ced00058f5aeec9e745d49059b41be9d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Powers of Congress Houses and Members of Congress
The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government o Article I describes structure of Congress n Bicameral legislature o Divided into two houses n Each state sends two Senators regardless of population. n Number of Representatives each state sends to the House is determined by state population. Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006

The Constitution Congress o Constitution sets out requirements for membership in the House and Senate n House of Representatives o 25 years of age o Reside in U. S. at least 7 years o Serve 2 year terms n Senate o 30 years of age o Reside in U. S. at least 9 years o Serve 6 year terms n ALL members of Congress must be legal residents of their states. Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006

The Representatives and Senators o The Job n Salary of $168, 000 (2007) with retirement benefits. n Office space in D. C. and at home o Plus free staff to fill it! n Travel allowances and franking privileges. o Free mail sent if it is official business. n Immunity o Legal protection that keeps them from being sued for anything they say while in office! n Often requires 10 to 14 hour days and lots of time away from the family Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006
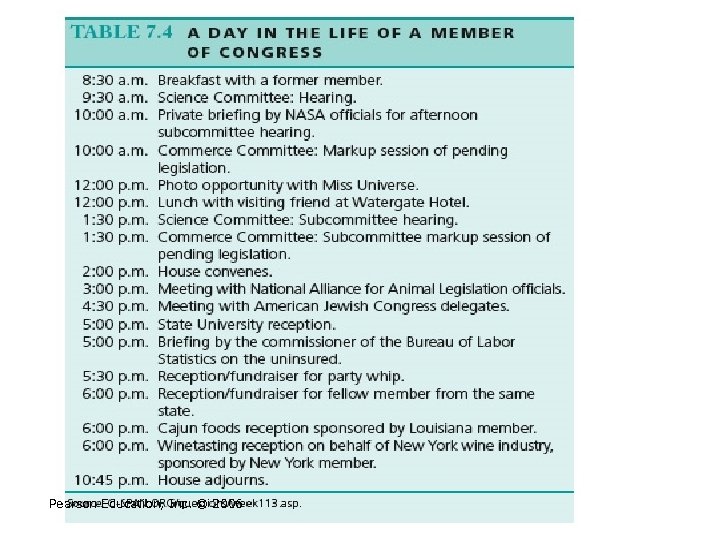
Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006
Congressional Demographics o Members tend to be n Better educated than the population in general o Over 2/3’s have advanced degrees. n Richer o Nearly 200 are millionaires n 21 Senators are worth at least 3. 1 million n Male n White n Average is 60 for Senators; 54 for House members. Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006
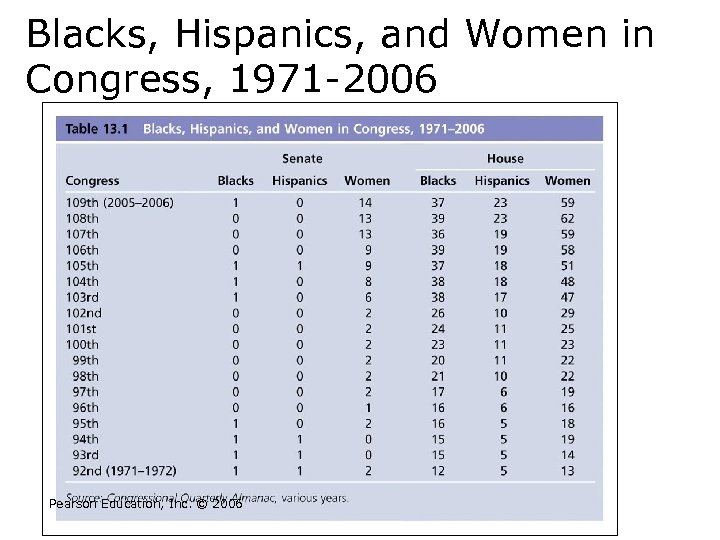
Blacks, Hispanics, and Women in Congress, 1971 -2006 Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006

Apportionment and Redistricting o Apportionment o Proportional process of allotting congressional seats to each state following the ten year census n Census = official count of our population o Redistricting (AKA gerrymandering) o Redrawing of congressional districts to reflect increases or decreases in seats allotted to the states n as well as population shifts within a state Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006
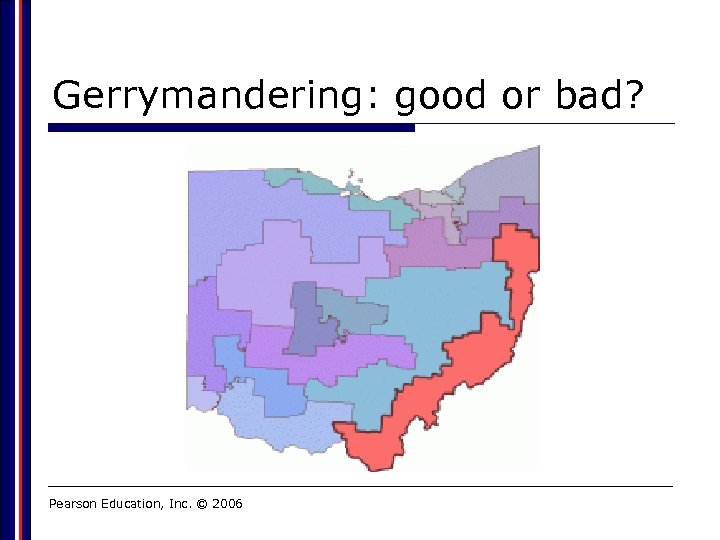
Gerrymandering: good or bad? Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006
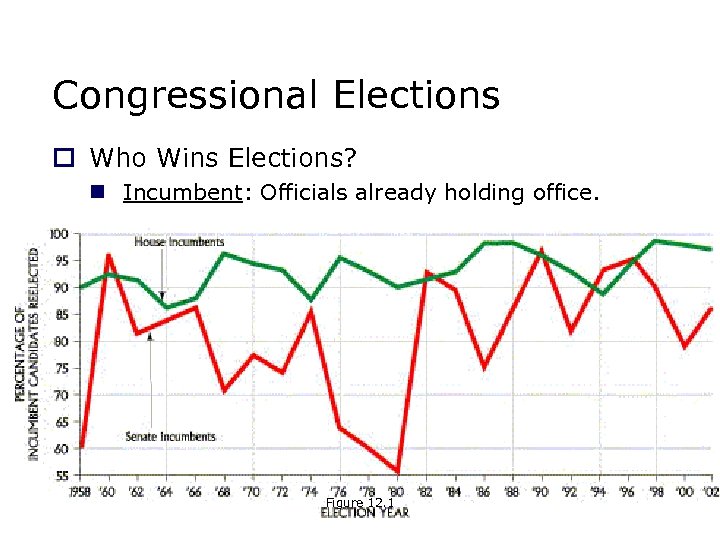
Congressional Elections o Who Wins Elections? n Incumbent: Officials already holding office. Figure 12. 1

Congressional Elections, cont. o The Advantages of Incumbents n Name recognition: o Once the public knows you, they vote for you! n Advertising: o The goal is to be visible to your voters. o Frequent trips home & newsletters are used. n Credit Claiming: o Service to individuals in their district. Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006

Congressional Elections, cont. o The Advantages of Incumbents n Weak Opponents: o Most opponents are inexperienced in politics. o Most opponents are unorganized and underfunded. n Campaign Spending: o PACs give most of their money to incumbents. Why? o Does PAC money “buy” votes in Congress? Pearson Education, Inc. © 2006
ced00058f5aeec9e745d49059b41be9d.ppt