9131b22f1189516a9a0b7d5d5d8a4dab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Powers of Congress Chapter 10 & 11
Powers of Congress Chapter 10 & 11
 Members of Congress
Members of Congress
 Why do we have a Bicameral Congress?
Why do we have a Bicameral Congress?
 US House of Representatives 435 Members Apportionment – representation is based on size of population. Today 1 rep for every 650, 000 citizens. Elected every two years.
US House of Representatives 435 Members Apportionment – representation is based on size of population. Today 1 rep for every 650, 000 citizens. Elected every two years.
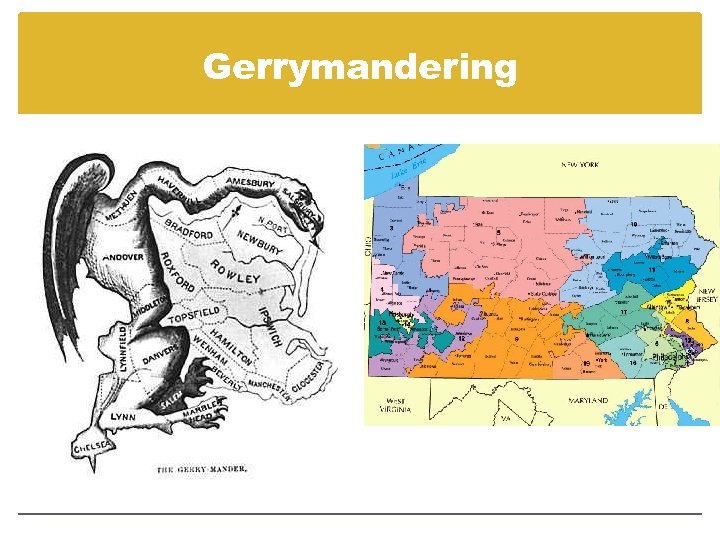 Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering
 House Qualifications Formal – Must be at least 25 years old Must have been a citizen of the US for at least 7 years. Must be a resident of the state you represent. Informal Name recognition Party affiliation Gender Ethnicity
House Qualifications Formal – Must be at least 25 years old Must have been a citizen of the US for at least 7 years. Must be a resident of the state you represent. Informal Name recognition Party affiliation Gender Ethnicity
 U. S. Senate
U. S. Senate
 Size, Election, Terms Two Senators from every state (100) Elected to Six year terms 17 th Amendment -1913 - provided for the direct election of Senators.
Size, Election, Terms Two Senators from every state (100) Elected to Six year terms 17 th Amendment -1913 - provided for the direct election of Senators.
 Qualifications 30 + years of age Citizen of US for 9+ years Resident of the state they represent.
Qualifications 30 + years of age Citizen of US for 9+ years Resident of the state they represent.
 Members of Congress Ch 10 Sec 4
Members of Congress Ch 10 Sec 4
 Personal/Political Backgrounds 535 Members Not a true representative cross section of the population. Typically white males aged 50 Breakdown of Minorities in House and Senate 43 African Americans, 26 Hispanics, 6 Asian Americans, 1 Native American – House 1 African American, 3 Hispanics, 1 Asian American, 1 Native Hawaiian - Senate
Personal/Political Backgrounds 535 Members Not a true representative cross section of the population. Typically white males aged 50 Breakdown of Minorities in House and Senate 43 African Americans, 26 Hispanics, 6 Asian Americans, 1 Native American – House 1 African American, 3 Hispanics, 1 Asian American, 1 Native Hawaiian - Senate
 Personal/Political Backgrounds Typically College Educated 70 Women in the House, 15 in Senate Typically from the state they represent
Personal/Political Backgrounds Typically College Educated 70 Women in the House, 15 in Senate Typically from the state they represent
 111 th Congress
111 th Congress
 Chapter 11 Powers of Congress
Chapter 11 Powers of Congress
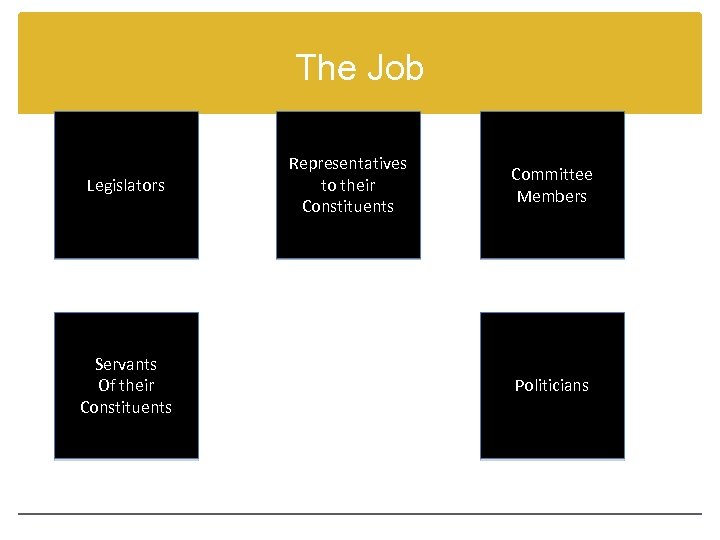 The Job Legislators Servants Of their Constituents Representatives to their Constituents Committee Members Politicians
The Job Legislators Servants Of their Constituents Representatives to their Constituents Committee Members Politicians
 Representatives of the people Represent the people through votes. How do they vote? Trustee – believe that each question they face deserves to be judged on its own merit. Delegate – vote solely on what their constituents would want. Partisan – vote uniformly along party lines. Politico – attempt to combine the first three
Representatives of the people Represent the people through votes. How do they vote? Trustee – believe that each question they face deserves to be judged on its own merit. Delegate – vote solely on what their constituents would want. Partisan – vote uniformly along party lines. Politico – attempt to combine the first three
 Committee Members All reps & Senators serve on a committee. Committees screen all issues/bills and decide what goes to the floor for a vote. Oversight Function – process by which Congress, through committees, checks to see that the various agencies in the executive branch are working effectively.
Committee Members All reps & Senators serve on a committee. Committees screen all issues/bills and decide what goes to the floor for a vote. Oversight Function – process by which Congress, through committees, checks to see that the various agencies in the executive branch are working effectively.
 Servants Each representative & Senator works to serve their constituents. How? Passports Small business loans Application to a military academy Etc…. .
Servants Each representative & Senator works to serve their constituents. How? Passports Small business loans Application to a military academy Etc…. .
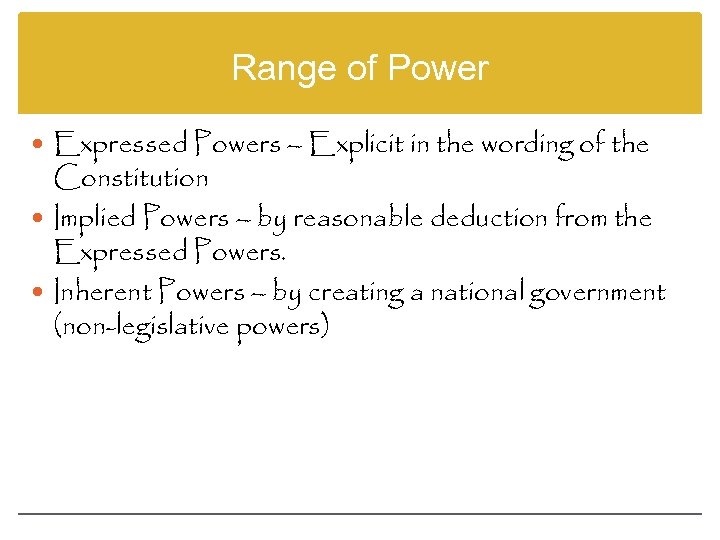 Range of Power Expressed Powers – Explicit in the wording of the Constitution Implied Powers – by reasonable deduction from the Expressed Powers. Inherent Powers – by creating a national government (non-legislative powers)
Range of Power Expressed Powers – Explicit in the wording of the Constitution Implied Powers – by reasonable deduction from the Expressed Powers. Inherent Powers – by creating a national government (non-legislative powers)
 Expressed Powers - Taxing Article 1, Section 8, Clause 1 – gives Congress the power to tax. Purpose – Common defence and welfare…protect American businesses.
Expressed Powers - Taxing Article 1, Section 8, Clause 1 – gives Congress the power to tax. Purpose – Common defence and welfare…protect American businesses.
 Expressed Powers - Taxing Limits on Taxing • • Congress can only tax for public purposes. No Tax levied on exports. Direct taxes must be apportioned by population. All indirect taxes must be uniform across the country. Article I, Sec 8, Clause 2 – gives Congress the power to borrow money on the credit of the country. No limits
Expressed Powers - Taxing Limits on Taxing • • Congress can only tax for public purposes. No Tax levied on exports. Direct taxes must be apportioned by population. All indirect taxes must be uniform across the country. Article I, Sec 8, Clause 2 – gives Congress the power to borrow money on the credit of the country. No limits
 Expressed Powers - Commerce Article 1, Sec 8, Clause 3 – gives Congress the power to regulate commerce with foreign nations and between States. Gibbons v. Ogden 1824 – USSC provided a broad view of what was deemed commerce…
Expressed Powers - Commerce Article 1, Sec 8, Clause 3 – gives Congress the power to regulate commerce with foreign nations and between States. Gibbons v. Ogden 1824 – USSC provided a broad view of what was deemed commerce…
 Expressed Powers - Currency Article 1, Sec 8, Clause 5 – “power to coin money and regulate the value thereof” First Federal use of paper money not until the Civil War.
Expressed Powers - Currency Article 1, Sec 8, Clause 5 – “power to coin money and regulate the value thereof” First Federal use of paper money not until the Civil War.
 Expressed Powers – War powers Article 1, Sec 8, Clauses 11 -16 Only Congress can declare war Raise an Army & Navy Call forth a militia War Powers Act 1973 -
Expressed Powers – War powers Article 1, Sec 8, Clauses 11 -16 Only Congress can declare war Raise an Army & Navy Call forth a militia War Powers Act 1973 -
 Expressed Powers - other Naturalization Postal Powers Copyrights & Patents Weights and Measures Power over Territories Eminent Domain Judicial Powers
Expressed Powers - other Naturalization Postal Powers Copyrights & Patents Weights and Measures Power over Territories Eminent Domain Judicial Powers
 Implied Powers Article 1, Sec 8, Clause 18 – Necessary and Proper Clause Mc. Culloch v Maryland 1819 – USSC rules in favor of a liberal view of implied powers.
Implied Powers Article 1, Sec 8, Clause 18 – Necessary and Proper Clause Mc. Culloch v Maryland 1819 – USSC rules in favor of a liberal view of implied powers.
 Nonlegislative Powers Article V US Constitution – gives Congress power to propose amendments by a 2/3 vote in both houses. Electoral Duties – 12 th Amendment gives Congress power to chose a President if no one wins a clear majority. Senate chooses the VP. 25 th Amendment – Congress has to approve a VP successor if present VP leaves office early.
Nonlegislative Powers Article V US Constitution – gives Congress power to propose amendments by a 2/3 vote in both houses. Electoral Duties – 12 th Amendment gives Congress power to chose a President if no one wins a clear majority. Senate chooses the VP. 25 th Amendment – Congress has to approve a VP successor if present VP leaves office early.
 Nonlegislative Powers Impeachment – process by which a President can be removed from office. House – brings charges (Impeach) Senate – holds a trial to decide on removal. Andrew Johnson, Bill Clinton
Nonlegislative Powers Impeachment – process by which a President can be removed from office. House – brings charges (Impeach) Senate – holds a trial to decide on removal. Andrew Johnson, Bill Clinton
 Nonlegislative Powers Executive Powers Appointments – Senate gets to approve all major Presidential appointments. Treaties – Senate must ratify all treaties made by the President.
Nonlegislative Powers Executive Powers Appointments – Senate gets to approve all major Presidential appointments. Treaties – Senate must ratify all treaties made by the President.
 Sleeping or otherwise placing your head on your desk EQUALS 60 Minutes!!!!
Sleeping or otherwise placing your head on your desk EQUALS 60 Minutes!!!!


