. NN Regression example (k = 6): x(3) 4 5 5 6 7 7 ? 5 5 6 4 x(1) 5 x(2) ? x x(4) 4 x(5) 3 3 x(6) 2 Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) 2 or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
Weighted k. NN Regression example (k = 6): x(3) 4 5 5 6 7 7 ? 5 5 6 4 x(1) 5 x(2) ? x x(4) 4 x(5) 3 3 x(6) 2 Weights can be determined as a function of neighbor’s number: w(x(i)) = w(i) 2 or as a function of a distance: w(x(i)) = w(d(x, x(i)))
 CNN Given a training set X, CNN works iteratively: 1. Scan all elements of X, looking for an element x whose nearest prototype from U has a different label than x. 2. Remove x from X and add it to U 3. Repeat the scan until no more prototypes are added to U. Use U instead of X for classification. It is efficient to scan the training examples in order of decreasing border ratio: a(x) = ||x'-y|| / ||x-y||
CNN Given a training set X, CNN works iteratively: 1. Scan all elements of X, looking for an element x whose nearest prototype from U has a different label than x. 2. Remove x from X and add it to U 3. Repeat the scan until no more prototypes are added to U. Use U instead of X for classification. It is efficient to scan the training examples in order of decreasing border ratio: a(x) = ||x'-y|| / ||x-y||
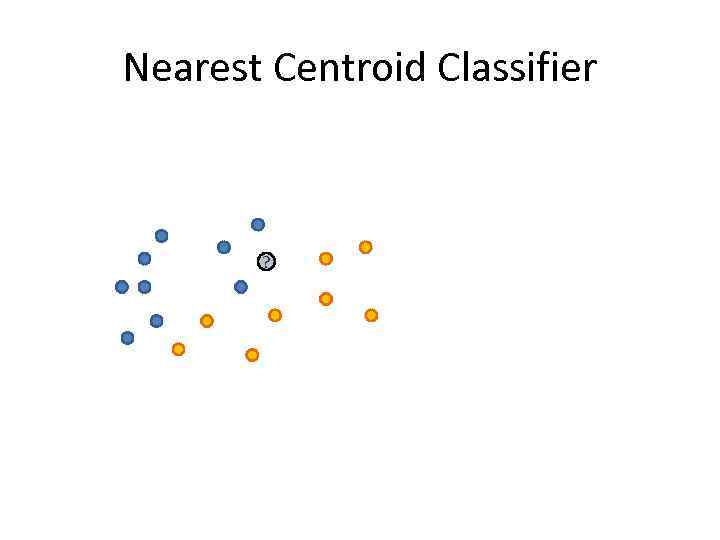 Nearest Centroid Classifier ?
Nearest Centroid Classifier ?
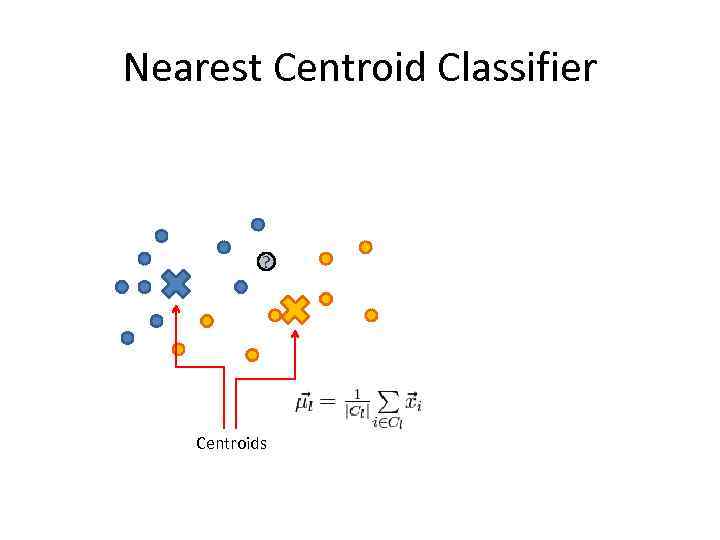 Nearest Centroid Classifier ? Centroids
Nearest Centroid Classifier ? Centroids
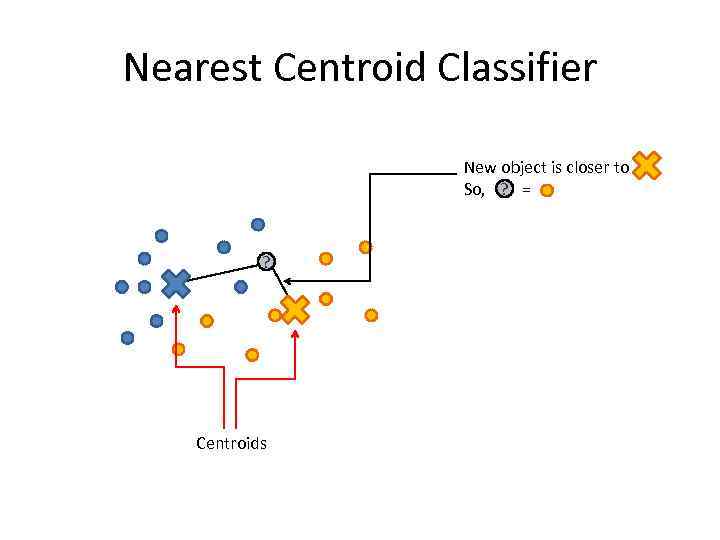 Nearest Centroid Classifier New object is closer to ? So, = ? Centroids
Nearest Centroid Classifier New object is closer to ? So, = ? Centroids
 Distance based methods 1. 2. 3. 4. k. NN – k Nearest Neighbors Weighted k. NN CNN – condensed nearest neighbors Nearest Centroid Classifier
Distance based methods 1. 2. 3. 4. k. NN – k Nearest Neighbors Weighted k. NN CNN – condensed nearest neighbors Nearest Centroid Classifier
 Bayesian methods 1. Data generation probabilistic model 2. Optimal Bayes classifier 3. PDF (Probabilistic Density Function) estimation 4. NDA - Normal Discriminant Analysis 5. Naïve Bayes classifier
Bayesian methods 1. Data generation probabilistic model 2. Optimal Bayes classifier 3. PDF (Probabilistic Density Function) estimation 4. NDA - Normal Discriminant Analysis 5. Naïve Bayes classifier
 Plan 1. 2. 3. 4. Previous lecture reminder Supervised learning: quality measures Distance (metric) based methods Bayesian methods (introduction)
Plan 1. 2. 3. 4. Previous lecture reminder Supervised learning: quality measures Distance (metric) based methods Bayesian methods (introduction)
 Course tasks • First deadline – 22 November: – Theoretical task – Intro Python task – Intro R task – 4 Contests • Second deadline – 13 December: – Team Data Mining Project – 2 -3 practical tasks on real data • Without deadlines: – “toys” – simple task on standard datasets or tasks “try to use package X in language Y and write a short report”
Course tasks • First deadline – 22 November: – Theoretical task – Intro Python task – Intro R task – 4 Contests • Second deadline – 13 December: – Team Data Mining Project – 2 -3 practical tasks on real data • Without deadlines: – “toys” – simple task on standard datasets or tasks “try to use package X in language Y and write a short report”


