Module_3b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Power. Point to accompany Module 3 b Chapter 11 Strategic Reward Management

Lecture objectives § Define reward management and describe how it has shifted from a transactional system to a human relations approach; § Identify the underlying principles of a reward strategy; § Explain how a reward strategy helps meet organisational and employee needs; § Apply the essential building blocks of total reward management to establish a reward strategy; § Explain performance pay and how it is associated with performance management and training and development; § Explain employee benefits and non-financial rewards. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Strategic reward management § Strategic reward management: The strategic formulation and implementation of equitable rewards that align with the strategic direction and values of an organization § Employee motivation § Organizational objectives Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Strategic reward management § Scientific management approach (Taylor, 1911) + Human relations (e. g. , Mayo, 1991) Ø QUANTITY & QUALITY for performance maximization § Reward strategy: Development, implementation and use of reward systems which enable individuals to compete work tasks that are aligned with organizational goals, structures and strategies. § T& D and Performance Management: continuous performance improvement v. Reward Management: continuous reinforcement of right performance. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

The reward system § Reward: An item (either tangible or intangible) received in recognition for behaviour or output § Intrinsic rewards: Are sourced from inside, or are internal to, the individual § § Extrinsic rewards: Are sourced outside, or are external to, the individual § § e. g. , work satisfaction e. g. , profit sharing, stock options Rewards need to be tailored to suit individuals Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Underlying principles of a reward strategy § Rewarding is a particularly important aspect of SHRM implementation § § The underlying principle of a reward strategy is motivation § § Assists in retaining valuable employees Content and process theories can be used to assist in motivating employees Remember: Everyone is motivated differently How are you motivated? ! Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Individual and organisational needs § Individual Needs § Organizational Needs § Perceived equity § Appropriate change § Regular rewards and performance reviews § Reinform the key values, culture and behaviours through clear performance criteria § High performers are rewarded § Ensure competitive rewards § Control costs while optimising value Reduce turnover Legal obligations Financial and nonfinancial needs § Organizational objectives § Content and process needs § § § Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
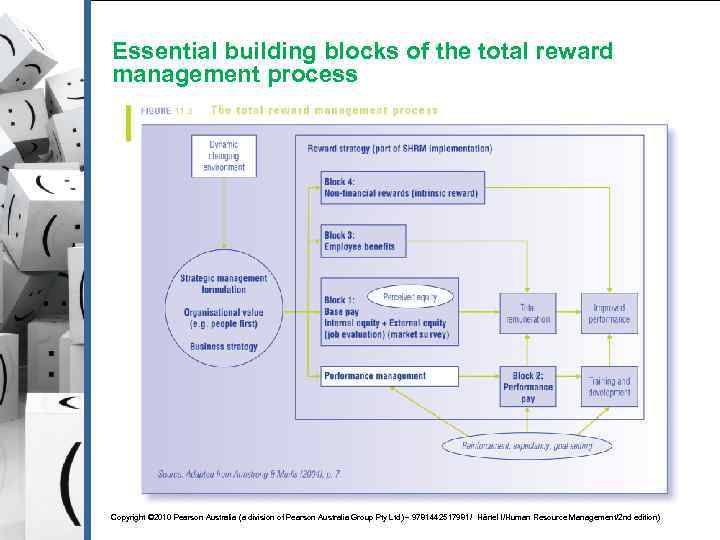
Essential building blocks of the total reward management process Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Block 1: Base pay § Base pay: The cash amount guaranteed for just turning up for work (i. e. salary or wage) § § Salary versus Wage Must consider the state/federal laws § IR in Australia has changed dramatically and HR managers need to be aware of these changes § Base pay can be established by considering internal and external equity § Three pay strategies to choose from: § Lead-lead policy § Lead-lag policy § Lag-lead policy Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Block 2: Performance pay § Performance pay: The pay individuals receive based upon their performance § § Discretionary bonus, incentives, profit sharing Block 2. 1: Performance management § § § Pay is determined by performance (i. e. , via an annual performance review) Link between pay and performance Block 2. 2: Training and development § Training and development is an important precursor and consequence of improved performance (see Figure 11. 3) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Block 3: Employee benefits § Employee benefits: All financial rewards that are not paid directly in cash to the employee § e. g. crèche facilities, company cars, flexi time Total remuneration = Block 1 + Block 2 + Block 3 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Block 4: Non-financial reward § Most people are motivated by financial rewards… but not always § Non-financial rewards play an important role in the reward management process: § § They are generally the most powerful performance motivators in an organisation’s reward management process Non-financial rewards pay more attention to ‘soft HRM’ issues Improved performance = Block 1 + Block 2 + Block 3 + Block 4 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Contemporary reward strategy features § Pay has undergone a tremendous transformation (from rigid to flexible) § These features help determine pay strategies designed to improve individual and organisational performance: § Employability pay; § Person-based pay; § Market-determined pay; § Team-based rewards; § Low degree of hierarchy Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Objectives achieved by reward management § Support the achievement of the organisation’s strategic objectives § Help communicate the organisation’s desired behaviours, values, performance, expectations § Promote employee development § Promote flexibility to cope with the dynamic changing environment § Provide a cost-effective pay structure § Achieve fairness and equity by rewarding people based on internal and external equity Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
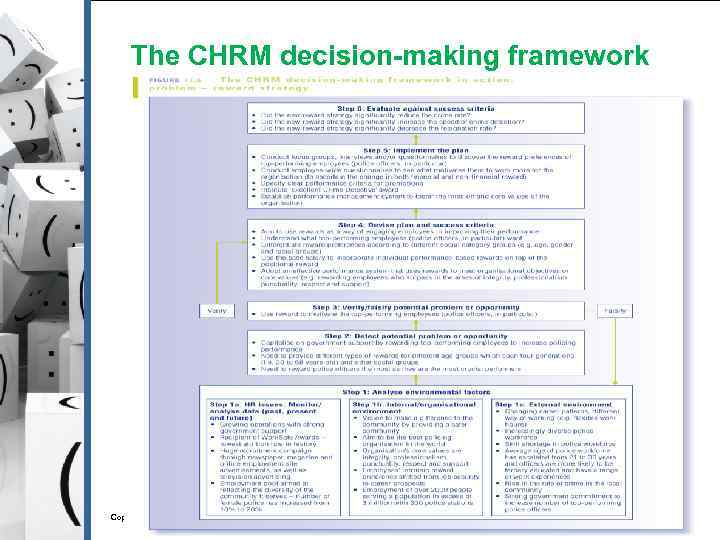
The CHRM decision-making framework Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Step 1 Analyse environmental factors § Monitor/analyse data (past, present and future): § § Internal/organisational environment: § § Growing operations with strong government support Vision to make a difference to the community by providing a safer community External environment: § Changing career patterns, different way of working (e. g. , flexible work hours) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Step 2 Detect potential problem or opportunity § Capitalise on government support by rewarding top-performing employees to increase policing performance § Need to provide different types of rewards for different age groups which span across four generations (i. e, . 20 to 68 years old) and other social groups § Need to reward police officers the most as they are the most crucial performers Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Step 3 Verify/falsify potential problem or opportunity § Use reward to motivate the top-performing employees (police officers in particular) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Step 4 Devise plan and success criteria § Aim to use rewards as a way of engaging employees in improving their performance § Understand what top-performing employees (police officers in particular) want § Differentiate reward preferences according to different social category groups (e. g. , age, gender and racial groups) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Step 4 Devise plan and success criteria (cont. ) § Use the base salary to incorporate individual performance-based rewards on top of the positional reward § Adopt an effective performance system that uses rewards to meet organisational objectives or core values (e. g. , rewarding employees who surpass in the areas of integrity, professionalism, punctuality, respect and support) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Step 5 Implement the plan § Conduct focus groups, interviews and/or questionnaires to discover the reward preferences of top-performing employees (police officers in particular) § Conduct employee-wide questionnaires to see what motivates them to work more for the organisation (to ascertain the change in both financial and non-financial rewards) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Step 5 Implement the plan (cont. ) § Specify clear performance criteria for promotions § Institute “Excellent Crime Detective” award § Establish performance management system to foster the mission and core values of the organisation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Step 6 Evaluate against success criteria § Did the new reward strategy significantly reduce the crime rate? § Did the new reward strategy significantly increase the speed of crime detection? § Did the new reward strategy significantly decrease the resignation rate? Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)

Conclusion § Reward management helps keep employees motivated § Employees are motivated differently § Intrinsic v. extrinsic rewards § Past experience, family and cultural values § HR managers should learn how to keep employees motivated so they continually achieve individual and organisational goals § If this is sustained, a competitive advantage may be achieved Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Module_3b.ppt