ac600297234c758f996554a1b3c9dd16.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Potential of Cyclotrons Werner Joho, PSI FFAG 2007, Grenoble 12. april 2007 W. Joho 2007
Potential of Cyclotrons Werner Joho, PSI FFAG 2007, Grenoble 12. april 2007 W. Joho 2007
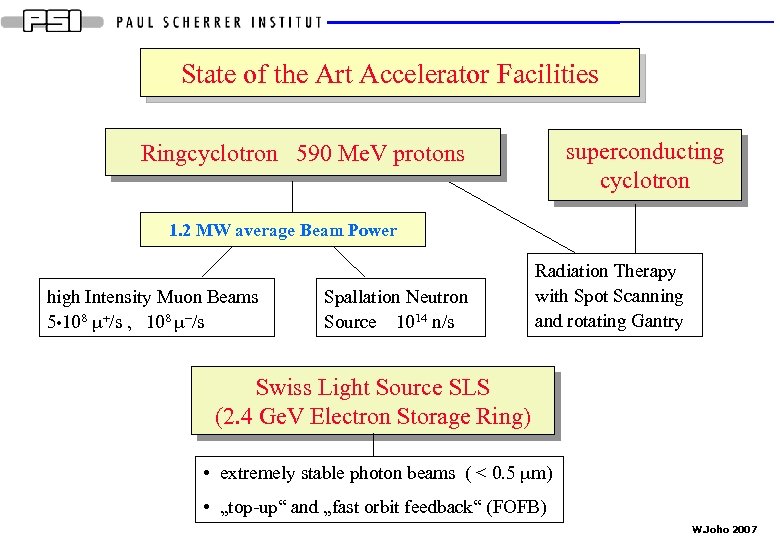 State of the Art Accelerator Facilities superconducting cyclotron Ringcyclotron 590 Me. V protons 1. 2 MW average Beam Power high Intensity Muon Beams 5 • 108 m+/s , 108 m-/s Spallation Neutron Source 1014 n/s Radiation Therapy with Spot Scanning and rotating Gantry Swiss Light Source SLS (2. 4 Ge. V Electron Storage Ring) • extremely stable photon beams ( < 0. 5 mm) • „top-up“ and „fast orbit feedback“ (FOFB) W. Joho 2007
State of the Art Accelerator Facilities superconducting cyclotron Ringcyclotron 590 Me. V protons 1. 2 MW average Beam Power high Intensity Muon Beams 5 • 108 m+/s , 108 m-/s Spallation Neutron Source 1014 n/s Radiation Therapy with Spot Scanning and rotating Gantry Swiss Light Source SLS (2. 4 Ge. V Electron Storage Ring) • extremely stable photon beams ( < 0. 5 mm) • „top-up“ and „fast orbit feedback“ (FOFB) W. Joho 2007
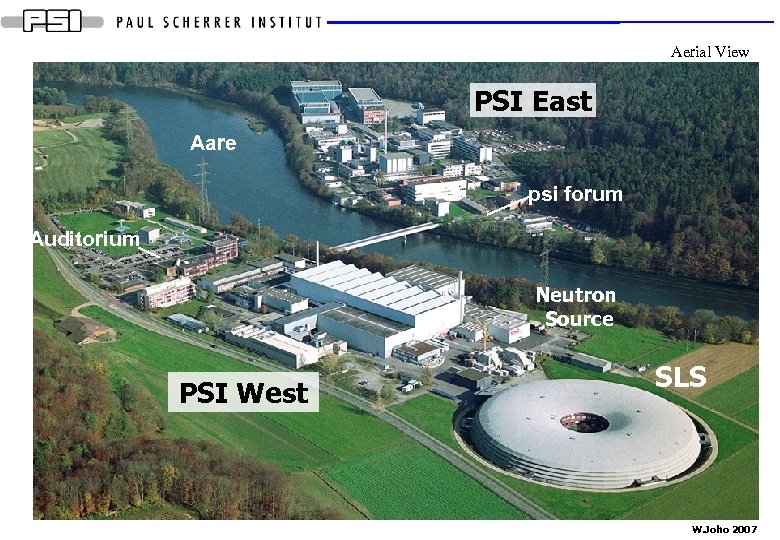 Aerial View PSI East Aare psi forum Auditorium Neutron Source PSI West SLS W. Joho 2007
Aerial View PSI East Aare psi forum Auditorium Neutron Source PSI West SLS W. Joho 2007
 The first Cyclotron 1931 E. O. Lawrence, M. S. Livingston Berkeley, California 4 inch diameter 1 k. V on the Dee 80 ke. V Protons W. Joho 2007
The first Cyclotron 1931 E. O. Lawrence, M. S. Livingston Berkeley, California 4 inch diameter 1 k. V on the Dee 80 ke. V Protons W. Joho 2007
 43 years later (1974) Ring Cyclotron 590 Me. V Protons 15 m Diameter Hans Willax, Jean Paul Blaser, Villigen, Switzerland W. Joho 2007
43 years later (1974) Ring Cyclotron 590 Me. V Protons 15 m Diameter Hans Willax, Jean Paul Blaser, Villigen, Switzerland W. Joho 2007
 Comet Cyclotron Radiation Therapy with 250 Me. V Protons Cyclotron: superconducting Magnet, 3 m Ø Collaboration: ACCEL & PSI W. Joho 2007
Comet Cyclotron Radiation Therapy with 250 Me. V Protons Cyclotron: superconducting Magnet, 3 m Ø Collaboration: ACCEL & PSI W. Joho 2007
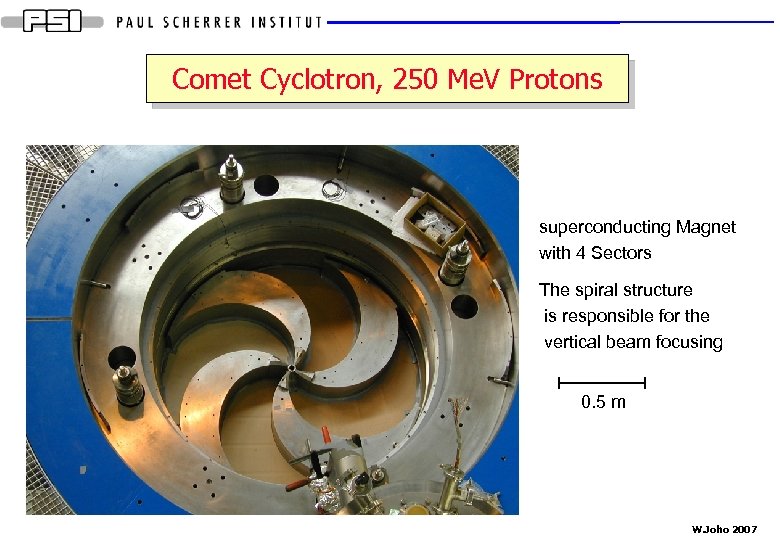 Comet Cyclotron, 250 Me. V Protons superconducting Magnet with 4 Sectors The spiral structure is responsible for the vertical beam focusing 0. 5 m W. Joho 2007
Comet Cyclotron, 250 Me. V Protons superconducting Magnet with 4 Sectors The spiral structure is responsible for the vertical beam focusing 0. 5 m W. Joho 2007
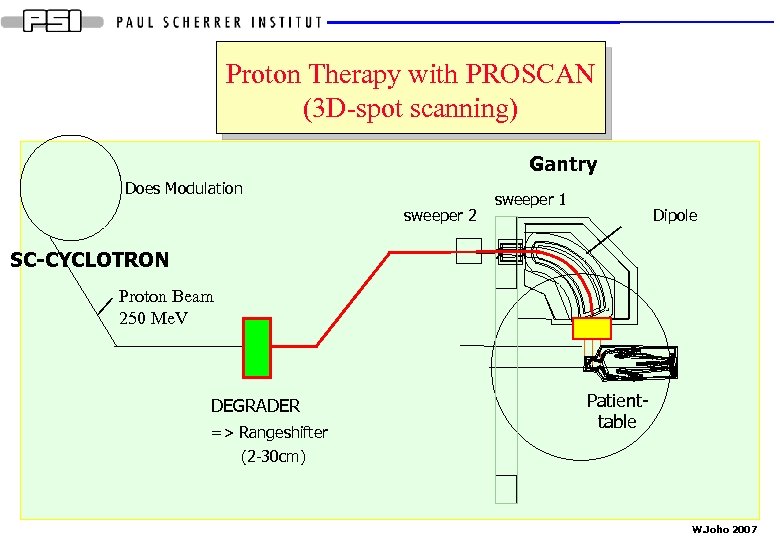 Proton Therapy with PROSCAN (3 D-spot scanning) Gantry Does Modulation sweeper 2 sweeper 1 Dipole SC-CYCLOTRON Proton Beam 250 Me. V DEGRADER => Rangeshifter Patienttable (2 -30 cm) W. Joho 2007
Proton Therapy with PROSCAN (3 D-spot scanning) Gantry Does Modulation sweeper 2 sweeper 1 Dipole SC-CYCLOTRON Proton Beam 250 Me. V DEGRADER => Rangeshifter Patienttable (2 -30 cm) W. Joho 2007
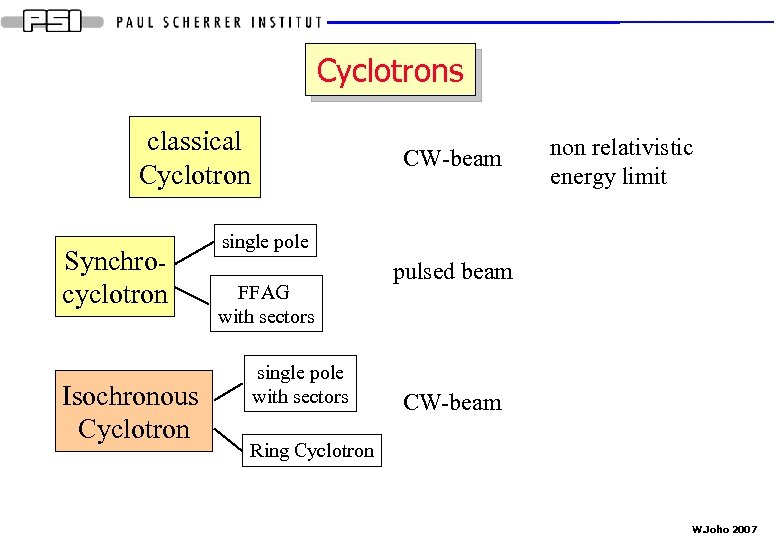 Cyclotrons classical Cyclotron Synchrocyclotron Isochronous Cyclotron CW-beam non relativistic energy limit single pole FFAG with sectors single pole with sectors pulsed beam CW-beam Ring Cyclotron W. Joho 2007
Cyclotrons classical Cyclotron Synchrocyclotron Isochronous Cyclotron CW-beam non relativistic energy limit single pole FFAG with sectors single pole with sectors pulsed beam CW-beam Ring Cyclotron W. Joho 2007
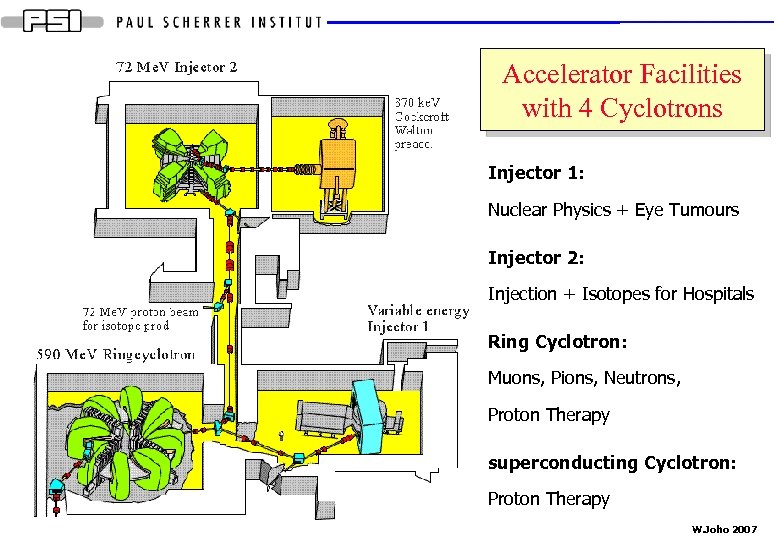 Accelerator Facilities with 4 Cyclotrons Injector 1: Nuclear Physics + Eye Tumours Injector 2: Injection + Isotopes for Hospitals Ring Cyclotron: Muons, Pions, Neutrons, Proton Therapy superconducting Cyclotron: Proton Therapy W. Joho 2007
Accelerator Facilities with 4 Cyclotrons Injector 1: Nuclear Physics + Eye Tumours Injector 2: Injection + Isotopes for Hospitals Ring Cyclotron: Muons, Pions, Neutrons, Proton Therapy superconducting Cyclotron: Proton Therapy W. Joho 2007
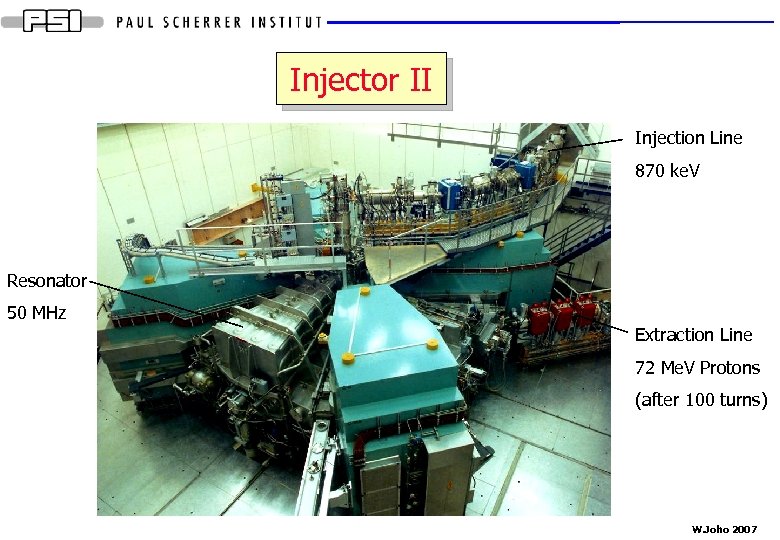 Injector II Injection Line 870 ke. V Resonator 50 MHz Extraction Line 72 Me. V Protons (after 100 turns) W. Joho 2007
Injector II Injection Line 870 ke. V Resonator 50 MHz Extraction Line 72 Me. V Protons (after 100 turns) W. Joho 2007
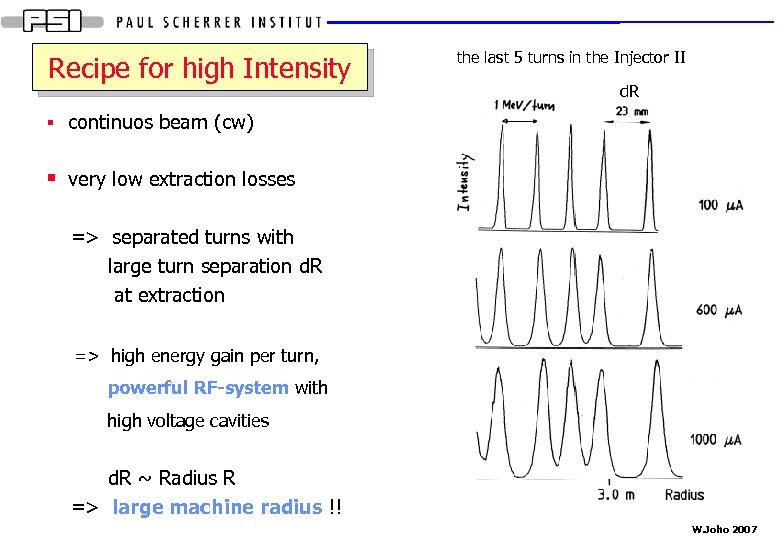 Recipe for high Intensity the last 5 turns in the Injector II d. R § continuos beam (cw) § very low extraction losses => separated turns with large turn separation d. R at extraction => high energy gain per turn, powerful RF-system with high voltage cavities d. R ~ Radius R => large machine radius !! W. Joho 2007
Recipe for high Intensity the last 5 turns in the Injector II d. R § continuos beam (cw) § very low extraction losses => separated turns with large turn separation d. R at extraction => high energy gain per turn, powerful RF-system with high voltage cavities d. R ~ Radius R => large machine radius !! W. Joho 2007
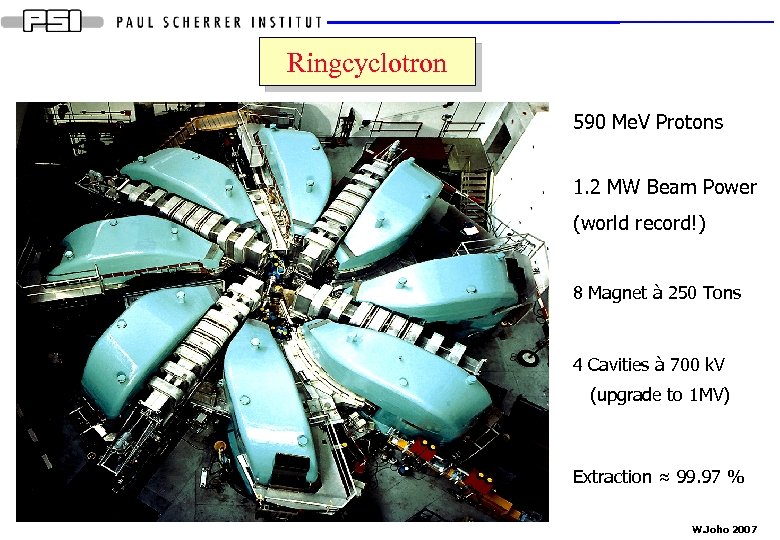 Ringcyclotron 590 Me. V Protons 1. 2 MW Beam Power (world record!) 8 Magnet à 250 Tons 4 Cavities à 700 k. V (upgrade to 1 MV) Extraction ≈ 99. 97 % W. Joho 2007
Ringcyclotron 590 Me. V Protons 1. 2 MW Beam Power (world record!) 8 Magnet à 250 Tons 4 Cavities à 700 k. V (upgrade to 1 MV) Extraction ≈ 99. 97 % W. Joho 2007
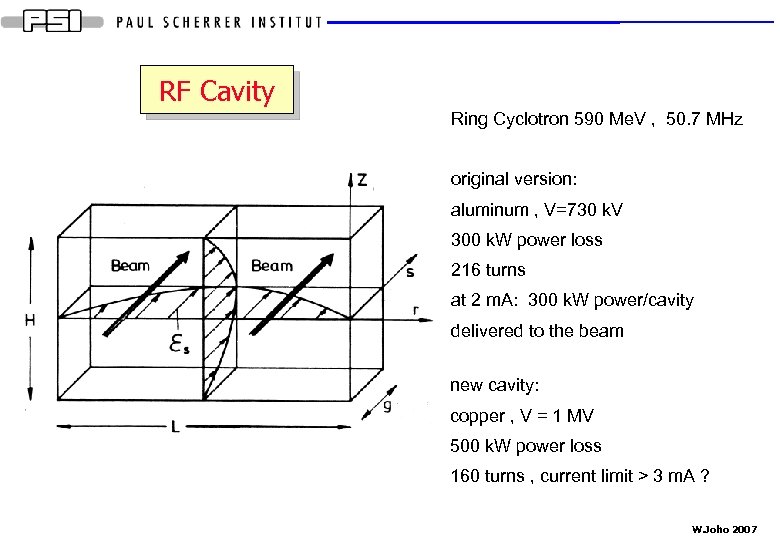 RF Cavity Ring Cyclotron 590 Me. V , 50. 7 MHz original version: aluminum , V=730 k. V 300 k. W power loss 216 turns at 2 m. A: 300 k. W power/cavity delivered to the beam new cavity: copper , V = 1 MV 500 k. W power loss 160 turns , current limit > 3 m. A ? W. Joho 2007
RF Cavity Ring Cyclotron 590 Me. V , 50. 7 MHz original version: aluminum , V=730 k. V 300 k. W power loss 216 turns at 2 m. A: 300 k. W power/cavity delivered to the beam new cavity: copper , V = 1 MV 500 k. W power loss 160 turns , current limit > 3 m. A ? W. Joho 2007
![y [mm] 2 T 1. 5 T Ring Cyclotron Contour lines of the magnetic y [mm] 2 T 1. 5 T Ring Cyclotron Contour lines of the magnetic](https://present5.com/presentation/ac600297234c758f996554a1b3c9dd16/image-15.jpg) y [mm] 2 T 1. 5 T Ring Cyclotron Contour lines of the magnetic field scaling of average field: B 0(R) ~ γ Increase from 72 -590 Me. V: 55% x [mm] W. Joho 2007
y [mm] 2 T 1. 5 T Ring Cyclotron Contour lines of the magnetic field scaling of average field: B 0(R) ~ γ Increase from 72 -590 Me. V: 55% x [mm] W. Joho 2007
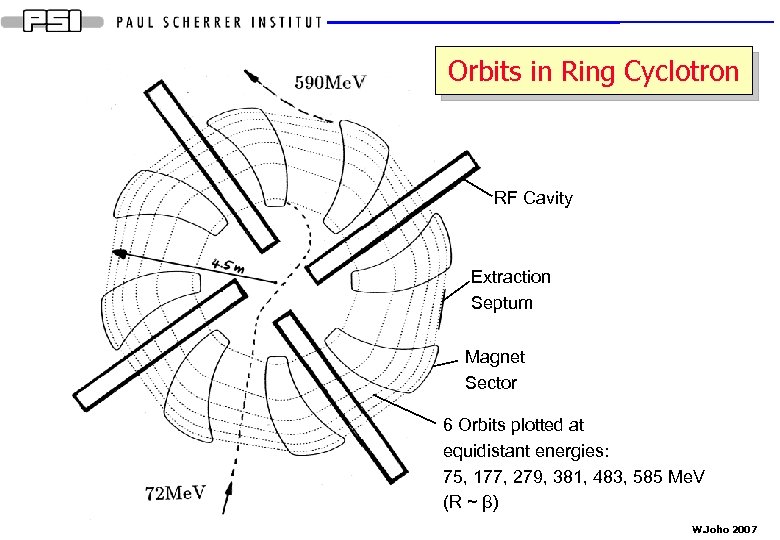 Orbits in Ring Cyclotron RF Cavity Extraction Septum Magnet Sector 6 Orbits plotted at equidistant energies: 75, 177, 279, 381, 483, 585 Me. V (R ~ β) W. Joho 2007
Orbits in Ring Cyclotron RF Cavity Extraction Septum Magnet Sector 6 Orbits plotted at equidistant energies: 75, 177, 279, 381, 483, 585 Me. V (R ~ β) W. Joho 2007
 how to scare young students!! (Al Garren 1962) better approach to get focusing frequencies: 1. simple approximations 2. numerical calculations Qr 2 ≈ 1+k Qz 2 ≈ -k +F (1+2 tan 2 d) W. Joho 2007
how to scare young students!! (Al Garren 1962) better approach to get focusing frequencies: 1. simple approximations 2. numerical calculations Qr 2 ≈ 1+k Qz 2 ≈ -k +F (1+2 tan 2 d) W. Joho 2007
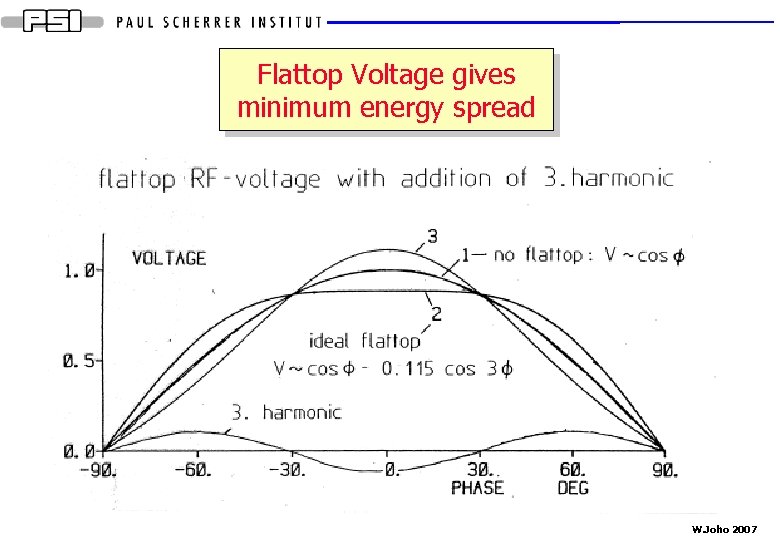 Flattop Voltage gives minimum energy spread W. Joho 2007
Flattop Voltage gives minimum energy spread W. Joho 2007
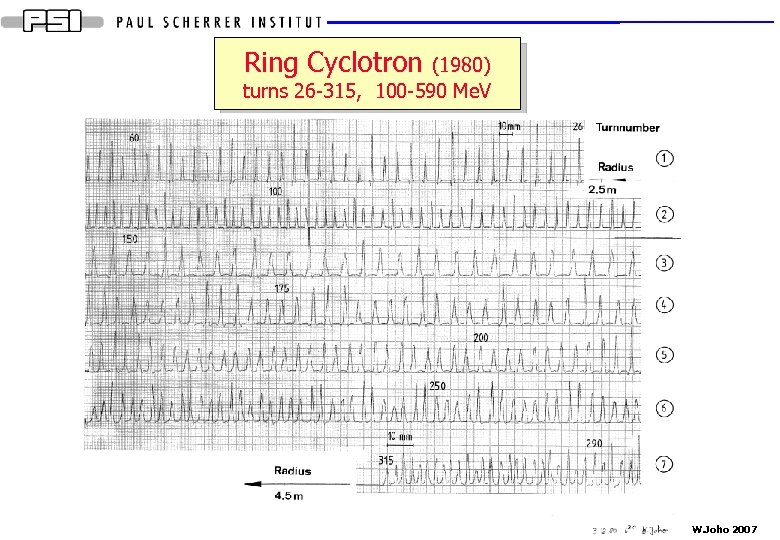 Ring Cyclotron (1980) turns 26 -315, 100 -590 Me. V W. Joho 2007
Ring Cyclotron (1980) turns 26 -315, 100 -590 Me. V W. Joho 2007
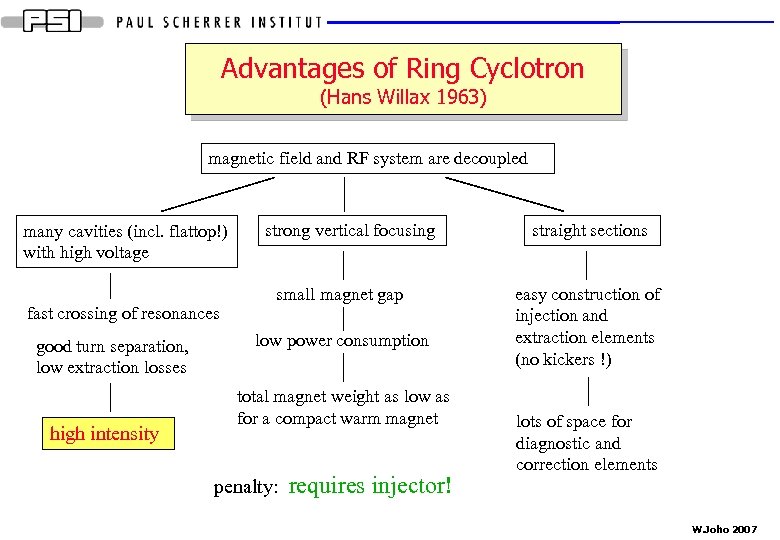 Advantages of Ring Cyclotron (Hans Willax 1963) magnetic field and RF system are decoupled many cavities (incl. flattop!) with high voltage fast crossing of resonances good turn separation, low extraction losses high intensity strong vertical focusing small magnet gap low power consumption total magnet weight as low as for a compact warm magnet penalty: requires injector! straight sections easy construction of injection and extraction elements (no kickers !) lots of space for diagnostic and correction elements W. Joho 2007
Advantages of Ring Cyclotron (Hans Willax 1963) magnetic field and RF system are decoupled many cavities (incl. flattop!) with high voltage fast crossing of resonances good turn separation, low extraction losses high intensity strong vertical focusing small magnet gap low power consumption total magnet weight as low as for a compact warm magnet penalty: requires injector! straight sections easy construction of injection and extraction elements (no kickers !) lots of space for diagnostic and correction elements W. Joho 2007
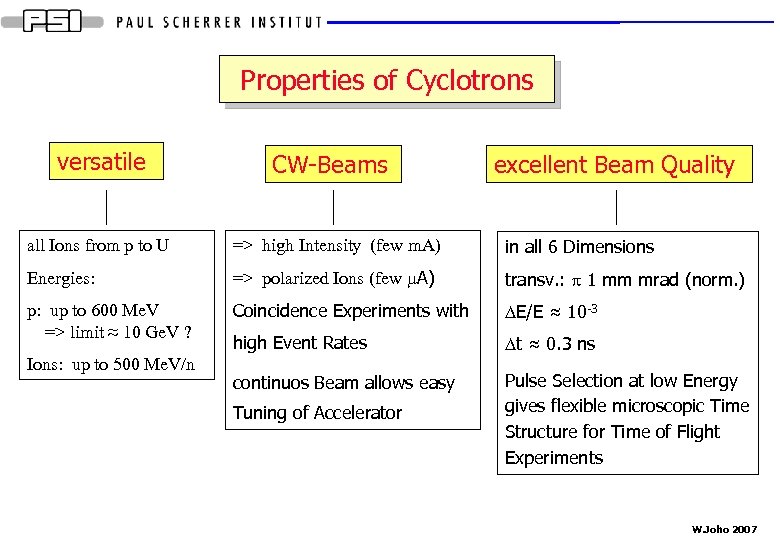 Properties of Cyclotrons versatile CW-Beams excellent Beam Quality all Ions from p to U => high Intensity (few m. A) in all 6 Dimensions Energies: => polarized Ions (few m. A) transv. : p 1 mm mrad (norm. ) p: up to 600 Me. V => limit ≈ 10 Ge. V ? Coincidence Experiments with DE/E ≈ 10 -3 high Event Rates Dt ≈ 0. 3 ns continuos Beam allows easy Pulse Selection at low Energy gives flexible microscopic Time Structure for Time of Flight Experiments Ions: up to 500 Me. V/n Tuning of Accelerator W. Joho 2007
Properties of Cyclotrons versatile CW-Beams excellent Beam Quality all Ions from p to U => high Intensity (few m. A) in all 6 Dimensions Energies: => polarized Ions (few m. A) transv. : p 1 mm mrad (norm. ) p: up to 600 Me. V => limit ≈ 10 Ge. V ? Coincidence Experiments with DE/E ≈ 10 -3 high Event Rates Dt ≈ 0. 3 ns continuos Beam allows easy Pulse Selection at low Energy gives flexible microscopic Time Structure for Time of Flight Experiments Ions: up to 500 Me. V/n Tuning of Accelerator W. Joho 2007
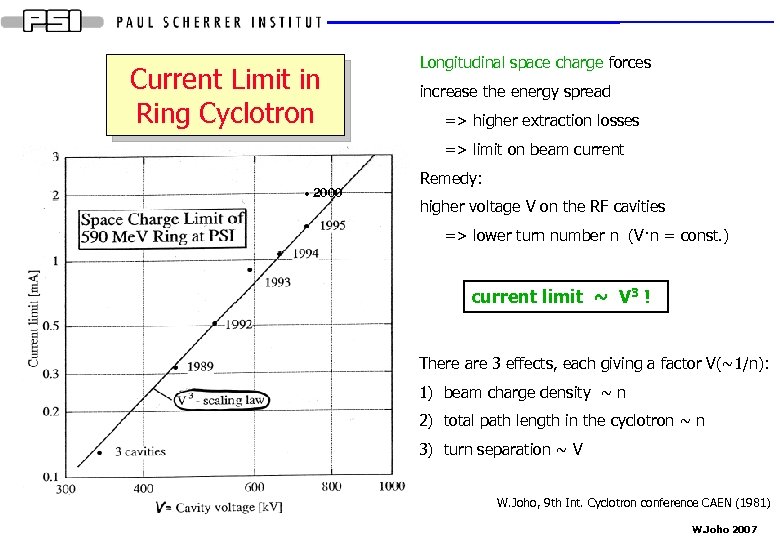 Current Limit in Ring Cyclotron Longitudinal space charge forces increase the energy spread => higher extraction losses => limit on beam current 2000 Remedy: higher voltage V on the RF cavities => lower turn number n (V·n = const. ) current limit ~ V 3 ! There are 3 effects, each giving a factor V(~1/n): 1) beam charge density ~ n 2) total path length in the cyclotron ~ n 3) turn separation ~ V W. Joho, 9 th Int. Cyclotron conference CAEN (1981) W. Joho 2007
Current Limit in Ring Cyclotron Longitudinal space charge forces increase the energy spread => higher extraction losses => limit on beam current 2000 Remedy: higher voltage V on the RF cavities => lower turn number n (V·n = const. ) current limit ~ V 3 ! There are 3 effects, each giving a factor V(~1/n): 1) beam charge density ~ n 2) total path length in the cyclotron ~ n 3) turn separation ~ V W. Joho, 9 th Int. Cyclotron conference CAEN (1981) W. Joho 2007
 Cyclotrons are still attractive ! § Commercial Cyclotrons for Radiation Therapy and Isotope Production § Acceleration of Radioactive Beams § Injectors for Ion Storage Rings § Intense Neutron Sources, replacing Reactors § Energy Amplifier Concept (Carlo Rubbia) § Transmutation of Nuclear Waste W. Joho 2007
Cyclotrons are still attractive ! § Commercial Cyclotrons for Radiation Therapy and Isotope Production § Acceleration of Radioactive Beams § Injectors for Ion Storage Rings § Intense Neutron Sources, replacing Reactors § Energy Amplifier Concept (Carlo Rubbia) § Transmutation of Nuclear Waste W. Joho 2007
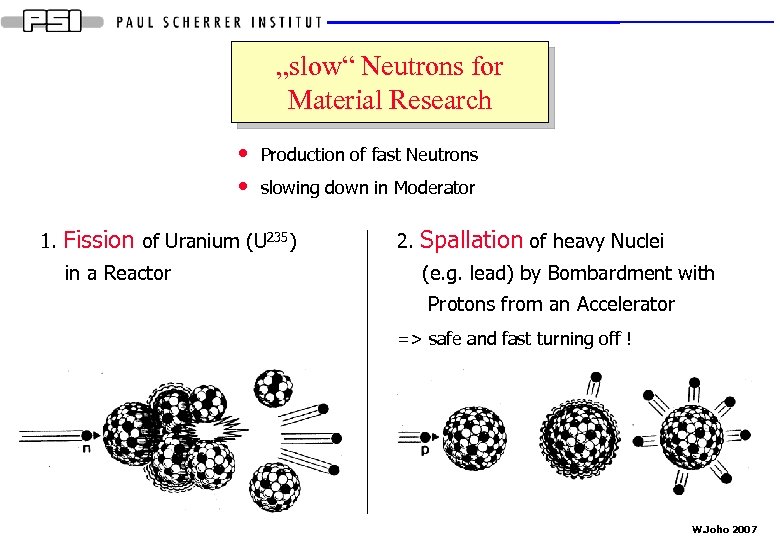 „slow“ Neutrons for Material Research • • 1. Production of fast Neutrons slowing down in Moderator Fission of Uranium (U 235) in a Reactor 2. Spallation of heavy Nuclei (e. g. lead) by Bombardment with Protons from an Accelerator => safe and fast turning off ! W. Joho 2007
„slow“ Neutrons for Material Research • • 1. Production of fast Neutrons slowing down in Moderator Fission of Uranium (U 235) in a Reactor 2. Spallation of heavy Nuclei (e. g. lead) by Bombardment with Protons from an Accelerator => safe and fast turning off ! W. Joho 2007
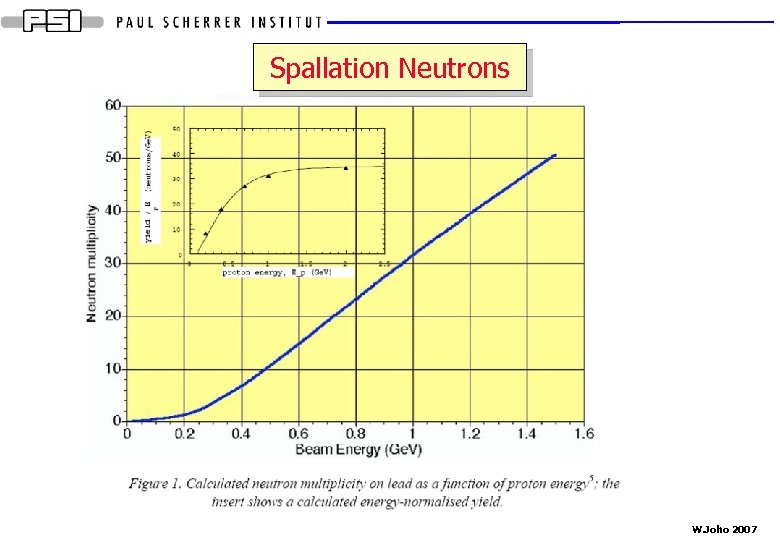 Spallation Neutrons W. Joho 2007
Spallation Neutrons W. Joho 2007
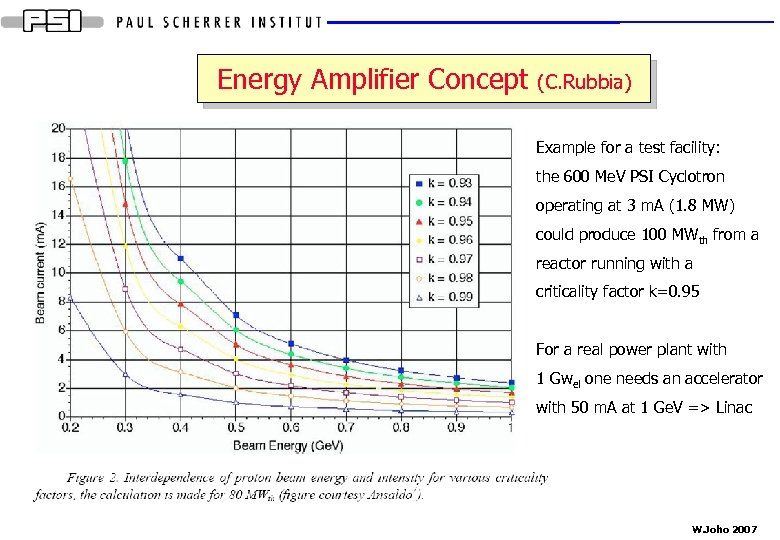 Energy Amplifier Concept (C. Rubbia) Example for a test facility: the 600 Me. V PSI Cyclotron operating at 3 m. A (1. 8 MW) could produce 100 MWth from a reactor running with a criticality factor k=0. 95 For a real power plant with 1 Gwel one needs an accelerator with 50 m. A at 1 Ge. V => Linac W. Joho 2007
Energy Amplifier Concept (C. Rubbia) Example for a test facility: the 600 Me. V PSI Cyclotron operating at 3 m. A (1. 8 MW) could produce 100 MWth from a reactor running with a criticality factor k=0. 95 For a real power plant with 1 Gwel one needs an accelerator with 50 m. A at 1 Ge. V => Linac W. Joho 2007
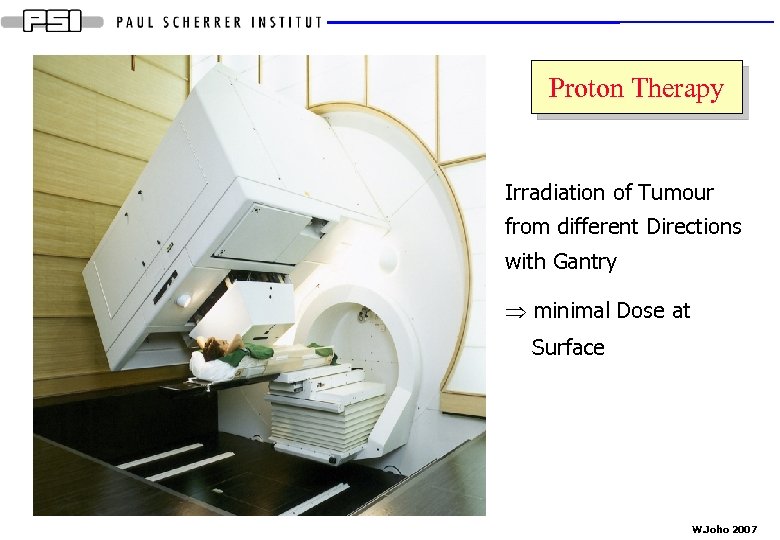 Proton Therapy Irradiation of Tumour from different Directions with Gantry Þ minimal Dose at Surface W. Joho 2007
Proton Therapy Irradiation of Tumour from different Directions with Gantry Þ minimal Dose at Surface W. Joho 2007
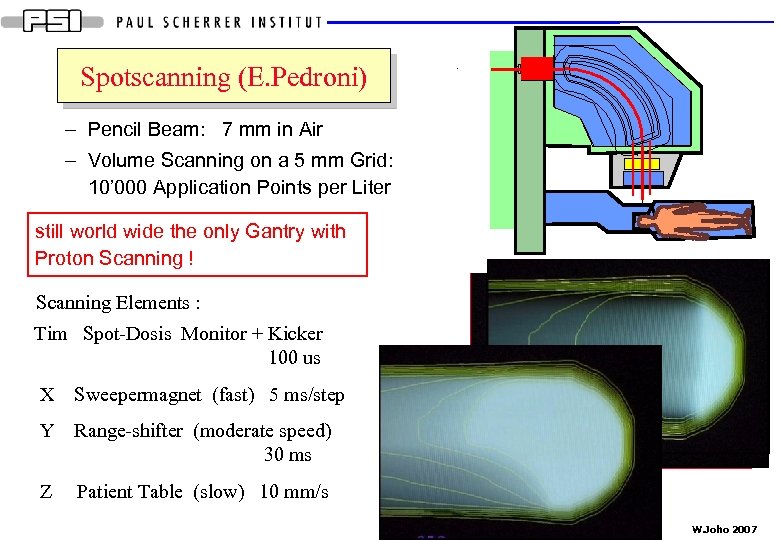 Spotscanning (E. Pedroni) – Pencil Beam: 7 mm in Air – Volume Scanning on a 5 mm Grid: 10’ 000 Application Points per Liter still world wide the only Gantry with Proton Scanning ! Scanning Elements : Tim Spot-Dosis Monitor + Kicker 100 us X Sweepermagnet (fast) 5 ms/step Y Range-shifter (moderate speed) 30 ms Z Patient Table (slow) 10 mm/s W. Joho 2007
Spotscanning (E. Pedroni) – Pencil Beam: 7 mm in Air – Volume Scanning on a 5 mm Grid: 10’ 000 Application Points per Liter still world wide the only Gantry with Proton Scanning ! Scanning Elements : Tim Spot-Dosis Monitor + Kicker 100 us X Sweepermagnet (fast) 5 ms/step Y Range-shifter (moderate speed) 30 ms Z Patient Table (slow) 10 mm/s W. Joho 2007
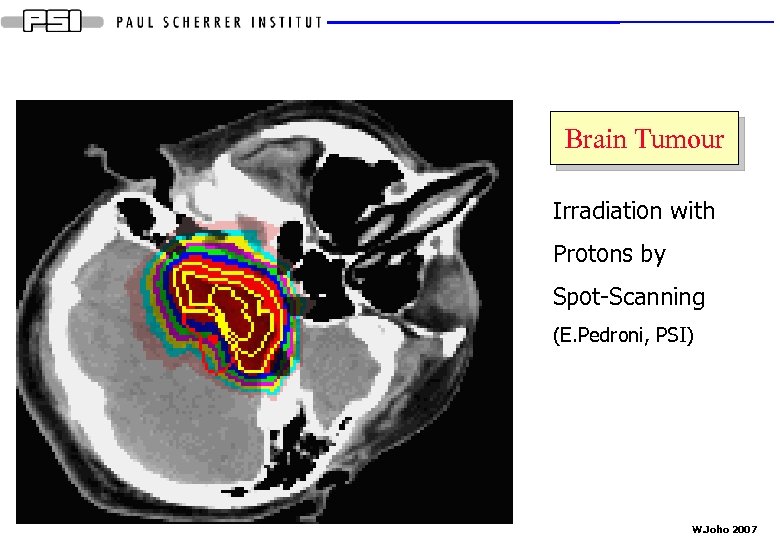 Brain Tumour Irradiation with Protons by Spot-Scanning (E. Pedroni, PSI) W. Joho 2007
Brain Tumour Irradiation with Protons by Spot-Scanning (E. Pedroni, PSI) W. Joho 2007
 References More information on the PSI Accelerator Facilities can be found in: www. psi. ch Some foils from talks by the author are found in: http: //abe. web. psi. ch/accelerators/vortraege. Werner. Joho/ vortraege. Werner. Joho. php In the paper “Fun with Formulas” there is e. g. a cute approximation for the end fields of a magnet with a binomial formula. W. Joho 2007
References More information on the PSI Accelerator Facilities can be found in: www. psi. ch Some foils from talks by the author are found in: http: //abe. web. psi. ch/accelerators/vortraege. Werner. Joho/ vortraege. Werner. Joho. php In the paper “Fun with Formulas” there is e. g. a cute approximation for the end fields of a magnet with a binomial formula. W. Joho 2007


