 Poverty eradication and good governance Why human rights matter
Poverty eradication and good governance Why human rights matter
 good governance and human rights: what’s the difference? Good governance • Defined by policy and practice • Focus on institutions • Subject to national policy and experience • Progressive Human rights • Defined by international law • Focus on people • Universal • Indivisible
good governance and human rights: what’s the difference? Good governance • Defined by policy and practice • Focus on institutions • Subject to national policy and experience • Progressive Human rights • Defined by international law • Focus on people • Universal • Indivisible
 Good governance and human rights: how are they related? • Without good governance, human rights are only “paper rights” • Without human rights, governance cannot be good • Commonalities: rule of law; participation; transparency; inclusiveness; responsive; accountable • Outcome oriented • Service to people – the servant leader
Good governance and human rights: how are they related? • Without good governance, human rights are only “paper rights” • Without human rights, governance cannot be good • Commonalities: rule of law; participation; transparency; inclusiveness; responsive; accountable • Outcome oriented • Service to people – the servant leader
 Poverty and economic growth • Income poverty is only one aspect about poverty • People are poor because they are deprived of basic needs • Are basic needs human rights? • economic and social rights • what’s the policy benefit?
Poverty and economic growth • Income poverty is only one aspect about poverty • People are poor because they are deprived of basic needs • Are basic needs human rights? • economic and social rights • what’s the policy benefit?
 Poverty is not only about -$$$ • Deprivation – the lack of basic needs • Discrimination – inequality and marginalization • Insecurity – physical, job, food, land tenure, housing • Voicelessness – excluded from power
Poverty is not only about -$$$ • Deprivation – the lack of basic needs • Discrimination – inequality and marginalization • Insecurity – physical, job, food, land tenure, housing • Voicelessness – excluded from power
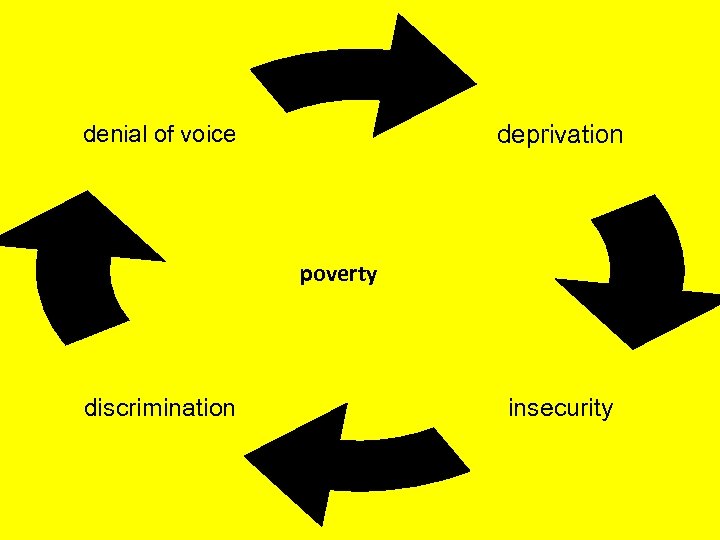 deprivation denial of voice poverty discrimination insecurity
deprivation denial of voice poverty discrimination insecurity
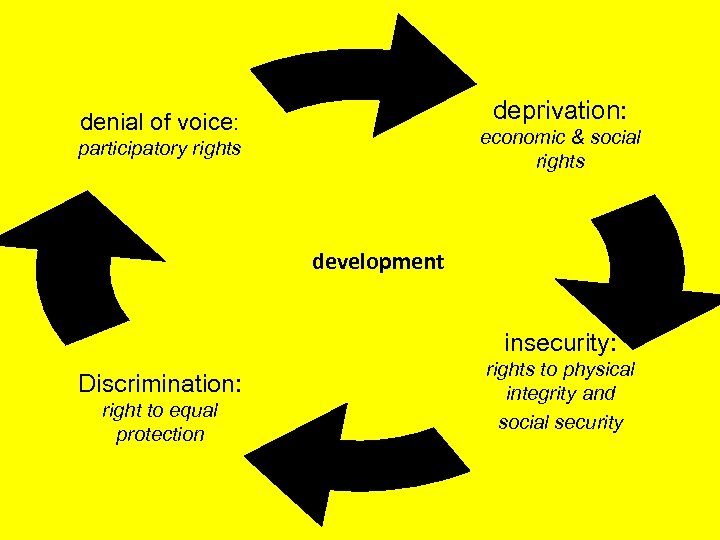 deprivation: denial of voice: economic & social rights participatory rights development insecurity: Discrimination: right to equal protection rights to physical integrity and social security
deprivation: denial of voice: economic & social rights participatory rights development insecurity: Discrimination: right to equal protection rights to physical integrity and social security
 Impediments to poverty eradication • Participation of the poor is not respected in planning and delivery • Law and systems do not work for the poor • Civil and political rights are disregarded • Development actors (state, NGO or corporate) are not transparent/accountable • There is too much investment in institutions, not enough on empowerment
Impediments to poverty eradication • Participation of the poor is not respected in planning and delivery • Law and systems do not work for the poor • Civil and political rights are disregarded • Development actors (state, NGO or corporate) are not transparent/accountable • There is too much investment in institutions, not enough on empowerment
 When I feed the poor, they call me a saint. But when I ask why the poor have no food, they call me a communist. Dom Helder Camara, Archbishop of Olinda and Recife, Brazil
When I feed the poor, they call me a saint. But when I ask why the poor have no food, they call me a communist. Dom Helder Camara, Archbishop of Olinda and Recife, Brazil
 Supply vs. demand of human rights • Investing in institutions – state, government & political party • Empowering citizens – Civil society; NGOs and business • Case study: Lokpal vs. FOI movement in India
Supply vs. demand of human rights • Investing in institutions – state, government & political party • Empowering citizens – Civil society; NGOs and business • Case study: Lokpal vs. FOI movement in India
 Why rights matter: • Universality: equal in rights and dignity • Human focus: not economic outcomes but impact on people’s lives • Inclusive: “who is being left behind? ” • Economic and social rights: structural equality in a market economy • Empowerment & accountability
Why rights matter: • Universality: equal in rights and dignity • Human focus: not economic outcomes but impact on people’s lives • Inclusive: “who is being left behind? ” • Economic and social rights: structural equality in a market economy • Empowerment & accountability