fd0a05924436326065bbdbfafd74f238.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 80

POWER MARKETS IN INDIA RAHUL BANERJEE SENIOR ADVISER , POWER MARKETS CERC Disclaimer : These are the person views of the Speaker 3/19/2018

We shall cover … Market Related Sections in Electricity Act Power Market Structure in India Market Regulations of CERC Power Market Data Regulators Role in Market Development International Power Markets Market Related Discussion Points 3/19/2018

How to view electricity ? Is electricity to be treated as a public good with universal service obligation of the state or is it a should be treated like a commodity and work on market based principles ? Double sided bidding or supply side bidding ? Unique Commodity- Higher Risk ? ◦ ◦ Consumer as soon as produced Network to Transmit Network Code – Operation flexibility lower Banker look for long term contracts 3/19/2018

Electricity Act 2003 Foundation stone for creation of a modern electricity industry Flows from overall liberalization of Indian economy 1948 act was a nationalization of electricity -to supply to semi urban and rural areas , created monolithic SEB and financial losses followed Created a new industry structure – unbundling of SEB , private sector, competition , open access , regulatory commissions New law, multiple interpretation , takes time to settle 3/19/2018
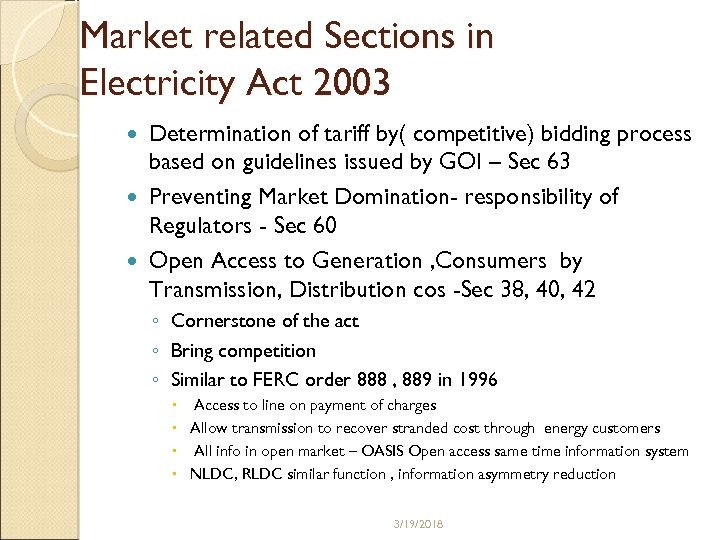
Market related Sections in Electricity Act 2003 Determination of tariff by( competitive) bidding process based on guidelines issued by GOI – Sec 63 Preventing Market Domination- responsibility of Regulators - Sec 60 Open Access to Generation , Consumers by Transmission, Distribution cos -Sec 38, 40, 42 ◦ Cornerstone of the act ◦ Bring competition ◦ Similar to FERC order 888 , 889 in 1996 Access to line on payment of charges Allow transmission to recover stranded cost through energy customers All info in open market – OASIS Open access same time information system NLDC, RLDC similar function , information asymmetry reduction 3/19/2018
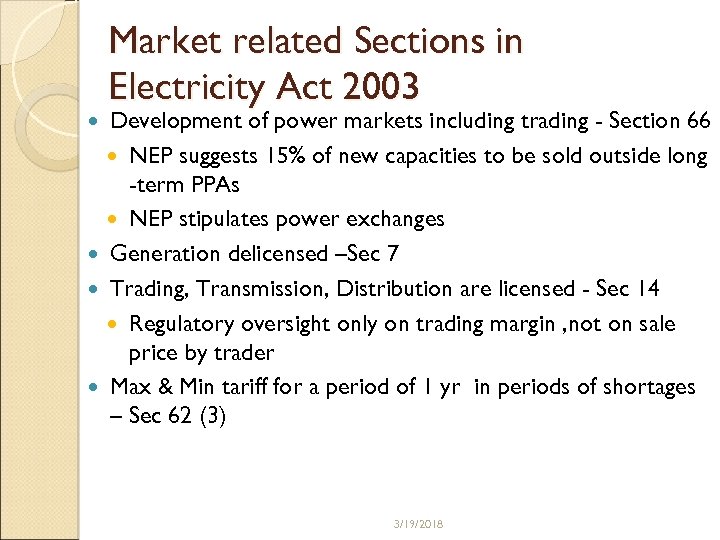
Market related Sections in Electricity Act 2003 Development of power markets including trading - Section 66 NEP suggests 15% of new capacities to be sold outside long -term PPAs NEP stipulates power exchanges Generation delicensed –Sec 7 Trading, Transmission, Distribution are licensed - Sec 14 Regulatory oversight only on trading margin , not on sale price by trader Max & Min tariff for a period of 1 yr in periods of shortages – Sec 62 (3) 3/19/2018

Why have a Power Market ? Markets - Ultimate payment security mechanism -superior to government guarantee ◦ Induces price risk , Reduces liquidity risk Risk Mitigation mechanism –from take or pay contracts ◦ Liquidity improves valuation of companies as risk reduces ◦ Cost of capital reduces as alternative platform to sell available Price acts as signal for new investments Merchant Power capacity and private sector investment Match short-term surplus with demand variation in a diverse country – optimal asset utilization Bring latent generation capacity - captive power plants to market 3/19/2018

Why have a power market ? Liquidity reduces business risk Increases price volatility Access to markets - Open Access – Key to competition ◦ Alternative to consumers - by using open access ◦ Industrial consumers getting access through PX and technology 3/19/2018

The shift Till 1980’s-Government promoted ◦ Capital Investment 1990’s -Government guaranteed PPA ◦ Single buyer 2003 onwards - Market based ◦ Multiple buyers and sellers ◦ Market is the risk mitigation ◦ Exit from contract in case of default Should not be abused 3/19/2018
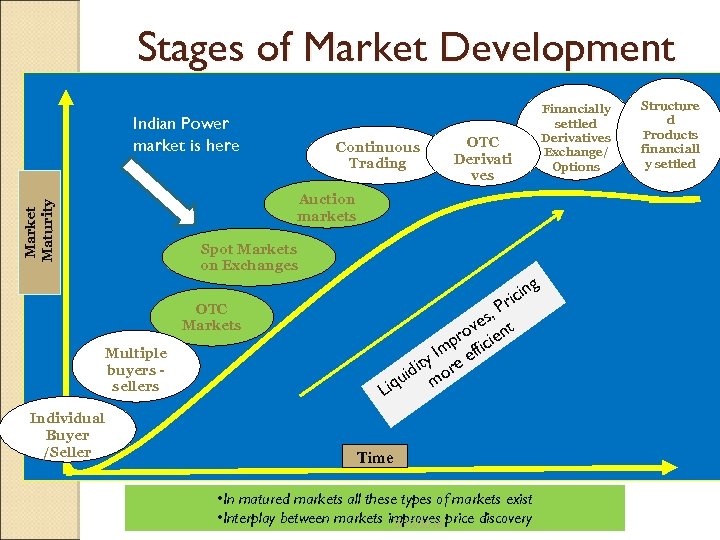
Stages of Market Development Indian Power market is here Continuous Trading OTC Derivati ves Market Maturity Auction markets Spot Markets on Exchanges g n ici r , P es t ov n pr ficie m y I re ef t idi o u m OTC Markets Multiple buyers sellers Individual Buyer /Seller Financially settled Derivatives Exchange/ Options Liq Time • In matured markets all these types of markets exist • Interplay between markets improves price discovery 3/19/2018 Structure d Products financiall y settled
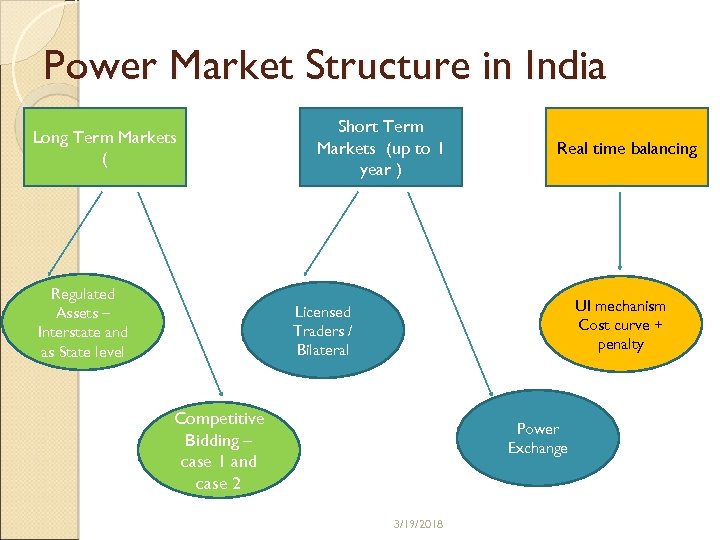
Power Market Structure in India Long Term Markets ( Regulated Assets – Interstate and as State level Short Term Markets (up to 1 year ) Real time balancing UI mechanism Cost curve + penalty Licensed Traders / Bilateral Competitive Bidding – case 1 and case 2 Power Exchange 3/19/2018
Different Types of Market Energy Market ◦ We do not have pure energy and capacity markets Capacity Market ◦ Case 1 Case 2 are Capacity and Energy Markets ◦ New Case 2 SBD is a pure capacity market ◦ Day ahead in some sense Real Time market ◦ UI , but is based on marginal cost of the fuel Transmission Market 3/19/2018
Capacity Markets Generators risk for project financing is taken care of Recovers his fixed cost , DSCR, ROE How to price capacity – is a real call option ◦ Buyer asks for electricity to be scheduled whenever the day ahead price is higher than the variable cost of this generators Fuel cost is a pass through to DISCOM Fuel cost is 60 % of total power cost Can be an alternative to Power Derivatives ? 3/19/2018
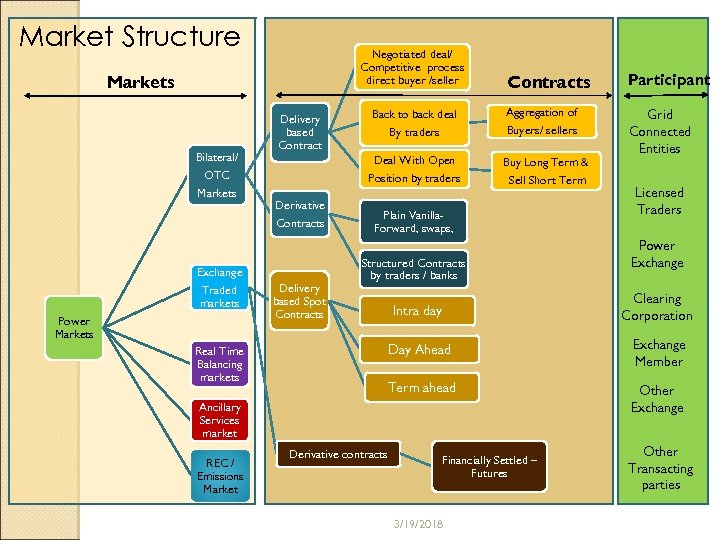
Market Structure Negotiated deal/ Competitive process direct buyer /seller Bilateral/ OTC Markets Derivative Contracts Exchange Traded markets Power Markets Delivery based Spot Contracts Participant Back to back deal By traders Aggregation of Buy Long Term & Grid Connected Entities Position by traders Delivery based Contracts Deal With Open Markets Sell Short Term Buyers/ sellers Plain Vanilla. Forward, swaps, Structured Contracts by traders / banks Power Exchange Intra day Clearing Corporation Day Ahead Exchange Member Term ahead Real Time Balancing markets Other Exchange Ancillary Services market REC / Emissions Market Licensed Traders Derivative contracts Financially Settled – Futures 3/19/2018 Other Transacting parties

Some Features of Short Term Power Markets Trading licensees (44) – Top 5 control 80 % of market HHI Index to monitor market power Traders also facilitating investments in new capacities New smaller category created to penetrate market Two Power exchanges - electronic platform for day ahead markets , week ahead markets , intra day (Similar to Nordpool) Assured payment security and risk management Prices Dissemination across country Reduce information asymmetry Provide equal bargaining power to all players in a supply deficit environment 3/19/2018

Short Term vs Long term Contract Utilities can enter into long term contracts for their future demand projections and in case demand does not grow as per their anticipation can sell any extra supply in the short term market as a part of their portfolio management System Operation - Large volume of short term transaction creates congestion in transmission due to unplanned power flow 3/19/2018

Short Term vs Long Term Contract - ST Acts as a payment security mechanism in case of default in long term contracts ST- Generation resource optimization and helps transfer power from surplus to deficit region in a geographically seasonally diverse country like India Is short term market a procurement market or a balancing market? Utilities to decided their own expectation of the market prices and demand projections. In long term contracts , utilities are stuck to a technology Long term contracts help to bring certainty of cash flow and are necessary for making projects bankable Long term contract can be done only if , contacts on fuel side can be done , else risk not mitigated , chance of contract reneging 3/19/2018

Regulations 3/19/2018

Trading Margin Regulation Trading - a licensed activity - Capital adequacy needed as taking risk on behalf of participants ◦ Networth , Liquidity criteria ◦ Capital intensive players absorb credit risk of DISCOM, risk mitigation for suppliers Trading margin imposed by regulator ◦ To ensure prices do not increase much ◦ Stymies innovation as there is no incentive to innovate and structure deals No margin on long term transactions Credit risk has gone up significantly for trader recently ◦ Liquidity and working capital constraint ◦ Bank not lending to Dicsom Margin on Short Term Transactions ◦ 4 paisa margin if power price less than Rs 3/kwh ◦ 7 Paisa margin if power price more than Rs 3/kwh 3/19/2018
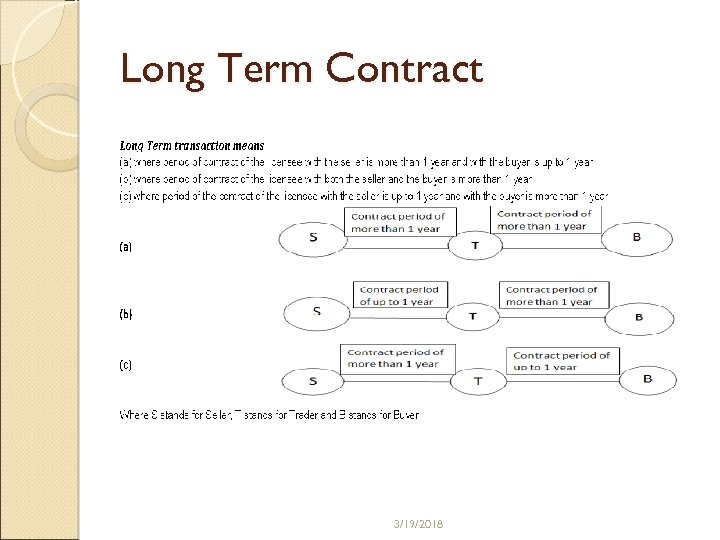
Long Term Contract 3/19/2018

Procedure, Terms and Conditions for grant of trading licence and other related matters Regulations, 2009 Notified in 24. 02. 2009 3 Amendments ◦ 16. 10. 2009 – Intra state removed ◦ 02. 06. 2010 – Category 4 added ◦ 11. 10. 2012 Inter state License also includes Intra. State trading as per Rule No. 9 of the Electricity Rules, 2005 already provides for it. 3/19/2018
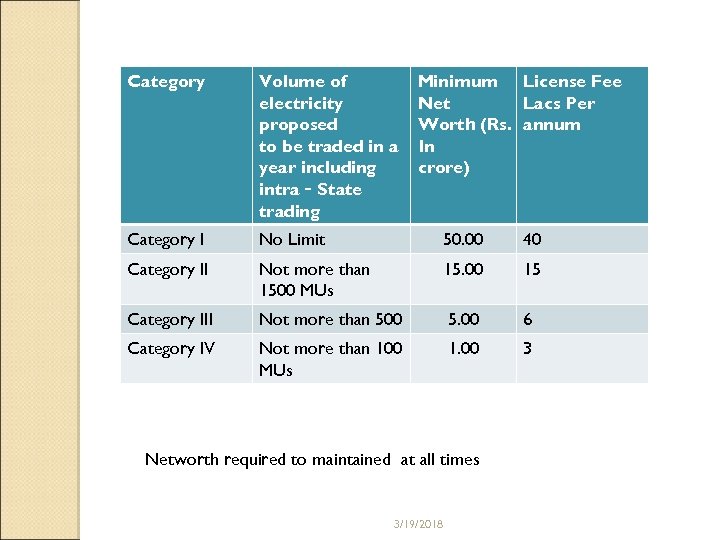
Category Volume of electricity proposed to be traded in a year including intra‐State trading Minimum License Fee Net Lacs Per Worth (Rs. annum In crore) Category I No Limit 50. 00 40 Category II Not more than 1500 MUs 15. 00 15 Category III Not more than 500 5. 00 6 Category IV Not more than 100 MUs 1. 00 3 Networth required to maintained at all times 3/19/2018

Salient Provisions Technical Qualification for availing Trading Licence- At least 1 full time professional possessing following qualification ◦ 10 years experience in power systems, engineering qualification ◦ 5 years in Finance commerce- CA/ ICWA/ MBA Finance Publication of license in newspaper as public notice Volume limit for a category inclusive of intra-state trade volume Networth requirement for both existing and new companies would be for last one year while applying for the licence Up-gradation of licence to a higher category without publication process as due diligence already completed Disgorgement of excess profit charged 3/19/2018

Salient Provisions Regulatory Audit of account in case necessary Intrastate reporting Deemed license to submit trading reports Contravention and Penalties defined into serious and non serous categories ◦ Warning to debarring upto 6 months 3/19/2018

Power Market Regulation Market Structure Market design and principles Power Exchange ◦ Approval, Prudential Norms ◦ Various Committees for governance ◦ Trading Systems ◦ Risk management and Default Settlement Market Oversight ◦ Market monitoring ◦ Reports and analysis 3/19/2018

Principles Of Market & Market Design Ø
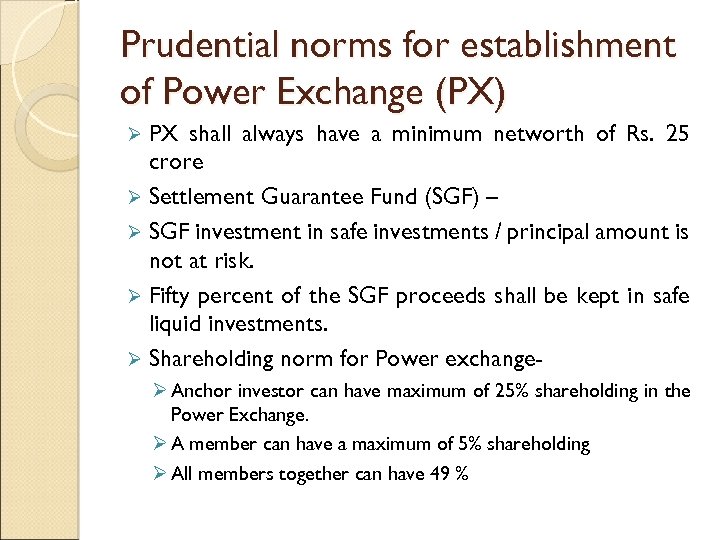
Prudential norms for establishment of Power Exchange (PX) PX shall always have a minimum networth of Rs. 25 crore Ø Settlement Guarantee Fund (SGF) – Ø SGF investment in safe investments / principal amount is not at risk. Ø Fifty percent of the SGF proceeds shall be kept in safe liquid investments. Ø Shareholding norm for Power exchangeØ Ø Anchor investor can have maximum of 25% shareholding in the Power Exchange. Ø A member can have a maximum of 5% shareholding Ø All members together can have 49 %
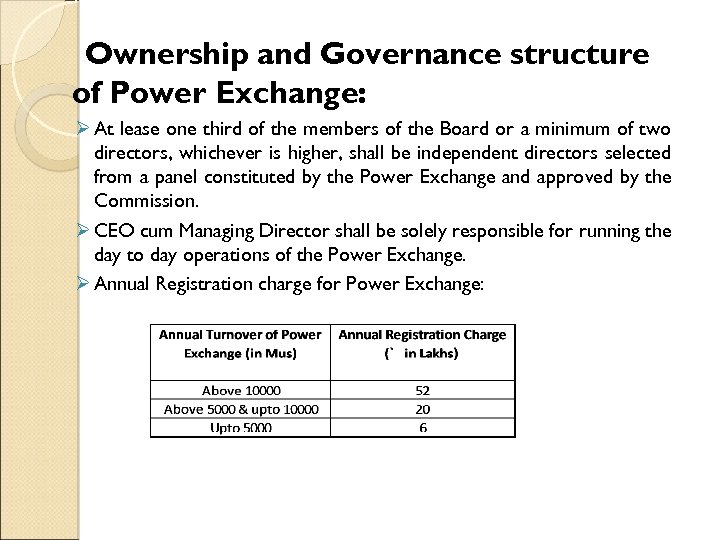
Ownership and Governance structure of Power Exchange: Ø At lease one third of the members of the Board or a minimum of two directors, whichever is higher, shall be independent directors selected from a panel constituted by the Power Exchange and approved by the Commission. Ø CEO cum Managing Director shall be solely responsible for running the day to day operations of the Power Exchange. Ø Annual Registration charge for Power Exchange:

Management of Power Exchange: Ø 2 Senior Management professional with ◦ 10 years experience in power systems, engineering qualification ◦ 5 years in Finance commerce- CA/ ICWA/ MBA Finance Ø Power Exchange shall constitute a Ø Risk Management Committee Ø Market Surveillance Committee Ø headed by an independent director Ø SGF management committee with adequate representation from members of Ø Exit policy predefined Ø No uncertainty for market participnats

Membership in Power Exchange Membership Categories: 1. Electricity Trader 2. Distribution licensee including deemed distribution licensee or a grid connected entity 3. Advisory Member Ø Member service charge shall not be more than 0. 75% of transaction value Ø Electricity traders margin will be as per trading margin Regulations

Information Technology Infrastructure and Trading System of PX Ø Audit of software application used for price discovery Ø Periodic IT system audit for data security, data integrity and operational efficiency and submit its reports to Commission annually Ø Disaster recovery site and alternate trading facility in case of emergency

Information dissemination by Power Exchange ØPrices, volumes and historic prices shall be made available on the website of the Exchange and should be in downloadable format. ØAn Exchange shall report price, transaction volume, buyers and sellers on its platform on monthly basis. Ø Whistle blower policy

Power Exchange Multiple power exchange model Voluntary participation Demutualised and Ring fenced Public interest independent directors For profit organizations- Market operator Co ordinate with system operator Two Power Exchanges operational , 3 rd in principle approval Electronic platforms Transparent price discovery and anonymous bidding Equal bargaining power to buyer and seller ◦ In a supply deficit market Helped in introducing open access at ground level Technology has acted as a great leveler ◦ Large participation , different from other markets where only wholesaler participates 3/19/2018

Power Exchange Standardized products High Liquidity ◦ Pricing improves Standardized risk management Electronic price dissemination ◦ Quick and nation wide ◦ Reduces information asymmetry 3/19/2018

Transmission Congestion How frequently congestion is happening ◦ Congestion has occurred every day in December 2012 and in all 15 minute time blocks every day How much flow is getting restricted due to congestion ◦ ((Uncongested volume cleared – Volume cleared taking into consideration congestion) / Volume cleared taking into consideration congested ) X 100 3/19/2018
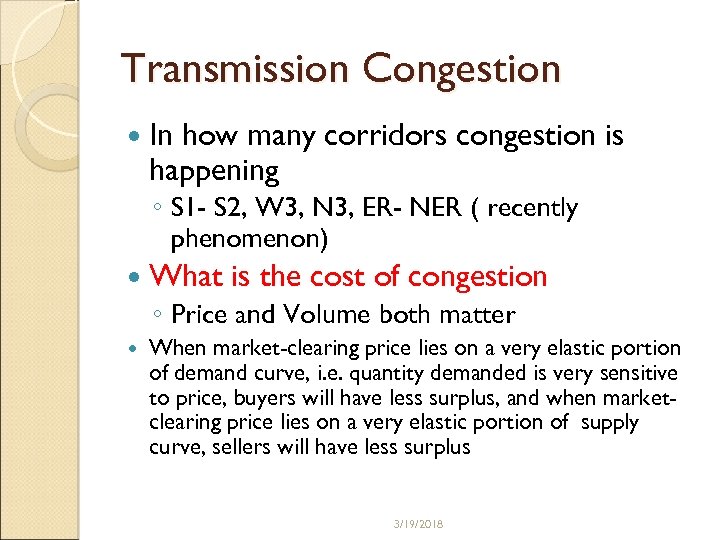
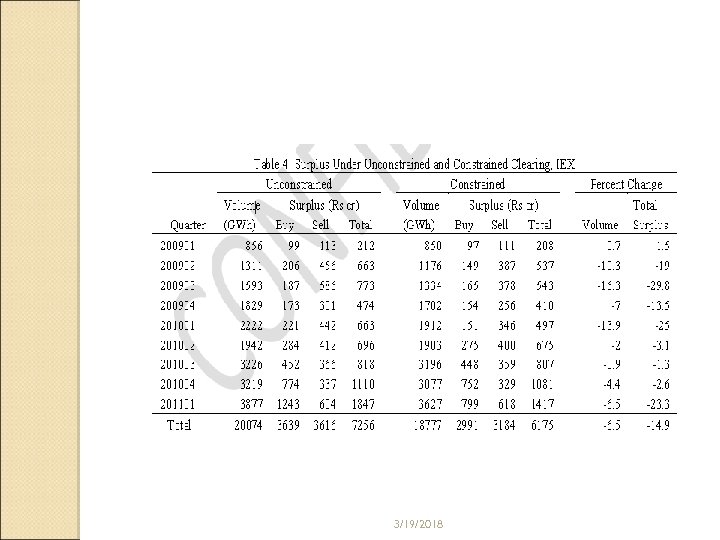
Transmission Congestion In how many corridors congestion is happening ◦ S 1 - S 2, W 3, N 3, ER- NER ( recently phenomenon) What is the cost of congestion ◦ Price and Volume both matter When market-clearing price lies on a very elastic portion of demand curve, i. e. quantity demanded is very sensitive to price, buyers will have less surplus, and when marketclearing price lies on a very elastic portion of supply curve, sellers will have less surplus 3/19/2018
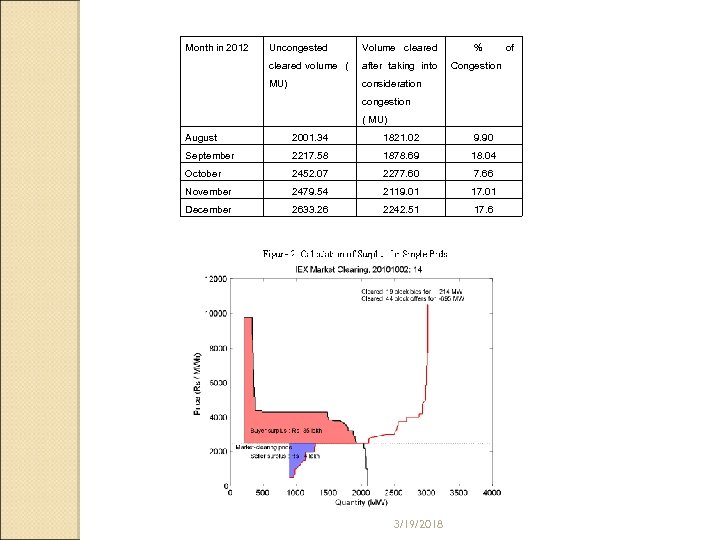
Month in 2012 Uncongested Volume cleared % cleared volume ( after taking into Congestion MU) consideration congestion ( MU) August 2001. 34 1821. 02 9. 90 September 2217. 58 1878. 69 18. 04 October 2452. 07 2277. 60 7. 66 November 2479. 54 2119. 01 17. 01 December 2633. 26 2242. 51 17. 6 3/19/2018 of
3/19/2018
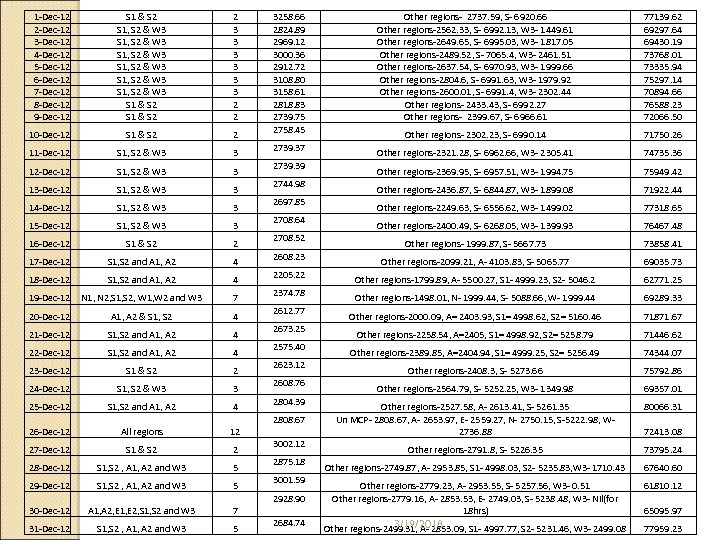
1 -Dec-12 2 -Dec-12 3 -Dec-12 4 -Dec-12 5 -Dec-12 6 -Dec-12 7 -Dec-12 8 -Dec-12 9 -Dec-12 S 1 & S 2 S 1, S 2 & W 3 S 1, S 2 & W 3 S 1 & S 2 2 3 3 3 2 2 10 -Dec-12 S 1 & S 2 2 11 -Dec-12 12 -Dec-12 13 -Dec-12 14 -Dec-12 15 -Dec-12 16 -Dec-12 17 -Dec-12 18 -Dec-12 19 -Dec-12 S 1, S 2 & W 3 S 1, S 2 & W 3 S 1 & S 2 S 1, S 2 and A 1, A 2 N 1, N 2, S 1, S 2, W 1, W 2 and W 3 3 3 2 4 4 7 20 -Dec-12 A 1, A 2 & S 1, S 2 4 21 -Dec-12 S 1, S 2 and A 1, A 2 4 22 -Dec-12 S 1, S 2 and A 1, A 2 4 23 -Dec-12 S 1 & S 2 2 24 -Dec-12 25 -Dec-12 26 -Dec-12 27 -Dec-12 28 -Dec-12 29 -Dec-12 30 -Dec-12 31 -Dec-12 S 1, S 2 & W 3 S 1, S 2 and A 1, A 2 All regions S 1 & S 2 S 1, S 2 , A 1, A 2 and W 3 A 1, A 2, E 1, E 2, S 1, S 2 and W 3 S 1, S 2 , A 1, A 2 and W 3 3 4 12 2 5 5 7 5 3258. 66 2824. 89 2969. 12 3000. 36 2912. 72 3108. 80 3158. 61 2818. 83 2739. 75 2758. 45 Other regions- 2737. 59, S- 6920. 66 Other regions-2562. 33, S- 6992. 13, W 3 - 1449. 61 Other regions-2649. 65, S- 6995. 03, W 3 - 1817. 05 Other regions-2489. 52, S- 7065. 4, W 3 - 2461. 51 Other regions-2637. 54, S- 6970. 93, W 3 - 1999. 66 Other regions-2804. 6, S- 6991. 63, W 3 - 1979. 92 Other regions-2600. 01, S- 6991. 4, W 3 - 2302. 44 Other regions- 2433. 43, S- 6992. 27 Other regions- 2399. 67, S- 6966. 61 77139. 62 69297. 64 69430. 19 73768. 01 73335. 94 75297. 14 70894. 66 76588. 23 72066. 50 Other regions- 2302. 23, S- 6990. 14 71750. 26 Other regions-2321. 28, S- 6962. 66, W 3 - 2305. 41 74735. 36 Other regions-2369. 95, S- 6957. 51, W 3 - 1994. 75 75949. 42 Other regions-2436. 87, S- 6844. 87, W 3 - 1899. 08 71922. 44 Other regions-2249. 63, S- 6556. 62, W 3 - 1499. 02 77318. 65 Other regions-2400. 49, S- 6268. 05, W 3 - 1399. 93 76467. 48 Other regions- 1999. 87, S- 5667. 73 73858. 41 Other regions-2099. 21, A- 4103. 83, S- 5065. 77 69035. 73 Other regions-1799. 89, A- 5500. 27, S 1 - 4999. 23, S 2 - 5046. 2 62771. 25 Other regions-1498. 01, N- 1999. 44, S- 5088. 66, W- 1999. 44 69289. 33 Other regions-2000. 09, A= 2403. 93, S 1= 4998. 62, S 2= 5160. 46 71871. 67 Other regions-2258. 54, A=2405, S 1= 4998. 92, S 2= 5258. 79 71446. 62 Other regions-2389. 85, A=2404. 94, S 1= 4999. 25, S 2= 5256. 49 74344. 07 Other regions-2408. 3, S- 5273. 66 75792. 86 Other regions-2564. 79, S- 5252. 25, W 3 - 1349. 98 69357. 01 Other regions-2527. 58, A- 2613. 41, S- 5261. 35 Un MCP- 2808. 67, A- 2653. 97, E- 2559. 27, N- 2750. 15, S-5222. 98, W 2736. 88 80066. 31 Other regions-2791. 8, S- 5226. 35 73795. 24 Other regions-2749. 87, A- 2953. 85, S 1 - 4998. 03, S 2 - 5235. 83, W 3 - 1710. 43 67640. 60 Other regions-2779. 23, A- 2953. 55, S- 5257. 56, W 3 - 0. 51 Other regions-2779. 16, A- 2853. 53, E- 2749. 03, S- 5238. 48, W 3 - Nil(for 18 hrs) 61810. 12 2928. 90 2684. 74 3/19/2018 Other regions-2499. 31, A- 2853. 09, S 1 - 4997. 77, S 2 - 5231. 46, W 3 - 2499. 08 2739. 37 2739. 39 2744. 98 2697. 85 2708. 64 2708. 52 2608. 23 2205. 22 2374. 78 2612. 77 2673. 25 2575. 40 2623. 12 2608. 76 2804. 39 2808. 67 3002. 12 2875. 18 3001. 59 72413. 08 65095. 97 77959. 23
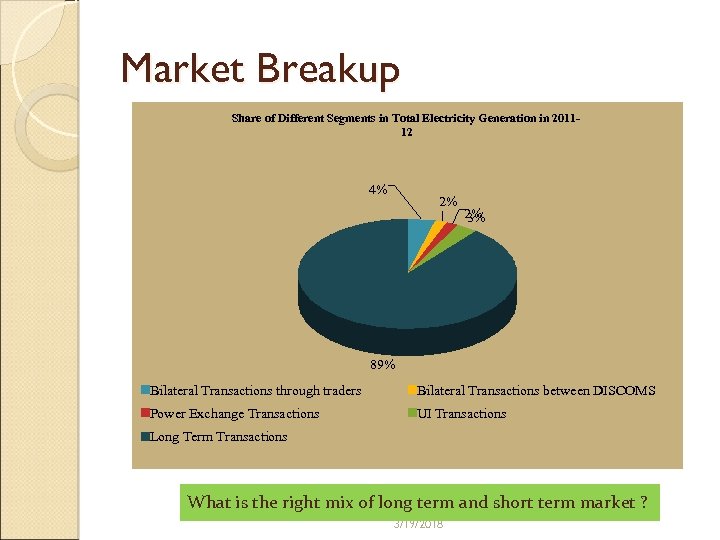
Market Breakup Share of Different Segments in Total Electricity Generation in 201112 4% 2% 2% 3% 89% Bilateral Transactions through traders Bilateral Transactions between DISCOMS Power Exchange Transactions UI Transactions Long Term Transactions What is the right mix of long term and short term market ? 3/19/2018
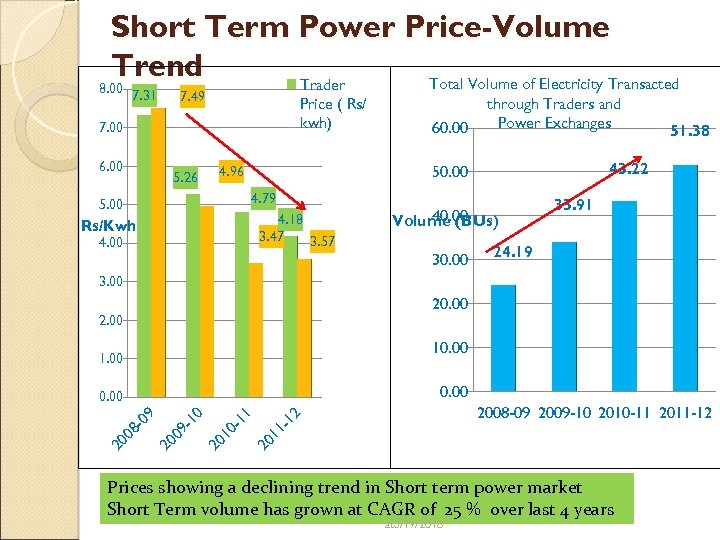
Short Term Power Price-Volume Trend Total Volume of Electricity Transacted Trader 8. 00 7. 31 7. 49 Price ( Rs/ kwh) 7. 00 6. 00 4. 79 5. 00 4. 18 3. 47 3. 57 Rs/Kwh 4. 00 40. 00 Volume (BUs) 30. 00 51. 38 43. 22 50. 00 4. 96 5. 26 60. 00 through Traders and Power Exchanges 33. 91 24. 19 3. 00 20. 00 2. 00 10. 00 1. 00 0. 00 11 2 2008 -09 2009 -10 2010 -11 2011 -12 20 1 1 01 20 1 0 91 20 0 80 9 0. 00 Prices showing a declining trend in Short term power market Short Term volume has grown at CAGR of 25 % over last 4 years at 3/19/2018
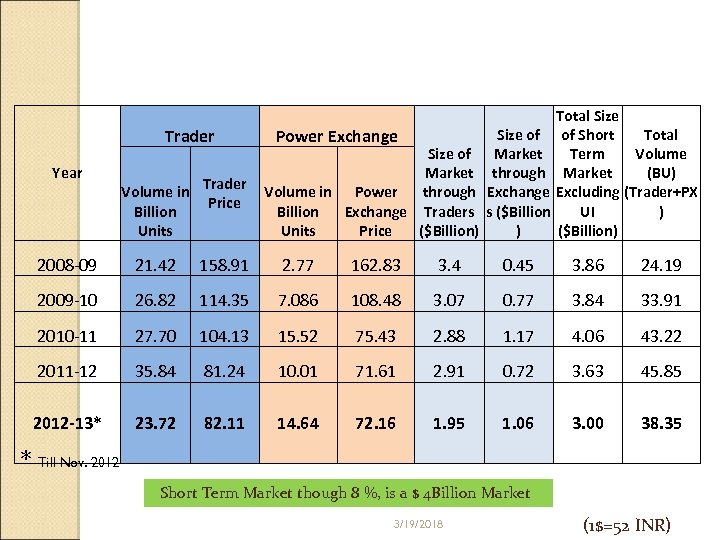
Short Term Price and Volume Trends Trader Year Volume in Billion Units Trader Price Power Exchange Size of Market Volume in Power through Billion Exchange Traders Units Price ($Billion) Size of Market through Exchange s ($Billion ) Total Size Total of Short Volume Term Market (BU) Excluding (Trader+PX UI ) ($Billion) 2008 -09 21. 42 158. 91 2. 77 162. 83 3. 4 0. 45 3. 86 24. 19 2009 -10 26. 82 114. 35 7. 086 108. 48 3. 07 0. 77 3. 84 33. 91 2010 -11 27. 70 104. 13 15. 52 75. 43 2. 88 1. 17 4. 06 43. 22 2011 -12 35. 84 81. 24 10. 01 71. 61 2. 91 0. 72 3. 63 45. 85 2012 -13* 23. 72 82. 11 14. 64 72. 16 1. 95 1. 06 3. 00 38. 35 * Till Nov. 2012 Short Term Market though 8 %, is a $ 4 Billion Market 3/19/2018 (1$=52 INR)
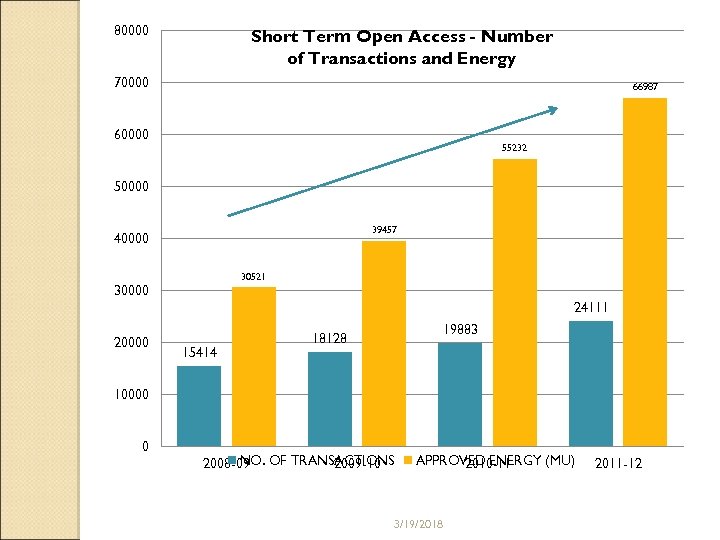
80000 Short Term Open Access - Number of Transactions and Energy 70000 66987 60000 55232 50000 39457 40000 30521 30000 24111 20000 15414 19883 18128 10000 0 NO. 2008 -09 OF TRANSACTIONS 2009 -10 APPROVED ENERGY (MU) 2010 -11 3/19/2018 2011 -12
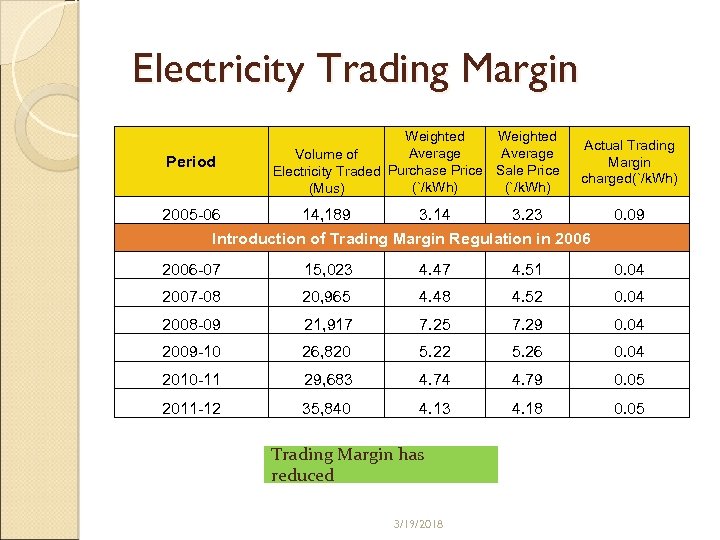
Electricity Trading Margin Period Weighted Average Volume of Electricity Traded Purchase Price Sale Price (`/k. Wh) (Mus) Actual Trading Margin charged(`/k. Wh) 2005 -06 14, 189 3. 14 3. 23 Introduction of Trading Margin Regulation in 2006 0. 09 2006 -07 15, 023 4. 47 4. 51 0. 04 2007 -08 20, 965 4. 48 4. 52 0. 04 2008 -09 21, 917 7. 25 7. 29 0. 04 2009 -10 26, 820 5. 22 5. 26 0. 04 2010 -11 29, 683 4. 74 4. 79 0. 05 2011 -12 35, 840 4. 13 4. 18 0. 05 Trading Margin has reduced 3/19/2018
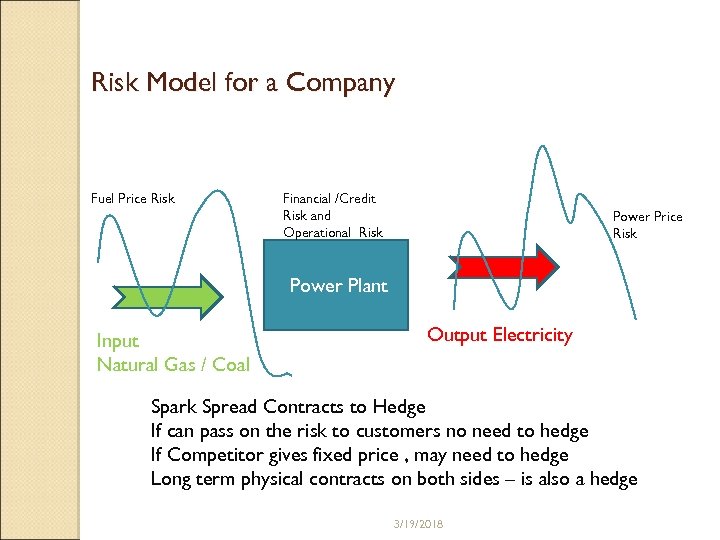
Risk Model for a Company Fuel Price Risk Financial /Credit Risk and Operational Risk Power Price Risk Power Plant Input Natural Gas / Coal Output Electricity Spark Spread Contracts to Hedge If can pass on the risk to customers no need to hedge If Competitor gives fixed price , may need to hedge Long term physical contracts on both sides – is also a hedge 3/19/2018
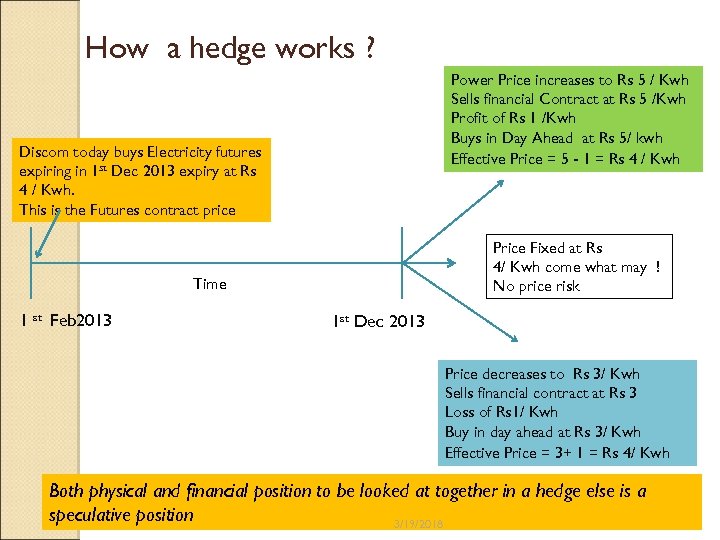
How a hedge works ? Power Price increases to Rs 5 / Kwh Sells financial Contract at Rs 5 /Kwh Profit of Rs 1 /Kwh Buys in Day Ahead at Rs 5/ kwh Effective Price = 5 - 1 = Rs 4 / Kwh Discom today buys Electricity futures expiring in 1 st Dec 2013 expiry at Rs 4 / Kwh. This is the Futures contract price Price Fixed at Rs 4/ Kwh come what may ! No price risk Time 1 st Feb 2013 1 st Dec 2013 Price decreases to Rs 3/ Kwh Sells financial contract at Rs 3 Loss of Rs 1/ Kwh Buy in day ahead at Rs 3/ Kwh Effective Price = 3+ 1 = Rs 4/ Kwh Both physical and financial position to be looked at together in a hedge else is a speculative position 3/19/2018
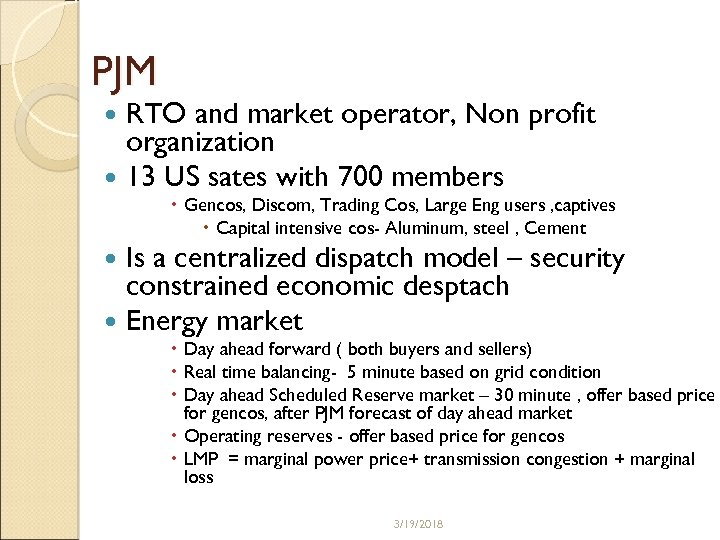
PJM RTO and market operator, Non profit organization 13 US sates with 700 members Gencos, Discom, Trading Cos, Large Eng users , captives Capital intensive cos- Aluminum, steel , Cement Is a centralized dispatch model – security constrained economic desptach Energy market Day ahead forward ( both buyers and sellers) Real time balancing- 5 minute based on grid condition Day ahead Scheduled Reserve market – 30 minute , offer based price for gencos, after PJM forecast of day ahead market Operating reserves - offer based price for gencos LMP = marginal power price+ transmission congestion + marginal loss 3/19/2018

PJM Reliability Pricing model – Capacity Market ◦ Capacity auction market upto 3 years ahead ◦ Every year incremental capacity auctioned as forecast improves ◦ All load serving entities have to forecast peak demand procure capacity through self supply, bilateral contracts , remaining through PJM capacity auctions ◦ Long term price signal for new genco investment ◦ Mandatory to participate in day ahead energy market thereafter participate 3/19/2018

Financial electricity derivatives in US NYMEX, ICE ◦ Derivative contracts settled on PJM prices ◦ Large number of contracts settled at various hub prices ◦ To hedge LMP price risk ◦ Large number of OTC contracts , Clearing done though exchange ◦ Not as liquid as gas markets 3/19/2018
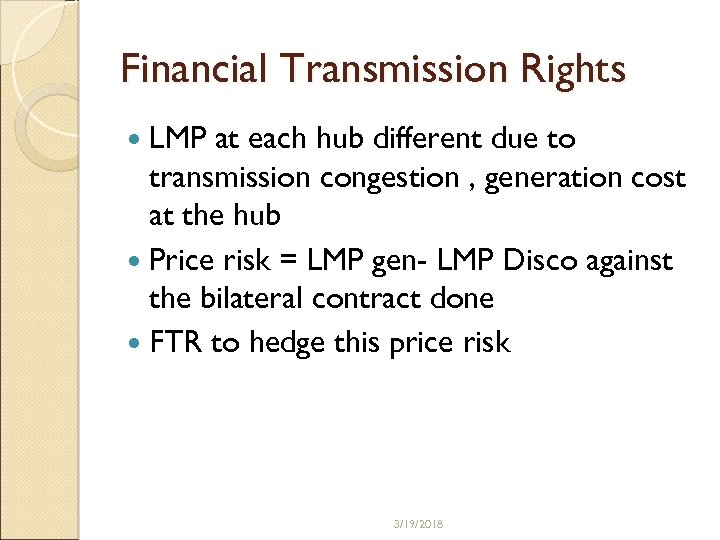
Financial Transmission Rights LMP at each hub different due to transmission congestion , generation cost at the hub Price risk = LMP gen- LMP Disco against the bilateral contract done FTR to hedge this price risk 3/19/2018

Nordpool Large power cos - State owned ◦ Market power mitigation through Unbundling vs integrated market Generation competition , Transmission regulated monopoly, Discom network regulated monopoly , retail competition ( many retailers ) In US -Discom is regulated monopoly in most states Market Design Day ahead Spot – Elspot- demand supply in full Nordic region ◦ Energy + transmission capacity right Balancing market – Elbas- Intra day upto 1 hour before delivery – Continuous market Financial Futures market – Upto 4 years ahead Participants can also do long term physical bilateral if they want = Spot physical + Financial Futures Provides flexibility and exit whereas bilateral ‘take or pay’ 3/19/2018

Nordpool Contract for difference(CFD) ◦ Basis risk between Financial contract ( settled on unconstrained system spot price ) and Bid area hedged with this TSO Dispatch based on market bids of participants 3/19/2018
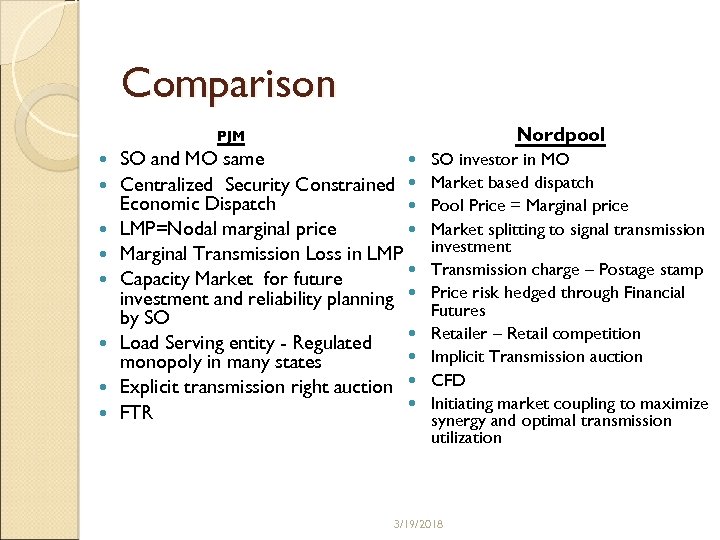
Comparison Nordpool PJM SO and MO same Centralized Security Constrained Economic Dispatch LMP=Nodal marginal price Marginal Transmission Loss in LMP Capacity Market for future investment and reliability planning by SO Load Serving entity - Regulated monopoly in many states Explicit transmission right auction FTR SO investor in MO Market based dispatch Pool Price = Marginal price Market splitting to signal transmission investment Transmission charge – Postage stamp Price risk hedged through Financial Futures Retailer – Retail competition Implicit Transmission auction CFD Initiating market coupling to maximize synergy and optimal transmission utilization 3/19/2018

Regulators role Regulator to think from systemic risk point of view As market size increase , market integrity to be maintained Role of regulator will be as watchdog of market Regulators role transformation from tariff fixation to market oversight 3/19/2018

Regulatory Institutions Level playing field to private sector as government was owner of the other assets Other sector regulators ◦ Protect small player from large institutions ◦ Unequal bargaining power ◦ Skewed market structure Evolving Organizations Cost of Compliance Stymie innovation Regulatory Certainty ◦ Open minded but not vacillate 3/19/2018

Role of CERC: Providing alternatives for power procurement through development of Power Market 3/19/2018

Alternatives to Procure Power o Created a Market Structure and Market Rules • License to electricity traders , power exchanges Multiple alternatives available to purchase power today • Directly through Open Access • Electricity Traders • Power Exchange o Open access in interstate transmission being encouraged o Approx 2000 industrial consumers and Discoms procuring electricity through Power Exchanges regularly 3/19/2018

o Development of Power Markets License to electricity traders • Large number of licensed traders (43) • Two Power Exchanges operational for last 3 years • Anonymous and Competitive price discovery • Based on real demand supply • Electronic platform • Quick Price dissemination across country o Introduced various products • Day ahead, week ahead, intraday/contingency traded, REC o Regulations notified • • Grant of Trading License Power Market Regulation Trading Margin Regulation Short Term Open Access Regulation CERC has helped create a robust market structure 3/19/2018

Role of CERC: Market Oversight and Grid Discipline 3/19/2018

Market Oversight Ensures that market is Free, Fair and Transparent o Regularly monitors Trading Margin and short term power prices o Publishes Monthly and Annual market reports for Information dissemination o CERC intervened in market when prices increased exorbitantly o • Price Cap introduced in day ahead market in September 2009 for 45 day period o Ensure large entities do not exercise market power CERC ensures Market Integrity 3/19/2018

Market Monitoring Focus is more on Short Term market presently ◦ Started creating a forward curve as no futures market exists Start monitoring long term , medium contracts also ◦ 92 % of market is long term ◦ State market difficult to monitor centrally ◦ Forward looking and not post facto only Look at open positions of traders -is a metric to monitor risk , not just prices – when price going down Financial health of gencos companies who have large number of contract – when sale price fixed and fuel cost increasing Contract reneging phenomena – is it increasing ? ◦ especially as contract period is 25 yrs Physical /Economic withholding of assets Generators cost curve monitor ? PJM , California do this 3/19/2018

Discussion Points - 1 Regulated as well as Merchant assets in same physical location ◦ Tariff determination and standard of performance ◦ Gaming by players Dedicated lines vs Transmission licensee ◦ Market power ◦ Should they be converted ? What is the Right mix of Long term and Short term market: ◦ Transmission planning is a issue ◦ Share of short term purchase in portfolio low but rising ◦ Is upto 15 - 30 % of total portfolio ( Rel Infra- JVVN) , Avg 5 % Should Long term PPA be perquisite to build a transmission line ? 3/19/2018

Discussion Points- 2 What is the corrcet risk sharing mechanism between generators and utilities? ◦ How long should the long term contracts be ? ◦ Evaluation escalable and non escalable Should we explore centralised disptach model like US ◦ Will be synergy in a large country be more ? ◦ Will there be fuel savings ? 3/19/2018

Discussion points - 3 Should merchant power plant be always available in shortage condition? ◦ Should they declare capacity daily? ◦ Is generator a public utility ? ◦ Has no assured return , why commit availability? How to equitably allocate corridor between license trader and power exchange to increase social welfare ? System operators role while scheduling contracts ? ◦ Tight spot , Should it be adjudicating? ◦ What is the way out ? 3/19/2018

Discussion Point- 4 Market Rules should compliment Grid reliability and security ◦ Revision of contracts vs Firm contracts Short term contract treated as firm contract in many markets , cannot be revised , supply from other generator to be arranged ◦ In case of grid failure How quickly revision should be communicated in unaffected areas Exposed to financial risk when revision done later Should they be insulated ? 3/19/2018

Discussion Points -5 Generation Capacity addition vs Fuel ◦ Stranded assets ? ◦ Should we stop and sort out issues first? More Transparent platform ◦ Electronic web based Open Registry ◦ SLDC to use this to give open access ◦ Like Depository for stocks ◦ 3/19/2018

Disclaimer – These are personal views and may not necessarily be the views of the Commission 3/19/2018

Mandate of CERC as per Act o Tariff Determination • Tariff for bulk supply from Central Government owned/inter-state generating companies and transmission companies (Consumer tariff is under the jurisdiction of State ERCs) o Regulating Inter State Transmission and Grid Code o Market Development – facilitating framework (Generation capacity planning responsibility of Government) o Licensing, Adjudication, Advice to Government 3/19/2018

Role CERC : Balancing Consumer Interest and Investment promotion need o Consumer interest served by • Enhanced Power Supply and Transmission Availability • Inducing Efficiency in operation of power plants – gains for Consumers • Ensuring Reliable Power Supply • Providing Alternatives to procure power o Investment Promotion: • • o Enabling framework for Market Access to Generators Development of Power Market Competition in Transmission Promoting Green Energy CERC is responsible for Oversight of Market and Grid Security 3/19/2018

What Regulatory Commission have achieved ? New Institutions, resource constraints Up against the might of government controlled monolithic behemoths Transparency in working Stakeholder consultation, public hearing Statement of reasons for any regulation Display of information on website 3/19/2018
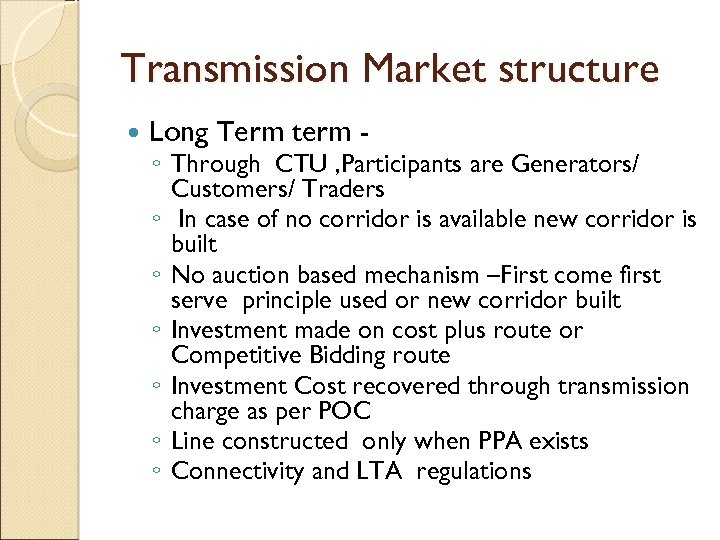
Transmission Market structure Long Term term - ◦ Through CTU , Participants are Generators/ Customers/ Traders ◦ In case of no corridor is available new corridor is built ◦ No auction based mechanism –First come first serve principle used or new corridor built ◦ Investment made on cost plus route or Competitive Bidding route ◦ Investment Cost recovered through transmission charge as per POC ◦ Line constructed only when PPA exists ◦ Connectivity and LTA regulations
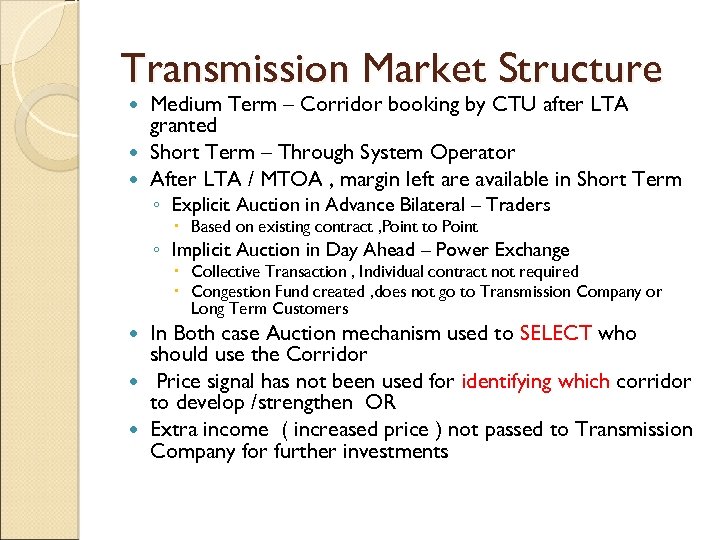
Transmission Market Structure Medium Term – Corridor booking by CTU after LTA granted Short Term – Through System Operator After LTA / MTOA , margin left are available in Short Term ◦ Explicit Auction in Advance Bilateral – Traders Based on existing contract , Point to Point ◦ Implicit Auction in Day Ahead – Power Exchange Collective Transaction , Individual contract not required Congestion Fund created , does not go to Transmission Company or Long Term Customers In Both case Auction mechanism used to SELECT who should use the Corridor Price signal has not been used for identifying which corridor to develop /strengthen OR Extra income ( increased price ) not passed to Transmission Company for further investments
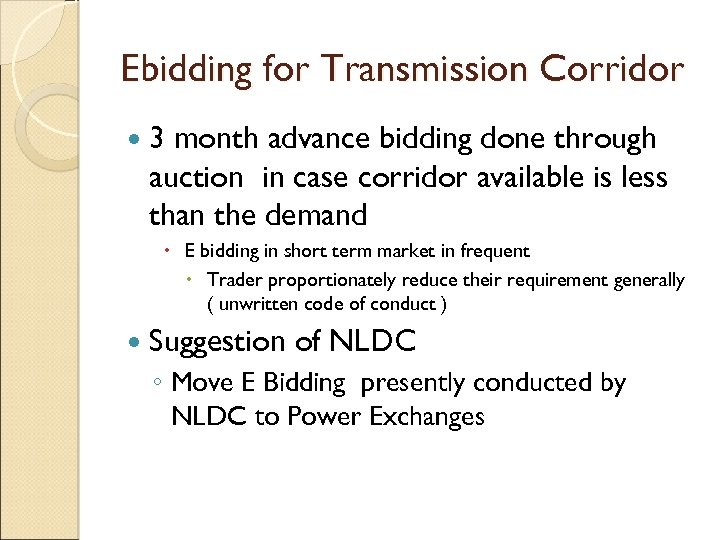
Ebidding for Transmission Corridor 3 month advance bidding done through auction in case corridor available is less than the demand E bidding in short term market in frequent Trader proportionately reduce their requirement generally ( unwritten code of conduct ) Suggestion of NLDC ◦ Move E Bidding presently conducted by NLDC to Power Exchanges

Ebidding for Transmission Corridor Operational Challenges presently ◦ Very elementary platform , run by NLDC ◦ Single price, no time differentiation ◦ For 15 min block , for full month W 3 to Nr , SR , WR – How bidding should be done for such cases How to identify which corridors to auction ? Any conflict of interest in case PX directed to also participate in e bidding for its corridor in future ?
Larger Implications At a policy level are we in for creating transmission corridor market ? Debate needed in following Are we promoting auction concept in Short term transmission market ? In short Term markets transmission market already exists Do we intend to extend this to Long term markets also at a later stage ? Auction Rights to physical owners of line Financial Transmission rights thereafter Is a good exit route in case of failed PPA E. g. PTC stuck with LTA Corridor in Jaypee Karcham Wangtoo Impact on the consumer – increase in cost of power ?

Role of CERC: Enabling framework for Investment in Generation 3/19/2018

Enabling framework for Investment in Generation… o Pre 2003: • Government guarantee on PPA required to attract investment in private generation • No markets – or alternatives to sell in case of default by buyer o EA 2003 and CERC regulations : • Concept of open access through Act : Framework by CERC o Interstate Open Access regulations • Allowed generators to sell power to any buyer across the country o Connectivity, Long term and Medium Term Open Access • Improved Market Access for generators • Provides certainty and surety of evacuation for new capacity 3/19/2018

Enabling framework for Investment in Generation … o Development of Power Market through regulations • Provided multiple buyer seller model • Multiple alternatives available to generators to sell power – directly, traders, power exchange o Regulatory approval for transmission network augmentation • Ensures Transmission Network expansion keeps pace with Generation capacity addition • Ensures new generation is not stranded o Introduced Point of Connection Tariff • Removes regional cascading of transmission charges • Level playing field among all generators to compete in Competitive bidding CERC’s framework has reduced various risks - default /payment risk, operational risk, liquidity risk in generation business 3/19/2018
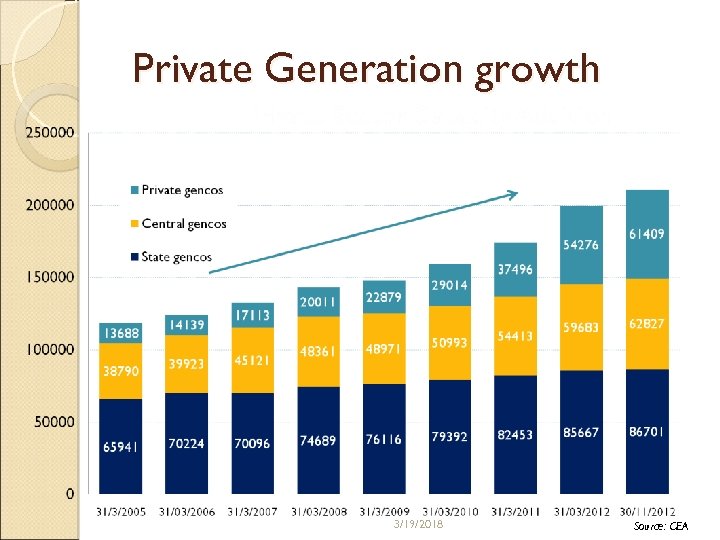
Private Generation growth 3/19/2018 Source: CEA

Discussion Points-4 How stakeholders should view PPP projects ? Public assets being built with private capital – How much profits should be allowed ? Should natural resources of country be allocated or auctioned ? ◦ Who gains in this process ? 3/19/2018
fd0a05924436326065bbdbfafd74f238.ppt