b1c6b0418053deb5e1cf844cd3e5a406.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Postwar America United States Chapter 17
Postwar America United States Chapter 17
 Veterans Return Home • 12 million soldiers return home at the end of the war. – Today the military has roughly 1. 5 million military personnel. • Very little jobs
Veterans Return Home • 12 million soldiers return home at the end of the war. – Today the military has roughly 1. 5 million military personnel. • Very little jobs
 GI Bill • Servicemen’s Readjustment Act of 1944. – Enacted to help veterans transition into civilian life. • Money for college and other job training • Could take out loans to buy homes • Today it is called Montgomery GI Bill
GI Bill • Servicemen’s Readjustment Act of 1944. – Enacted to help veterans transition into civilian life. • Money for college and other job training • Could take out loans to buy homes • Today it is called Montgomery GI Bill
 GI Bill
GI Bill
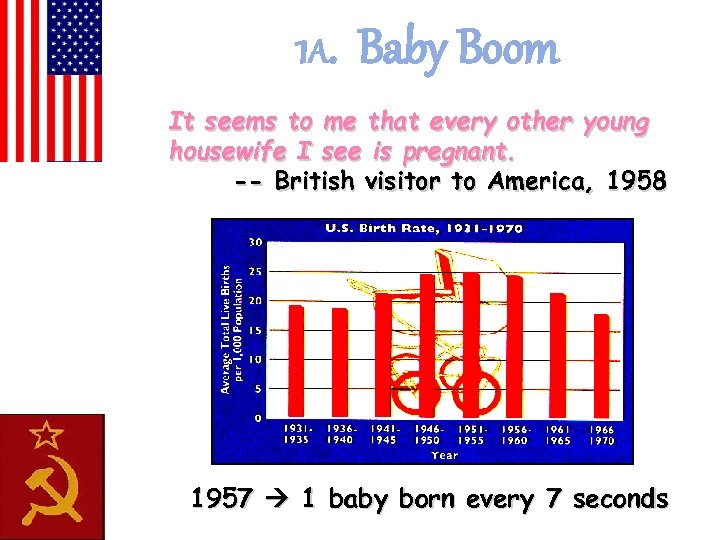 1 A. Baby Boom It seems to me that every other young housewife I see is pregnant. -- British visitor to America, 1958 1957 1 baby born every 7 seconds
1 A. Baby Boom It seems to me that every other young housewife I see is pregnant. -- British visitor to America, 1958 1957 1 baby born every 7 seconds
 U. S. Transition from War to Peace • During the War – Government restrictions • After the War – People wanted products • Baby Boom • Labor Unions – Taft-Hartley Act
U. S. Transition from War to Peace • During the War – Government restrictions • After the War – People wanted products • Baby Boom • Labor Unions – Taft-Hartley Act
 Minorities after the War • African Americans – Executive Order 9981 • Hispanic Veterans – Felix Longoria
Minorities after the War • African Americans – Executive Order 9981 • Hispanic Veterans – Felix Longoria
 1948 Presidential Election • Truman not popular even with Democrats • Republican Thomas Dewey was sure to win. • Truman refuses to give up.
1948 Presidential Election • Truman not popular even with Democrats • Republican Thomas Dewey was sure to win. • Truman refuses to give up.
 Truman Wins Election
Truman Wins Election
 Truman’s Plan • Fair Deal – Didn’t help very much because of lack of support from Congress • Korean War
Truman’s Plan • Fair Deal – Didn’t help very much because of lack of support from Congress • Korean War
 Enough of Truman • Stevenson vs. Eisenhower – Eisenhower • Stop Korean War
Enough of Truman • Stevenson vs. Eisenhower – Eisenhower • Stop Korean War
 VP Nixon and the Checkers Speech • Reporters found that Nixon had $18, 000 worth of political gifts from supports. – At the time it wasn’t illegal – Is it today? • Nixon goes on television and defends his actions.
VP Nixon and the Checkers Speech • Reporters found that Nixon had $18, 000 worth of political gifts from supports. – At the time it wasn’t illegal – Is it today? • Nixon goes on television and defends his actions.

 New Strategy for Eisenhower
New Strategy for Eisenhower
![Truman vs. Eisenhower “Containment” [George Kennan] 1. Marshall Plan 2. Truman Doctrine 3. Berlin Truman vs. Eisenhower “Containment” [George Kennan] 1. Marshall Plan 2. Truman Doctrine 3. Berlin](https://present5.com/presentation/b1c6b0418053deb5e1cf844cd3e5a406/image-15.jpg) Truman vs. Eisenhower “Containment” [George Kennan] 1. Marshall Plan 2. Truman Doctrine 3. Berlin Airlift 4. NATO 5. NSC #68 6. Korean War “Brinksmanship” [John Foster Dulles] 1. Mutual security agreements. 2. Massive retaliation. 3. M. A. D. 4. “Domino Theory” 5. CIA & covert operations 6. Eisenhower Doctrine 7. “$ Diplomacy” – Part
Truman vs. Eisenhower “Containment” [George Kennan] 1. Marshall Plan 2. Truman Doctrine 3. Berlin Airlift 4. NATO 5. NSC #68 6. Korean War “Brinksmanship” [John Foster Dulles] 1. Mutual security agreements. 2. Massive retaliation. 3. M. A. D. 4. “Domino Theory” 5. CIA & covert operations 6. Eisenhower Doctrine 7. “$ Diplomacy” – Part
 Suburbanization
Suburbanization
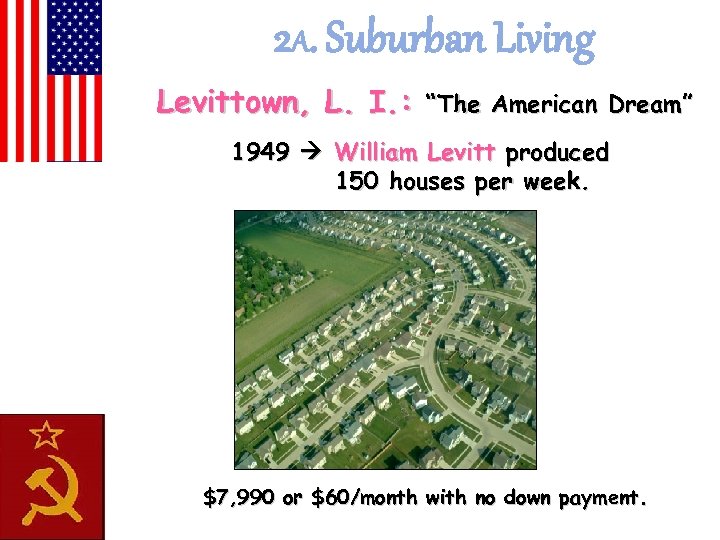 2 A. Suburban Living Levittown, L. I. : “The American Dream” 1949 William Levitt produced 150 houses per week. $7, 990 or $60/month with no down payment.
2 A. Suburban Living Levittown, L. I. : “The American Dream” 1949 William Levitt produced 150 houses per week. $7, 990 or $60/month with no down payment.
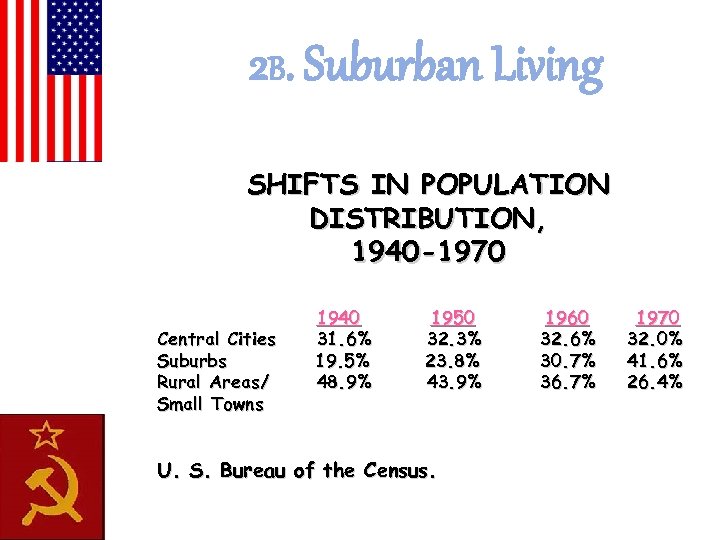 2 B. Suburban Living SHIFTS IN POPULATION DISTRIBUTION, 1940 -1970 Central Cities Suburbs Rural Areas/ Small Towns 1940 31. 6% 19. 5% 48. 9% 1950 32. 3% 23. 8% 43. 9% U. S. Bureau of the Census. 1960 32. 6% 30. 7% 36. 7% 1970 32. 0% 41. 6% 26. 4%
2 B. Suburban Living SHIFTS IN POPULATION DISTRIBUTION, 1940 -1970 Central Cities Suburbs Rural Areas/ Small Towns 1940 31. 6% 19. 5% 48. 9% 1950 32. 3% 23. 8% 43. 9% U. S. Bureau of the Census. 1960 32. 6% 30. 7% 36. 7% 1970 32. 0% 41. 6% 26. 4%
 The Culture of the Car The U. S. population was on the move in the 1950 s. NE & Mid-W S & SW (“Sunbelt” states) 1955 Disneyland opened in Southern California. (40% of the guests came from outside California, most by car. ) Frontier Land Main Street Tomorrow Land
The Culture of the Car The U. S. population was on the move in the 1950 s. NE & Mid-W S & SW (“Sunbelt” states) 1955 Disneyland opened in Southern California. (40% of the guests came from outside California, most by car. ) Frontier Land Main Street Tomorrow Land
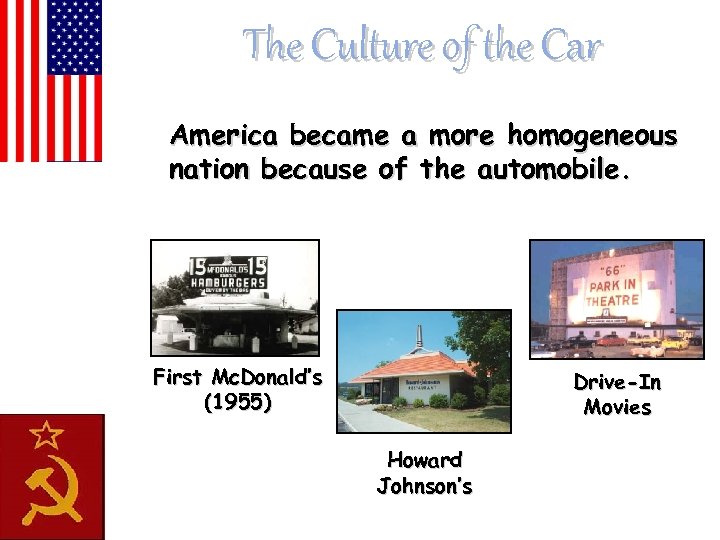 The Culture of the Car America became a more homogeneous nation because of the automobile. First Mc. Donald’s (1955) Drive-In Movies Howard Johnson’s
The Culture of the Car America became a more homogeneous nation because of the automobile. First Mc. Donald’s (1955) Drive-In Movies Howard Johnson’s
 The Eisenhower Interstate Highway System
The Eisenhower Interstate Highway System
 Interstate Highway System • Network of high-speed roads for interstate travel • 1956 -40, 000 mile system planned • Replaces “Historic Route 66” • Trucks replace railroads as means of freight transportation
Interstate Highway System • Network of high-speed roads for interstate travel • 1956 -40, 000 mile system planned • Replaces “Historic Route 66” • Trucks replace railroads as means of freight transportation
 Technology Spurs Productivity • War-Time Technology turned to private sector – Atomic Energy – Computers
Technology Spurs Productivity • War-Time Technology turned to private sector – Atomic Energy – Computers
 Franchising
Franchising
 A Changing Workplace Automation: 1947 -1957 factory workers decreased by 4. 3%, eliminating 1. 5 million blue-collar jobs. By 1956 more white-collar than blue-collar jobs in the U. S. Computers Mark I (1944). First IBM mainframe computer (1951). Corporate Consolidation: By 1960 600 corporations (1/2% of all U. S. companies) accounted for 53% of total corporate income. WHY? ? Cold War military buildup.
A Changing Workplace Automation: 1947 -1957 factory workers decreased by 4. 3%, eliminating 1. 5 million blue-collar jobs. By 1956 more white-collar than blue-collar jobs in the U. S. Computers Mark I (1944). First IBM mainframe computer (1951). Corporate Consolidation: By 1960 600 corporations (1/2% of all U. S. companies) accounted for 53% of total corporate income. WHY? ? Cold War military buildup.
 Multinational Corporations
Multinational Corporations
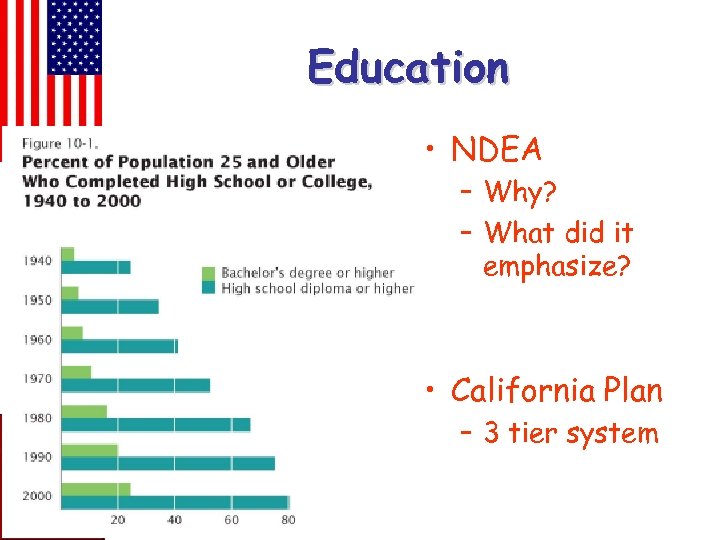 Education • NDEA – Why? – What did it emphasize? • California Plan – 3 tier system
Education • NDEA – Why? – What did it emphasize? • California Plan – 3 tier system


