b63122b39d05b89b106a7b6727120bd9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

Practical approach to a bleeding child Peri Kamalakar, MD Director The Valerie Fund Children’s Centers For Cancer &Blood Disorders At Saint Barnabas Health Care System Associate Director, Hemophilia Center Newark Beth israel Medical Center

Practical approach to a bleeding child OBJECTIVES: • Overview of hemostasis • Clinical approach in making a diagnosis • Review the most common bleeding conditions • Discuss the current treatment strategies
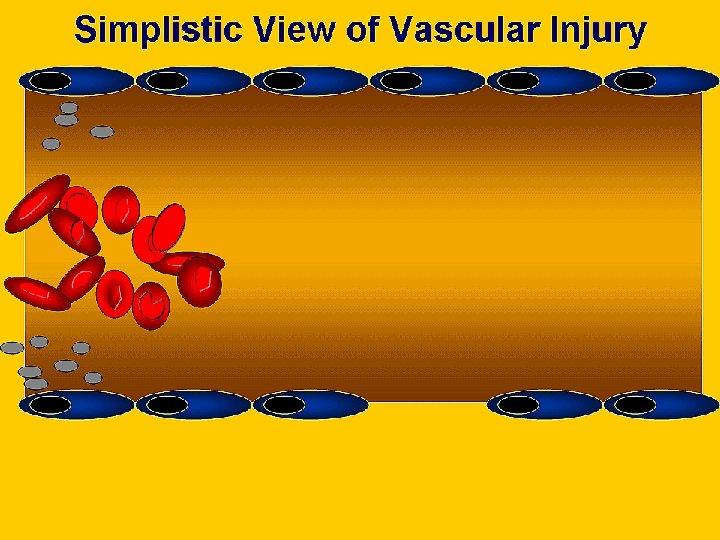
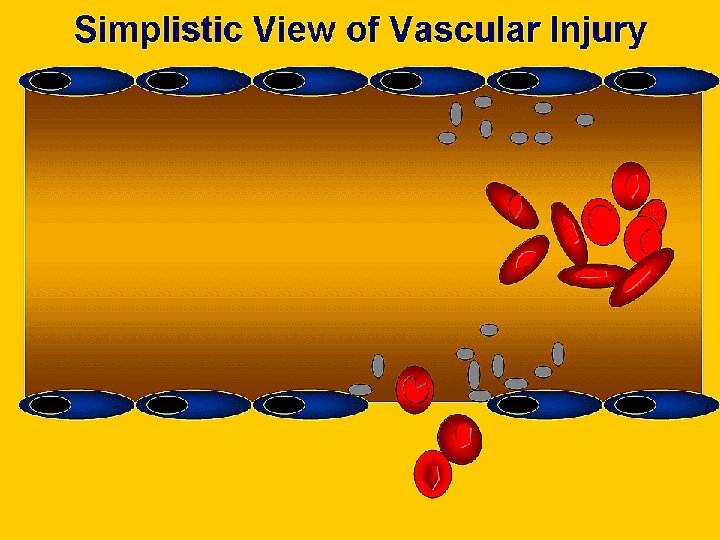
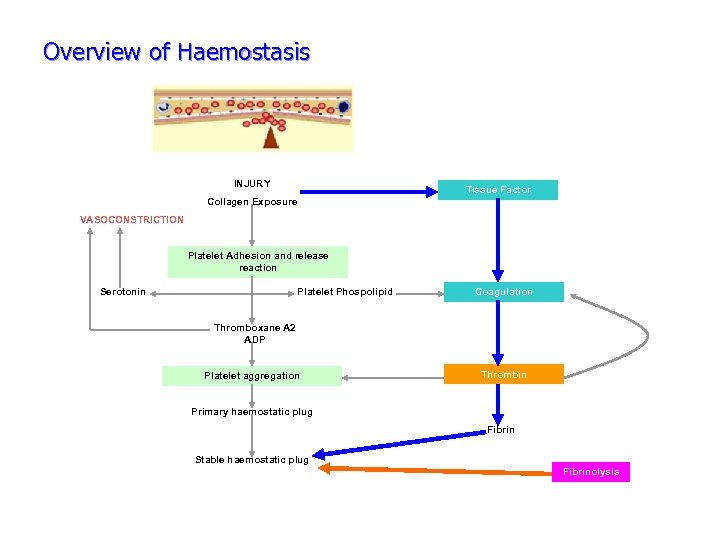
Overview of Haemostasis INJURY Tissue Factor Collagen Exposure VASOCONSTRICTION Platelet Adhesion and release reaction Serotonin Platelet Phospolipid Coagulation Thromboxane A 2 ADP Platelet aggregation Thrombin Primary haemostatic plug Fibrin Stable haemostatic plug Fibrinolysis
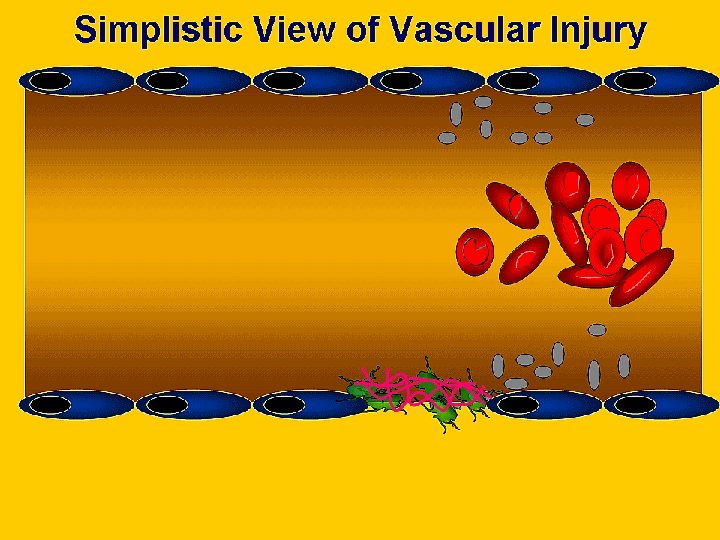
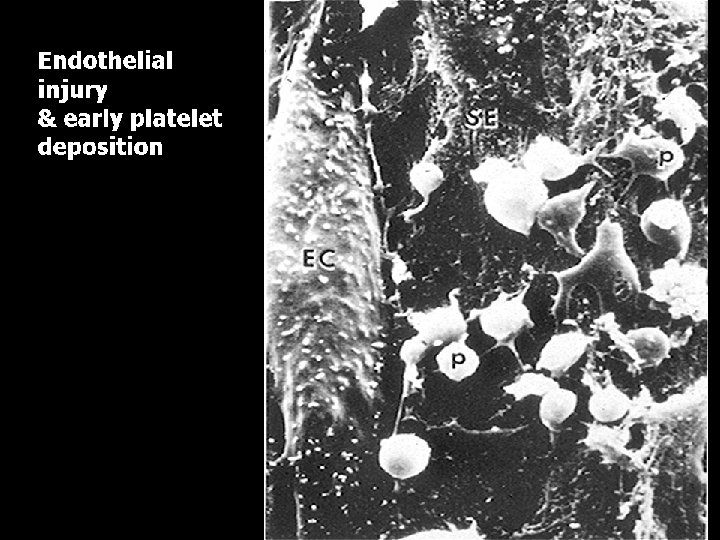
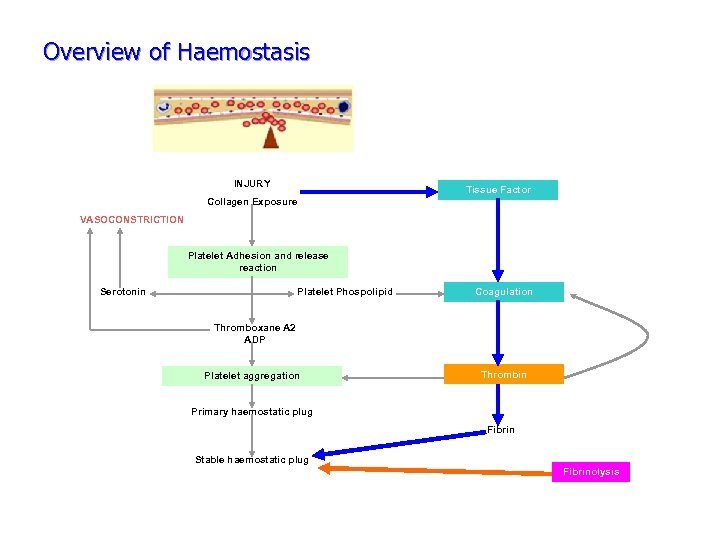
Overview of Haemostasis INJURY Tissue Factor Collagen Exposure VASOCONSTRICTION Platelet Adhesion and release reaction Serotonin Platelet Phospolipid Coagulation Thromboxane A 2 ADP Platelet aggregation Thrombin Primary haemostatic plug Fibrin Stable haemostatic plug Fibrinolysis
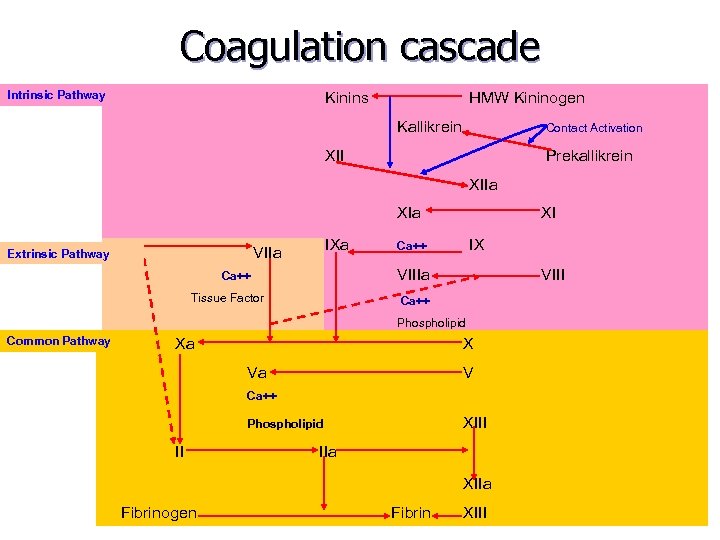
Coagulation cascade Intrinsic Pathway Kinins HMW Kininogen Kallikrein Contact Activation XII Prekallikrein XIIa XIa Extrinsic Pathway VII IXa VIIa XI IX Ca++ VIIIa Ca++ Tissue Factor VIII Ca++ Phospholipid Common Pathway Xa X Va V Ca++ XIII Phospholipid II IIa XIIa Fibrinogen Fibrin XIII
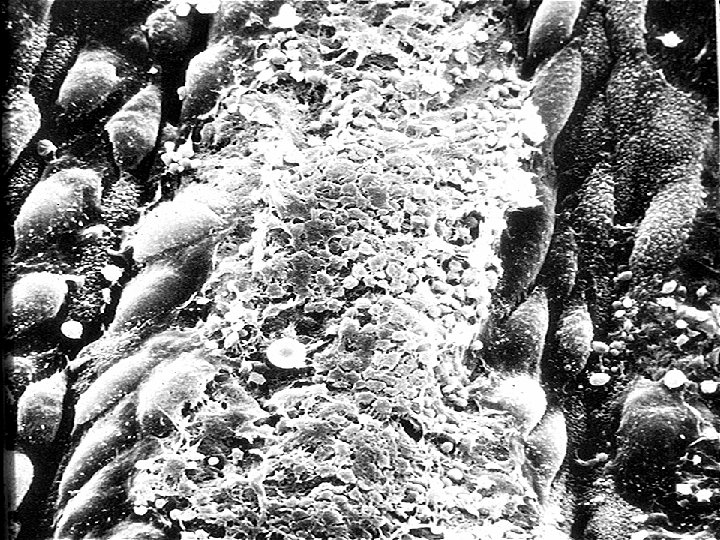

PRACTICAL APPROACH TO A CHILD WITH BLEEDING HISTORY • HISTORY – HISTORY >AGE OF ONSET > SEX >FREQUENCY >LOCATION / TYPE OF BLEEDING >DURATION OF BLEEDING > MEDICATIONS > ASSOCIATED SYMPTOMS > REVIEW OF SYSTEMS

Approach to a bleeding patient – What is the type of bleeding disorder? Primary hemostasis – Vascular causes Platelets-Number vs. Function Fibrin formation – clotting factors Premature clot dissolution- post clot formation

. Approach to a bleeding patient –Is a bleeding tendency present? Easy Bruising Mucosal bleeding Menorrhagia Surgical Hemorrhage – Procedure vs. Diathesis Postpartum Hemorrhage Joint and Muscle bleed –Severity of trauama

. Approach to a bleeding patient –Is the disorder Familial or Acquired? Family history – MOTHER & OTHER FEMALE MEMBERS IN THE IMMEDIATE FAMILY – Detailed Menstrual history

• Vascular causes – First and foremost rule out infectious causes – “Meningococcemia” Vasculitis – Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Hemangiomas- Kassalback-Merritt syndrome

• • • Petechiae and Purpura Infectious – Meningococcemia – Rocky mountain spotted fever – Group A strep – Atypical measles – Echovirus 9, 4, 7 – Epstein-Barr virus – Coxsackie virus A 9

• Non-infectious • – Normal platelets • HSP • Coagulation disorders • Trauma • – Low platelets • ITP • Leukemia

PRACTICAL APPROACH TO A CHILD WITH BLEEDING HISTORY • PHYSICAL EXAMINATION> PETICHEAE >ECHYMOSES >JOINT BLEED &DEEPSEATED HEMATOMAS > HEPATOSPLENOMEGALY >SIGNIFICANT LYMPHADENOPATHY > ACTIVE AND PLAYFUL VS. ILL LOOKING > DYSMORPHIC FEATURES > CAFÉ-AU-LAIT SPOTS >TELANGIECATIC VESSELS >HEMANGIOMAS

PRACTICAL APPROACH TO A CHILD WITH BLEEDING HISTORY • LABORATORY WORK UPP. M. D - > C. B. C. /PLATELET COUNT >PERIPHERAL SMEAR- MORPHOLOGY > P. T. [Prothrombin time] > a. P. T. T. [ Activated partial thromboplastin time] --------------------------------Hemophilia service -> T. T. [Thrombin time] > Bleeding time >Platelet aggregation studies > Factor assay

Pandora’s box: coagulation test v. The results are as good as the sample is. Standards: Time from sample to test: PT 24 hours , PTT 4 hours. Blood/citrate ratio: 9 : 1.
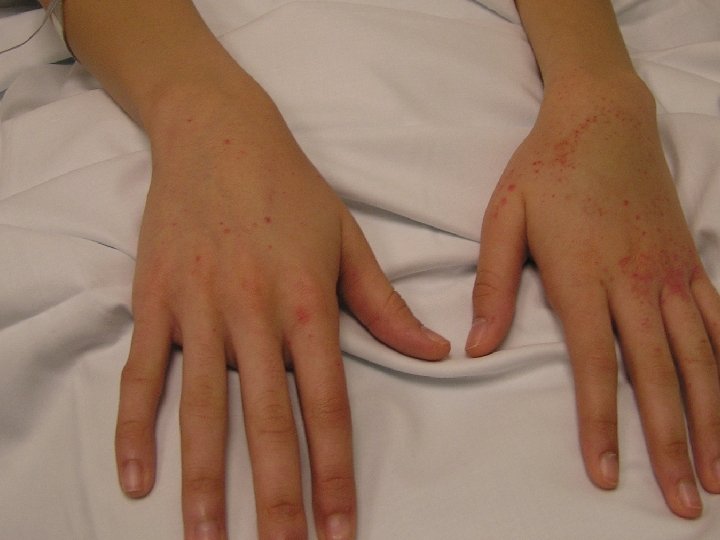
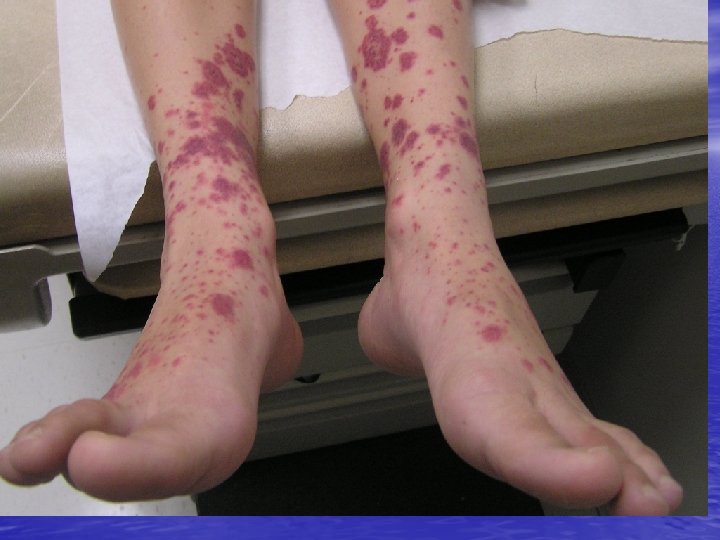

Bleeding disorders • Platelets– Acquired causes much more common Thrombocytopenia more common than functional defects Inherited disorders – both number &functional defects are extremely rare

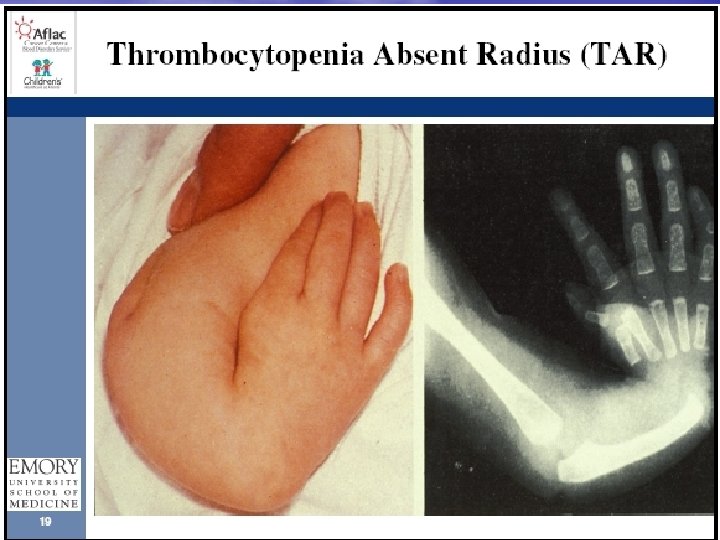
PLATELETS – NUMBER Acquired causes are most common I. T. P. Infections CONGENITAL THROMBOCYTOPENIAS T. A. R. syndrome

• I. T. P. - Most have benign &limited course Treatment options. Conservative –wait &watch Aggressive. Steroids Iv. IGG Rhogam Rituximab

PLATELETS • Functional disorders. Acquired- Aspirin; Uremia Inherited – Glanzman’s Bernard-Soulier Gray platelet syndrome

von Willebrand Disease • The most common inherited bleeding disorder • Occurs in 1% of the population • Less than 10% of patients have bleeding events due to v. WD
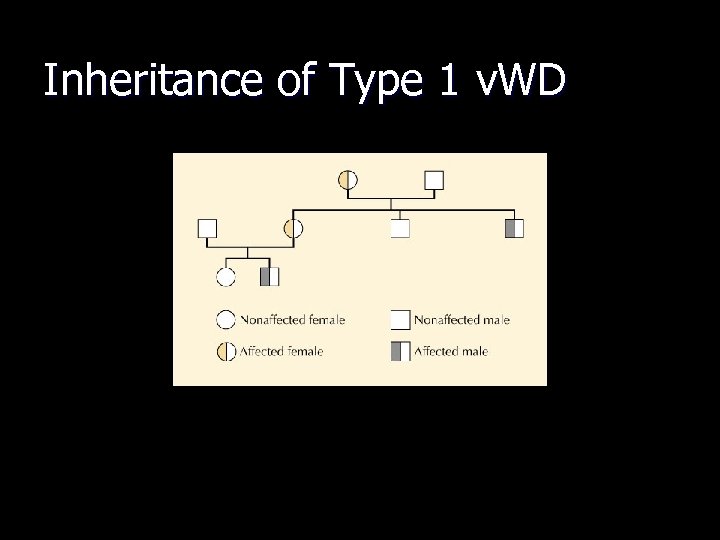
Inheritance of Type 1 v. WD
Functions of v. WF • Binds to platelet receptor GP Ib and to • • subendothelial structures such as collagen serving as bridge between platelets and subendothelium in damaged vessels Acts as bridge between adjacent platelets in vessels with high shear (arterioles) forming small platelet aggregates Binds to circulating factor VIII protecting it and prolonging FVIII t 1/2 in the circulation from 2 to 8 -12 hours

Symptoms of v. WD • Easy bruisability • Epistaxis or gingival bleeding • Menorrhagia • Post-partum hemorrhage • Post-surgical bleeding • Bleeding post-dental extraction

Sub types of VW Partial quantitative deficiency Classification of v. WD of v. WF Type 1 Type 2 Qualitative variants of v. WF • A • B • • M N Type 3 Absence of HMW v. WF multimers Same as 2 A and increased affinity for platelet gp Ib Abnormal function not caused by absence of HMW multimers Decreased affinity for factor VIII Complete deficiencey of v. WF & Behave as Severe Hemophilia A

Treatment Guidelines in VWD TYPE 1 2 A 2 B 2 M 2 N 3 TREATMENT DDAVP/FVIII-VWF FVIII-VWF

DDAVP (1 -desamino-8 -D-arginine vasopressin) • Parenteral form: DDAVP (for IV or SC use, 0. 3 ug/kg) • Highly concentrated intranasal spray form: Stimate nasal spray (150 -300 ug )

Hemophilia

Hemophilia • Caused by an absence or decreased amount of a procoagulant – • VIII -Hemophilia A affects ~ 1: 5000 males • XI -Hemophilia B affects ~ 1: 30000 males • XI –Hemophilia C – Rare /Ethnicity
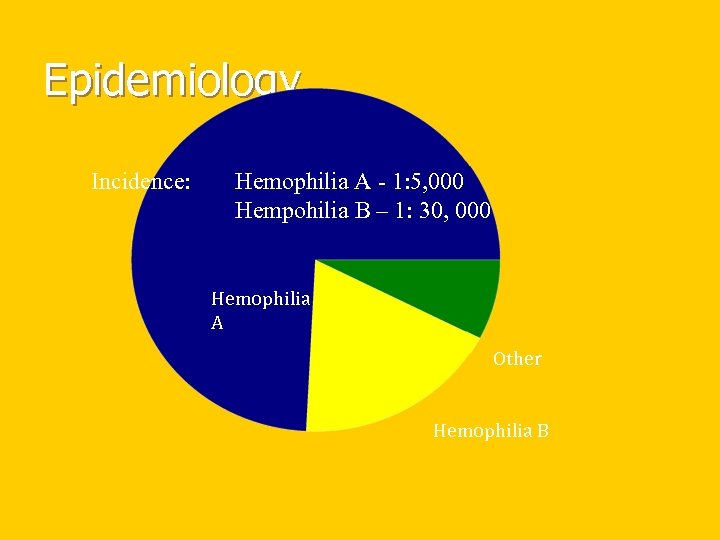
Epidemiology Incidence: Hemophilia A - 1: 5, 000 Hempohilia B – 1: 30, 000 Hemophilia A Other Hemophilia B

Inheritance
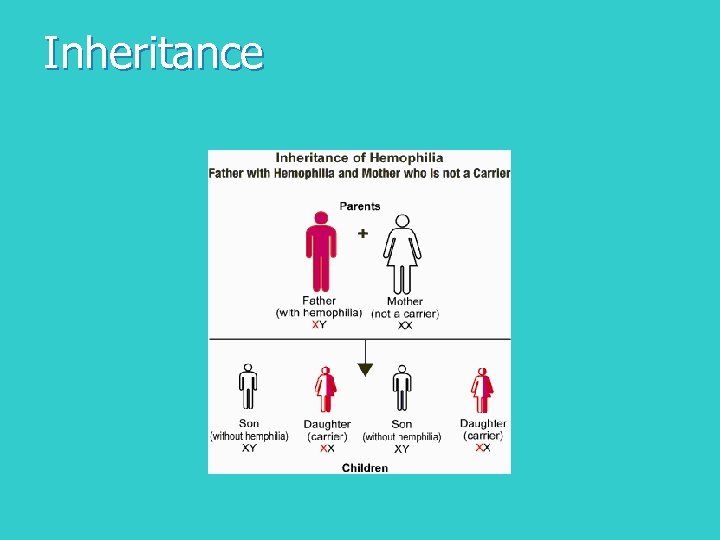
Inheritance

Woman can have hemophilia • Lyonization of the normal X chromosome • Turner syndrome ( XO) • Father with hemophilia/ mom as a carrier • v. W type 2 N ( Normandy)

HEMOPHILIA SEVERITY LEVELS • Severe <1% activity level - Spontaneous bleeds • Moderate 1 to 5% activity --Trauma/surgery bleeds Occasional joint bleeds • Mild 5 to 30% activity - Major trauma/surgery Rare joint bleeds

Factor replacement • 1 u/kg raises FVIII levels 2% 1/2 life : 12 hrs • 1 u/kg raises FIX levels 1 % 1/2 life 20 -24 hrs

Minor Bleeding Episodes • Early joint bleeds • Soft tissue & muscle bleeds • Nose & gum bleeding not responding to local measures • Treatment of minor bleeding episodes – 40 - 50% correction – FVIII : 25 units / kg – FIX : 50 units / kg

Major Bleeding Episodes • Advanced soft tissue & muscle bleeds • Head & neck injuries • Gastrointestinal bleeding • Advanced joint bleeding • Treatment of major bleeding episodes • 80 – 100 % correction • FVIII : 50 units / kg • FIX : 100 units / kg

Current Products • Plasma Products: plasma-derived factor VIII concentrate • Porcine Factor: – Use was halted due to parvovirus/retrovirus sequences discovered • Recombinant products: – First Generation: Recombinate, Kogenate, Helixate – Second Generation: Kogenate FS, Helixate FS – Third Generation: Advate • DDAVP: – Causes release of factor VIII/v. WF – Increased factor activity in 30 -60” – For mild hemophiliacs and mild bleeding symptoms

Replacement therapy: Joint disease • Prophylaxis – Primary – Secondary • Intensive infusion therapy • Dose escalation modified prophylaxis
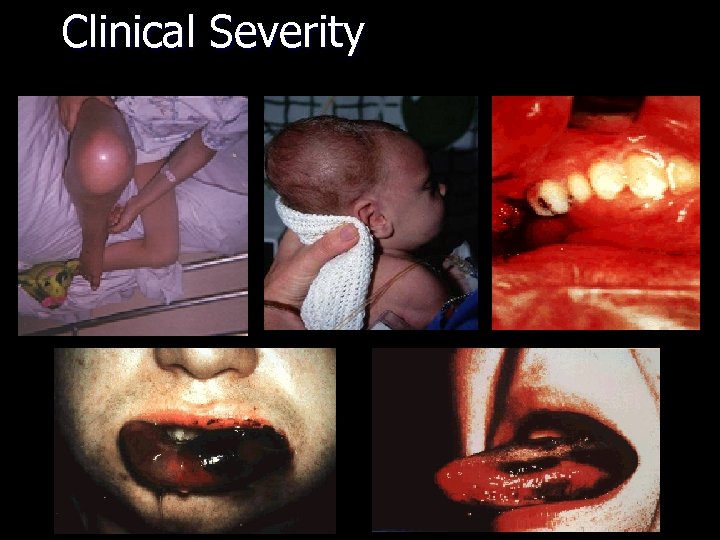
Clinical Severity
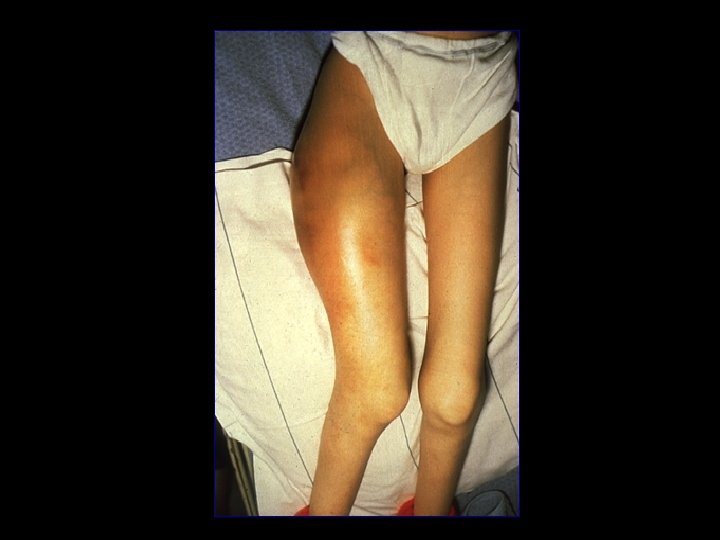
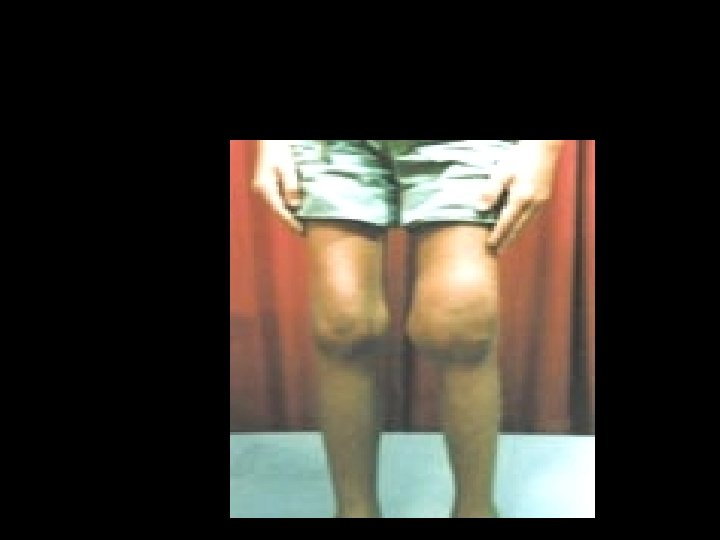
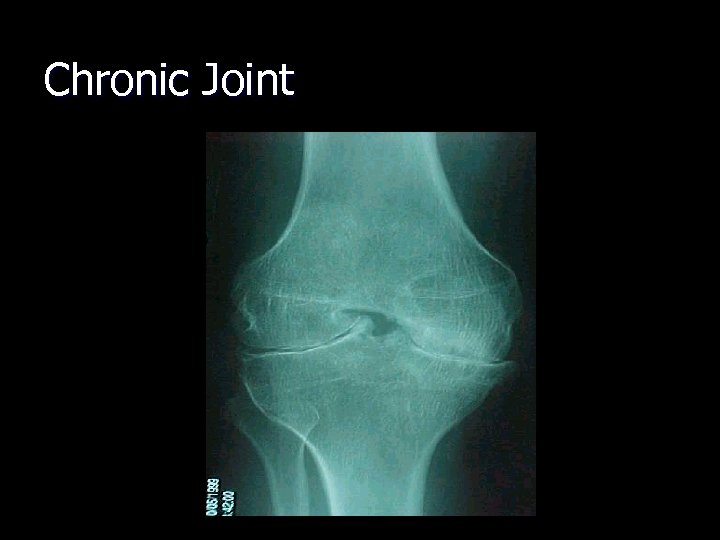
Chronic Joint

Hemophilia Treatment Center Team Members • Patient / Family • Hematologist • Nurse • Social Worker • Physical Therapist • Orthopedist • Primary Care • Infectious Disease • Genetics • Pharmacy • Dental • Hepatologist

Basis for Comprehensive Care • Hematologist • • • – Assumes overall care Musculoskeletal – Orthopedic Surgeon, Physical therapist Nursing – Coordination of home/clinic care for rapid treatment at the earliest symptoms suggestive of a bleed Dental Genetic Counseling Infectious Disease Psychosocial – social worker

Role of Hemophilia Treatment Centers • State-of-the-art medical treatment for persons with hemophilia through out the life span • Education • Research • Outreach • Model of comprehensive care for chronic disease
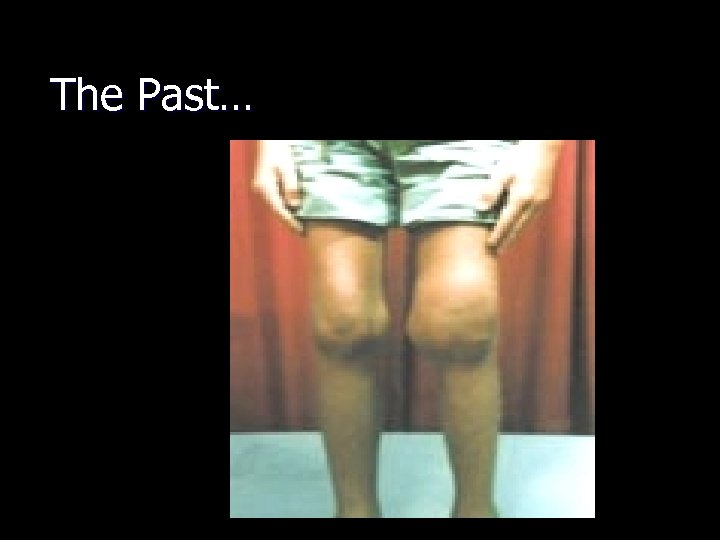
The Past…

Present …the promise of achieving your potential

Made possible by a STRONG & Dedicated Hemophilia parent association and dedicated NJHA staff

Thank you
b63122b39d05b89b106a7b6727120bd9.ppt