1dd6335087b1d8054fe77d07b59d1721.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

PPPs in Backbone and Access Networks in developing countries : Benefits and Legal Issues 21 January, 2010 The World Bank Group – ICT Department Rémy Fekete, Partner
Introduction § Significant impact of Broadband for Economic Development Economy-wide impacts based on sharing costs and benefits Better circulation of information – Ensuring access of the network Every 10 -percentage-point increase in penetration of broadband services triggers a 1. 3 -percentage-point increase in economic growth § A needed structure to offer a new dynamic Inadequate technology Digital divide § § Page 2 Large gaps in geographical coverage Reinforcement of economic inequalities fekete@gide. com
Introduction § A dead-end situation: Private initiative alone will not… National budgets alone cannot… …fully answer ICT development demand § PPPs have emerged as an effective tool for overcoming this tangled- up situation by combining private sector know-how with public interest aims. § Average yearly PPP investment increased by 118% between 2000 and 2006 in telecommunications. Page 3 fekete@gide. com

1 - What is a PPP ? 1. 1 Definitions § PPP: any form of partnership between the public authorities and the private sector that aim to ensure the funding, construction, renovation, management or maintenance of infrastructure or to provide a public service. § Build a PPP project on a sector diagnostic A realistic assessment of the sector constraints must be set up: 1 - The legal, regulatory and policy framework. 2 - The technical issues. 3 - The financial, economic and social issues. Page 4 fekete@gide. com
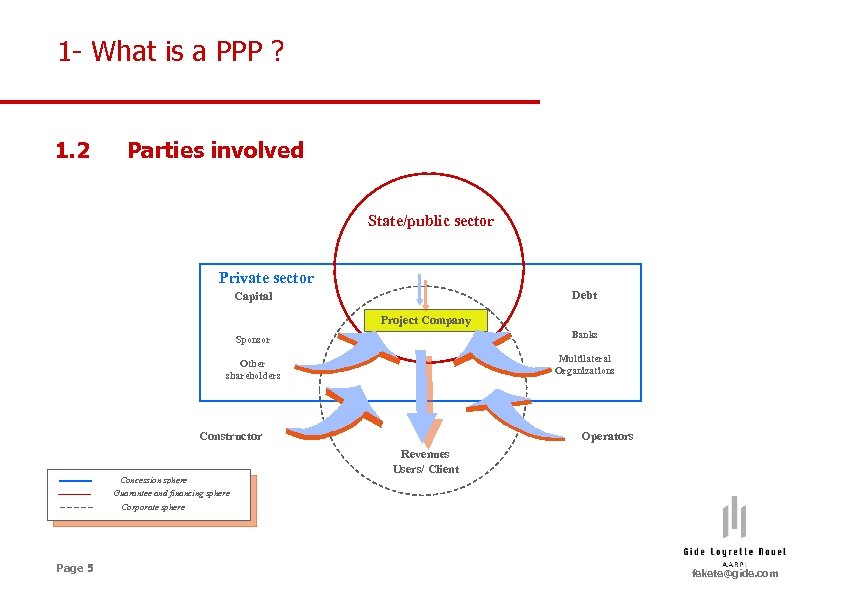
1 - What is a PPP ? 1. 2 Parties involved State/public sector Private sector Debt Capital Project Company Sponsor Banks Other shareholders Multilateral Organizations Constructor Concession sphere Guarantee and financing sphere Operators Revenues Users/ Client Corporate sphere Page 5 fekete@gide. com
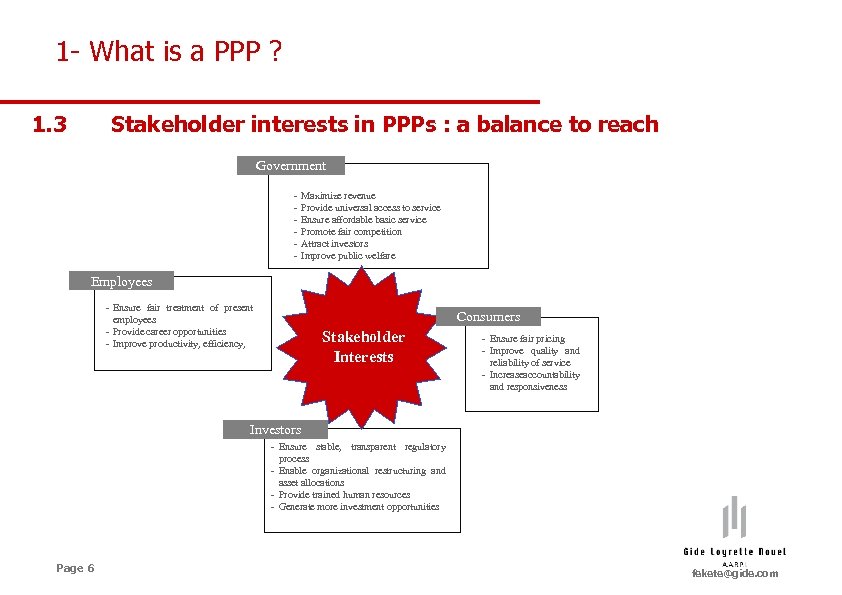
1 - What is a PPP ? 1. 3 Stakeholder interests in PPPs : a balance to reach Government - Maximize revenue Provide universal access to service Ensure affordable basic service Promote fair competition Attract investors Improve public welfare Employees - Ensure fair treatment of present employees - Provide career opportunities - Improve productivity, efficiency, Consumers Stakeholder Interests - Ensure fair pricing - Improve quality and reliability of service - Increaseaccountability and responsiveness Investors - Ensure stable, transparent regulatory process - Enable organizational restructuring and asset allocations - Provide trained human resources - Generate more investment opportunities Page 6 fekete@gide. com

1 - What is a PPP ? 1. 4 Three key characteristics of PPP projects A contractual agreement defining the roles and responsabilities of the parties and in particular the ownership of the infrastructure Sensible risk sharing among the public and private sector partners Financial rewards to the private party commensurate with the achievement of pre specified outputs. Page 7 fekete@gide. com
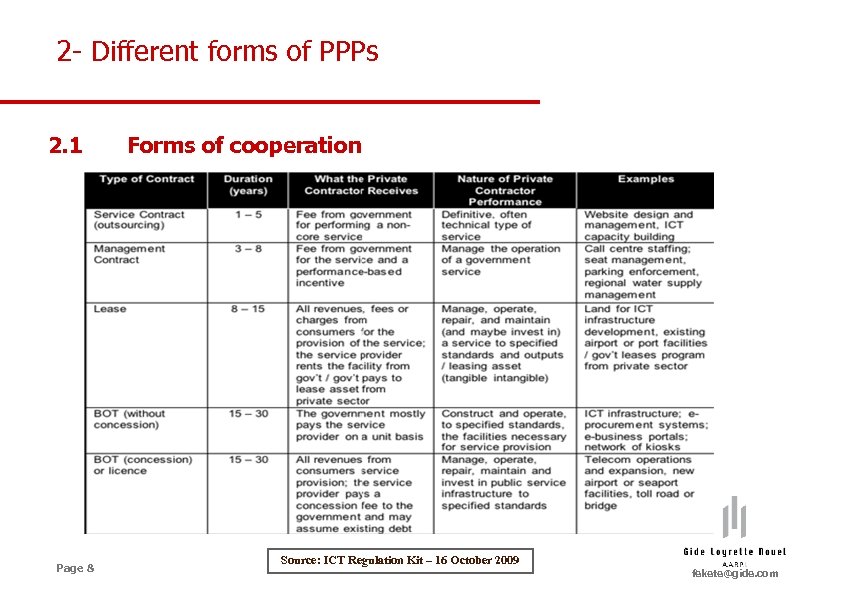
2 - Different forms of PPPs 2. 1 Page 8 Forms of cooperation Source: ICT Regulation Kit – 16 October 2009 fekete@gide. com
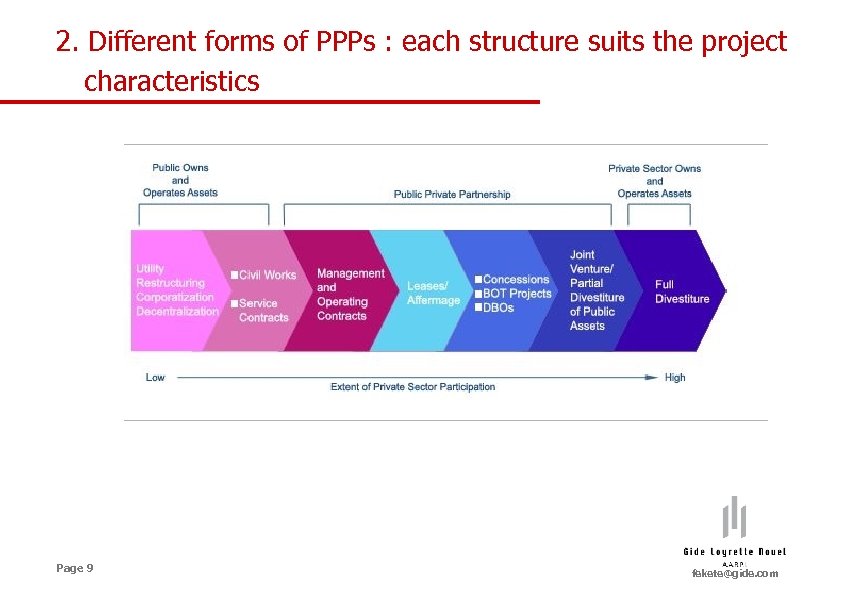
2. Different forms of PPPs : each structure suits the project characteristics Page 9 fekete@gide. com

2 - Different forms of PPPs Financial options of PPP projects 2. 2 § Loan Agreement / Grant / Subsidy Key questions: Which party supports the maximum amount of risk? Which financial guarantee can be implemented? Are By Laws in compliance with the scope of the PPP project? § Joint venture / Public party becomes a shareholder of an ad hoc entity Key questions: What is the scope of the exit clause? Is there any Golden share clause? How is the valuation of the public’s shares made? Page 10 fekete@gide. com
3 - An attractive structure for ICT in Developing Countries A few figures to illustrate: § Strong increase in mobile penetration Ø § Strong increase in web users Ø § Page 11 eg. : from 2% in 2003 to 33% in 2008 in Africa eg. : yearly growth rate of 30, 6% between 2003 and 2008 in Africa Installation of intercontinental undersea optic fiber cable systems fekete@gide. com
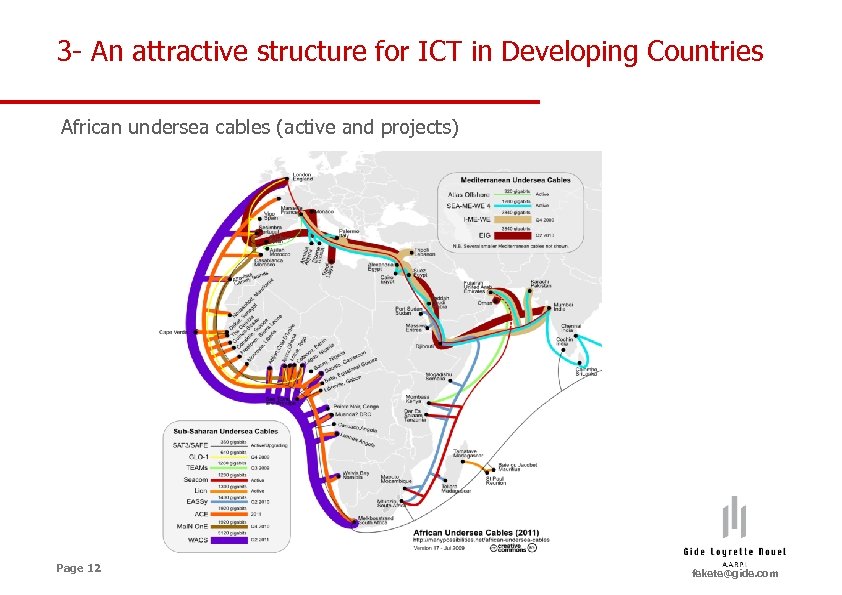
3 - An attractive structure for ICT in Developing Countries African undersea cables (active and projects) Page 12 fekete@gide. com
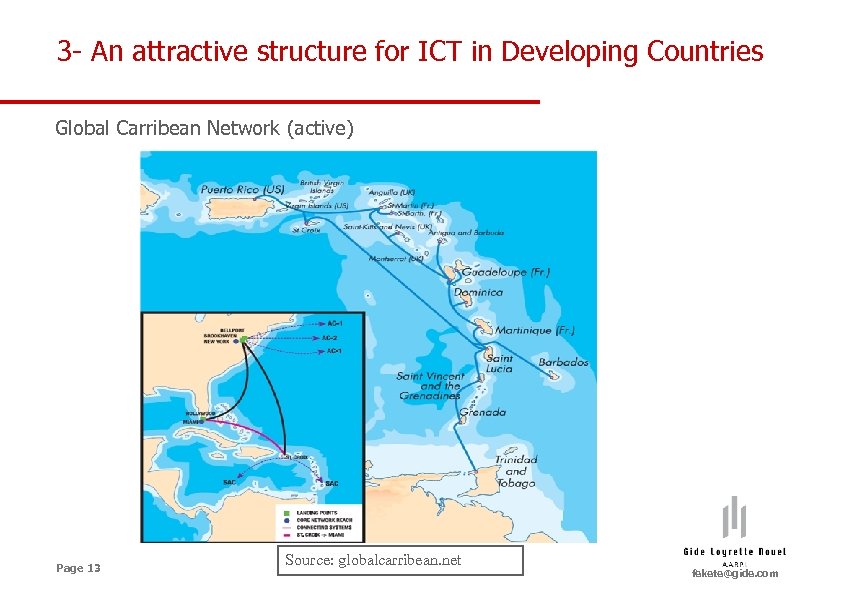
3 - An attractive structure for ICT in Developing Countries Global Carribean Network (active) Page 13 Source: globalcarribean. net fekete@gide. com
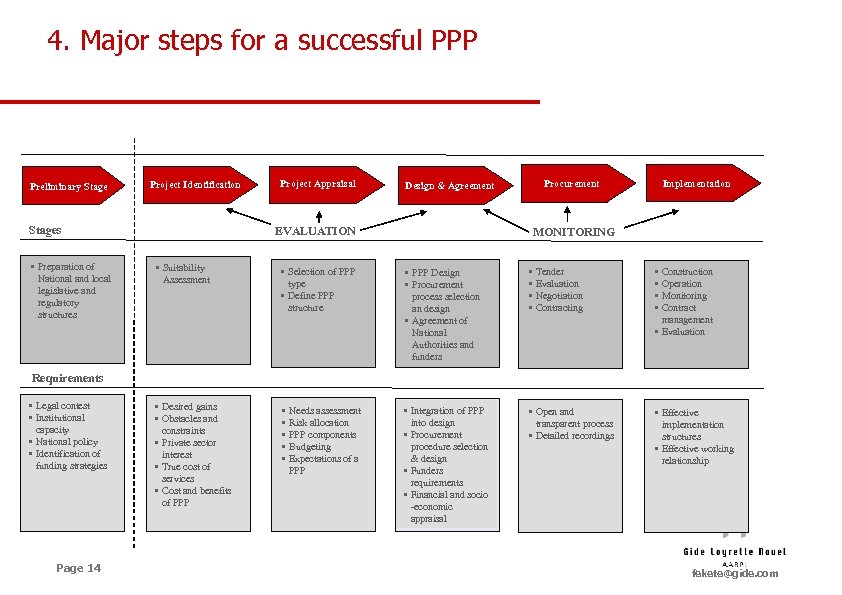
4. Major steps for a successful PPP Preliminary Stage Project Identification Stages • Preparation of National and local legislative and regulatory structures Project Appraisal Procurement Design & Agreement EVALUATION Implementation MONITORING • Suitability Assessment • Selection of PPP type • Define PPP structure • PPP Design • Procurement process selection an design • Agreement of National Authorities and funders • • • Desired gains • Obstacles and constraints • Private sector interest • True cost of services • Cost and benefits of PPP • • • Integration of PPP into design • Procurement procedure selection & design • Funders requirements • Financial and socio -economic appraisal • Open and transparent process • Detailed recordings Tender Evaluation Negotiation Contracting • • Construction Operation Monitoring Contract management • Evaluation Requirements • Legal contest • Institutional capacity • National policy • Identification of funding strategies Page 14 Needs assessment Risk allocation PPP components Budgeting Expectations of a PPP • Effective implementation structures • Effective working relationship fekete@gide. com
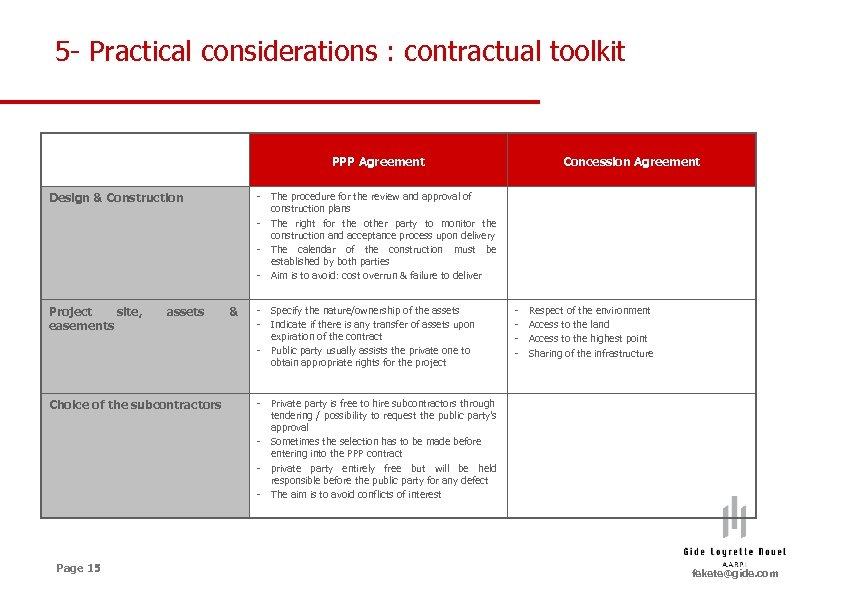
5 - Practical considerations : contractual toolkit PPP Agreement Design & Construction Project site, easements assets - The procedure for the review and approval of construction plans - The right for the other party to monitor the construction and acceptance process upon delivery - The calendar of the construction must be established by both parties - Aim is to avoid: cost overrun & failure to deliver & - Choice of the subcontractors Page 15 Concession Agreement Specify the nature/ownership of the assets Indicate if there is any transfer of assets upon expiration of the contract Public party usually assists the private one to obtain appropriate rights for the project - Respect of the environment Access to the land Access to the highest point Sharing of the infrastructure - Private party is free to hire subcontractors through tendering / possibility to request the public party’s approval - Sometimes the selection has to be made before entering into the PPP contract - private party entirely free but will be held responsible before the public party for any defect - The aim is to avoid conflicts of interest fekete@gide. com
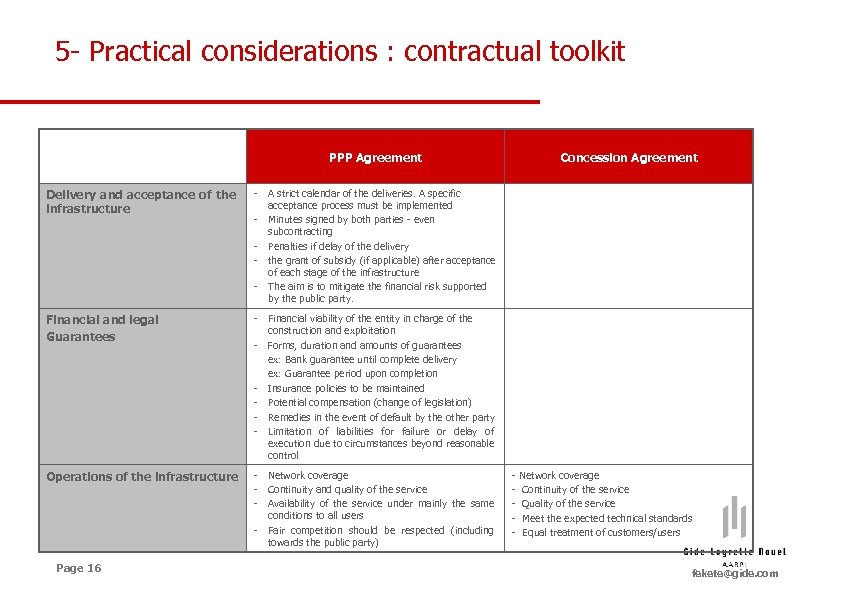
5 - Practical considerations : contractual toolkit PPP Agreement Delivery and acceptance of the infrastructure - Financial and legal Guarantees - - Operations of the infrastructure Page 16 Concession Agreement A strict calendar of the deliveries. A specific acceptance process must be implemented Minutes signed by both parties - even subcontracting Penalties if delay of the delivery the grant of subsidy (if applicable) after acceptance of each stage of the infrastructure The aim is to mitigate the financial risk supported by the public party. Financial viability of the entity in charge of the construction and exploitation Forms, duration and amounts of guarantees ex: Bank guarantee until complete delivery ex: Guarantee period upon completion Insurance policies to be maintained Potential compensation (change of legislation) Remedies in the event of default by the other party Limitation of liabilities for failure or delay of execution due to circumstances beyond reasonable control - Network coverage - Continuity and quality of the service - Availability of the service under mainly the same conditions to all users - Fair competition should be respected (including towards the public party) - Network coverage - Continuity of the service - Quality of the service - Meet the expected technical standards - Equal treatment of customers/users fekete@gide. com
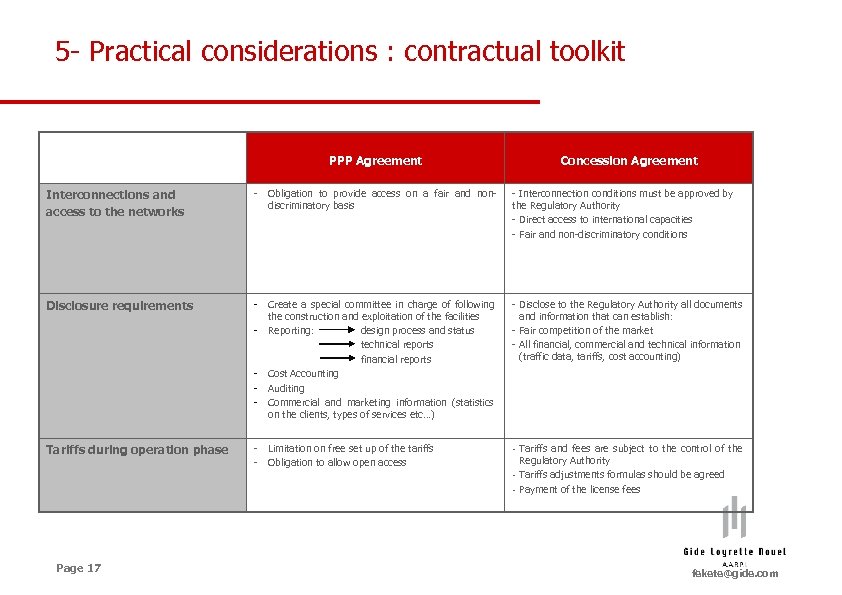
5 - Practical considerations : contractual toolkit PPP Agreement Concession Agreement Interconnections and access to the networks - Obligation to provide access on a fair and nondiscriminatory basis - Interconnection conditions must be approved by the Regulatory Authority - Direct access to international capacities - Fair and non-discriminatory conditions Disclosure requirements - Create a special committee in charge of following the construction and exploitation of the facilities - Reporting: design process and status technical reports financial reports - Cost Accounting - Auditing - Commercial and marketing information (statistics on the clients, types of services etc…) - Disclose to the Regulatory Authority all documents and information that can establish: - Fair competition of the market - All financial, commercial and technical information (traffic data, tariffs, cost accounting) Tariffs during operation phase - - Tariffs and fees are subject to the control of the Regulatory Authority - Tariffs adjustments formulas should be agreed - Payment of the license fees Page 17 Limitation on free set up of the tariffs Obligation to allow open access fekete@gide. com

Conclusion § New verbal designation for a pre-existing but evolving legal structure. Moving responsibilities from the public to the private sector, creating a new dynamic. § Wide coverage in telecommunications requires this PPP structure to enhance the networks. § Key role to play in ensuring a successful economic and social development of poor and fragile populations. Page 18 fekete@gide. com
Rémy Fekete, Partner fekete@gide. com Abu Dhabi Alger Belgrade Bruxelles Gide Loyrette Nouel Bucarest Association d'avocats à responsabilité professionnelle individuelle Budapest Casablanca Dubai 26, cours Albert 1 er 75008 Paris - France Tél. +33 (0)1 40 75 61 90 Fax +33 (0)1 43 59 69 83 Hanoi Hô Chi Minh Ville Hong Kong www. gide. com Istanbul Kiev Londres Moscou THANK YOU QUESTIONS New York Paris Pékin Prague Riyad St-Pétersbourg Shanghai Tunis Page 19 Varsovie fekete@gide. com
1dd6335087b1d8054fe77d07b59d1721.ppt