Module_2a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Power. Point to accompany Module 2 a Chapter 8 HR planning, Job design, Recruitment and Selection
Power. Point to accompany Module 2 a Chapter 8 HR planning, Job design, Recruitment and Selection
 Lecture objectives § Discuss HR planning and describe its practical application in contemporary contexts § Describe and define job analysis and job design § Discuss the key features of strategic recruitment and selection § Explain strategic selection and its methodologies in the light of validity, reliability and legality issues § Explain strategic recruitment and selection and its practical application in contemporary contexts Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Lecture objectives § Discuss HR planning and describe its practical application in contemporary contexts § Describe and define job analysis and job design § Discuss the key features of strategic recruitment and selection § Explain strategic selection and its methodologies in the light of validity, reliability and legality issues § Explain strategic recruitment and selection and its practical application in contemporary contexts Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Human resource planning § Human resource planning (HRP): A dynamic planning process which involves: § § § Ongoing environmental scanning An analysis of organisational objectives, strategies and policies in order to ascertain the right quantity and quality of employees when and where necessary “Finding the right person for the right job at the right time” Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Human resource planning § Human resource planning (HRP): A dynamic planning process which involves: § § § Ongoing environmental scanning An analysis of organisational objectives, strategies and policies in order to ascertain the right quantity and quality of employees when and where necessary “Finding the right person for the right job at the right time” Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
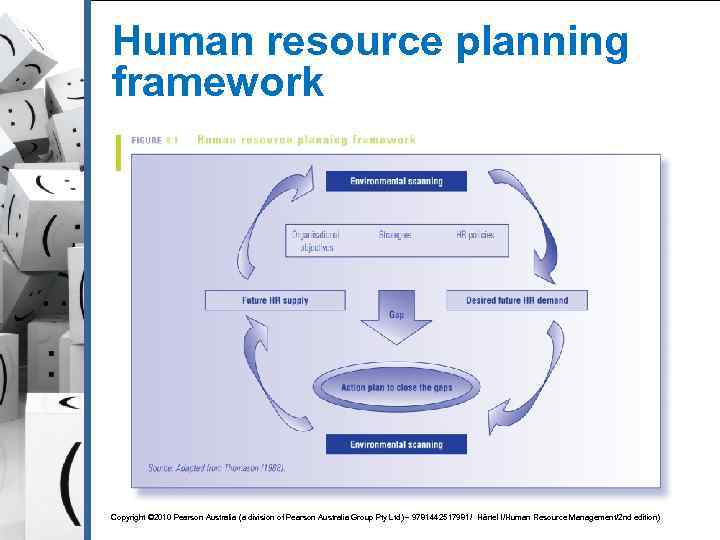 Human resource planning framework Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Human resource planning framework Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Environmental influence on HRP § The environment can influence HRP and environmental scanning must take place: § § § Internal scanning: Analysing the internal environment of an organisation (e. g. , company climate, culture and staff) External scanning: The systematic identification and analysis of key trends in the external environment and the monitoring of their impact on HR strategies Environmental scanning is the starting point of HRP Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Environmental influence on HRP § The environment can influence HRP and environmental scanning must take place: § § § Internal scanning: Analysing the internal environment of an organisation (e. g. , company climate, culture and staff) External scanning: The systematic identification and analysis of key trends in the external environment and the monitoring of their impact on HR strategies Environmental scanning is the starting point of HRP Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Approaches to HRP § HRP is usually conducted on a yearly basis (i. e. at the end of 2005 for 2006) § HRP is usually performed by HR managers (in consultation with line and senior managers) § As a strategic process, HRP has three major steps: § Demand forecasting § Supply forecasting § Filling the gap between demand supply to ensure skill optimisation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Approaches to HRP § HRP is usually conducted on a yearly basis (i. e. at the end of 2005 for 2006) § HRP is usually performed by HR managers (in consultation with line and senior managers) § As a strategic process, HRP has three major steps: § Demand forecasting § Supply forecasting § Filling the gap between demand supply to ensure skill optimisation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Demand supply forecasting § § Demand Forecasting: Estimating the quality/quantity of employees required to meet organisational objectives § e. g. , trend projection, multiple regression, Delphi technique, nominal group technique (NGT) Supply Forecasting: Determining how many employees the company will require to meet the demand § Internal labour supply § § Skill inventory form and replacement chart External labour supply e. g. unemployed, retired, full-time students and those over the legal age to work Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Demand supply forecasting § § Demand Forecasting: Estimating the quality/quantity of employees required to meet organisational objectives § e. g. , trend projection, multiple regression, Delphi technique, nominal group technique (NGT) Supply Forecasting: Determining how many employees the company will require to meet the demand § Internal labour supply § § Skill inventory form and replacement chart External labour supply e. g. unemployed, retired, full-time students and those over the legal age to work Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Job analysis § § § Job analysis: A systematic analysis of the tasks, duties and responsibilities of a job as well as the necessary cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities a person needs to perform the job adequately. A job analysis forms job-related criteria for recruitment and selection. Thus, it is an important part of enabling a fair and transparent process. Job description Person specification* (more suitable for dynamic nature of jobs, i. e. , need for ‘adaptive performance’) Job context* Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Job analysis § § § Job analysis: A systematic analysis of the tasks, duties and responsibilities of a job as well as the necessary cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities a person needs to perform the job adequately. A job analysis forms job-related criteria for recruitment and selection. Thus, it is an important part of enabling a fair and transparent process. Job description Person specification* (more suitable for dynamic nature of jobs, i. e. , need for ‘adaptive performance’) Job context* Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Job analysis methods § Interviews § Structured questionnaires § 360 degree feedback § Diary § Direct observation v Each method is subject to criticism § Be aware of these criticisms before employing a method! § Job analysts can combine methods to obtain more accurate information about optimizing the person-job fit. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Job analysis methods § Interviews § Structured questionnaires § 360 degree feedback § Diary § Direct observation v Each method is subject to criticism § Be aware of these criticisms before employing a method! § Job analysts can combine methods to obtain more accurate information about optimizing the person-job fit. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Advantages and disadvantages of job analysis methods Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Advantages and disadvantages of job analysis methods Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Job analysis methods (cont’d) § Whatever technique is used, the resulting set of information needs to: § Be manageable; § Be defined behaviourally (to be specific and observable); § Identify accurately independent competencies; and § Be comprehensive, accessible and compatible with an organisation’s vision, goals and culture Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Job analysis methods (cont’d) § Whatever technique is used, the resulting set of information needs to: § Be manageable; § Be defined behaviourally (to be specific and observable); § Identify accurately independent competencies; and § Be comprehensive, accessible and compatible with an organisation’s vision, goals and culture Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Job design § Job design: The way that an entire job is organised and categorised § Job design is grouped into 4 categories: § § Job enlargement § Job rotation § § Job specialisation Job enrichment Job evaluation is the final stage of job analysis Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Job design § Job design: The way that an entire job is organised and categorised § Job design is grouped into 4 categories: § § Job enlargement § Job rotation § § Job specialisation Job enrichment Job evaluation is the final stage of job analysis Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Strategic recruitment § Recruitment: The process of generating a pool of qualified candidates for a particular job who can best contribute to the strategic objectives of the organisation. § Recruitment is a crucial function of SHRM § § § It determines the quantity and quality of future employees It determines the type of organisation created and the organisational capability to achieve success Recruitment activities should be aligned with business strategy and culture to ensure a ‘good fit’ Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Strategic recruitment § Recruitment: The process of generating a pool of qualified candidates for a particular job who can best contribute to the strategic objectives of the organisation. § Recruitment is a crucial function of SHRM § § § It determines the quantity and quality of future employees It determines the type of organisation created and the organisational capability to achieve success Recruitment activities should be aligned with business strategy and culture to ensure a ‘good fit’ Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Attraction activities § § Applicants may be sourced internally or externally Internal attraction activities: § advertising on the company intranet, in company newsletters, on noticeboards, via job bidding or using the HRIS § Benefits: cost; time; familiarity of candidate; familiarity of the organisation; increased morale and motivation; thorough understanding of the candidate’s cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Attraction activities § § Applicants may be sourced internally or externally Internal attraction activities: § advertising on the company intranet, in company newsletters, on noticeboards, via job bidding or using the HRIS § Benefits: cost; time; familiarity of candidate; familiarity of the organisation; increased morale and motivation; thorough understanding of the candidate’s cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Attraction activities (Cont’d) § External attraction activities: § Advertising on the Internet, in newspapers/magazines, job fares, recruitment agencies and word of mouth. § Benefits: a large talent pool; acquisition of new knowledge, skills, abilities and attitudes and opportunity to increase diversity in the workplace. § Recruitment agencies are external organisations that conduct the initial stages of recruitment. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Attraction activities (Cont’d) § External attraction activities: § Advertising on the Internet, in newspapers/magazines, job fares, recruitment agencies and word of mouth. § Benefits: a large talent pool; acquisition of new knowledge, skills, abilities and attitudes and opportunity to increase diversity in the workplace. § Recruitment agencies are external organisations that conduct the initial stages of recruitment. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Technology in recruitment § E-recruitment: The process of recruiting via the intranet (internal) and Internet (external) § Benefits of e-recruitment include: § Reach: unlimited exposure § Cost: less advertising costs § Speed & accessibility: immediate advertisement § Flexibility: unlimited length of advertisement § Interaction: employers and candidate interactions § Integrating the recruitment system with other computerised HR functions Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Technology in recruitment § E-recruitment: The process of recruiting via the intranet (internal) and Internet (external) § Benefits of e-recruitment include: § Reach: unlimited exposure § Cost: less advertising costs § Speed & accessibility: immediate advertisement § Flexibility: unlimited length of advertisement § Interaction: employers and candidate interactions § Integrating the recruitment system with other computerised HR functions Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Becoming an employer of choice § An organisation becomes an employer of choice when it is better able to attract and retain talent than its competitors. § When human wellbeing is put at the centre of HRM, an organisatoin has a positive reputation - it is seen as a positive work environment. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Becoming an employer of choice § An organisation becomes an employer of choice when it is better able to attract and retain talent than its competitors. § When human wellbeing is put at the centre of HRM, an organisatoin has a positive reputation - it is seen as a positive work environment. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Recruiter selection § Whether internal or external recruiters are used, it is important to ensure that they are knowledgeable about the organisation and the target job. § Openness to diversity and committed to equity § Internal recruiters viewed as representatives of organisation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Recruiter selection § Whether internal or external recruiters are used, it is important to ensure that they are knowledgeable about the organisation and the target job. § Openness to diversity and committed to equity § Internal recruiters viewed as representatives of organisation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Strategic selection § Selection: Identifying candidates who can best contribute to the strategic objectives of the organisation § To select the most suitable person for an organisation: § What is the candidate’s can do ability (i. e. , cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities)? § What is the candidate’s will do ability (i. e. , discretionary cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities)? § How well will the candidate’s cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities fit into the organisation? Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Strategic selection § Selection: Identifying candidates who can best contribute to the strategic objectives of the organisation § To select the most suitable person for an organisation: § What is the candidate’s can do ability (i. e. , cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities)? § What is the candidate’s will do ability (i. e. , discretionary cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities)? § How well will the candidate’s cognitive, affective and behavioural qualities fit into the organisation? Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Selection methods § § Sources of information about job candidates Pre-employment screening § § Realistic Job Preview (RJP) Selection methods § Interviews (structured; panel and group) § Application forms and resumes § Employment tests § Psychological tests § Assessment centres § Biographical information blanks Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Selection methods § § Sources of information about job candidates Pre-employment screening § § Realistic Job Preview (RJP) Selection methods § Interviews (structured; panel and group) § Application forms and resumes § Employment tests § Psychological tests § Assessment centres § Biographical information blanks Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Contemporary selection methods § There has been a shift away from taskcentred approaches (e. g. use of job/position descriptions) to personcentred approaches Ø In order to reflect the dynamic environment, selection criteria have shifted from focusing on specific technical capabilities to the qualities linked to adaptive performance (e. g. cognitive flexibility, proactive personality, and learning orientation) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Contemporary selection methods § There has been a shift away from taskcentred approaches (e. g. use of job/position descriptions) to personcentred approaches Ø In order to reflect the dynamic environment, selection criteria have shifted from focusing on specific technical capabilities to the qualities linked to adaptive performance (e. g. cognitive flexibility, proactive personality, and learning orientation) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Selection Criteria § § Selection criteria are the key workrelated factors used to make the decision to hire or not to hire a person. The criteria should be established based upon two areas of performance: § Task performance (i. e. , individual ability to perform job-related tasks) § Contextual performance (i. e. , incumbent’s behaviour at work which promotes a positive work environment) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Selection Criteria § § Selection criteria are the key workrelated factors used to make the decision to hire or not to hire a person. The criteria should be established based upon two areas of performance: § Task performance (i. e. , individual ability to perform job-related tasks) § Contextual performance (i. e. , incumbent’s behaviour at work which promotes a positive work environment) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
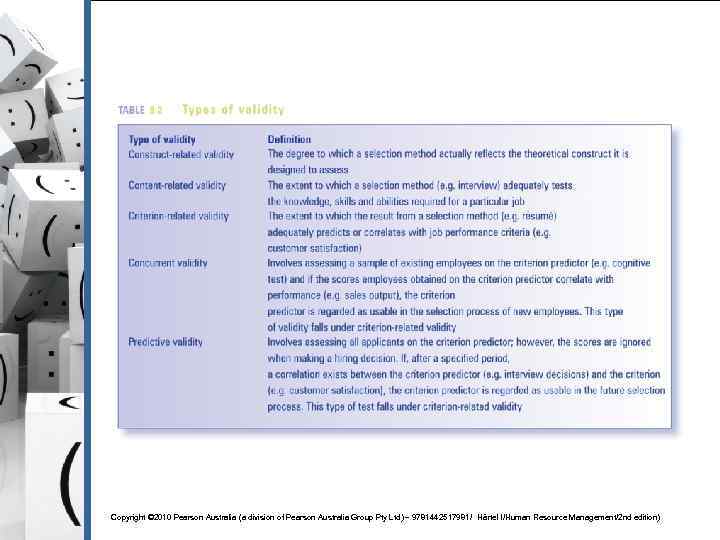
 Implication of selection methods and criteria § Reliability refers to the degree to which interviews, tests, and other selection procedures produce comparable data over a period of time and the degree to which two or more methods produce similar results. § Validity refers to the extent to which something measures what it claims to measure. § Legality refers to the assessment of the selection method against current employment legislation – especially employment opportunities legislation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Implication of selection methods and criteria § Reliability refers to the degree to which interviews, tests, and other selection procedures produce comparable data over a period of time and the degree to which two or more methods produce similar results. § Validity refers to the extent to which something measures what it claims to measure. § Legality refers to the assessment of the selection method against current employment legislation – especially employment opportunities legislation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
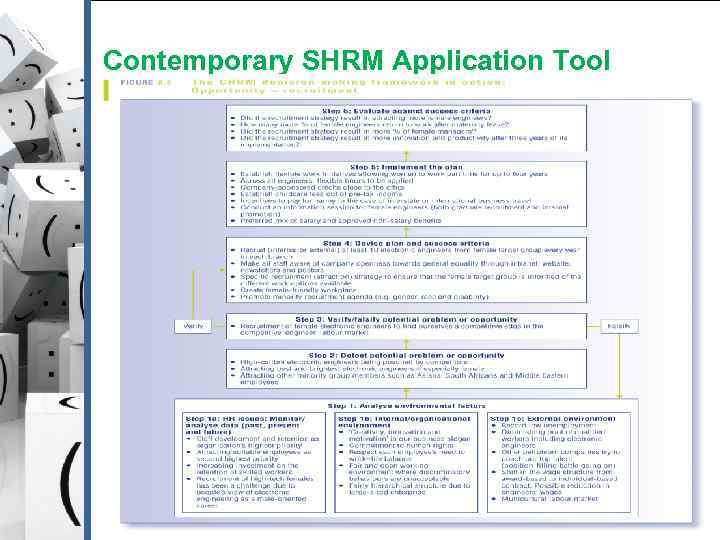 Contemporary SHRM Application Tool Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Contemporary SHRM Application Tool Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Step 1 Analyse environmental factors § Monitor/analyse data (past, present and future): § § Internal/organisational environment: § § Staff development and retention as organisation’s highest priority ‘Creativity, innovation and motivation’ is our business slogan External environment: § Record low unemployment Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Step 1 Analyse environmental factors § Monitor/analyse data (past, present and future): § § Internal/organisational environment: § § Staff development and retention as organisation’s highest priority ‘Creativity, innovation and motivation’ is our business slogan External environment: § Record low unemployment Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Step 2 Detect potential problem or opportunity § High-calibre electronic engineers being poached by competitors § Attracting best and brightest electronic engineers - especially female § Attracting other minority group members such as Asians, South Africans and Middle Eastern employees Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Step 2 Detect potential problem or opportunity § High-calibre electronic engineers being poached by competitors § Attracting best and brightest electronic engineers - especially female § Attracting other minority group members such as Asians, South Africans and Middle Eastern employees Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Step 3 Verify/falsify potential problem or opportunity § Recruitment of female electronic engineers to find ourselves a competitive edge in the competitive ‘engineer’ labour market Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Step 3 Verify/falsify potential problem or opportunity § Recruitment of female electronic engineers to find ourselves a competitive edge in the competitive ‘engineer’ labour market Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Step 4 Devise plan and success criteria § Recruit (internal or external) at least 10 electronic engineers from female target group every year in each branch § Make all staff aware of company openness toward gender equality through intranet, website, newsletters and posters § Specific recruitment (attraction) strategy to ensure that the female target group is informed of the different work options available § Create female-friendly workplace § Promote minority recruitment agenda (e. g. gender, race and disability) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Step 4 Devise plan and success criteria § Recruit (internal or external) at least 10 electronic engineers from female target group every year in each branch § Make all staff aware of company openness toward gender equality through intranet, website, newsletters and posters § Specific recruitment (attraction) strategy to ensure that the female target group is informed of the different work options available § Create female-friendly workplace § Promote minority recruitment agenda (e. g. gender, race and disability) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Step 5 Implement the plan § § § § Establish flexible work initiatives allowing women to work part time for up to 4 years Across all engineers, flexible hours to be applied. Company sponsored crèche close to the office Establish child care fees out of pre-tax income Incentives to pay for nanny in the case of interstate or international business travel Conduct an information session for female engineers (both graduate recruitment or internal promotion) Preferred mix of salary and approved non-salary benefits Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Step 5 Implement the plan § § § § Establish flexible work initiatives allowing women to work part time for up to 4 years Across all engineers, flexible hours to be applied. Company sponsored crèche close to the office Establish child care fees out of pre-tax income Incentives to pay for nanny in the case of interstate or international business travel Conduct an information session for female engineers (both graduate recruitment or internal promotion) Preferred mix of salary and approved non-salary benefits Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Step 6 Evaluate against success criteria § Did the recruitment strategy result in attracting more female engineers? § How many % more of female engineers return to work after their maternity leave? § Did the recruitment strategy result in a higher % of female managers? § Did the recruitment strategy result in more innovation and productivity after three years of its implementation? Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Step 6 Evaluate against success criteria § Did the recruitment strategy result in attracting more female engineers? § How many % more of female engineers return to work after their maternity leave? § Did the recruitment strategy result in a higher % of female managers? § Did the recruitment strategy result in more innovation and productivity after three years of its implementation? Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
 Conclusion § To obtain a competitive advantage there needs to be a clear link between organisational strategies and resources § § This may be achieved in part through HRP Recruitment and selection are the initial stages of HRM § They are crucial to obtaining a competitive advantage § Having the right people in the right jobs at the right time can contribute to competitive advantage Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)
Conclusion § To obtain a competitive advantage there needs to be a clear link between organisational strategies and resources § § This may be achieved in part through HRP Recruitment and selection are the initial stages of HRM § They are crucial to obtaining a competitive advantage § Having the right people in the right jobs at the right time can contribute to competitive advantage Copyright © 2010 Pearson Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) – 9781442517981/ Härtel l/Human Resource Management/2 nd edition)


