be507411a671f43c176a1666394c7583.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Practical Approaches for Using Health Indicators & Promoting Librarian & Public Health Partnerships Module 3 Nancy Allee, MLS, MPH, AHIP Deputy Director, Health Sciences Libraries University of Michigan Webinar, February 3, 2010 Health Indicators, Part III
Practical Approaches for Using Health Indicators & Promoting Librarian & Public Health Partnerships Module 3 Nancy Allee, MLS, MPH, AHIP Deputy Director, Health Sciences Libraries University of Michigan Webinar, February 3, 2010 Health Indicators, Part III
 Health indicators: 4 -part series • • • Part I: “Health Indicators: Overview” Wednesday, January 20 th, 1: 00 pm EST – Understand the variety of health indicators, their data sources, their key attributes, context and use – Presenter: Cheryl Wold, Wold & Associates – Archived webinar available: XXX Part II: “Community Health Status Indicators (CHSI)” Wednesday, January 27 th, 1: 00 pm EST – Learn to navigate and use the Community Health Status Indicators (CHSI) effectively to find county-level data – Presenter: Nancy Allee, Deputy Director, Health Sciences Libraries, University of Michigan Part III: “Practical Approaches for Using Health Indicators” Wednesday, February 3 rd, 1: 00 pm EST – Discover ways in which librarians can become more engaged with others in improving the health of their communities and become knowledgeable about ways in which CHSI data can be used in working with the public health practice community – Presenter: Nancy Allee, Deputy Director, Health Sciences Libraries, University of Michigan Part IV: “Examples of Important New Indicator Projects” Date/Time: To Be Announced – Become familiar with several important indicator efforts including State of the USA, MATCH, and two local level examples – Presenter: Cheryl Wold, Wold & Associates Registration and archived webinars: http: //www. nlm. nih. gov/nichsr/healthindicators/ Health Indicators, Part III
Health indicators: 4 -part series • • • Part I: “Health Indicators: Overview” Wednesday, January 20 th, 1: 00 pm EST – Understand the variety of health indicators, their data sources, their key attributes, context and use – Presenter: Cheryl Wold, Wold & Associates – Archived webinar available: XXX Part II: “Community Health Status Indicators (CHSI)” Wednesday, January 27 th, 1: 00 pm EST – Learn to navigate and use the Community Health Status Indicators (CHSI) effectively to find county-level data – Presenter: Nancy Allee, Deputy Director, Health Sciences Libraries, University of Michigan Part III: “Practical Approaches for Using Health Indicators” Wednesday, February 3 rd, 1: 00 pm EST – Discover ways in which librarians can become more engaged with others in improving the health of their communities and become knowledgeable about ways in which CHSI data can be used in working with the public health practice community – Presenter: Nancy Allee, Deputy Director, Health Sciences Libraries, University of Michigan Part IV: “Examples of Important New Indicator Projects” Date/Time: To Be Announced – Become familiar with several important indicator efforts including State of the USA, MATCH, and two local level examples – Presenter: Cheryl Wold, Wold & Associates Registration and archived webinars: http: //www. nlm. nih. gov/nichsr/healthindicators/ Health Indicators, Part III
 Today’s presentation • Part I: – Brief Review of the Community Health Status Indicators (CHSI) – Ways in which CHSI data and resources can be used in working with the public health practice community • Part II: – NLM & NN/LM library resources complementary to CHSI • Part III: – Librarian engagement in productive partnerships with the public health practice community – Case study: University of Michigan, Health Sciences Libraries, Public Health 2. 0 project Health Indicators, Part III
Today’s presentation • Part I: – Brief Review of the Community Health Status Indicators (CHSI) – Ways in which CHSI data and resources can be used in working with the public health practice community • Part II: – NLM & NN/LM library resources complementary to CHSI • Part III: – Librarian engagement in productive partnerships with the public health practice community – Case study: University of Michigan, Health Sciences Libraries, Public Health 2. 0 project Health Indicators, Part III
 Presenter’s background Nancy Allee (nallee@umich. edu) Degrees in Library Science & Public Health MLA CE’s –Community Health Status Indicators –Evidence Based Public Health –Public Health 2. 0 (Social Media) NLM & Partners in Information Access –Chair: Public Health Training Subcommittee –Project Director: Public Health Information & Data Tutorials project & developer of Evidence Based Public Health Module Past chair of the Public Health / Health Administration Section of the Medical Library Association Health Indicators, Part III
Presenter’s background Nancy Allee (nallee@umich. edu) Degrees in Library Science & Public Health MLA CE’s –Community Health Status Indicators –Evidence Based Public Health –Public Health 2. 0 (Social Media) NLM & Partners in Information Access –Chair: Public Health Training Subcommittee –Project Director: Public Health Information & Data Tutorials project & developer of Evidence Based Public Health Module Past chair of the Public Health / Health Administration Section of the Medical Library Association Health Indicators, Part III
 Brief review What are health indicators? What are the Community Health Status Indicators (CHSI)? What are peer counties? What are the uses of and who are the users of CHSI? Health Indicators, Part III
Brief review What are health indicators? What are the Community Health Status Indicators (CHSI)? What are peer counties? What are the uses of and who are the users of CHSI? Health Indicators, Part III
 What are health indicators? • An indicator is “a summary measure that aims to describe in a few numbers as much detail as possible about a system to help understand, compare, predict, improve, and innovate. ” • [Source: The Good Indicators Guide http: //www. apho. org. uk/resource/item. aspx? RID=44584 ] • A health indicator is “a characteristic of an individual, population, or environment which is subject to measurement and can be used to describe one or more aspects of the health of an individual or population. ” • [Source: Definition of Wellness web site http: //www. definitionofwellness. com/dictionary/health-indicator. html] Health Indicators, Part III
What are health indicators? • An indicator is “a summary measure that aims to describe in a few numbers as much detail as possible about a system to help understand, compare, predict, improve, and innovate. ” • [Source: The Good Indicators Guide http: //www. apho. org. uk/resource/item. aspx? RID=44584 ] • A health indicator is “a characteristic of an individual, population, or environment which is subject to measurement and can be used to describe one or more aspects of the health of an individual or population. ” • [Source: Definition of Wellness web site http: //www. definitionofwellness. com/dictionary/health-indicator. html] Health Indicators, Part III
 What is CHSI? (Community Health Status Indicators) • A collection of nationally available health indicators for counties, helping to present a “total picture” of local health. • A resource for monitoring and analyzing community health status and its determinants at the county level. • The goal of CHSI is to give local public health agencies another tool for improving their community’s health by identifying data resources and facilitating the setting of priorities. • CHSI supports the mission and goals of public health, the 10 essential public health services, Healthy People 2010 initiatives, and evidence-based policy and research.
What is CHSI? (Community Health Status Indicators) • A collection of nationally available health indicators for counties, helping to present a “total picture” of local health. • A resource for monitoring and analyzing community health status and its determinants at the county level. • The goal of CHSI is to give local public health agencies another tool for improving their community’s health by identifying data resources and facilitating the setting of priorities. • CHSI supports the mission and goals of public health, the 10 essential public health services, Healthy People 2010 initiatives, and evidence-based policy and research.
 What is the “community” in Community Health Status Indicators? • Individual counties – data for 3, 141 U. S. counties • Peer counties – counties similar in population size and other selected characteristics (e. g. poverty level, age distribution, density) Health Indicators, Part III
What is the “community” in Community Health Status Indicators? • Individual counties – data for 3, 141 U. S. counties • Peer counties – counties similar in population size and other selected characteristics (e. g. poverty level, age distribution, density) Health Indicators, Part III
 Uses of & users of CHSI and health indicators • Uses of – – – – Public policy Public health programs Interventions Partnerships Research Grants Publications • Users of – – – – Public health officials Public health workers Librarians Academics Government agencies Nonprofit organizations General public Anyone with an interest in local public health data Health Indicators, Part III
Uses of & users of CHSI and health indicators • Uses of – – – – Public policy Public health programs Interventions Partnerships Research Grants Publications • Users of – – – – Public health officials Public health workers Librarians Academics Government agencies Nonprofit organizations General public Anyone with an interest in local public health data Health Indicators, Part III
 CHSI reports Each CHSI report includes data on access and utilization of healthcare services, birth and death measures, Healthy People 2010 targets and U. S. birth and death rates, vulnerable populations, riskfactors for premature deaths, communicable diseases and environmental health. In addition, the presentation of the data allows for comparisons of a county to its peer counties as well as U. S. rates and Healthy People 2010 targets. Health Indicators, Part III
CHSI reports Each CHSI report includes data on access and utilization of healthcare services, birth and death measures, Healthy People 2010 targets and U. S. birth and death rates, vulnerable populations, riskfactors for premature deaths, communicable diseases and environmental health. In addition, the presentation of the data allows for comparisons of a county to its peer counties as well as U. S. rates and Healthy People 2010 targets. Health Indicators, Part III
 How can I access the CHSI web site? http: //www. communityhealth. hhs. gov/
How can I access the CHSI web site? http: //www. communityhealth. hhs. gov/
 CHSI: How to use your county’s report Health Indicators, Part III
CHSI: How to use your county’s report Health Indicators, Part III
 “Celebrate your success” • In areas where a county’s health status excels, celebrate the good news and spread the word. Let the community know about its good health where the indicators are positive. • Symbols – Apple = favorable status – Magnifying glass = unfavorable status Health Indicators, Part III
“Celebrate your success” • In areas where a county’s health status excels, celebrate the good news and spread the word. Let the community know about its good health where the indicators are positive. • Symbols – Apple = favorable status – Magnifying glass = unfavorable status Health Indicators, Part III
 “Learn from one another” By comparing a county with its “peer counties” that have similar characteristics, local public health agencies may be able to uncover reasons for rate differences. In areas where county rates are higher than others, share information about model programs that are making a difference, and think of other counties as good resources while working to improve the health of residents where a county’s health status is lower. Peer counties may be tackling similar challenges. Communities can learn from one another as they work to create innovative solutions for improving health. Health Indicators, Part III
“Learn from one another” By comparing a county with its “peer counties” that have similar characteristics, local public health agencies may be able to uncover reasons for rate differences. In areas where county rates are higher than others, share information about model programs that are making a difference, and think of other counties as good resources while working to improve the health of residents where a county’s health status is lower. Peer counties may be tackling similar challenges. Communities can learn from one another as they work to create innovative solutions for improving health. Health Indicators, Part III
 “Involve health care providers and policy makers” Share the CHSI report widely – with board of health members, city council, county commissioners, state legislators, and business leaders. Can also share with health care professionals working in private practice, schools, clinics, hospitals, as well as colleagues in social services, housing, food and nutrition, and other related programs. Improving health status takes a team effort. Health Indicators, Part III
“Involve health care providers and policy makers” Share the CHSI report widely – with board of health members, city council, county commissioners, state legislators, and business leaders. Can also share with health care professionals working in private practice, schools, clinics, hospitals, as well as colleagues in social services, housing, food and nutrition, and other related programs. Improving health status takes a team effort. Health Indicators, Part III
 “Develop healthy community partners” Help publicize the CHSI reports through press releases, editorial boards, web sites, community meetings, schools and parent/teacher organizations, libraries, and other places where people will become better educated about areas that need improvement. Involve them in identifying barriers to good health and coming up with solutions for improving health status where needed. Health Indicators, Part III
“Develop healthy community partners” Help publicize the CHSI reports through press releases, editorial boards, web sites, community meetings, schools and parent/teacher organizations, libraries, and other places where people will become better educated about areas that need improvement. Involve them in identifying barriers to good health and coming up with solutions for improving health status where needed. Health Indicators, Part III
 “Take another look” The CHSI Report uses national-level data from several sources, many of which contain valuable county-level data. Examining these data may help identify areas where local or state data can fill critical gaps or where national data can be enhanced. If the CHSI Report shows areas in a county that need improvement, this might offer the funding justification for additional surveillance to track health status indicators. Better data may be needed to target programs and policies. Health Indicators, Part III
“Take another look” The CHSI Report uses national-level data from several sources, many of which contain valuable county-level data. Examining these data may help identify areas where local or state data can fill critical gaps or where national data can be enhanced. If the CHSI Report shows areas in a county that need improvement, this might offer the funding justification for additional surveillance to track health status indicators. Better data may be needed to target programs and policies. Health Indicators, Part III
 “Integrate your CHSI report into existing health planning and assessment activities” The CHSI Report is designed to fit into existing public health planning resources used by local public health agencies. Make the CHSI Report work by integrating it into an agency’s planning activities and action steps. The CHSI Report will be useful with other tools as well. Data on the federal Healthy People 2010 targets for the U. S. are also included in the CHSI Report. Use these targets to set goals for the community. Use the CHSI Report and other data to provide a baseline for marking your progress towards Healthy People 2010. Health Indicators, Part III
“Integrate your CHSI report into existing health planning and assessment activities” The CHSI Report is designed to fit into existing public health planning resources used by local public health agencies. Make the CHSI Report work by integrating it into an agency’s planning activities and action steps. The CHSI Report will be useful with other tools as well. Data on the federal Healthy People 2010 targets for the U. S. are also included in the CHSI Report. Use these targets to set goals for the community. Use the CHSI Report and other data to provide a baseline for marking your progress towards Healthy People 2010. Health Indicators, Part III
 CHSI media resources Health Indicators, Part III
CHSI media resources Health Indicators, Part III
 CHSI: “NLM resources”
CHSI: “NLM resources”
 CHSI: “NLM resources” Health Indicators, Part III
CHSI: “NLM resources” Health Indicators, Part III
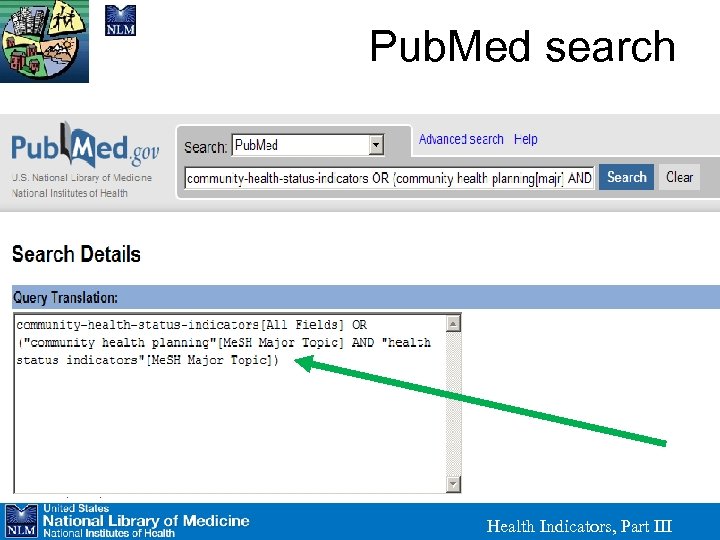 Pub. Med search Health Indicators, Part III
Pub. Med search Health Indicators, Part III
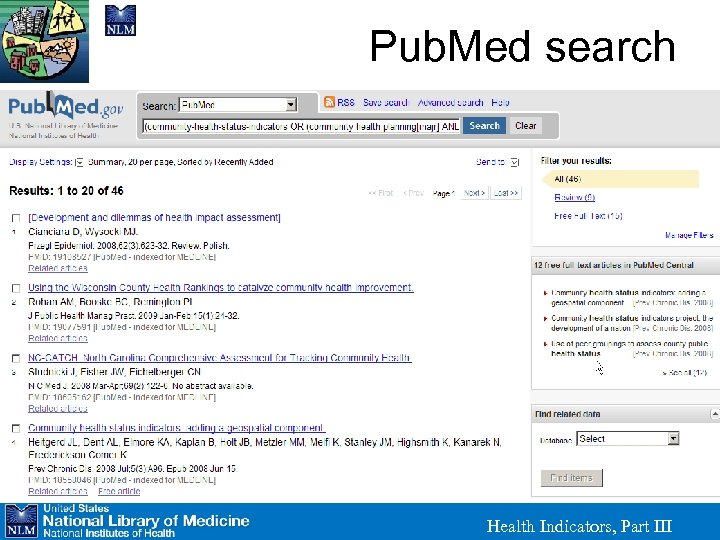 Pub. Med search Health Indicators, Part III
Pub. Med search Health Indicators, Part III
 Pub. Med search “To make these indicators more useful interviewees wanted. . . indicator trend data and indicator comparisons of districts with similar population structures. ” Health Indicators, Part III
Pub. Med search “To make these indicators more useful interviewees wanted. . . indicator trend data and indicator comparisons of districts with similar population structures. ” Health Indicators, Part III
 CHSI: “Public health resources” Health Indicators, Part III
CHSI: “Public health resources” Health Indicators, Part III
 CHSI: “Public health resources” Health Indicators, Part III
CHSI: “Public health resources” Health Indicators, Part III
 Disaster information management research center Health Indicators, Part III
Disaster information management research center Health Indicators, Part III
 Enviro-health links Health Indicators, Part III
Enviro-health links Health Indicators, Part III
 Environmental health and toxicology Health Indicators, Part III
Environmental health and toxicology Health Indicators, Part III
 Healthy People 2010 information access project Health Indicators, Part III
Healthy People 2010 information access project Health Indicators, Part III
 Healthy People 2010 information access project Health Indicators, Part III
Healthy People 2010 information access project Health Indicators, Part III
 Health services research projects in progress Health Indicators, Part III
Health services research projects in progress Health Indicators, Part III
 Health services/sciences research resources Health Indicators, Part III
Health services/sciences research resources Health Indicators, Part III
 Health services/technology assessment text Health Indicators, Part III
Health services/technology assessment text Health Indicators, Part III
 Health disparities & minority health information resources Health Indicators, Part III
Health disparities & minority health information resources Health Indicators, Part III
 Outreach activities & resources Health Indicators, Part III
Outreach activities & resources Health Indicators, Part III
 PH Partners Health Indicators, Part III
PH Partners Health Indicators, Part III
 Toxmap Health Indicators, Part III
Toxmap Health Indicators, Part III
 NNLM South Central Region Houston Academy of Medicine – Texas Medical Center Library http: //nnlm. gov/training/publichealth/ Health Indicators, Part III
NNLM South Central Region Houston Academy of Medicine – Texas Medical Center Library http: //nnlm. gov/training/publichealth/ Health Indicators, Part III
 NN/LM. gov http: //nnlm. gov/outreach/community/ Health Indicators, Part III
NN/LM. gov http: //nnlm. gov/outreach/community/ Health Indicators, Part III
 NN/LM. gov http: //nnlm. gov/outreach/community/ Health Indicators, Part III
NN/LM. gov http: //nnlm. gov/outreach/community/ Health Indicators, Part III
 NN/LM. gov http: //nnlm. gov/evaluation/guides. html#A 2 Health Indicators, Part III
NN/LM. gov http: //nnlm. gov/evaluation/guides. html#A 2 Health Indicators, Part III
 Univ. of Michigan Health Sciences Libraries http: //www. lib. umich. edu/health-sciences-libraries Health Indicators, Part III
Univ. of Michigan Health Sciences Libraries http: //www. lib. umich. edu/health-sciences-libraries Health Indicators, Part III
 Creating a Roadmap: Local Public Health 2. 0 Health Indicators, Part III
Creating a Roadmap: Local Public Health 2. 0 Health Indicators, Part III
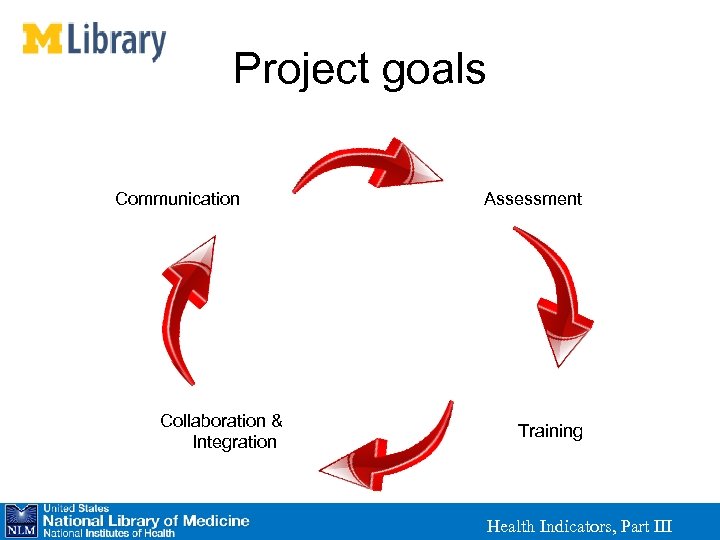 Project goals Communication Collaboration & Integration Assessment Training Health Indicators, Part III
Project goals Communication Collaboration & Integration Assessment Training Health Indicators, Part III
 Survey results • Online via Survey. Monkey • www. surveymonkey. com • 50 survey questions • 150 participants, Genesee • 80 participants, Monroe • 168 surveys completed • 73% response rate Health Indicators, Part III
Survey results • Online via Survey. Monkey • www. surveymonkey. com • 50 survey questions • 150 participants, Genesee • 80 participants, Monroe • 168 surveys completed • 73% response rate Health Indicators, Part III
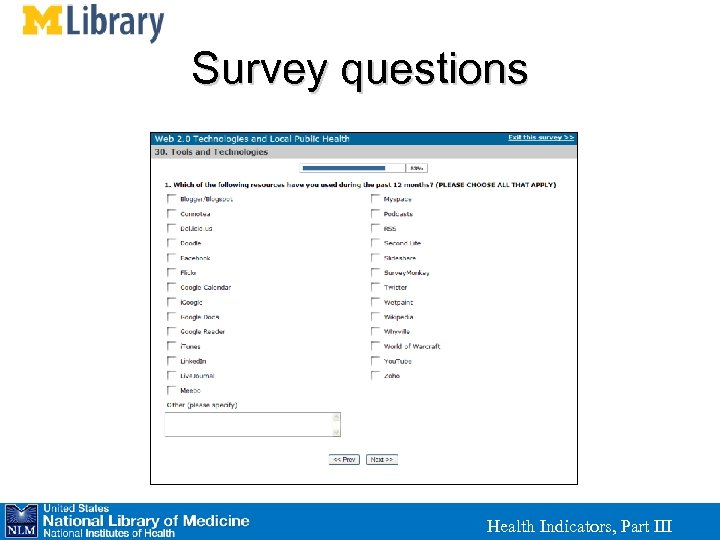 Survey questions Health Indicators, Part III
Survey questions Health Indicators, Part III
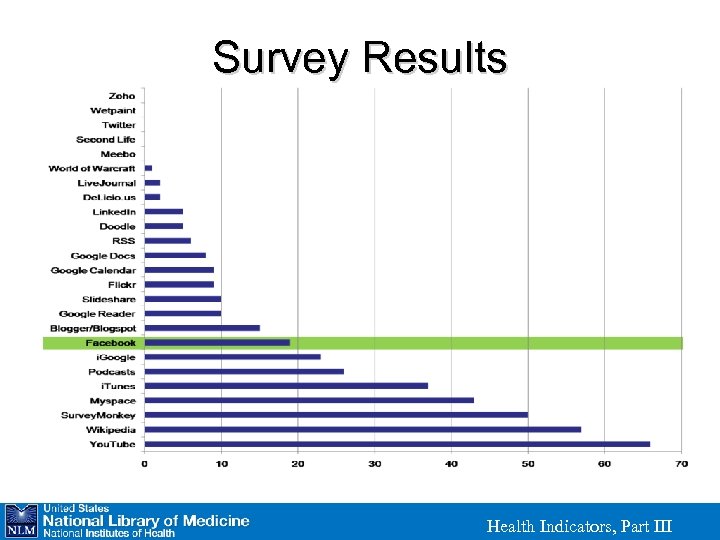 Survey Results Health Indicators, Part III
Survey Results Health Indicators, Part III
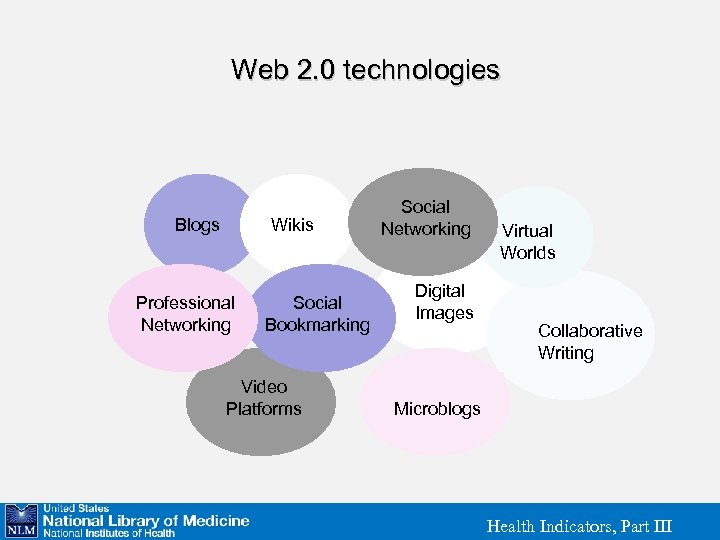 Web 2. 0 technologies Blogs Wikis Professional Networking Social Bookmarking Video Platforms Social Networking Digital Images Virtual Worlds Collaborative Writing Microblogs Health Indicators, Part III
Web 2. 0 technologies Blogs Wikis Professional Networking Social Bookmarking Video Platforms Social Networking Digital Images Virtual Worlds Collaborative Writing Microblogs Health Indicators, Part III
 Genesee County Health Department Intranet Health Indicators, Part III
Genesee County Health Department Intranet Health Indicators, Part III
 Public Health 2. 0 project presentations at library and public health conferences – American Public Health Association – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Public Health Information Network – International Congress on Medical Libraries 2009 – Medical Library Association – National Library of Medicine, Partners in Information Access for the Public Health Workforce Health Indicators, Part III
Public Health 2. 0 project presentations at library and public health conferences – American Public Health Association – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Public Health Information Network – International Congress on Medical Libraries 2009 – Medical Library Association – National Library of Medicine, Partners in Information Access for the Public Health Workforce Health Indicators, Part III
 Public Health 2. 0 @ ICML ‘ 09 http: //espace. library. uq. edu. au/view/UQ: 179802 Health Indicators, Part III
Public Health 2. 0 @ ICML ‘ 09 http: //espace. library. uq. edu. au/view/UQ: 179802 Health Indicators, Part III
 Second Life and Public Health Video http: //www. lib. umich. edu/node/21249 Health Indicators, Part III
Second Life and Public Health Video http: //www. lib. umich. edu/node/21249 Health Indicators, Part III
 Practical approaches to library & public health partnerships • Establish buy-in before the project begins • Be responsive to public health department priorities and needs • Be aware of local technology issues related to social media use • Identify funding sources
Practical approaches to library & public health partnerships • Establish buy-in before the project begins • Be responsive to public health department priorities and needs • Be aware of local technology issues related to social media use • Identify funding sources
 Summary of today’s webinar Practical approaches for using CHSI data & resources National Library of Medicine resources complementary to CHSI Practical approaches for libraries partnering with the public health community Health Indicators, Part III
Summary of today’s webinar Practical approaches for using CHSI data & resources National Library of Medicine resources complementary to CHSI Practical approaches for libraries partnering with the public health community Health Indicators, Part III
 A quote and a question “In the health community today, librarians are too quiet. ” Richard Horton (2008). The diplomatic library. Lancet. Vol 372, August 23, 2008, p. 623. Available from www. thelancet. com Q: Do you agree or disagree? And why? Health Indicators, Part III
A quote and a question “In the health community today, librarians are too quiet. ” Richard Horton (2008). The diplomatic library. Lancet. Vol 372, August 23, 2008, p. 623. Available from www. thelancet. com Q: Do you agree or disagree? And why? Health Indicators, Part III
 10 Essential Public Health Services • • • Monitor health status to identify community health problems Diagnose and investigate health problems and health hazards in the community Inform, educate, and empower people about health issues Mobilize community partnerships to identify and solve health problems Develop policies and plans that support individual and community health efforts Enforce laws and regulations that protect health and ensure safety Link people to needed personal health services and assure the provision of health care when otherwise unavailable Assure a competent public health and personal health care workforce Evaluate effectiveness, accessibility, and quality of personal and populationbased health services Research for new insights and innovative solutions to health problems Source: Public Health Functions Steering Committee, Fall 1994. http: //www. health. gov/phfunctions/public. htm Health Indicators, Part III
10 Essential Public Health Services • • • Monitor health status to identify community health problems Diagnose and investigate health problems and health hazards in the community Inform, educate, and empower people about health issues Mobilize community partnerships to identify and solve health problems Develop policies and plans that support individual and community health efforts Enforce laws and regulations that protect health and ensure safety Link people to needed personal health services and assure the provision of health care when otherwise unavailable Assure a competent public health and personal health care workforce Evaluate effectiveness, accessibility, and quality of personal and populationbased health services Research for new insights and innovative solutions to health problems Source: Public Health Functions Steering Committee, Fall 1994. http: //www. health. gov/phfunctions/public. htm Health Indicators, Part III
 “ 10 Essential Library Services for Public Health” 1. Provide access to public health information resources and research. 2. Provide training and instruction on resources that support the mission and goals of public health. 3. Develop web-based resources that aid the work of public health researchers and practitioners. 4. Partner in research, teaching, and quality improvement initiatives. 5. Actively participate on grant-funded projects. 6. Conduct public health information needs assessments. 7. Share expertise in evaluating public health information. • Q: Here are 7 ideas as a starting point. Other suggestions/recommendations? Health Indicators, Part III
“ 10 Essential Library Services for Public Health” 1. Provide access to public health information resources and research. 2. Provide training and instruction on resources that support the mission and goals of public health. 3. Develop web-based resources that aid the work of public health researchers and practitioners. 4. Partner in research, teaching, and quality improvement initiatives. 5. Actively participate on grant-funded projects. 6. Conduct public health information needs assessments. 7. Share expertise in evaluating public health information. • Q: Here are 7 ideas as a starting point. Other suggestions/recommendations? Health Indicators, Part III
 Upcoming webinar • “Examples of Important New Indicator Projects” • Date/Time: To Be Announced – Become familiar with several important indicator efforts including State of the USA, MATCH, and two local level examples – Presenter: Cheryl Wold, Wold & Associates • Registration: http: //www. nlm. nih. gov/nichsr/healthindicators/ Health Indicators, Part III
Upcoming webinar • “Examples of Important New Indicator Projects” • Date/Time: To Be Announced – Become familiar with several important indicator efforts including State of the USA, MATCH, and two local level examples – Presenter: Cheryl Wold, Wold & Associates • Registration: http: //www. nlm. nih. gov/nichsr/healthindicators/ Health Indicators, Part III
 Contact information Nancy Allee Health Sciences Libraries University of Michigan nallee@umich. edu Health Indicators, Part III
Contact information Nancy Allee Health Sciences Libraries University of Michigan nallee@umich. edu Health Indicators, Part III


