b82e361eef0609d2e2ce46b244a59bb5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Power. Point Design Template Catchment based and Real-time based Permitting add your subheading By Fanlin Meng Supervisors: David Butler Guangtao Fu July 4 th, 2013 Safe and Sure Group reading meeting

Outline 1 2 Aims and objectives 3 2 Introduction Research proposals
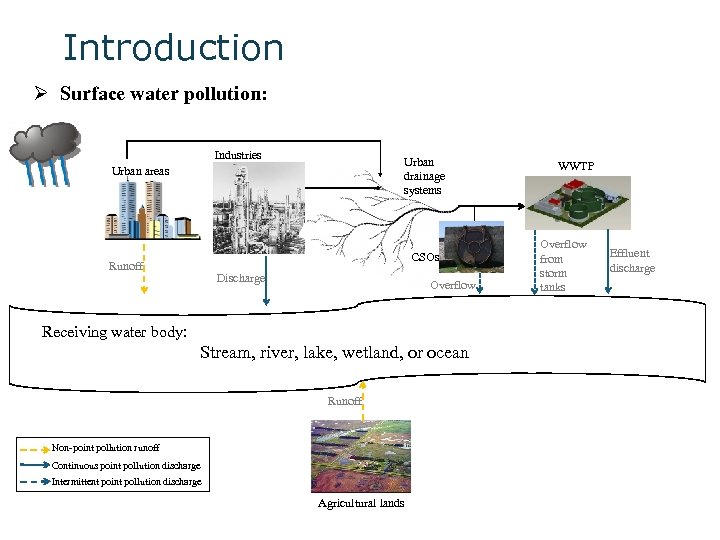
Introduction Ø Surface water pollution: Industries Urban drainage systems Urban areas CSOs Runoff Discharge Overflow Receiving water body: Stream, river, lake, wetland, or ocean Runoff Non-point pollution runoff Continuous point pollution discharge Intermittent point pollution discharge Agricultural lands WWTP Overflow from storm tanks Effluent discharge
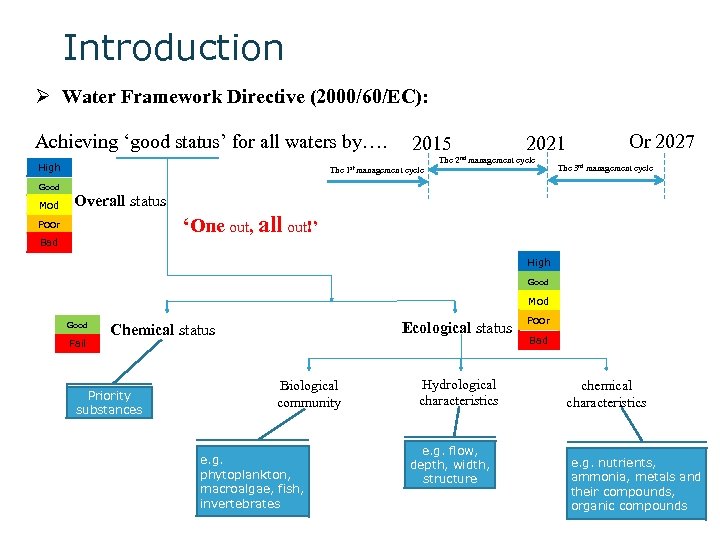
Introduction Ø Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC): Achieving ‘good status’ for all waters by…. 2015 2021 The 2 nd management cycle High The 1 st management cycle Or 2027 The 3 rd management cycle Good Mod Overall status ‘One out, all out!’ Poor Bad High Good Mod Good Fail Ecological status Chemical status Priority substances Biological community e. g. phytoplankton, macroalgae, fish, invertebrates Hydrological characteristics e. g. flow, depth, width, structure Poor Bad chemical characteristics e. g. nutrients, ammonia, metals and their compounds, organic compounds
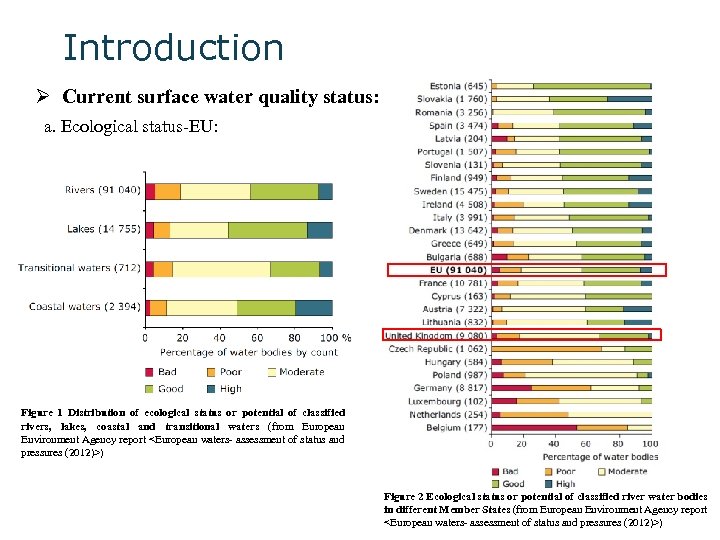
Introduction Ø Current surface water quality status: a. Ecological status-EU: Figure 1 Distribution of ecological status or potential of classified rivers, lakes, coastal and transitional waters (from European Environment Agency report <European waters- assessment of status and pressures (2012)>) Figure 2 Ecological status or potential of classified river water bodies in different Member States (from European Environment Agency report <European waters- assessment of status and pressures (2012)>)
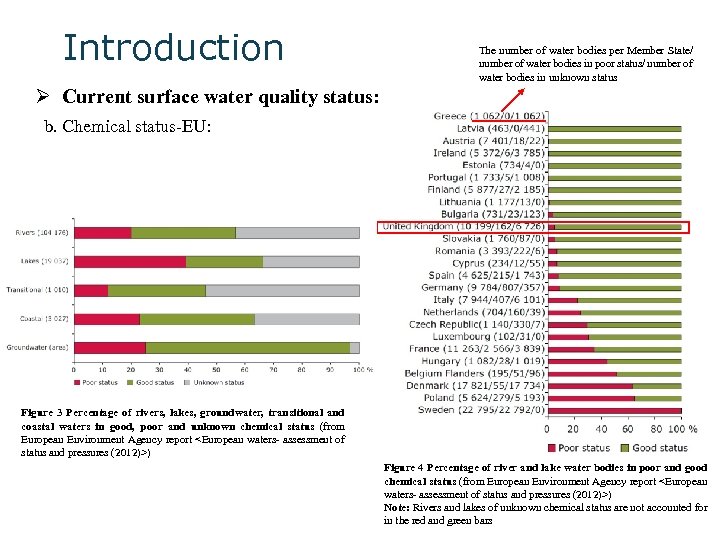
Introduction The number of water bodies per Member State/ number of water bodies in poor status/ number of water bodies in unknown status Ø Current surface water quality status: b. Chemical status-EU: Figure 3 Percentage of rivers, lakes, groundwater, transitional and coastal waters in good, poor and unknown chemical status (from European Environment Agency report <European waters- assessment of status and pressures (2012)>) Figure 4 Percentage of river and lake water bodies in poor and good chemical status (from European Environment Agency report <European waters- assessment of status and pressures (2012)>) Note: Rivers and lakes of unknown chemical status are not accounted for in the red and green bars
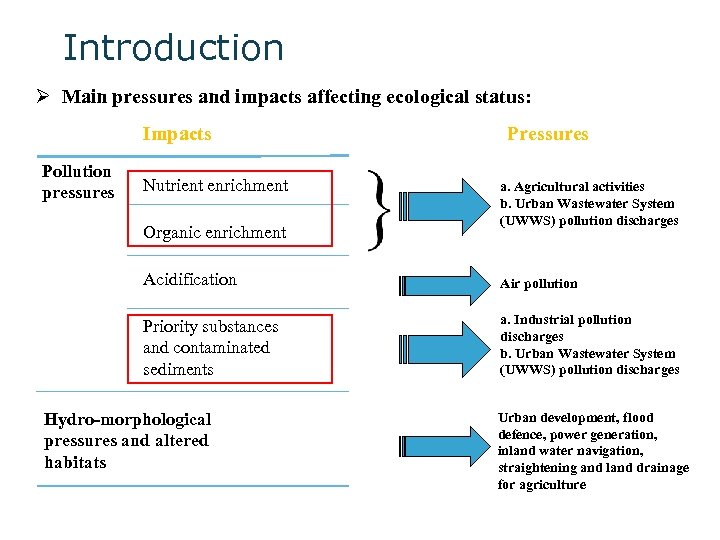
Introduction Ø Main pressures and impacts affecting ecological status: Impacts Pollution pressures Nutrient enrichment Organic enrichment Pressures a. Agricultural activities b. Urban Wastewater System (UWWS) pollution discharges Acidification Air pollution Priority substances and contaminated sediments a. Industrial pollution discharges b. Urban Wastewater System (UWWS) pollution discharges Hydro-morphological pressures and altered habitats Urban development, flood defence, power generation, inland water navigation, straightening and land drainage for agriculture
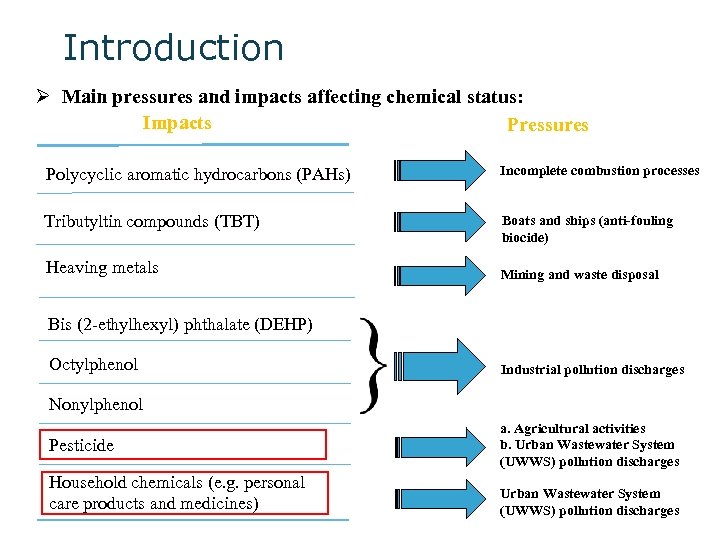
Introduction Ø Main pressures and impacts affecting chemical status: Impacts Pressures Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) Incomplete combustion processes Tributyltin compounds (TBT) Boats and ships (anti-fouling biocide) Heaving metals Mining and waste disposal Bis (2 -ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) Octylphenol Industrial pollution discharges Nonylphenol Pesticide Household chemicals (e. g. personal care products and medicines) a. Agricultural activities b. Urban Wastewater System (UWWS) pollution discharges
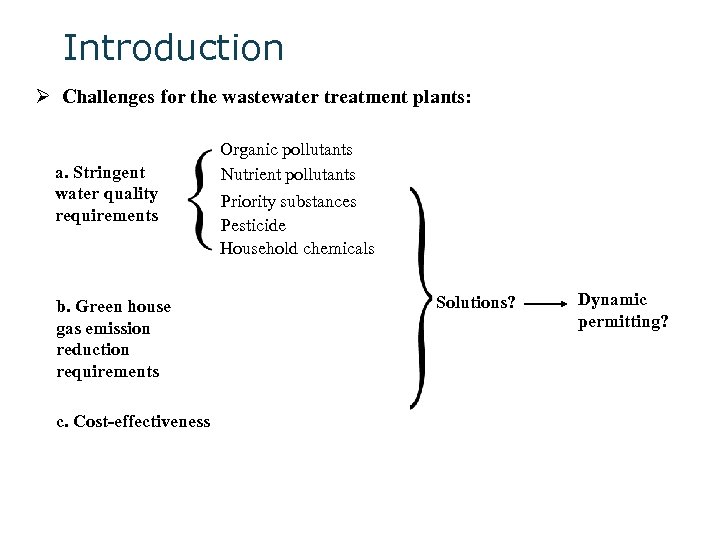
Introduction Ø Challenges for the wastewater treatment plants: a. Stringent water quality requirements b. Green house gas emission reduction requirements c. Cost-effectiveness Organic pollutants Nutrient pollutants Priority substances Pesticide Household chemicals Solutions? Dynamic permitting?

Outline 1 2 Aims and objectives 3 10 Introduction Research proposals

Aims and objectives Aim: The project aims to explore the advantages and disadvantages of the catchment based and real-time-based permitting in an integrated urban wastewater system. Objectives: o. Review on the existing permitting policies in England Wales, and other typical areas/countries; o. Try potential real-time controls on the Benchmark case to acquire the relationships between control variables/effluent quality/operation cost/GHG emission; o. Establish the integrated urban wastewater system model for a real-life case and conduct the dynamic permitting research; o. Draft a guideline for the innovative permitting approaches; o. Write up the degree thesis and the journal and conference papers; o. Courses, trainings and conferences; 11

Outline 1 2 Aims and objectives 3 12 Introduction Research proposals
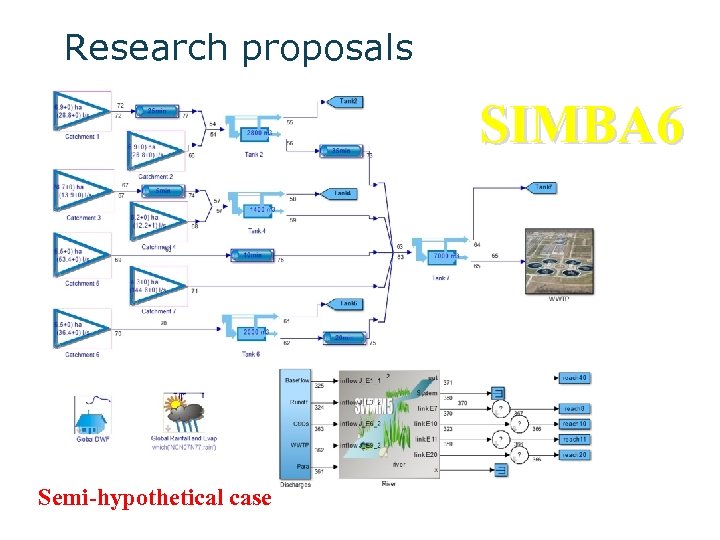
Research proposals SIMBA 6 Semi-hypothetical case
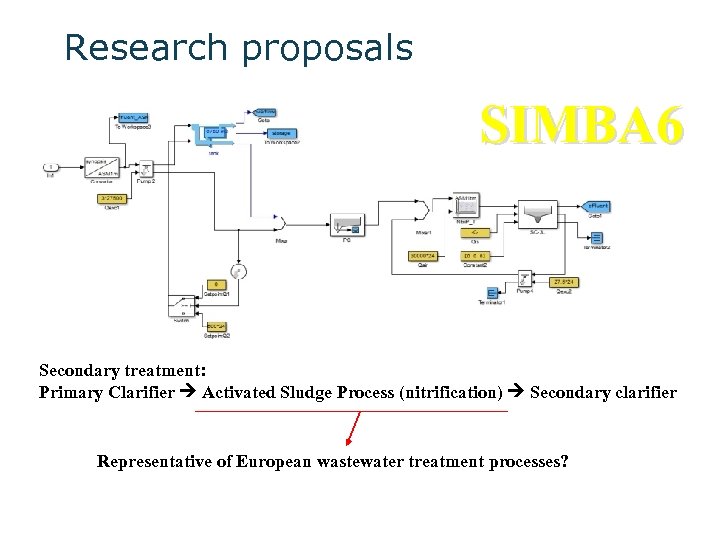
Research proposals SIMBA 6 Secondary treatment: Primary Clarifier Activated Sludge Process (nitrification) Secondary clarifier Representative of European wastewater treatment processes?
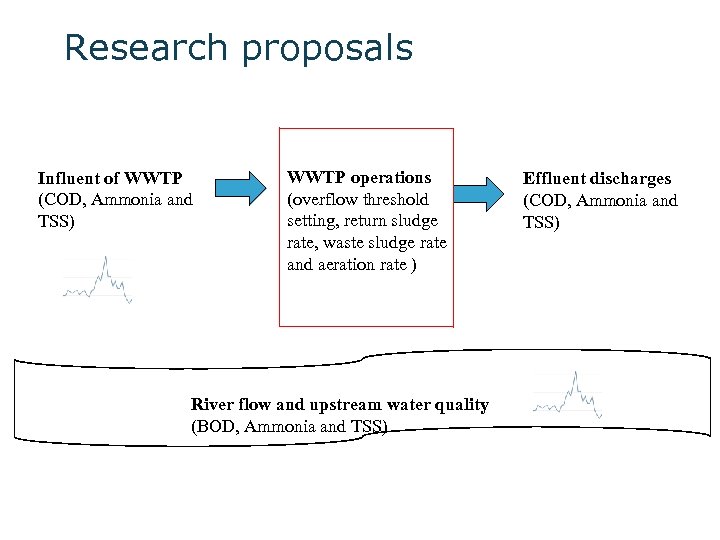
Research proposals Influent of WWTP (COD, Ammonia and TSS) WWTP operations (overflow threshold setting, return sludge rate, waste sludge rate and aeration rate ) River flow and upstream water quality (BOD, Ammonia and TSS) Effluent discharges (COD, Ammonia and TSS)

Thank you! SANITAS Project progress meeting
b82e361eef0609d2e2ce46b244a59bb5.ppt