12864f8cdec09a9ac33daa02d6dd98c8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 143

Power. Point® Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community Ninth Edition College Human Anatomy & Physiology CHAPTER 17 Blood © Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Blood Composition • Blood – Fluid connective tissue – Plasma – non-living fluid matrix – Formed elements – living blood "cells" suspended in plasma • Erythrocytes (red blood cells, or RBCs) • Leukocytes (white blood cells, or WBCs) • Platelets © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Blood Composition • Spun tube of blood yields three layers – Plasma on top (~55%) – Erythrocytes on bottom (~45%) – WBCs and platelets in Buffy coat (< 1%) • Hematocrit – Percent of blood volume that is RBCs – 47% ± 5% for males; 42% ± 5% for females © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
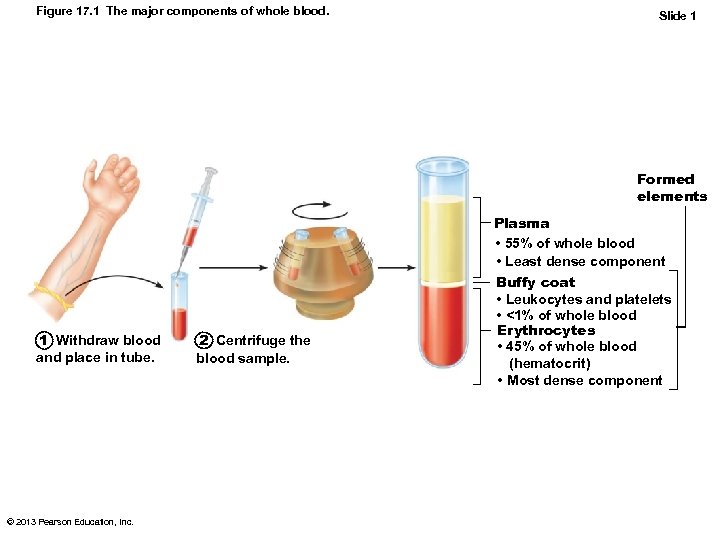
Figure 17. 1 The major components of whole blood. Slide 1 Formed elements 1 Withdraw blood and place in tube. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Centrifuge the blood sample. Plasma • 55% of whole blood • Least dense component Buffy coat • Leukocytes and platelets • <1% of whole blood Erythrocytes • 45% of whole blood (hematocrit) • Most dense component
Figure 17. 1 The major components of whole blood. 1 Withdraw blood and place in tube. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 2
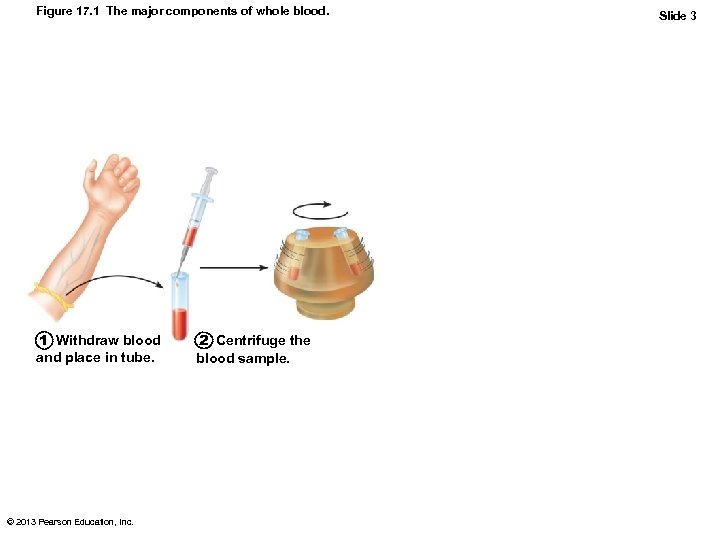
Figure 17. 1 The major components of whole blood. 1 Withdraw blood and place in tube. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Centrifuge the blood sample. Slide 3
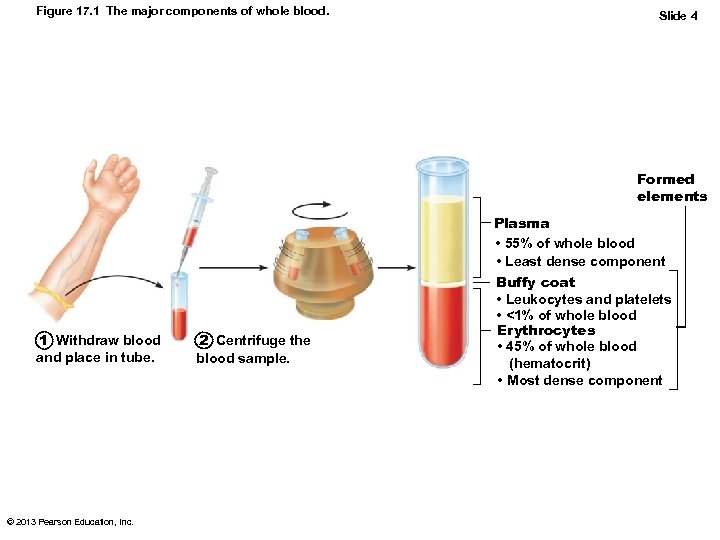
Figure 17. 1 The major components of whole blood. Slide 4 Formed elements 1 Withdraw blood and place in tube. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Centrifuge the blood sample. Plasma • 55% of whole blood • Least dense component Buffy coat • Leukocytes and platelets • <1% of whole blood Erythrocytes • 45% of whole blood (hematocrit) • Most dense component

Physical Characteristics and Volume • Sticky, opaque fluid with metallic taste • Color varies with O 2 content – High O 2 - scarlet; Low O 2 - dark red • p. H 7. 35– 7. 45 • ~8% of body weight • Average volume – 5– 6 L for males; 4– 5 L for females © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Functions of Blood • Functions include – Distributing substances – Regulating blood levels of substances – Protection © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Distribution Functions • Delivering O 2 and nutrients to body cells • Transporting metabolic wastes to lungs and kidneys for elimination • Transporting hormones from endocrine organs to target organs © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Regulation Functions • Maintaining body temperature by absorbing and distributing heat • Maintaining normal p. H using buffers; alkaline reserve of bicarbonate ions • Maintaining adequate fluid volume in circulatory system © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Protection Functions • Preventing blood loss – Plasma proteins and platelets initiate clot formation • Preventing infection – Antibodies – Complement proteins – WBCs © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Blood Plasma • 90% water • Over 100 dissolved solutes – Nutrients, gases, hormones, wastes, proteins, inorganic ions – Plasma proteins most abundant solutes • Remain in blood; not taken up by cells • Proteins produced mostly by liver • 60% albumin; 36% globulins; 4% fibrinogen © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
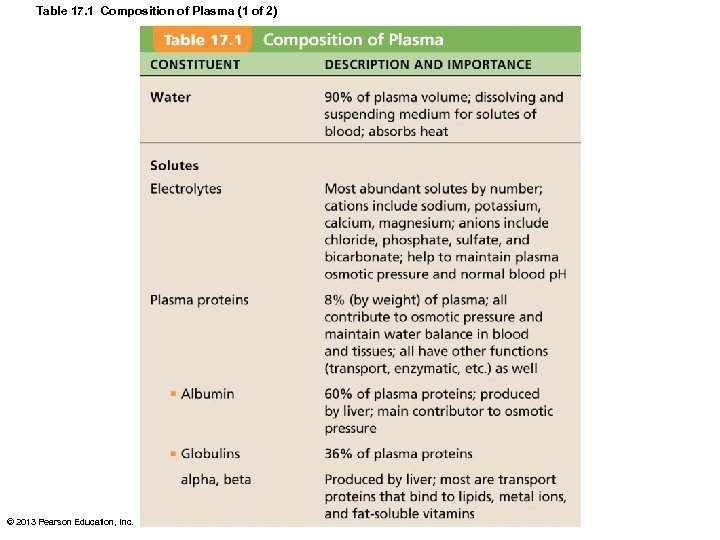
Table 17. 1 Composition of Plasma (1 of 2) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
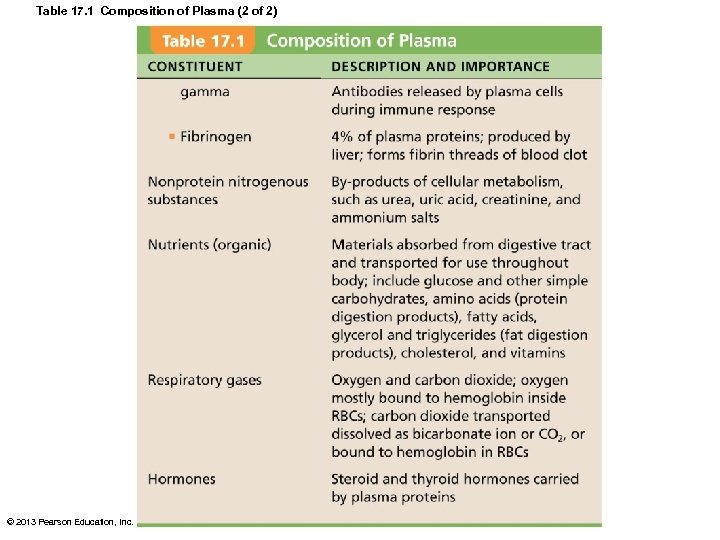
Table 17. 1 Composition of Plasma (2 of 2) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Albumin • 60% of plasma protein • Functions – Substance carrier – Blood buffer – Major contributor of plasma osmotic pressure © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Formed Elements • • Only WBCs are complete cells RBCs have no nuclei or other organelles Platelets are cell fragments Most formed elements survive in bloodstream only few days • Most blood cells originate in bone marrow and do not divide © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
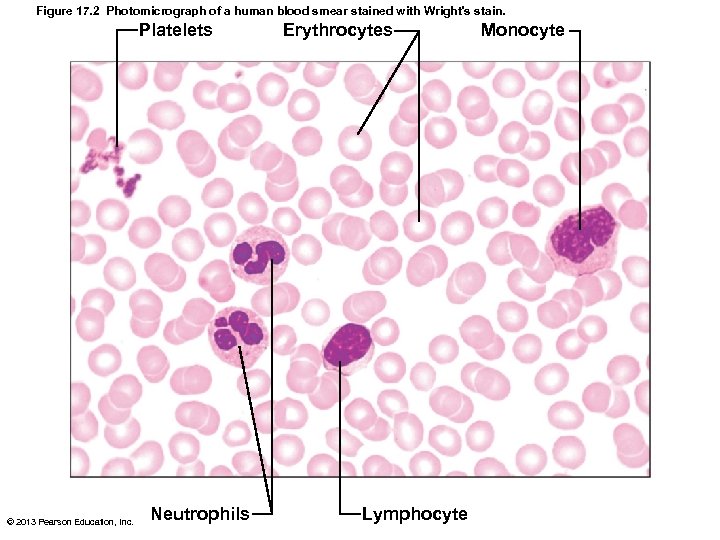
Figure 17. 2 Photomicrograph of a human blood smear stained with Wright's stain. Platelets © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Neutrophils Erythrocytes Lymphocyte Monocyte
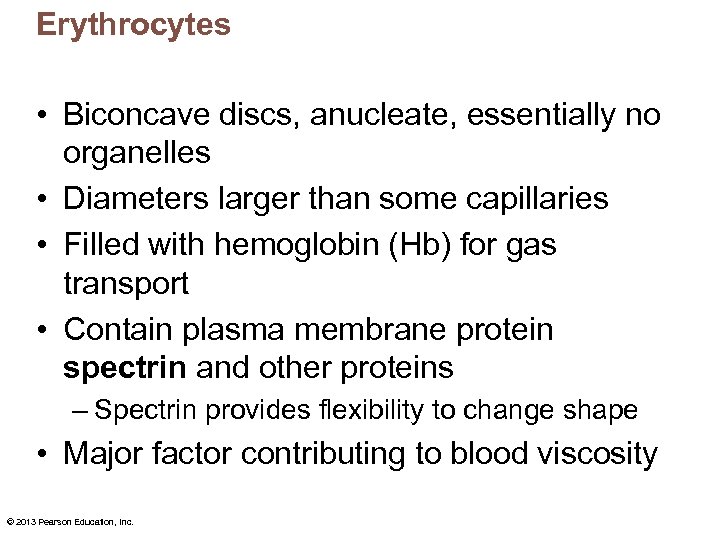
Erythrocytes • Biconcave discs, anucleate, essentially no organelles • Diameters larger than some capillaries • Filled with hemoglobin (Hb) for gas transport • Contain plasma membrane protein spectrin and other proteins – Spectrin provides flexibility to change shape • Major factor contributing to blood viscosity © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
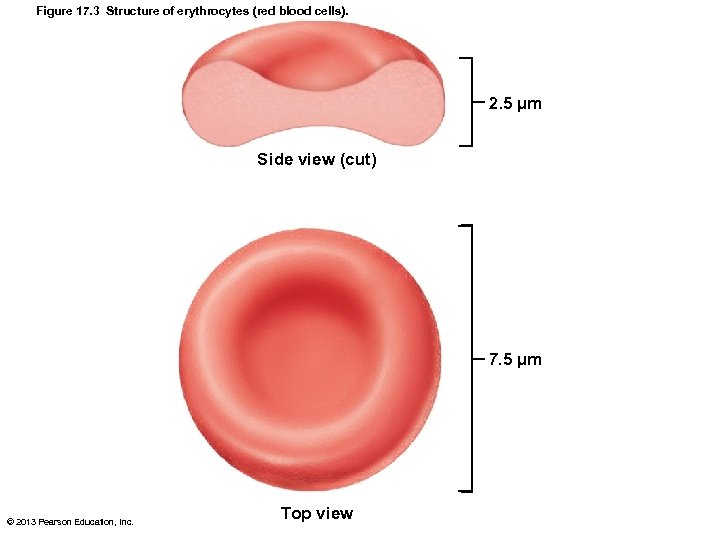
Figure 17. 3 Structure of erythrocytes (red blood cells). 2. 5 µm Side view (cut) 7. 5 µm © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Top view
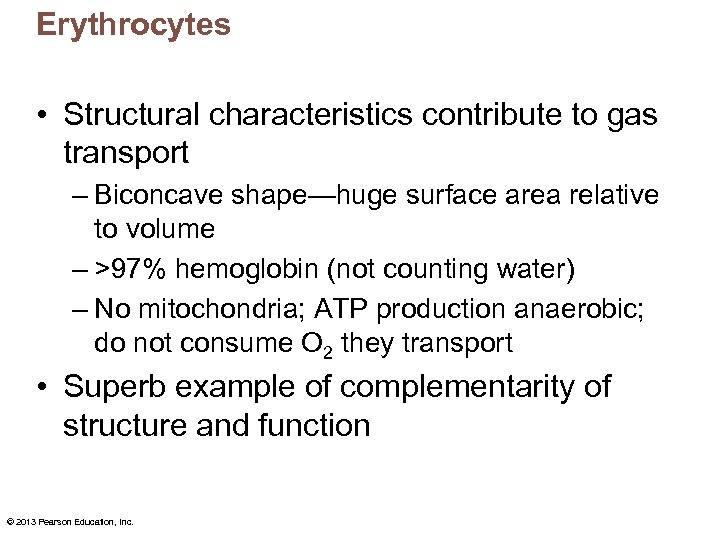
Erythrocytes • Structural characteristics contribute to gas transport – Biconcave shape—huge surface area relative to volume – >97% hemoglobin (not counting water) – No mitochondria; ATP production anaerobic; do not consume O 2 they transport • Superb example of complementarity of structure and function © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Erythrocyte Function • RBCs dedicated to respiratory gas transport • Hemoglobin binds reversibly with oxygen • Normal values – Males - 13– 18 g/100 ml; Females - 12– 16 g/100 ml © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Hemoglobin Structure • Globin composed of 4 polypeptide chains – Two alpha and two beta chains • Heme pigment bonded to each globin chain – Gives blood red color • Heme's central iron atom binds one O 2 • Each Hb molecule can transport four O 2 • Each RBC contains 250 million Hb molecules © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
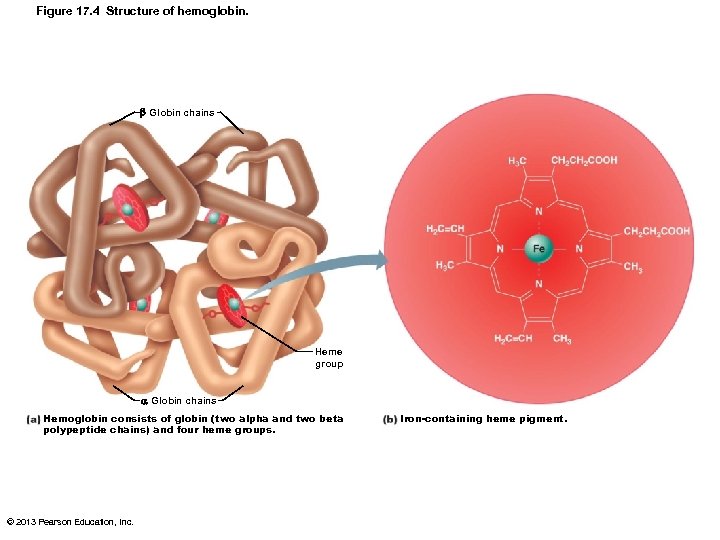
Figure 17. 4 Structure of hemoglobin. Globin chains Heme group Globin chains Hemoglobin consists of globin (two alpha and two beta polypeptide chains) and four heme groups. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Iron-containing heme pigment.
Hemoglobin (Hb) • O 2 loading in lungs – Produces oxyhemoglobin (ruby red) • O 2 unloading in tissues – Produces deoxyhemoglobin or reduced hemoglobin (dark red) • CO 2 loading in tissues – 20% of CO 2 in blood binds to Hb carbaminohemoglobin © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Hematopoiesis • Blood cell formation in red bone marrow – Composed of reticular connective tissue and blood sinusoids • In adult, found in axial skeleton, girdles, and proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Hematopoiesis • Hematopoietic stem cells (Hemocytoblasts) – Give rise to all formed elements – Hormones and growth factors push cell toward specific pathway of blood cell development – Committed cells cannot change • New blood cells enter blood sinusoids © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Erythropoiesis: Red Blood Cell Production • Stages – Myeloid stem cell transformed into proerythroblast – In 15 days proerythroblasts develop into basophilic, then polychromatic, then orthochromatic erythroblasts, and then into reticulocytes – Reticulocytes enter bloodstream; in 2 days mature RBC © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Erythropoiesis • As myeloid stem cell transforms 1. Ribosomes synthesized 2. Hemoglobin synthesized; iron accumulates 3. Ejection of nucleus; formation of reticulocyte (young RBC) • Reticulocyte ribosomes degraded; Then become mature erythrocytes • Reticulocyte count indicates rate of RBC formation © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
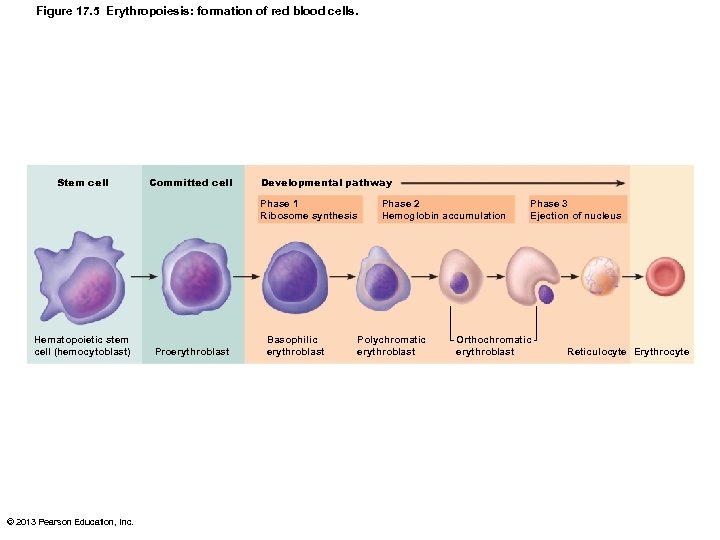
Figure 17. 5 Erythropoiesis: formation of red blood cells. Stem cell Committed cell Developmental pathway Phase 1 Ribosome synthesis Hematopoietic stem cell (hemocytoblast) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Proerythroblast Basophilic erythroblast Phase 2 Hemoglobin accumulation Polychromatic erythroblast Phase 3 Ejection of nucleus Orthochromatic erythroblast Reticulocyte Erythrocyte

Regulation of Erythropoiesis • • Too few RBCs leads to tissue hypoxia Too many RBCs increases blood viscosity > 2 million RBCs made per second Balance between RBC production and destruction depends on – Hormonal controls – Adequate supplies of iron, amino acids, and B vitamins © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Hormonal Control of Erythropoiesis • Hormone Erythropoietin (EPO) – Direct stimulus for erythropoiesis – Always small amount in blood to maintain basal rate • High RBC or O 2 levels depress production – Released by kidneys (some from liver) in response to hypoxia • Dialysis patients have low RBC counts © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Hormonal Control of Erythropoiesis • Causes of hypoxia – Decreased RBC numbers due to hemorrhage or increased destruction – Insufficient hemoglobin per RBC (e. g. , iron deficiency) – Reduced availability of O 2 (e. g. , high altitudes) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Hormonal Control of Erythropoiesis • Effects of EPO – Rapid maturation of committed marrow cells – Increased circulating reticulocyte count in 1– 2 days • Some athletes abuse artificial EPO – Dangerous consequences • Testosterone enhances EPO production, resulting in higher RBC counts in males © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
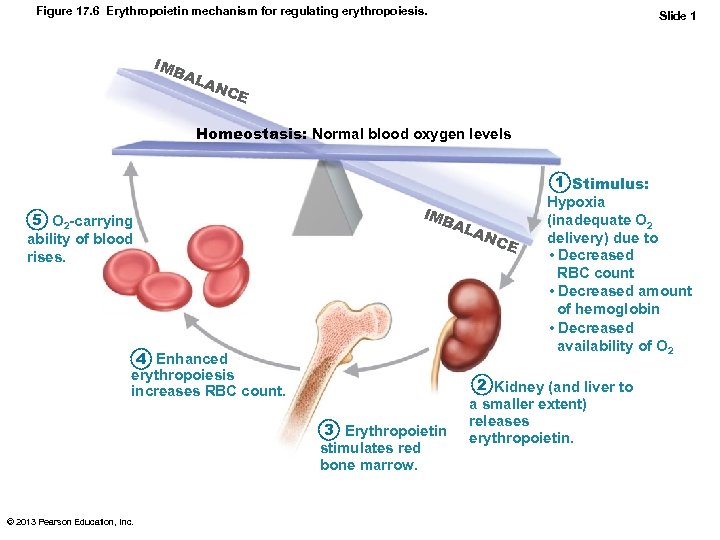
Figure 17. 6 Erythropoietin mechanism for regulating erythropoiesis. IMB AL Slide 1 AN CE Homeostasis: Normal blood oxygen levels 5 O 2 -carrying ability of blood rises. IMB AL 4 Enhanced erythropoiesis increases RBC count. 3 Erythropoietin stimulates red bone marrow. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. AN C E 1 Stimulus: Hypoxia (inadequate O 2 delivery) due to • Decreased RBC count • Decreased amount of hemoglobin • Decreased availability of O 2 2 Kidney (and liver to a smaller extent) releases erythropoietin.
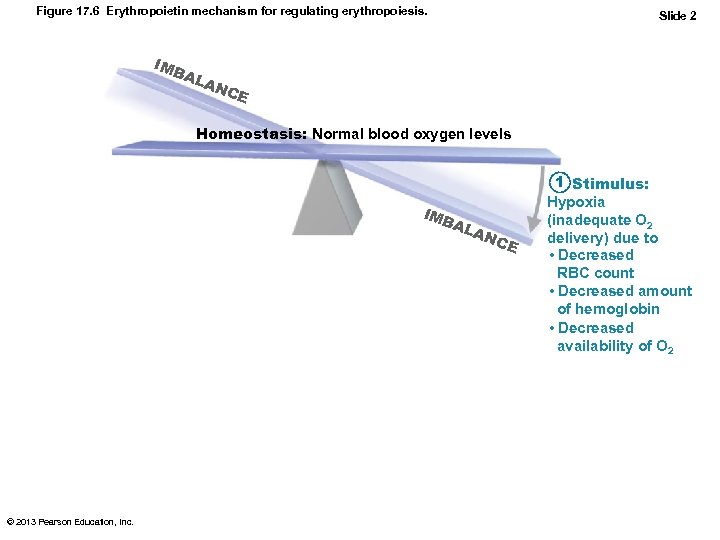
Figure 17. 6 Erythropoietin mechanism for regulating erythropoiesis. IMB AL Slide 2 AN CE Homeostasis: Normal blood oxygen levels IMB AL © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. AN C E 1 Stimulus: Hypoxia (inadequate O 2 delivery) due to • Decreased RBC count • Decreased amount of hemoglobin • Decreased availability of O 2
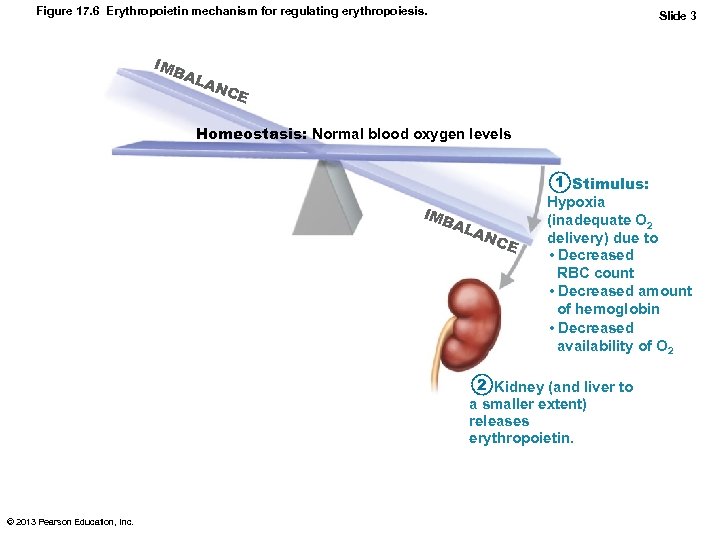
Figure 17. 6 Erythropoietin mechanism for regulating erythropoiesis. IMB AL Slide 3 AN CE Homeostasis: Normal blood oxygen levels IMB AL AN C E 1 Stimulus: Hypoxia (inadequate O 2 delivery) due to • Decreased RBC count • Decreased amount of hemoglobin • Decreased availability of O 2 2 Kidney (and liver to a smaller extent) releases erythropoietin. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
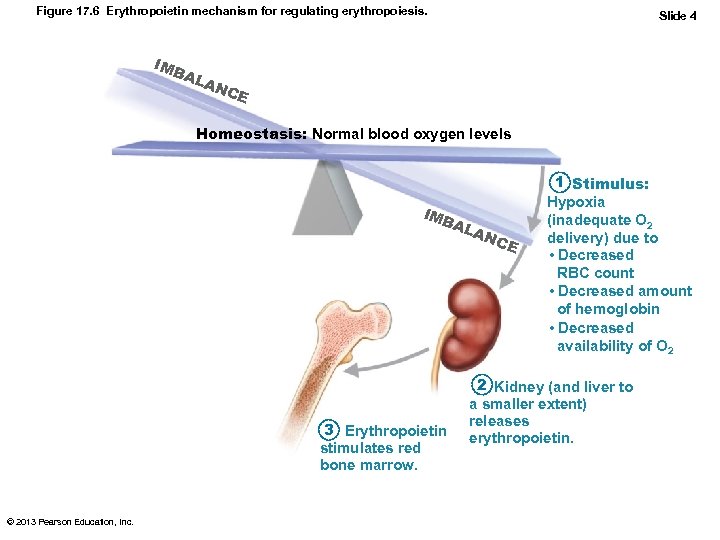
Figure 17. 6 Erythropoietin mechanism for regulating erythropoiesis. IMB AL Slide 4 AN CE Homeostasis: Normal blood oxygen levels IMB AL 3 Erythropoietin stimulates red bone marrow. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. AN C E 1 Stimulus: Hypoxia (inadequate O 2 delivery) due to • Decreased RBC count • Decreased amount of hemoglobin • Decreased availability of O 2 2 Kidney (and liver to a smaller extent) releases erythropoietin.
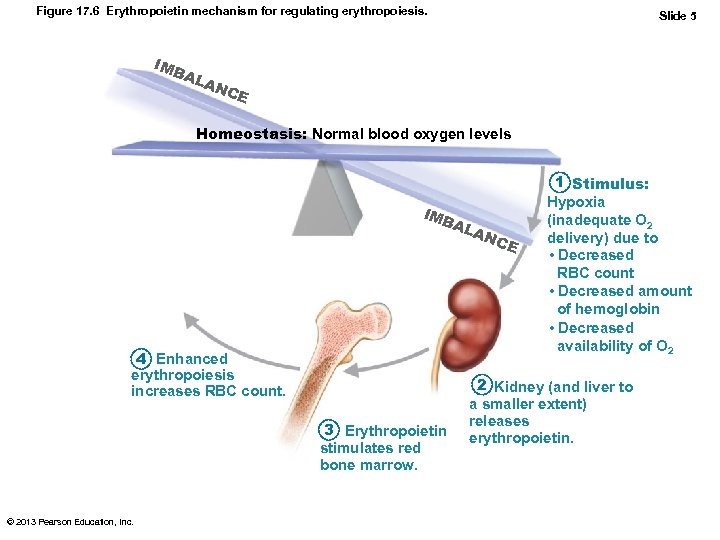
Figure 17. 6 Erythropoietin mechanism for regulating erythropoiesis. IMB AL Slide 5 AN CE Homeostasis: Normal blood oxygen levels IMB AL 4 Enhanced erythropoiesis increases RBC count. 3 Erythropoietin stimulates red bone marrow. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. AN C E 1 Stimulus: Hypoxia (inadequate O 2 delivery) due to • Decreased RBC count • Decreased amount of hemoglobin • Decreased availability of O 2 2 Kidney (and liver to a smaller extent) releases erythropoietin.
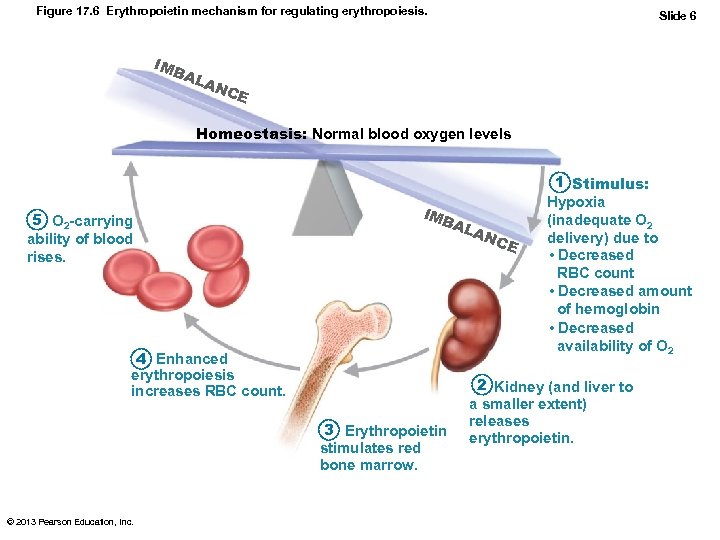
Figure 17. 6 Erythropoietin mechanism for regulating erythropoiesis. IMB AL Slide 6 AN CE Homeostasis: Normal blood oxygen levels 5 O 2 -carrying ability of blood rises. IMB AL 4 Enhanced erythropoiesis increases RBC count. 3 Erythropoietin stimulates red bone marrow. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. AN C E 1 Stimulus: Hypoxia (inadequate O 2 delivery) due to • Decreased RBC count • Decreased amount of hemoglobin • Decreased availability of O 2 2 Kidney (and liver to a smaller extent) releases erythropoietin.
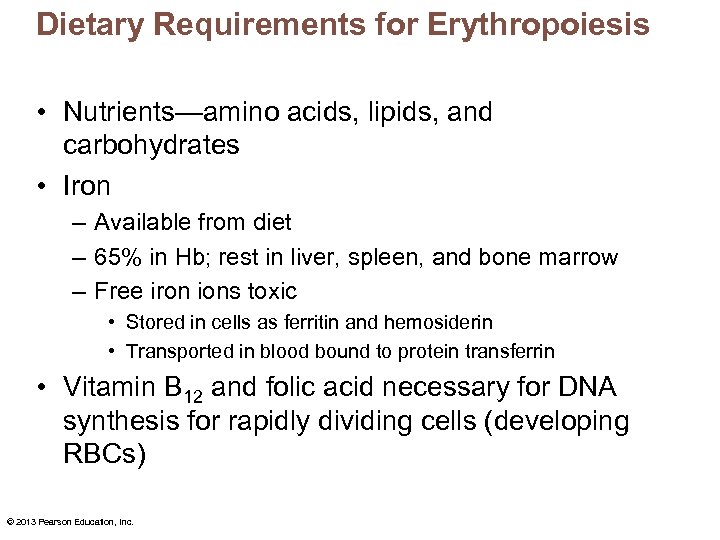
Dietary Requirements for Erythropoiesis • Nutrients—amino acids, lipids, and carbohydrates • Iron – Available from diet – 65% in Hb; rest in liver, spleen, and bone marrow – Free iron ions toxic • Stored in cells as ferritin and hemosiderin • Transported in blood bound to protein transferrin • Vitamin B 12 and folic acid necessary for DNA synthesis for rapidly dividing cells (developing RBCs) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Fate and Destruction of Erythrocytes • Life span: 100– 120 days – No protein synthesis, growth, division • Old RBCs become fragile; Hb begins to degenerate • Get trapped in smaller circulatory channels especially in spleen • Macrophages engulf dying RBCs in spleen © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Fate and Destruction of Erythrocytes • Heme and globin are separated – Iron salvaged for reuse – Heme degraded to yellow pigment bilirubin – Liver secretes bilirubin (in bile) into intestines • Degraded to pigment urobilinogen • Pigment leaves body in feces as stercobilin – Globin metabolized into amino acids • Released into circulation © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
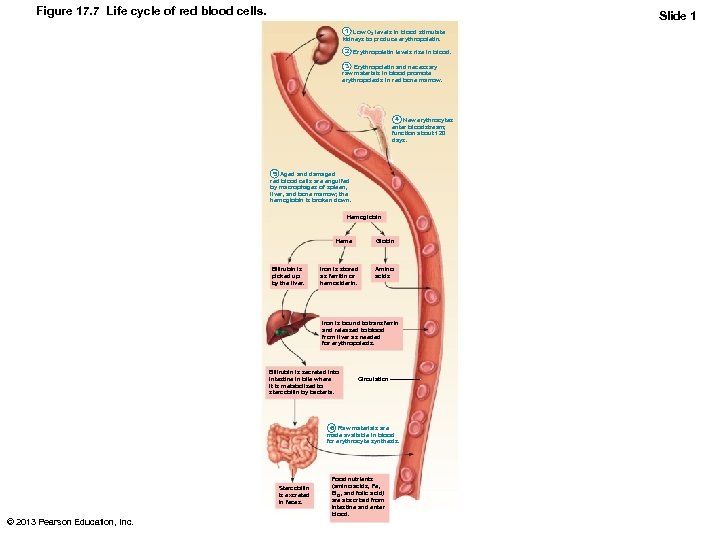
Figure 17. 7 Life cycle of red blood cells. Slide 1 1 Low O 2 levels in blood stimulate kidneys to produce erythropoietin. 2 Erythropoietin levels rise in blood. 3 Erythropoietin and necessary raw materials in blood promote erythropoiesis in red bone marrow. 4 New erythrocytes enter bloodstream; function about 120 days. 5 Aged and damaged red blood cells are engulfed by macrophages of spleen, liver, and bone marrow; the hemoglobin is broken down. Hemoglobin Heme Bilirubin is picked up by the liver. Globin Iron is stored as ferritin or hemosiderin. Amino acids Iron is bound to transferrin and released to blood from liver as needed for erythropoiesis. Bilirubin is secreted into intestine in bile where it is metabolized to stercobilin by bacteria. Circulation 6 Raw materials are made available in blood for erythrocyte synthesis. Stercobilin is excreted in feces. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Food nutrients (amino acids, Fe, B 12, and folic acid) are absorbed from intestine and enter blood.
Figure 17. 7 Life cycle of red blood cells. Slide 2 1 Low O 2 levels in blood stimulate kidneys to produce erythropoietin. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 17. 7 Life cycle of red blood cells. Slide 3 1 Low O 2 levels in blood stimulate kidneys to produce erythropoietin. 2 Erythropoietin levels rise in blood. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
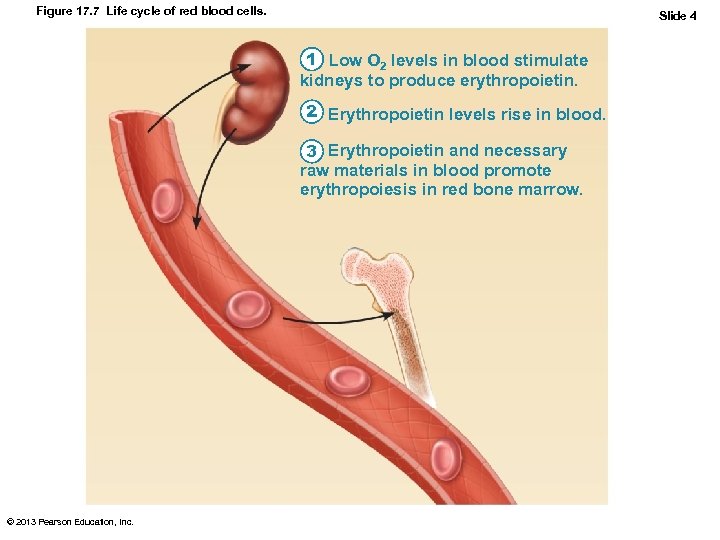
Figure 17. 7 Life cycle of red blood cells. Slide 4 1 Low O 2 levels in blood stimulate kidneys to produce erythropoietin. 2 Erythropoietin levels rise in blood. 3 Erythropoietin and necessary raw materials in blood promote erythropoiesis in red bone marrow. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
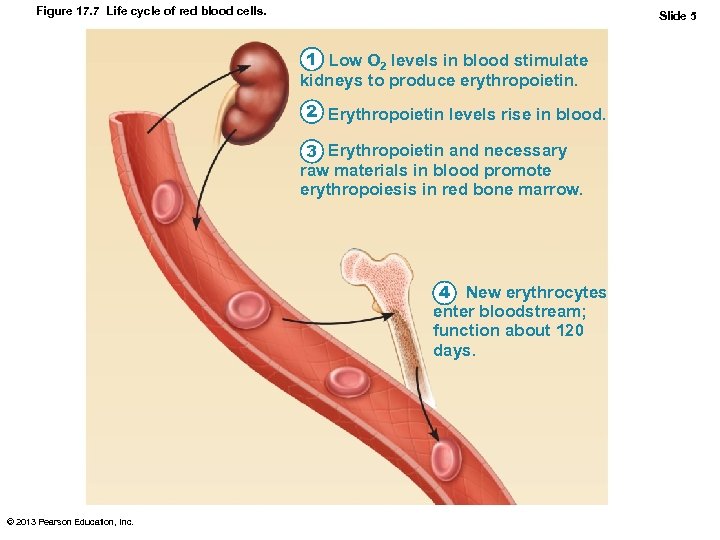
Figure 17. 7 Life cycle of red blood cells. Slide 5 1 Low O 2 levels in blood stimulate kidneys to produce erythropoietin. 2 Erythropoietin levels rise in blood. 3 Erythropoietin and necessary raw materials in blood promote erythropoiesis in red bone marrow. 4 New erythrocytes enter bloodstream; function about 120 days. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
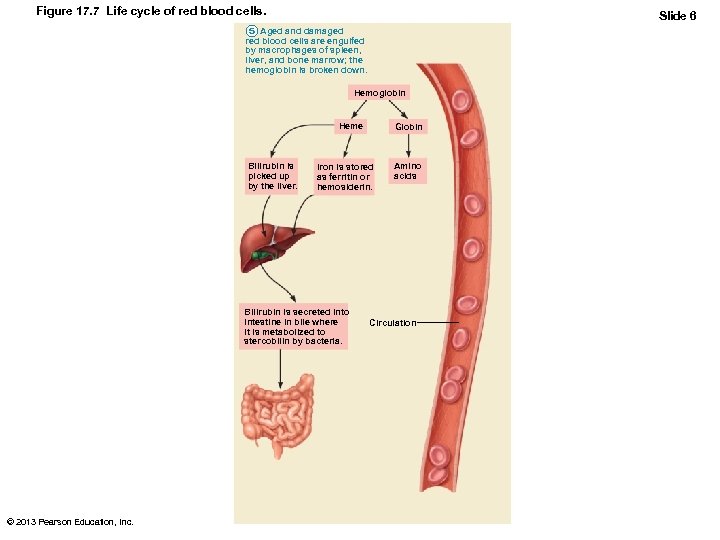
Figure 17. 7 Life cycle of red blood cells. Slide 6 5 Aged and damaged red blood cells are engulfed by macrophages of spleen, liver, and bone marrow; the hemoglobin is broken down. Hemoglobin Heme Bilirubin is picked up by the liver. Iron is stored as ferritin or hemosiderin. Bilirubin is secreted into intestine in bile where it is metabolized to stercobilin by bacteria. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Globin Amino acids Circulation
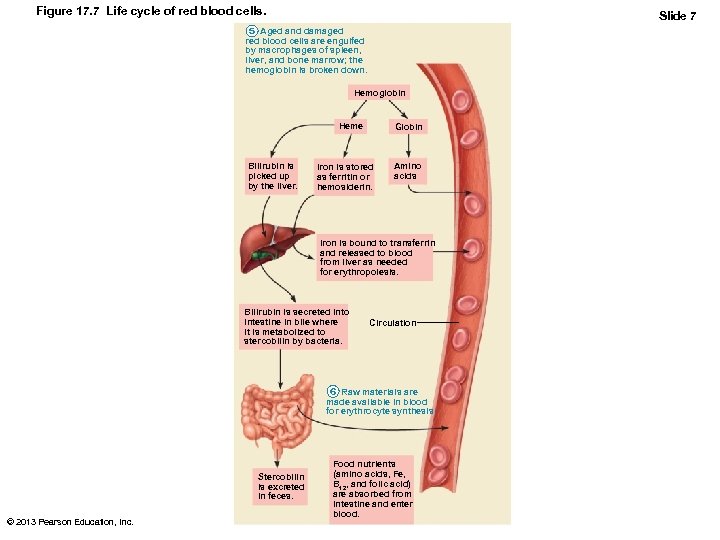
Figure 17. 7 Life cycle of red blood cells. Slide 7 5 Aged and damaged red blood cells are engulfed by macrophages of spleen, liver, and bone marrow; the hemoglobin is broken down. Hemoglobin Heme Bilirubin is picked up by the liver. Globin Iron is stored as ferritin or hemosiderin. Amino acids Iron is bound to transferrin and released to blood from liver as needed for erythropoiesis. Bilirubin is secreted into intestine in bile where it is metabolized to stercobilin by bacteria. Circulation 6 Raw materials are made available in blood for erythrocyte synthesis. Stercobilin is excreted in feces. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Food nutrients (amino acids, Fe, B 12, and folic acid) are absorbed from intestine and enter blood.
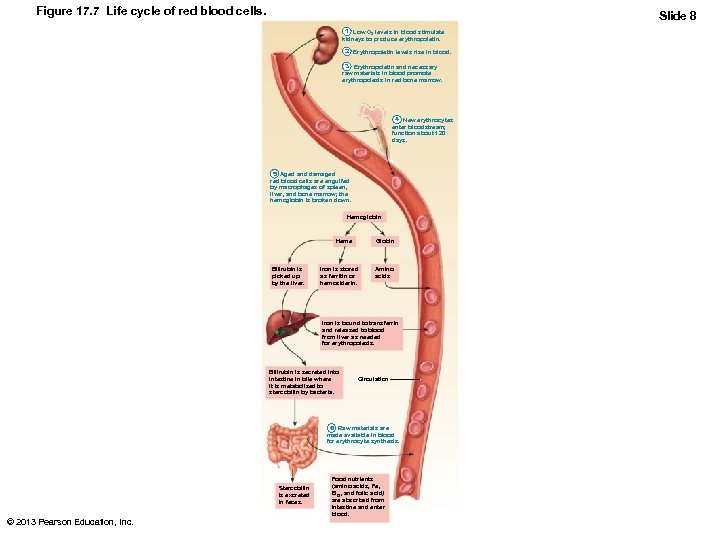
Figure 17. 7 Life cycle of red blood cells. Slide 8 1 Low O 2 levels in blood stimulate kidneys to produce erythropoietin. 2 Erythropoietin levels rise in blood. 3 Erythropoietin and necessary raw materials in blood promote erythropoiesis in red bone marrow. 4 New erythrocytes enter bloodstream; function about 120 days. 5 Aged and damaged red blood cells are engulfed by macrophages of spleen, liver, and bone marrow; the hemoglobin is broken down. Hemoglobin Heme Bilirubin is picked up by the liver. Globin Iron is stored as ferritin or hemosiderin. Amino acids Iron is bound to transferrin and released to blood from liver as needed for erythropoiesis. Bilirubin is secreted into intestine in bile where it is metabolized to stercobilin by bacteria. Circulation 6 Raw materials are made available in blood for erythrocyte synthesis. Stercobilin is excreted in feces. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Food nutrients (amino acids, Fe, B 12, and folic acid) are absorbed from intestine and enter blood.

Erythrocyte Disorders • Anemia – Blood has abnormally low O 2 -carrying capacity – Sign rather than disease itself – Blood O 2 levels cannot support normal metabolism – Accompanied by fatigue, pallor, shortness of breath, and chills © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Causes of Anemia • Three groups – Blood loss – Low RBC production – High RBC destruction © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Causes of Anemia: Blood Loss • Hemorrhagic anemia – Blood loss rapid (e. g. , stab wound) – Treated by blood replacement • Chronic hemorrhagic anemia – Slight but persistent blood loss • Hemorrhoids, bleeding ulcer – Primary problem treated © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Causes of Anemia: Low RBC Production • Iron-deficiency anemia – Caused by hemorrhagic anemia, low iron intake, or impaired absorption – Microcytic, hypochromic RBCs – Iron supplements to treat © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Causes of Anemia: Low RBC Production • Pernicious anemia – Autoimmune disease - destroys stomach mucosa – Lack of intrinsic factor needed to absorb B 12 • Deficiency of vitamin B 12 – RBCs cannot divide macrocytes – Treated with B 12 injections or nasal gel – Also caused by low dietary B 12 (vegetarians) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Causes of Anemia: Low RBC Production • Renal anemia – Lack of EPO – Often accompanies renal disease – Treated with synthetic EPO © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Causes of Anemia: Low RBC Production • Aplastic anemia – Destruction or inhibition of red marrow by drugs, chemicals, radiation, viruses – Usually cause unknown – All cell lines affected • Anemia; clotting and immunity defects – Treated short-term with transfusions; longterm with transplanted stem cells © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Causes of Anemia: High RBC Destruction • Hemolytic anemias – Premature RBC lysis – Caused by • Hb abnormalities • Incompatible transfusions • Infections © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Causes of Anemia: High RBC Destruction • Usually genetic basis for abnormal Hb • Globin abnormal – Fragile RBCs lyse prematurely © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Causes of Anemia: High RBC Destruction • Thalassemias – Typically Mediterranean ancestry – One globin chain absent or faulty – RBCs thin, delicate, deficient in Hb – Many subtypes • Severity from mild to severe © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Causes of Anemia: High RBC Destruction • Sickle-cell anemia – Hemoglobin S • One amino acid wrong in a globin beta chain – RBCs crescent shaped when unload O 2 or blood O 2 low – RBCs rupture easily and block small vessels • Poor O 2 delivery; pain © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Sickle-cell Anemia • Black people of African malarial belt and descendants • Malaria – Kills 1 million each year • Sickle-cell gene – Two copies Sickle-cell anemia – One copy Sickle-cell trait; milder disease; better chance to survive malaria © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Sickle-cell Anemia: Treatments • Acute crisis treated with transfusions; inhaled nitric oxide • Preventing sickling – Hydroxyurea induces fetal hemoglobin (which does not sickle) formation – Blocking RBC ion channels – Stem cell transplants – Gene therapy © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
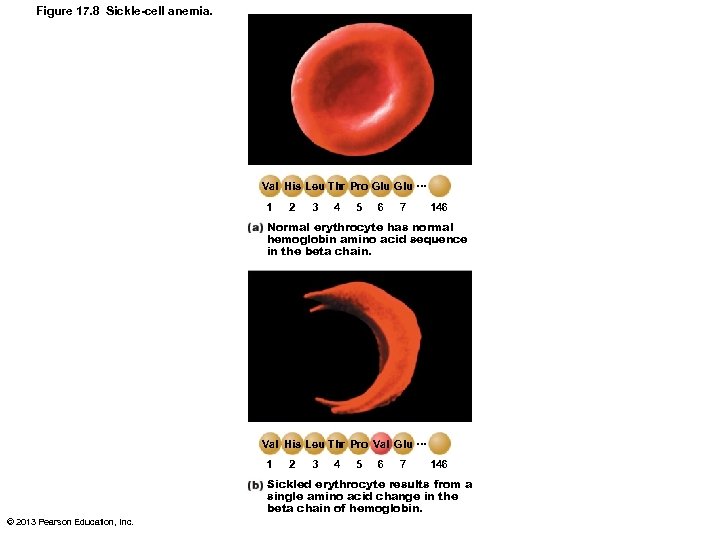
Figure 17. 8 Sickle-cell anemia. Val His Leu Thr Pro Glu … 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 146 Normal erythrocyte has normal hemoglobin amino acid sequence in the beta chain. Val His Leu Thr Pro Val Glu … 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 146 Sickled erythrocyte results from a single amino acid change in the beta chain of hemoglobin. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Erythrocyte Disorders • Polycythemia vera – Bone marrow cancer excess RBCs – Severely increased blood viscosity • Secondary polycythemia – Less O 2 available (high altitude) or EPO production increases higher RBC count – Blood doping © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Leukocytes • Make up <1% of total blood volume – 4, 800 – 10, 800 WBCs/μl blood • Function in defense against disease – Can leave capillaries via diapedesis – Move through tissue spaces by ameboid motion and positive chemotaxis • Leukocytosis: WBC count over 11, 000/mm 3 – Normal response to infection © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Leukocytes: Two Categories • Granulocytes – Visible cytoplasmic granules – Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils • Agranulocytes – No visible cytoplasmic granules – Lymphocytes, monocytes • Decreasing abundance in blood – Never let monkeys eat bananas © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
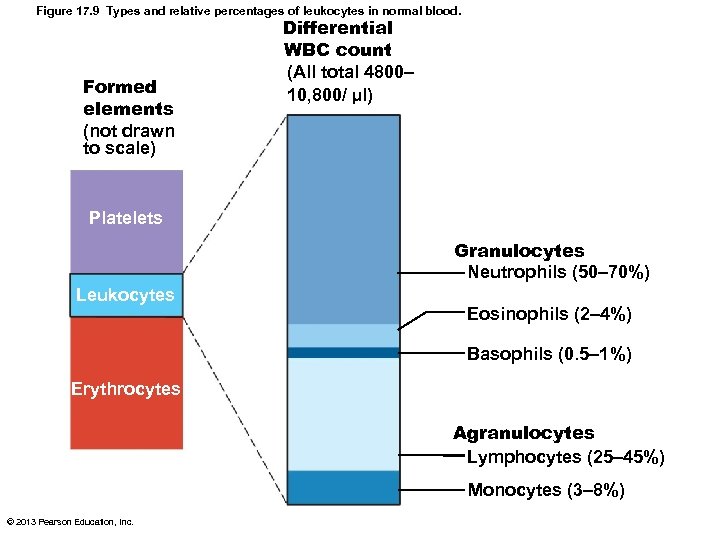
Figure 17. 9 Types and relative percentages of leukocytes in normal blood. Formed elements (not drawn to scale) Differential WBC count (All total 4800– 10, 800/ µl) Platelets Granulocytes Neutrophils (50– 70%) Leukocytes Eosinophils (2– 4%) Basophils (0. 5– 1%) Erythrocytes Agranulocytes Lymphocytes (25– 45%) Monocytes (3– 8%) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Granulocytes • Granulocytes – Larger and shorter-lived than RBCs – Lobed nuclei – Cytoplasmic granules stain specifically with Wright's stain – All phagocytic to some degree © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Neutrophils • Most numerous WBCs • Also called Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs or polys) • Granules stain lilac; contain hydrolytic enzymes or defensins • 3 -6 lobes in nucleus; twice size of RBCs • Very phagocytic—"bacteria slayers" © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Eosinophils • Red-staining granules • Bilobed nucleus • Granules lysosome-like – Release enzymes to digest parasitic worms • Role in allergies and asthma • Role in modulating immune response © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Basophils • Rarest WBCs • Nucleus deep purple with 1 -2 constrictions • Large, purplish-black (basophilic) granules contain histamine – Histamine: inflammatory chemical that acts as vasodilator to attract WBCs to inflamed sites • Are functionally similar to mast cells © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
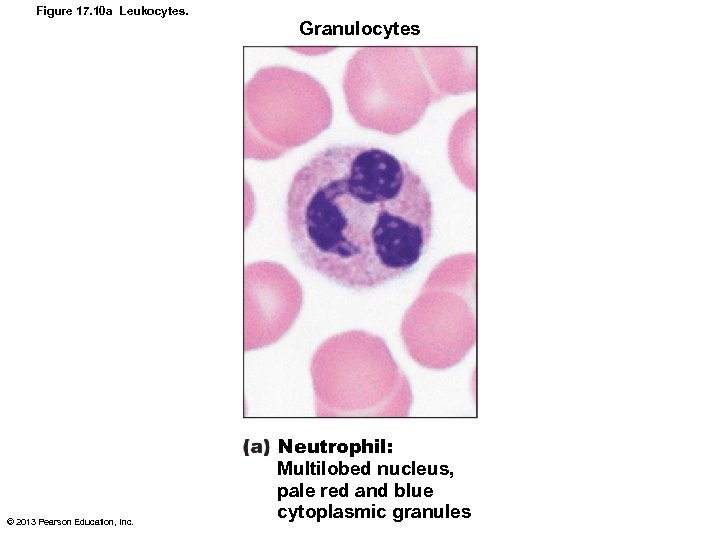
Figure 17. 10 a Leukocytes. Granulocytes © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Neutrophil: Multilobed nucleus, pale red and blue cytoplasmic granules
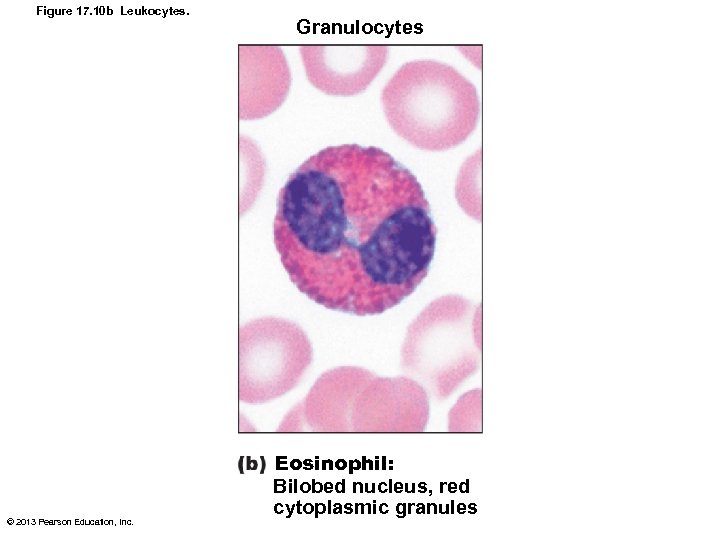
Figure 17. 10 b Leukocytes. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Granulocytes Eosinophil: Bilobed nucleus, red cytoplasmic granules
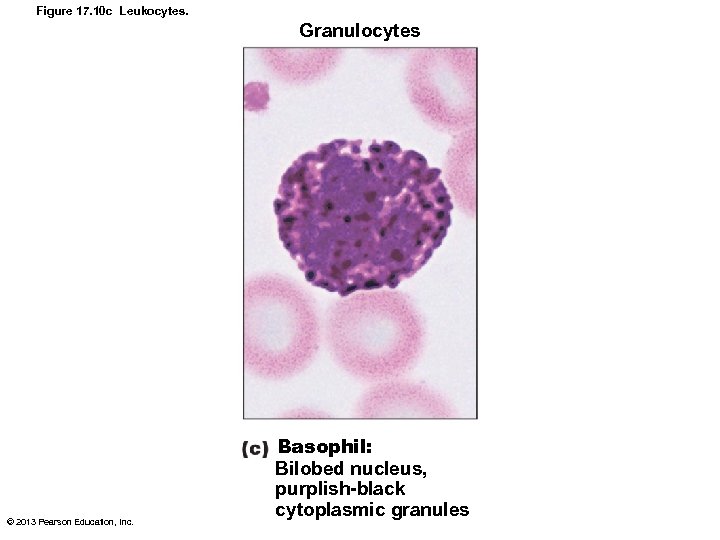
Figure 17. 10 c Leukocytes. Granulocytes © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Basophil: Bilobed nucleus, purplish-black cytoplasmic granules

Agranulocytes • Agranulocytes – Lack visible cytoplasmic granules – Have spherical or kidney-shaped nuclei © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Lymphocytes • Second most numerous WBC • Large, dark-purple, circular nuclei with thin rim of blue cytoplasm • Mostly in lymphoid tissue (e. g. , lymph nodes, spleen); few circulate in blood • Crucial to immunity © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Lymphocytes • Two types – T lymphocytes (T cells) act against virusinfected cells and tumor cells – B lymphocytes (B cells) give rise to plasma cells, which produce antibodies © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Monocytes • Largest leukocytes • Abundant pale-blue cytoplasm • Dark purple-staining, U- or kidney-shaped nuclei © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Monocytes • Leave circulation, enter tissues, and differentiate into macrophages – Actively phagocytic cells; crucial against viruses, intracellular bacterial parasites, and chronic infections • Activate lymphocytes to mount an immune response © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
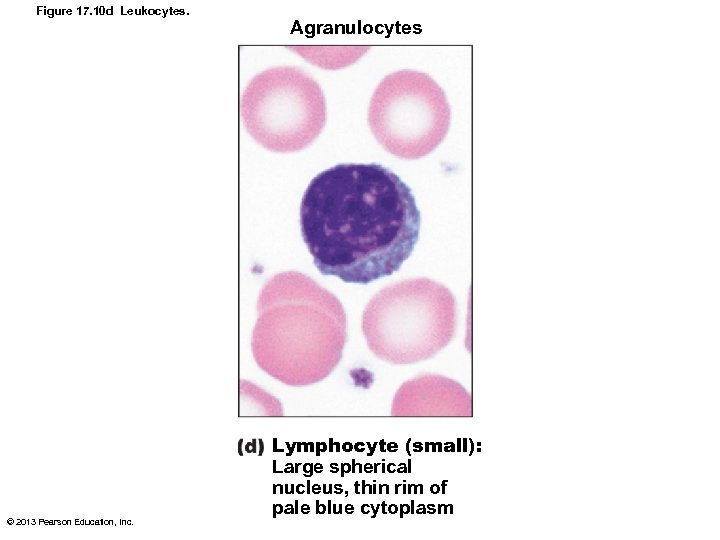
Figure 17. 10 d Leukocytes. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Agranulocytes Lymphocyte (small): Large spherical nucleus, thin rim of pale blue cytoplasm
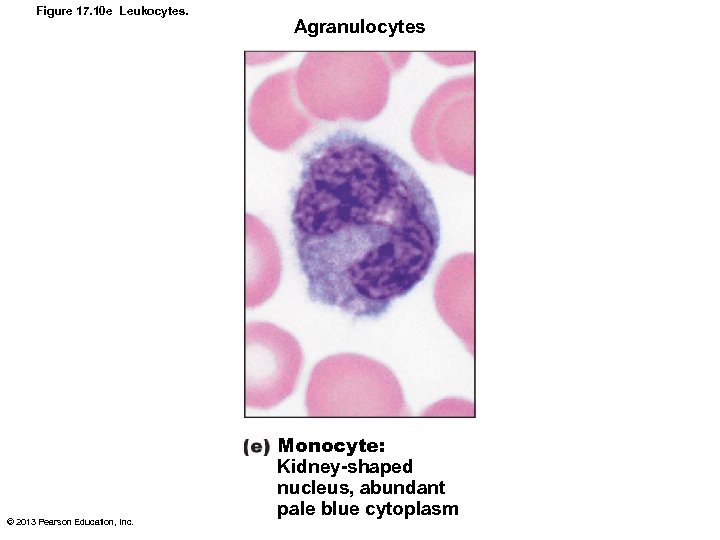
Figure 17. 10 e Leukocytes. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Agranulocytes Monocyte: Kidney-shaped nucleus, abundant pale blue cytoplasm
Leukopoiesis • Production of WBCs – Stimulated by 2 types of chemical messengers from red bone marrow and mature WBCs • Interleukins (e. g. , IL-3, IL-5) • Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) named for WBC type they stimulate (e. g. , granulocyte-CSF stimulates granulocytes) • All leukocytes originate from hemocytoblasts © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Leukopoiesis • Lymphoid stem cells lymphocytes • Myeloid stem cells all others • Progression of all granulocytes – Myeloblast promyelocyte band mature cell • Granulocytes stored in bone marrow • 3 times more WBCs produced than RBCs – Shorter life span; die fighting microbes © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Leukopoiesis • Progression of agranulocytes differs • Monocytes – live several months – Share common precursor with neutrophils – Monoblast promonocyte • Lymphocytes – live few hours to decades – Lymphoid stem cell T lymphocyte precursors (travel to thymus) and B lymphocyte precursors © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
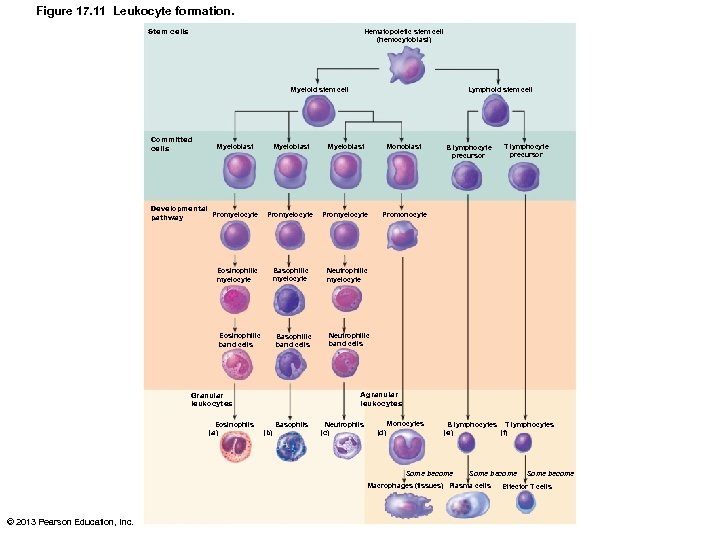
Figure 17. 11 Leukocyte formation. Stem cells Hematopoietic stem cell (hemocytoblast) Lymphoid stem cell Myeloid stem cell Committed cells Myeloblast Developmental Promyelocyte pathway Eosinophilic myelocyte Myeloblast Monoblast Promyelocyte Basophilic myelocyte Eosinophilic band cells Basophilic band cells Neutrophilic myelocyte Neutrophilic band cells Agranular leukocytes Granular leukocytes Eosinophils (a) (b) Basophils Neutrophils (c) Monocytes (d) B lymphocytes T lymphocytes (e) (f) Some become Macrophages (tissues) Plasma cells © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. T lymphocyte precursor Promonocyte B lymphocyte precursor Some become Effector T cells

Leukocyte disorders • Leukopenia – Abnormally low WBC count—drug induced • Leukemias – all fatal if untreated – – Cancer overproduction of abnormal WBCs Named according to abnormal WBC clone involved Myeloid leukemia involves myeloblast descendants Lymphocytic leukemia involves lymphocytes • Acute leukemia derives from stem cells; primarily affects children • Chronic leukemia more prevalent in older people © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Leukemia • Cancerous leukocytes fill red bone marrow – Other lines crowded out anemia; bleeding • Immature nonfunctional WBCs in bloodstream • Death from internal hemorrhage; overwhelming infections • Treatments – Irradiation, antileukemic drugs; stem cell transplants © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Infectious Mononucleosis • Highly contagious viral disease – Epstein-Barr virus • High numbers atypical agranulocytes • Symptoms – Tired, achy, chronic sore throat, low fever • Runs course with rest © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Platelets • Cytoplasmic fragments of megakaryocytes • Blue-staining outer region; purple granules • Granules contain serotonin, Ca 2+, enzymes, ADP, and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) – Act in clotting process • Normal = 150, 000 – 400, 000 platelets /ml of blood © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Platelets • Form temporary platelet plug that helps seal breaks in blood vessels • Circulating platelets kept inactive and mobile by nitric oxide (NO) and prostacyclin from endothelial cells lining blood vessels • Age quickly; degenerate in about 10 days • Formation regulated by thrombopoietin • Derive from megakaryoblast – Mitosis but no cytokinesis megakaryocyte - large cell with multilobed nucleus © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
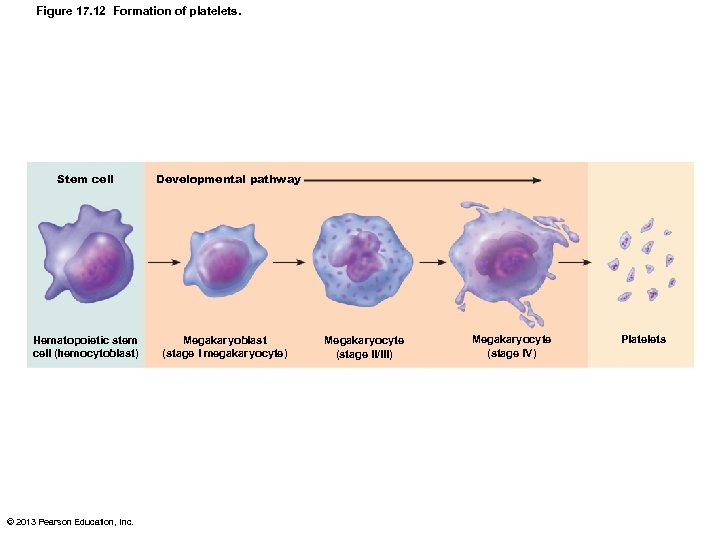
Figure 17. 12 Formation of platelets. Stem cell Hematopoietic stem cell (hemocytoblast) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Developmental pathway Megakaryoblast (stage I megakaryocyte) Megakaryocyte (stage II/III) Megakaryocyte (stage IV) Platelets
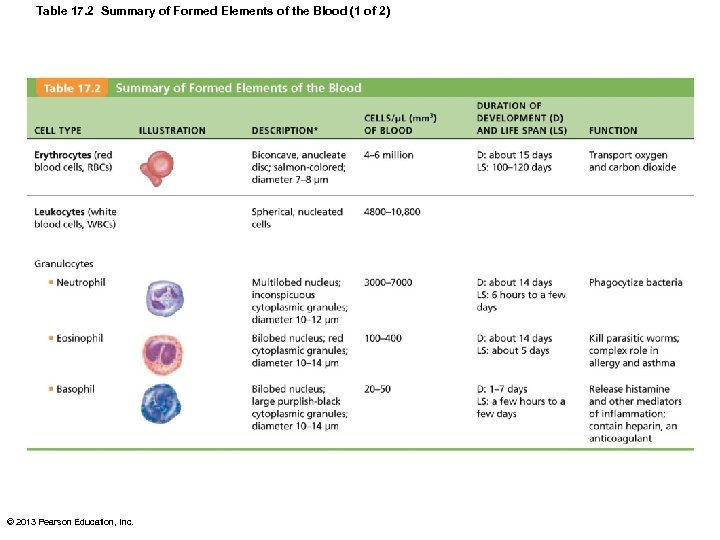
Table 17. 2 Summary of Formed Elements of the Blood (1 of 2) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
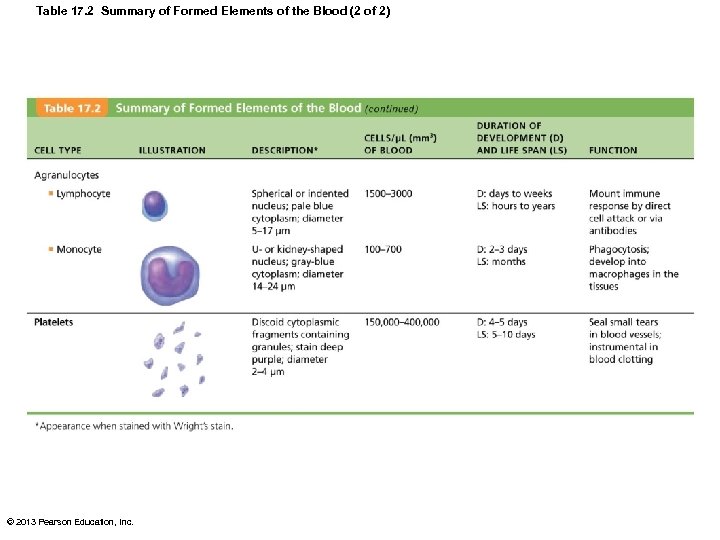
Table 17. 2 Summary of Formed Elements of the Blood (2 of 2) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Hemostasis • Fast series of reactions for stoppage of bleeding • Requires clotting factors, and substances released by platelets and injured tissues • Three steps 1. Vascular spasm 2. Platelet plug formation 3. Coagulation (blood clotting) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Hemostasis: Vascular Spasm • Vasoconstriction of damaged blood vessel • Triggers – Direct injury to vascular smooth muscle – Chemicals released by endothelial cells and platelets – Pain reflexes • Most effective in smaller blood vessels © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Hemostasis: Platelet Plug Formation • Positive feedback cycle • Damaged endothelium exposes collagen fibers – Platelets stick to collagen fibers via plasma protein von Willebrand factor – Swell, become spiked and sticky, and release chemical messengers • ADP causes more platelets to stick and release their contents • Serotonin and thromboxane A 2 enhance vascular spasm and platelet aggregation © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Hemostasis: Coagulation • Reinforces platelet plug with fibrin threads • Blood transformed from liquid to gel • Series of reactions using clotting factors (procoagulants) – # I – XIII; most plasma proteins – Vitamin K needed to synthesize 4 of them © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
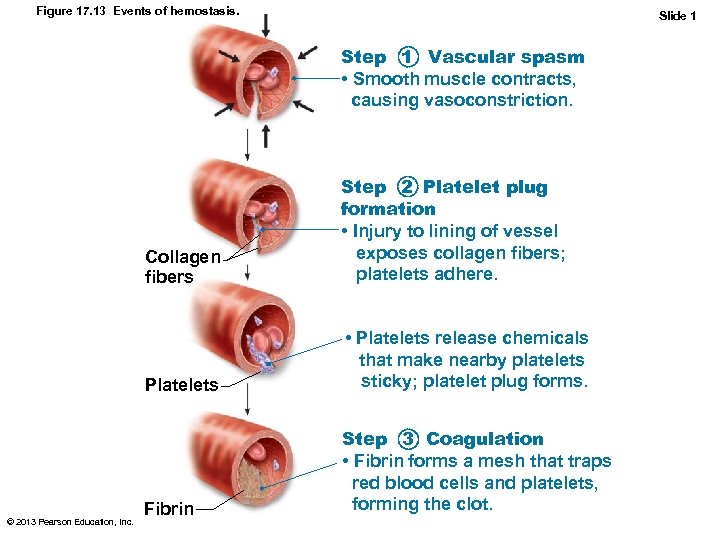
Figure 17. 13 Events of hemostasis. Slide 1 Step 1 Vascular spasm • Smooth muscle contracts, causing vasoconstriction. Collagen fibers Platelets © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Step 2 Platelet plug formation • Injury to lining of vessel exposes collagen fibers; platelets adhere. • Platelets release chemicals that make nearby platelets sticky; platelet plug forms. Fibrin Step 3 Coagulation • Fibrin forms a mesh that traps red blood cells and platelets, forming the clot.
Figure 17. 13 Events of hemostasis. Slide 2 Step 1 Vascular spasm • Smooth muscle contracts, causing vasoconstriction. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
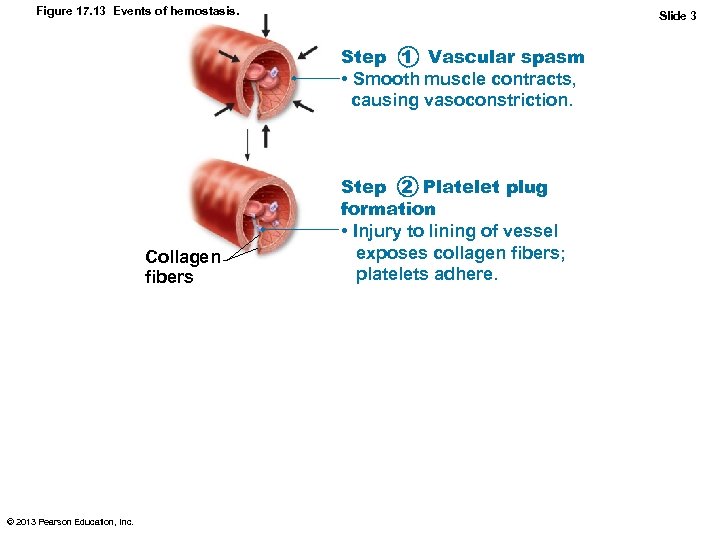
Figure 17. 13 Events of hemostasis. Slide 3 Step 1 Vascular spasm • Smooth muscle contracts, causing vasoconstriction. Collagen fibers © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Step 2 Platelet plug formation • Injury to lining of vessel exposes collagen fibers; platelets adhere.
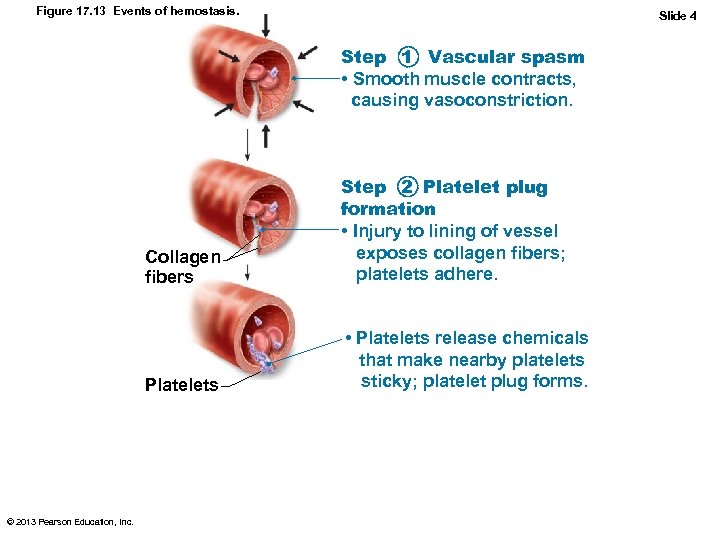
Figure 17. 13 Events of hemostasis. Slide 4 Step 1 Vascular spasm • Smooth muscle contracts, causing vasoconstriction. Collagen fibers Platelets © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Step 2 Platelet plug formation • Injury to lining of vessel exposes collagen fibers; platelets adhere. • Platelets release chemicals that make nearby platelets sticky; platelet plug forms.
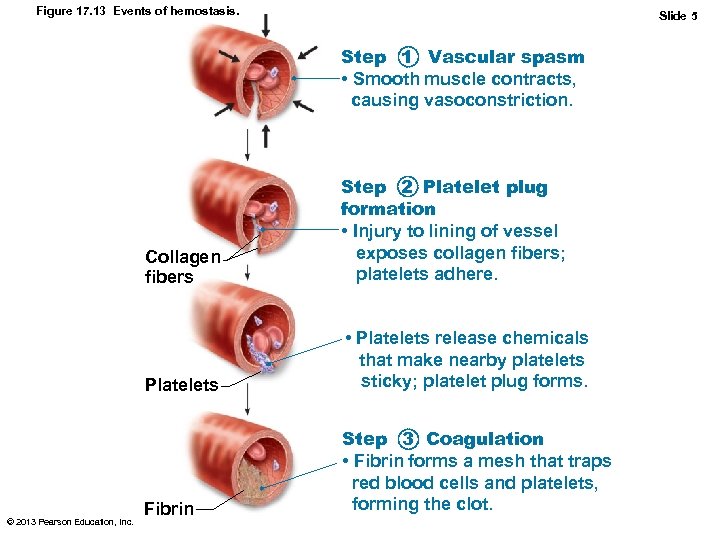
Figure 17. 13 Events of hemostasis. Slide 5 Step 1 Vascular spasm • Smooth muscle contracts, causing vasoconstriction. Collagen fibers Platelets © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Step 2 Platelet plug formation • Injury to lining of vessel exposes collagen fibers; platelets adhere. • Platelets release chemicals that make nearby platelets sticky; platelet plug forms. Fibrin Step 3 Coagulation • Fibrin forms a mesh that traps red blood cells and platelets, forming the clot.
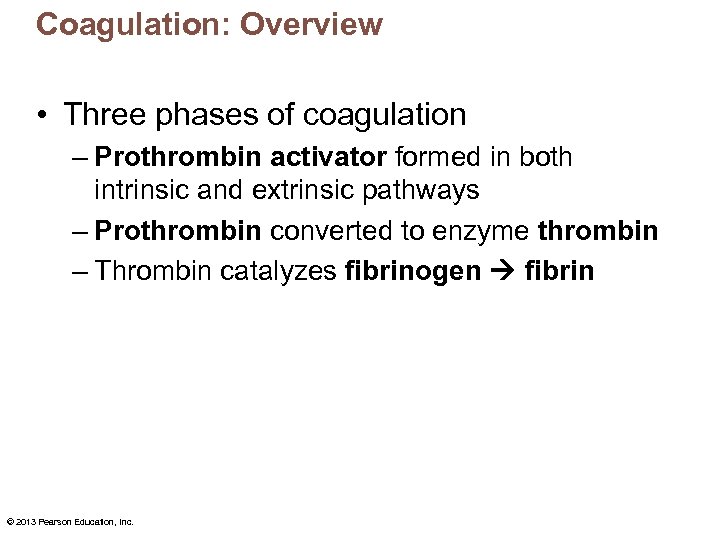
Coagulation: Overview • Three phases of coagulation – Prothrombin activator formed in both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways – Prothrombin converted to enzyme thrombin – Thrombin catalyzes fibrinogen fibrin © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Coagulation Phase 1: Two Pathways to Prothrombin Activator • Initiated by either intrinsic or extrinsic pathway (usually both) – Triggered by tissue-damaging events – Involves a series of procoagulants – Each pathway cascades toward factor X • Factor X complexes with Ca 2+, PF 3, and factor V to form prothrombin activator © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Coagulation Phase 1: Two Pathways to Prothrombin Activator • Intrinsic pathway – Triggered by negatively charged surfaces (activated platelets, collagen, glass) – Uses factors present within blood (intrinsic) • Extrinsic pathway – Triggered by exposure to tissue factor (TF) or factor III (an extrinsic factor) – Bypasses several steps of intrinsic pathway, so faster © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Coagulation Phase 2: Pathway to Thrombin • Prothrombin activator catalyzes transformation of prothrombin to active enzyme thrombin • Once prothrombin activator formed, clot forms in 10– 15 seconds © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Coagulation Phase 3: Common Pathway to the Fibrin Mesh • Thrombin converts soluble fibrinogen to fibrin • Fibrin strands form structural basis of clot • Fibrin causes plasma to become a gel-like trap formed elements • Thrombin (with Ca 2+) activates factor XIII which: – Cross-links fibrin – Strengthens and stabilizes clot © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
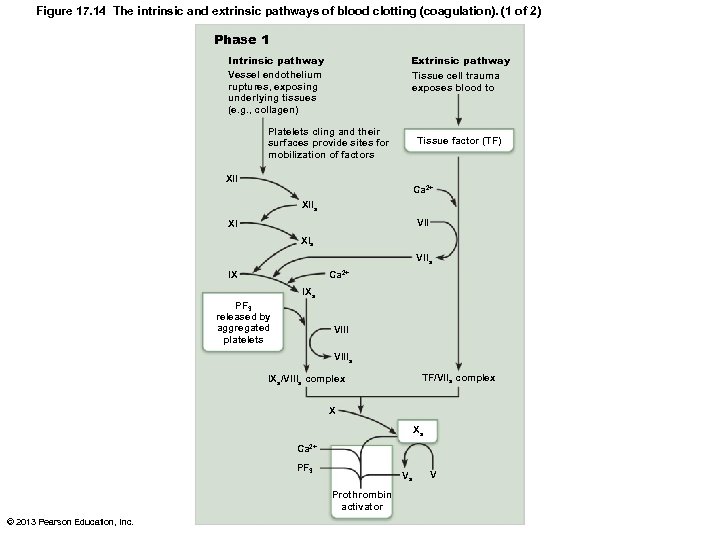
Figure 17. 14 The intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of blood clotting (coagulation). (1 of 2) Phase 1 Intrinsic pathway Vessel endothelium ruptures, exposing underlying tissues (e. g. , collagen) Extrinsic pathway Tissue cell trauma exposes blood to Platelets cling and their surfaces provide sites for mobilization of factors Tissue factor (TF) XII Ca 2+ XIIa VII XI XIa VIIa Ca 2+ IX IXa PF 3 released by aggregated platelets VIIIa TF/VIIa complex IXa/VIIIa complex X Xa Ca 2+ PF 3 Va Prothrombin activator © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. V
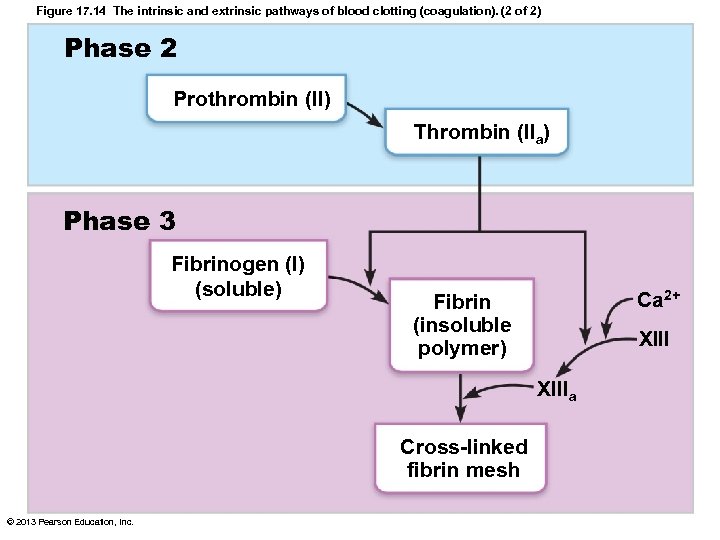
Figure 17. 14 The intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of blood clotting (coagulation). (2 of 2) Phase 2 Prothrombin (II) Thrombin (IIa) Phase 3 Fibrinogen (I) (soluble) Ca 2+ Fibrin (insoluble polymer) XIIIa Cross-linked fibrin mesh © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
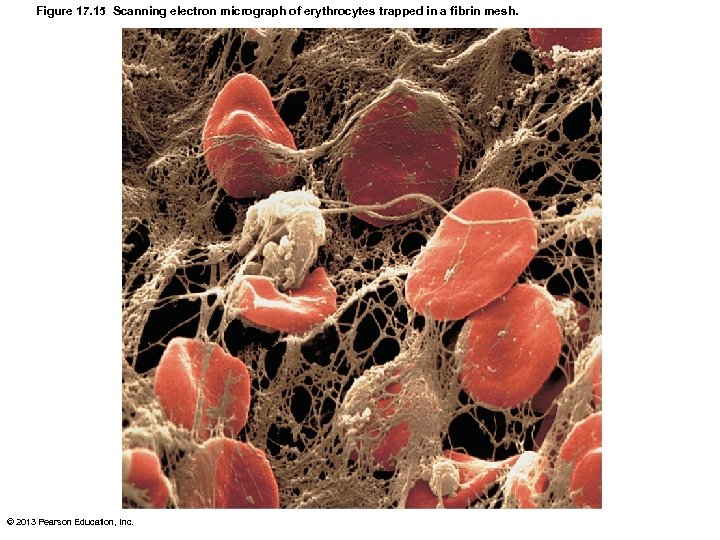
Figure 17. 15 Scanning electron micrograph of erythrocytes trapped in a fibrin mesh. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Clot Retraction • Stabilizes clot • Actin and myosin in platelets contract within 30– 60 minutes • Contraction pulls on fibrin strands, squeezing serum from clot • Draws ruptured blood vessel edges together © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Vessel Repair • Vessel is healing as clot retraction occurs • Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulates division of smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts to rebuild blood vessel wall • Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) stimulates endothelial cells to multiply and restore endothelial lining © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Fibrinolysis • Removes unneeded clots after healing • Begins within two days; continues for several • Plasminogen in clot is converted to plasmin by tissue plasminogen activator (t. PA), factor XII and thrombin • Plasmin is a fibrin-digesting enzyme © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Factors Limiting Clot Growth or Formation • Two mechanisms limit clot size – Swift removal and dilution of clotting factors – Inhibition of activated clotting factors • Thrombin bound onto fibrin threads • Antithrombin III inactivates unbound thrombin • Heparin in basophil and mast cells inhibits thrombin by enhancing antithrombin III © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Factors Preventing Undesirable Clotting • Platelet adhesion is prevented by – Smooth endothelium of blood vessels prevents platelets from clinging – Antithrombic substances nitric oxide and prostacyclin secreted by endothelial cells – Vitamin E quinone acts as potent anticoagulant © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Disorders of Hemostasis • Thromboembolic disorders: undesirable clot formation • Bleeding disorders: abnormalities that prevent normal clot formation • Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) – Involves both types of disorders © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Thromboembolic Conditions • Thrombus: clot that develops and persists in unbroken blood vessel – May block circulation leading to tissue death • Embolus: thrombus freely floating in bloodstream • Embolism: embolus obstructing a vessel – E. g. , pulmonary and cerebral emboli • Risk factors – atherosclerosis, inflammation, slowly flowing blood or blood stasis from immobility © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Anticoagulant Drugs • Aspirin – Antiprostaglandin that inhibits thromboxane A 2 • Heparin – Anticoagulant used clinically for pre- and postoperative cardiac care • Warfarin (Coumadin) – Used for those prone to atrial fibrillation – Interferes with action of vitamin K • Dabigatran directly inhibits thrombin © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Bleeding Disorders • Thrombocytopenia: deficient number of circulating platelets – Petechiae appear due to spontaneous, widespread hemorrhage – Due to suppression or destruction of red bone marrow (e. g. , malignancy, radiation, drugs) – Platelet count <50, 000/μl is diagnostic – Treated with transfusion of concentrated platelets © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Bleeding Disorders • Impaired liver function – Inability to synthesize procoagulants – Causes include vitamin K deficiency, hepatitis, and cirrhosis – Impaired fat absorption and liver disease can also prevent liver from producing bile, impairing fat and vitamin K absorption © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Bleeding Disorders • Hemophilia includes several similar hereditary bleeding disorders – Hemophilia A: most common type (77% of all cases); factor VIII deficiency – Hemophilia B: factor IX deficiency – Hemophilia C: mild type; factor XI deficiency • Symptoms include prolonged bleeding, especially into joint cavities • Treated with plasma transfusions and injection of missing factors – Increased hepatitis and HIV risk © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) • Clotting causes bleeding – Widespread clotting blocks intact blood vessels – Severe bleeding occurs because residual blood unable to clot • Occurs as pregnancy complication; in septicemia, or incompatible blood transfusions © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Transfusions • Whole-blood transfusions used when blood loss rapid and substantial • Packed red cells (plasma and WBCs removed) transfused to restore oxygencarrying capacity • Transfusion of incompatible blood can be fatal © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Human Blood Groups • RBC membranes bear 30 types of glycoprotein antigens – Anything perceived as foreign; generates an immune response – Promoters of agglutination; called agglutinogens • Mismatched transfused blood perceived as foreign – May be agglutinated and destroyed; can be fatal • Presence or absence of each antigen is used to classify blood cells into different groups © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Blood Groups • Antigens of ABO and Rh blood groups cause vigorous transfusion reactions • Other blood groups (MNS, Duffy, Kell, and Lewis) usually weak agglutinogens © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

ABO Blood Groups • Types A, B, AB, and O • Based on presence or absence of two agglutinogens (A and B) on surface of RBCs • Blood may contain preformed anti-A or anti -B antibodies (agglutinins) – Act against transfused RBCs with ABO antigens not present on recipient's RBCs • Anti-A or anti-B form in blood at about 2 months of age; adult levels by 8 -10 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
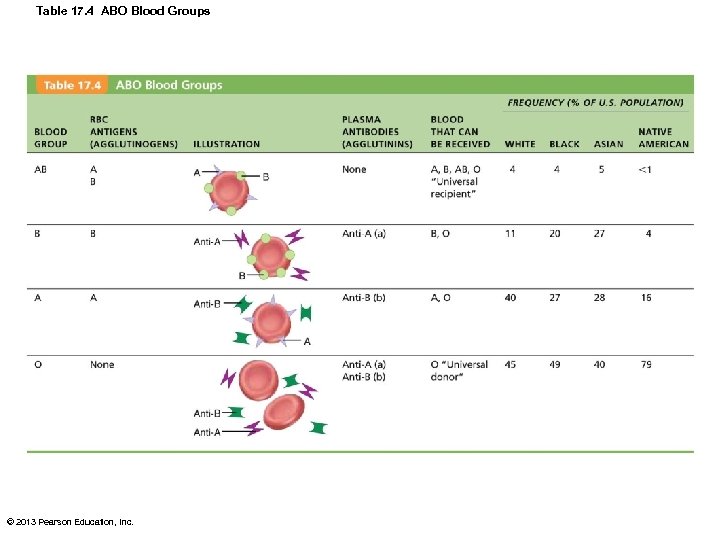
Table 17. 4 ABO Blood Groups © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Rh Blood Groups • 52 named Rh agglutinogens (Rh factors) • C, D, and E are most common • Rh+ indicates presence of D antigen – 85% Americans Rh+ © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Rh Blood Groups • Anti-Rh antibodies not spontaneously formed in Rh– individuals – Anti-Rh antibodies form if Rh– individual receives Rh+ blood, or Rh– mom carrying Rh+ fetus • Second exposure to Rh+ blood will result in typical transfusion reaction © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Homeostatic Imbalance: Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn • Also called erythroblastosis fetalis – Only occurs in Rh– mom with Rh+ fetus • Rh– mom exposed to Rh+ blood of fetus during delivery of first baby – baby healthy – Mother synthesizes anti-Rh antibodies • Second pregnancy – Mom's anti-Rh antibodies cross placenta and destroy RBCs of Rh+ baby © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Homeostatic Imbalance: Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn • Baby treated with prebirth transfusions and exchange transfusions after birth • Rho. GAM serum containing anti-Rh can prevent Rh– mother from becoming sensitized © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Transfusion Reactions • Occur if mismatched blood infused • Donor's cells – Attacked by recipient's plasma agglutinins – Agglutinate and clog small vessels – Rupture and release hemoglobin into bloodstream • Result in – Diminished oxygen-carrying capacity – Diminished blood flow beyond blocked vessels – Hemoglobin in kidney tubules renal failure © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Transfusion Reactions • Symptoms – Fever, chills, low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, nausea, vomiting • Treatment – Preventing kidney damage • Fluids and diuretics to wash out hemoglobin © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Transfusions • Type O universal donor – No A or B antigens • Type AB universal recipient – No anti-A or anti-B antibodies • Misleading - other agglutinogens cause transfusion reactions • Autologous transfusions – Patient predonates © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Before Transfusion • Blood typing – Mixing RBCs with antibodies against its agglutinogen(s) causes clumping of RBCs – Done for ABO and for Rh factor • Cross matching – Mix recipient's serum with donor RBCs – Mix recipient's RBCs with donor serum © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
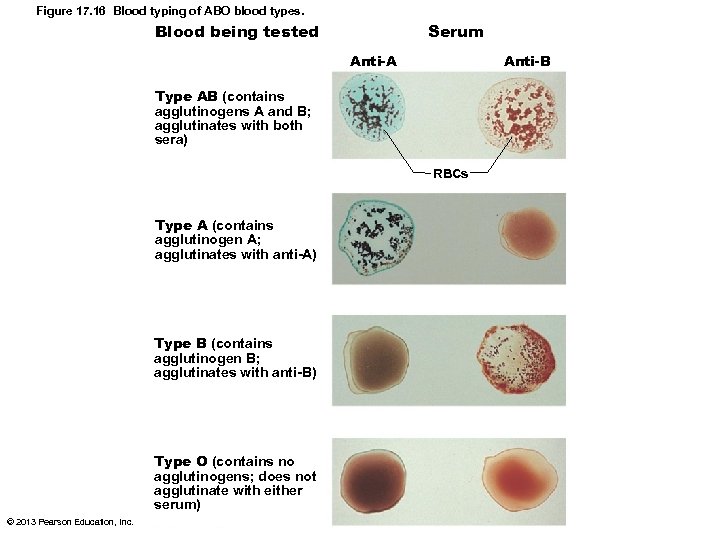
Figure 17. 16 Blood typing of ABO blood types. Serum Blood being tested Anti-B Anti-A Type AB (contains agglutinogens A and B; agglutinates with both sera) RBCs Type A (contains agglutinogen A; agglutinates with anti-A) Type B (contains agglutinogen B; agglutinates with anti-B) Type O (contains no agglutinogens; does not agglutinate with either serum) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Restoring Blood Volume • Death from shock may result from low blood volume • Volume must be replaced immediately with – Normal saline or multiple-electrolyte solution (Ringer's solution) that mimics plasma electrolyte composition – Plasma expanders (e. g. , purified human serum albumin, hetastarch, and dextran) • Mimic osmotic properties of albumin • More expensive and may cause significant complications © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Diagnostic Blood Tests • Hematocrit – test for anemia • Blood glucose tests – diabetes • Microscopic examination reveals variations in size and shape of RBCs, indications of anemias © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
Diagnostic Blood Tests • Differential WBC count • Prothrombin time and platelet counts assess hemostasis • SMAC, a blood chemistry profile – liver and kidney disorders • Complete blood count (CBC) – checks formed elements, hematocrit, hemoglobin © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Developmental Aspects • Fetal blood cells form in fetal yolk sac, liver, and spleen • Red bone marrow is primary hematopoietic area by seventh month • Blood cells develop from mesenchymal cells called blood islands • The fetus forms Hemoglobin F, which has higher affinity for O 2 than hemoglobin A formed after birth © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.

Developmental Aspects • Blood diseases of aging – Chronic leukemias, anemias, clotting disorders – Usually precipitated by disorders of heart, blood vessels, or immune system © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
12864f8cdec09a9ac33daa02d6dd98c8.ppt