fcf8f25da02bc3c2c635e43f40d3ccf2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 Postpartum Complications
Postpartum Complications
 Postpartum Complications Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH) Ø Leading cause of maternal morbidity in the United states Ø Life-threatening event that can occur with little warning and is often unrecognized until the mother has profound symptoms Ø Early, acute, or primary PPH occurs within 24 hours of birth Ø Late or secondary PPH occurs more than 24 hours but less than 6
Postpartum Complications Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH) Ø Leading cause of maternal morbidity in the United states Ø Life-threatening event that can occur with little warning and is often unrecognized until the mother has profound symptoms Ø Early, acute, or primary PPH occurs within 24 hours of birth Ø Late or secondary PPH occurs more than 24 hours but less than 6
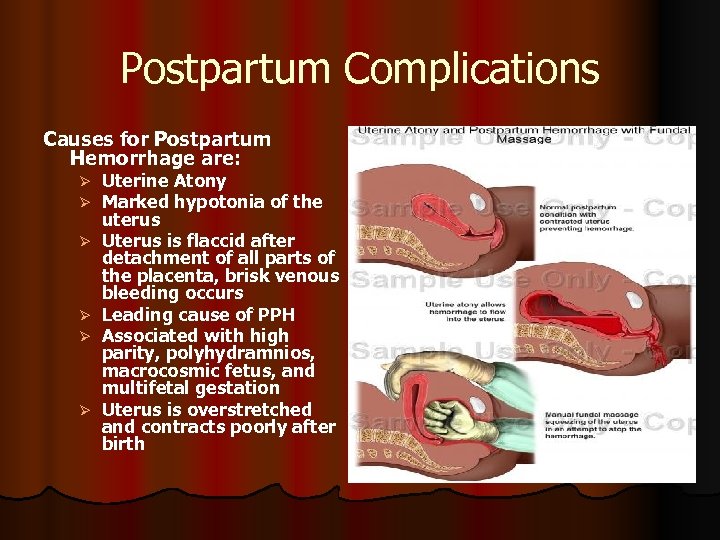 Postpartum Complications Causes for Postpartum Hemorrhage are: Ø Ø Ø Uterine Atony Marked hypotonia of the uterus Uterus is flaccid after detachment of all parts of the placenta, brisk venous bleeding occurs Leading cause of PPH Associated with high parity, polyhydramnios, macrocosmic fetus, and multifetal gestation Uterus is overstretched and contracts poorly after birth
Postpartum Complications Causes for Postpartum Hemorrhage are: Ø Ø Ø Uterine Atony Marked hypotonia of the uterus Uterus is flaccid after detachment of all parts of the placenta, brisk venous bleeding occurs Leading cause of PPH Associated with high parity, polyhydramnios, macrocosmic fetus, and multifetal gestation Uterus is overstretched and contracts poorly after birth
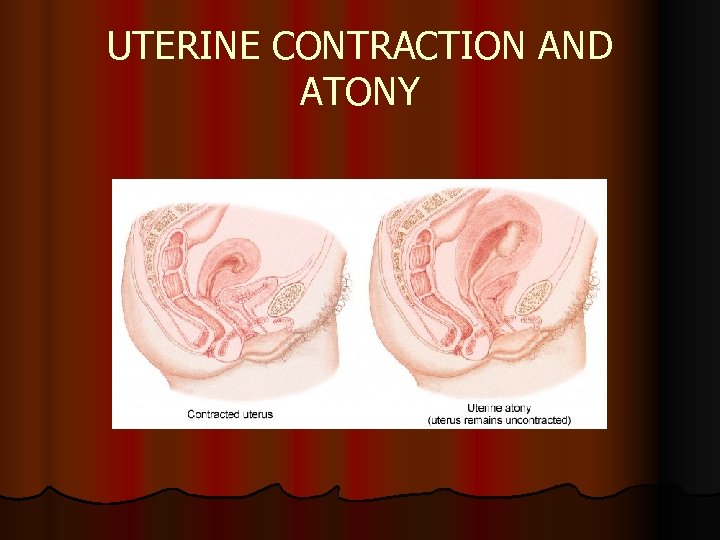 UTERINE CONTRACTION AND ATONY
UTERINE CONTRACTION AND ATONY
 Retained Placenta May result from partial separation of a normal placenta Ø Entrapment of the partially or completely separated placenta by an hourglass constriction ring of the uterus Ø Mismanagement of the third stage of labor Ø Abnormal adherence of the entire placenta or portion of the placenta to the uterine wall Ø
Retained Placenta May result from partial separation of a normal placenta Ø Entrapment of the partially or completely separated placenta by an hourglass constriction ring of the uterus Ø Mismanagement of the third stage of labor Ø Abnormal adherence of the entire placenta or portion of the placenta to the uterine wall Ø
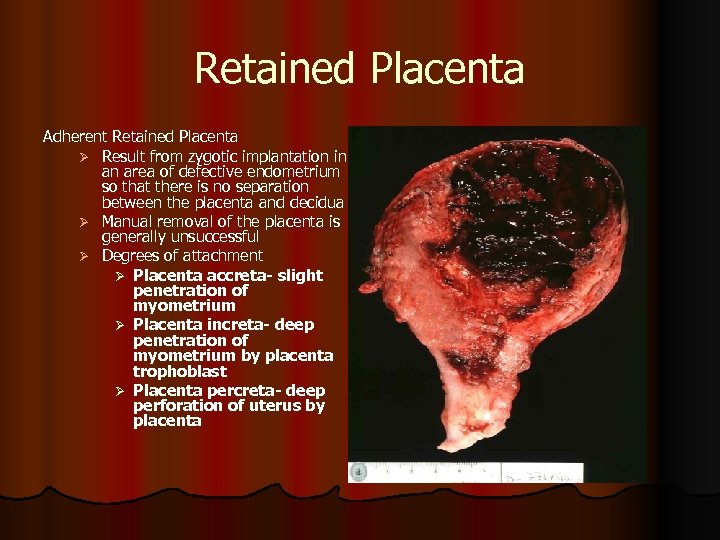 Retained Placenta Adherent Retained Placenta Ø Result from zygotic implantation in an area of defective endometrium so that there is no separation between the placenta and decidua Ø Manual removal of the placenta is generally unsuccessful Ø Degrees of attachment Ø Placenta accreta- slight penetration of myometrium Ø Placenta increta- deep penetration of myometrium by placenta trophoblast Ø Placenta percreta- deep perforation of uterus by placenta
Retained Placenta Adherent Retained Placenta Ø Result from zygotic implantation in an area of defective endometrium so that there is no separation between the placenta and decidua Ø Manual removal of the placenta is generally unsuccessful Ø Degrees of attachment Ø Placenta accreta- slight penetration of myometrium Ø Placenta increta- deep penetration of myometrium by placenta trophoblast Ø Placenta percreta- deep perforation of uterus by placenta
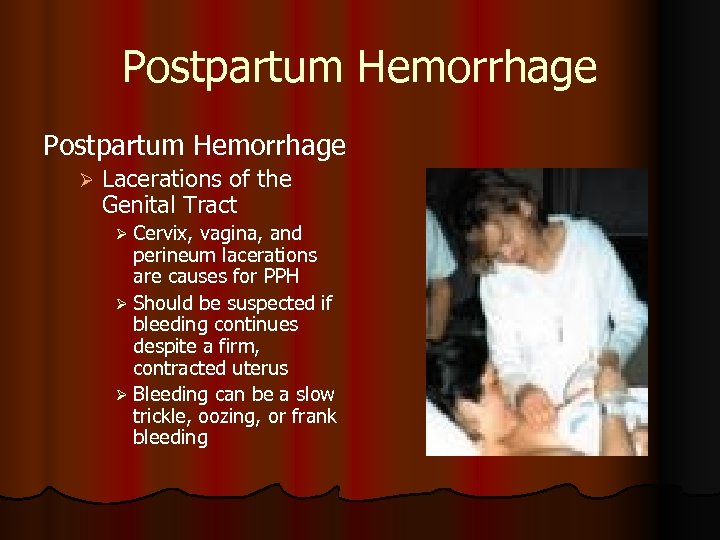 Postpartum Hemorrhage Ø Lacerations of the Genital Tract Ø Cervix, vagina, and perineum lacerations are causes for PPH Ø Should be suspected if bleeding continues despite a firm, contracted uterus Ø Bleeding can be a slow trickle, oozing, or frank bleeding
Postpartum Hemorrhage Ø Lacerations of the Genital Tract Ø Cervix, vagina, and perineum lacerations are causes for PPH Ø Should be suspected if bleeding continues despite a firm, contracted uterus Ø Bleeding can be a slow trickle, oozing, or frank bleeding
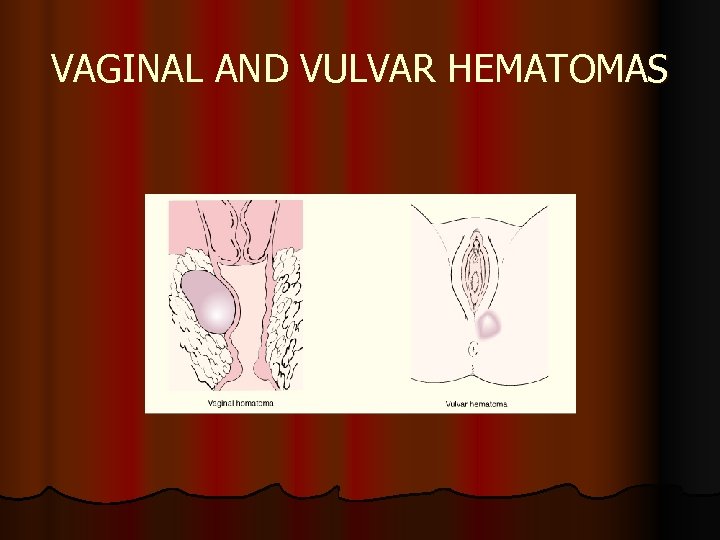
 Postpartum Hemorrhage Lacerations of the Genital Tract Ø Pelvic Hematomas Ø Vulvar, vaginal, or retroperineal Ø Vulvar hematomas are the most common Ø Vaginal hematomas occur most often with a forcepsassisted delivery, episiotomy, and with primigraividas Ø Woman complains of a persistent perineal or rectal pain, or a feeling of pressure in the vagina
Postpartum Hemorrhage Lacerations of the Genital Tract Ø Pelvic Hematomas Ø Vulvar, vaginal, or retroperineal Ø Vulvar hematomas are the most common Ø Vaginal hematomas occur most often with a forcepsassisted delivery, episiotomy, and with primigraividas Ø Woman complains of a persistent perineal or rectal pain, or a feeling of pressure in the vagina
 HEMATOMA l ASSESSMENT l Abnormal severe pain l Pressure in the perineal area l Sensitive, bulging mass in the perineal area with discolored skin l Inability to void l Decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit levels l Signs of shock, such as pallor, tachycardia, and hypotension, if significant blood loss has occurred
HEMATOMA l ASSESSMENT l Abnormal severe pain l Pressure in the perineal area l Sensitive, bulging mass in the perineal area with discolored skin l Inability to void l Decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit levels l Signs of shock, such as pallor, tachycardia, and hypotension, if significant blood loss has occurred
 HEMATOMA l IMPLEMENTATION Monitor vital signs l Monitor client for abnormal pain, especially with forceps delivery l Place ice to the hematoma site l Administer analgesics as prescribed l Monitor intake and output (I&O) l Encourage fluids and voiding l Prepare for urinary catheterization if the client is unable to void l
HEMATOMA l IMPLEMENTATION Monitor vital signs l Monitor client for abnormal pain, especially with forceps delivery l Place ice to the hematoma site l Administer analgesics as prescribed l Monitor intake and output (I&O) l Encourage fluids and voiding l Prepare for urinary catheterization if the client is unable to void l
 HEMATOMA l IMPLEMENTATION l Administer blood products as prescribed l Monitor for signs of infection, such as increased temperature, pulse rate, and WBC count l Administer antibiotics as prescribed, as infection is common following hematoma formation l Prepare for incision and evacuation of hematoma if necessary
HEMATOMA l IMPLEMENTATION l Administer blood products as prescribed l Monitor for signs of infection, such as increased temperature, pulse rate, and WBC count l Administer antibiotics as prescribed, as infection is common following hematoma formation l Prepare for incision and evacuation of hematoma if necessary
 VAGINAL AND VULVAR HEMATOMAS
VAGINAL AND VULVAR HEMATOMAS
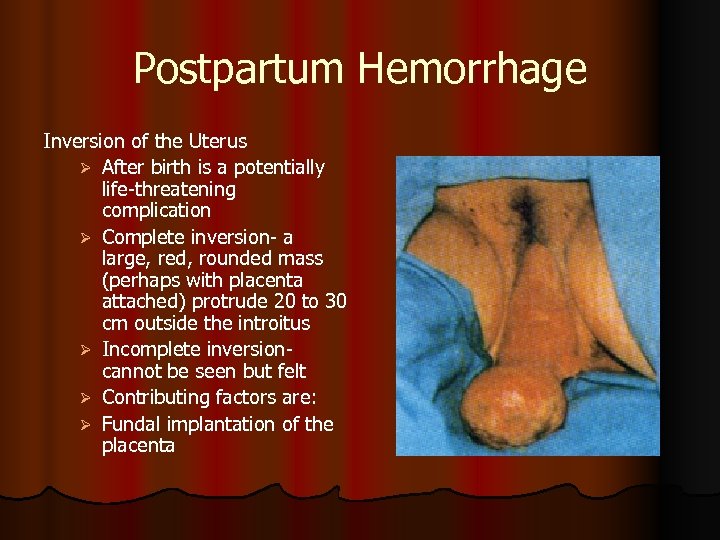 Postpartum Hemorrhage Inversion of the Uterus Ø After birth is a potentially life-threatening complication Ø Complete inversion- a large, red, rounded mass (perhaps with placenta attached) protrude 20 to 30 cm outside the introitus Ø Incomplete inversion- cannot be seen but felt Ø Contributing factors are: Ø Fundal implantation of the placenta
Postpartum Hemorrhage Inversion of the Uterus Ø After birth is a potentially life-threatening complication Ø Complete inversion- a large, red, rounded mass (perhaps with placenta attached) protrude 20 to 30 cm outside the introitus Ø Incomplete inversion- cannot be seen but felt Ø Contributing factors are: Ø Fundal implantation of the placenta
 HEMATOMA l IMPLEMENTATION Monitor vital signs l Monitor client for abnormal pain, especially with forceps delivery l Place ice to the hematoma site l Administer analgesics as prescribed l Monitor intake and output (I&O) l Encourage fluids and voiding l Prepare for urinary catheterization if the client is unable to void l
HEMATOMA l IMPLEMENTATION Monitor vital signs l Monitor client for abnormal pain, especially with forceps delivery l Place ice to the hematoma site l Administer analgesics as prescribed l Monitor intake and output (I&O) l Encourage fluids and voiding l Prepare for urinary catheterization if the client is unable to void l
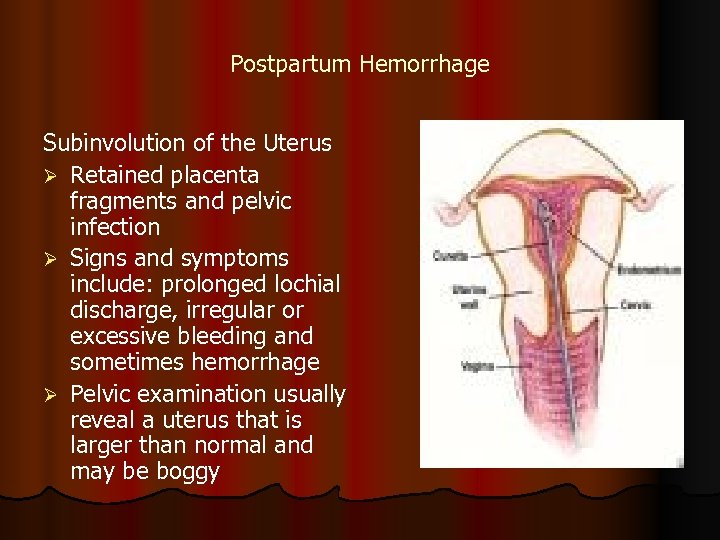 Postpartum Hemorrhage Subinvolution of the Uterus Ø Retained placenta fragments and pelvic infection Ø Signs and symptoms include: prolonged lochial discharge, irregular or excessive bleeding and sometimes hemorrhage Ø Pelvic examination usually reveal a uterus that is larger than normal and may be boggy
Postpartum Hemorrhage Subinvolution of the Uterus Ø Retained placenta fragments and pelvic infection Ø Signs and symptoms include: prolonged lochial discharge, irregular or excessive bleeding and sometimes hemorrhage Ø Pelvic examination usually reveal a uterus that is larger than normal and may be boggy
 HEMORRHAGE l IMPLEMENTATION Massage fundus, with care, not to over massage l Notify physician or health care provider if hemorrhage occurs l Monitor vital signs and fundus every 5 to 15 minutes l Remain with the client l Assess and estimate blood loss by pad count l Assess level of consciousness l Administer fluids and monitor I&O l
HEMORRHAGE l IMPLEMENTATION Massage fundus, with care, not to over massage l Notify physician or health care provider if hemorrhage occurs l Monitor vital signs and fundus every 5 to 15 minutes l Remain with the client l Assess and estimate blood loss by pad count l Assess level of consciousness l Administer fluids and monitor I&O l
 A nurse is monitoring a new mother in the forth stage of labor for signs of hemorrhage. Which of the following would indicate an early sign of excessive blood loss? l 1. A temperature of 100. 4º F l 2. An increased pulse rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute l 3. An increase in the respiratory rate from 16 to 20 breaths per minute l 4. A blood pressure change from 130/88 to 124/80 mm Hg
A nurse is monitoring a new mother in the forth stage of labor for signs of hemorrhage. Which of the following would indicate an early sign of excessive blood loss? l 1. A temperature of 100. 4º F l 2. An increased pulse rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute l 3. An increase in the respiratory rate from 16 to 20 breaths per minute l 4. A blood pressure change from 130/88 to 124/80 mm Hg
 HEMORRHAGE l IMPLEMENTATION l Monitor hemoglobin and hematocrit levels l Maintain asepsis since hemorrhage predisposes to infection l Prepare for the administration of oxytocin (Pitocin) if prescribed l Prepare for the administration of blood transfusions if prescribed
HEMORRHAGE l IMPLEMENTATION l Monitor hemoglobin and hematocrit levels l Maintain asepsis since hemorrhage predisposes to infection l Prepare for the administration of oxytocin (Pitocin) if prescribed l Prepare for the administration of blood transfusions if prescribed
 The physician has written an order to administer methylergonovine (Methergine) to a postpartum client with uterine atony. The nurse would contact the physician to verify the order if which of the following conditions is present in the mother? l 1. Excessive lochia l 2. Excessive bleeding and saturation of more than one peripad per hour l 3. Hypertension l 4. Difficulty locating the uterine fundus
The physician has written an order to administer methylergonovine (Methergine) to a postpartum client with uterine atony. The nurse would contact the physician to verify the order if which of the following conditions is present in the mother? l 1. Excessive lochia l 2. Excessive bleeding and saturation of more than one peripad per hour l 3. Hypertension l 4. Difficulty locating the uterine fundus
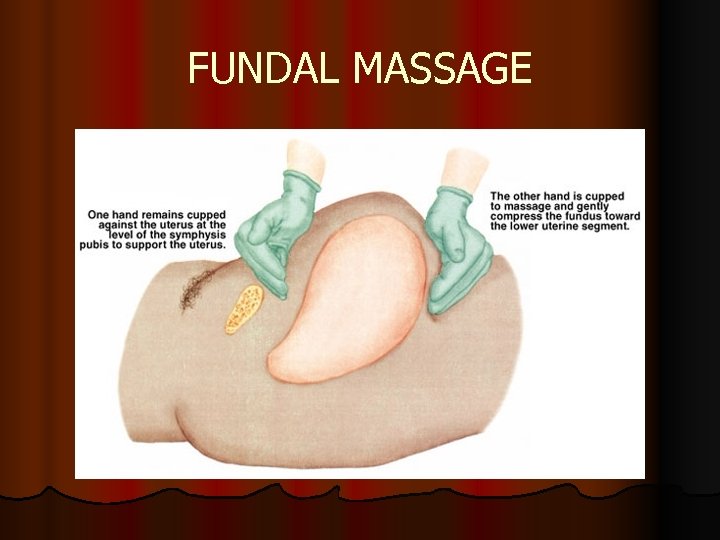 FUNDAL MASSAGE
FUNDAL MASSAGE
 A nurse is monitoring a postpartum client in the fourth stage of labor. Which finding would indicate a complication related to a laceration of the birth canal? l 1. The presence of dark red lochia l 2. Palpation of the fundus at the level of the umbilicus l 3. Palpation of the uterus as a firm contracted ball l 4. The saturation of more than one peripad per hour
A nurse is monitoring a postpartum client in the fourth stage of labor. Which finding would indicate a complication related to a laceration of the birth canal? l 1. The presence of dark red lochia l 2. Palpation of the fundus at the level of the umbilicus l 3. Palpation of the uterus as a firm contracted ball l 4. The saturation of more than one peripad per hour
 A postpartum client complains of pain and a feeling of pressure in the vulvar area. Based on the client’s complaints, the nurse performs an assessment, expecting to note: l 1. An elevated blood pressure l 2. Bradycardia l 3. A firm fundus l 4. A discolored mass on the vulva
A postpartum client complains of pain and a feeling of pressure in the vulvar area. Based on the client’s complaints, the nurse performs an assessment, expecting to note: l 1. An elevated blood pressure l 2. Bradycardia l 3. A firm fundus l 4. A discolored mass on the vulva
 Postpartum Complications Nursing Care for the Woman with a Postpartum hemorrhage Vital signs Ø Uterine consistency Ø Administration of oxytocin or other drugs to stimulate uterine contractions Ø Assessing for bladder distention Ø
Postpartum Complications Nursing Care for the Woman with a Postpartum hemorrhage Vital signs Ø Uterine consistency Ø Administration of oxytocin or other drugs to stimulate uterine contractions Ø Assessing for bladder distention Ø
 Postpartum Complications Hemorrhagic (Hypovolemic) Shock is an emergency situation in which the perfusion of body organs may become severely compromised and death occur Ø Medical management includes: Ø Restoring circulating blood volume and treating the cause of the hemorrhage Ø Rapid infusion of a crystalloid solution is given at a rate of 3000 ml for 1000 ml of blood loss Ø
Postpartum Complications Hemorrhagic (Hypovolemic) Shock is an emergency situation in which the perfusion of body organs may become severely compromised and death occur Ø Medical management includes: Ø Restoring circulating blood volume and treating the cause of the hemorrhage Ø Rapid infusion of a crystalloid solution is given at a rate of 3000 ml for 1000 ml of blood loss Ø
 Postpartum Complications Hemorrhagic Shock Ø Nursing Care includes: Ø Monitors the woman’s pulse and blood pressure Ø Evaluates the woman’s skin temperature, color, and turgor, as well the assessment of the woman’s mucous membranes Ø Auscultation of the woman’s breath sounds before the initiation of fluid replacement Ø Administration of oxygen
Postpartum Complications Hemorrhagic Shock Ø Nursing Care includes: Ø Monitors the woman’s pulse and blood pressure Ø Evaluates the woman’s skin temperature, color, and turgor, as well the assessment of the woman’s mucous membranes Ø Auscultation of the woman’s breath sounds before the initiation of fluid replacement Ø Administration of oxygen
 Coagulopathies Ø Ø Ø Ø Idiopathic Thrombocytopenia Purpura (ITP) An autoimmune disorder in which antiplatelets decrease the life span of the platelets Thrombocytopenia, capillary fragility, and increase bleeding time are diagnostic findings ITP may cause severe hemorrhage after cesarean birth or from cervical or vaginal laceration Increased incidence of postpartum uterine bleeding and vaginal hematomas Medical management includes Control of platelet stability
Coagulopathies Ø Ø Ø Ø Idiopathic Thrombocytopenia Purpura (ITP) An autoimmune disorder in which antiplatelets decrease the life span of the platelets Thrombocytopenia, capillary fragility, and increase bleeding time are diagnostic findings ITP may cause severe hemorrhage after cesarean birth or from cervical or vaginal laceration Increased incidence of postpartum uterine bleeding and vaginal hematomas Medical management includes Control of platelet stability
 Coagulopathies Ø von Willebrand Disease A type of hemophilia and is probably the most common of all heredity bleeding disorders Ø Most common congenital clotting defects in American women of child bearing age Ø Results from a factor VIII deficiency and platelet dysfunction Ø That is transmitted as an incomplete autosomal dominant trait to both sexes Ø
Coagulopathies Ø von Willebrand Disease A type of hemophilia and is probably the most common of all heredity bleeding disorders Ø Most common congenital clotting defects in American women of child bearing age Ø Results from a factor VIII deficiency and platelet dysfunction Ø That is transmitted as an incomplete autosomal dominant trait to both sexes Ø
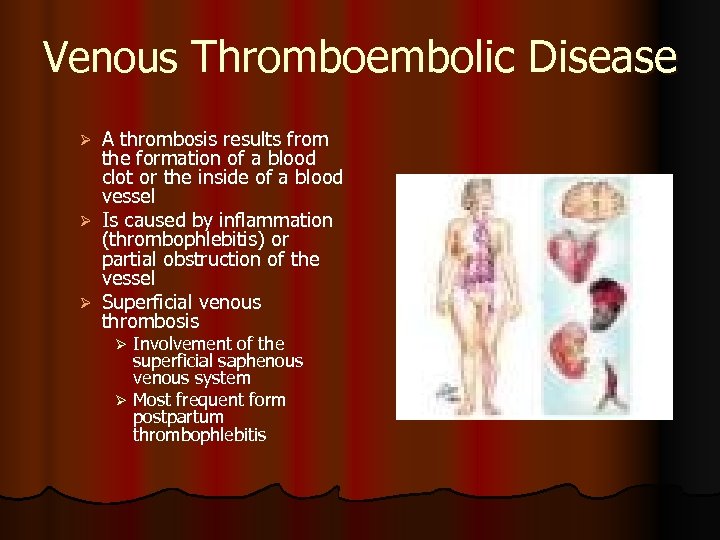 Venous Thromboembolic Disease A thrombosis results from the formation of a blood clot or the inside of a blood vessel Ø Is caused by inflammation (thrombophlebitis) or partial obstruction of the vessel Ø Superficial venous thrombosis Ø Involvement of the superficial saphenous venous system Ø Most frequent form postpartum thrombophlebitis Ø
Venous Thromboembolic Disease A thrombosis results from the formation of a blood clot or the inside of a blood vessel Ø Is caused by inflammation (thrombophlebitis) or partial obstruction of the vessel Ø Superficial venous thrombosis Ø Involvement of the superficial saphenous venous system Ø Most frequent form postpartum thrombophlebitis Ø
 HOMANS’ SIGN
HOMANS’ SIGN
 THE VENOUS SYSTEM
THE VENOUS SYSTEM
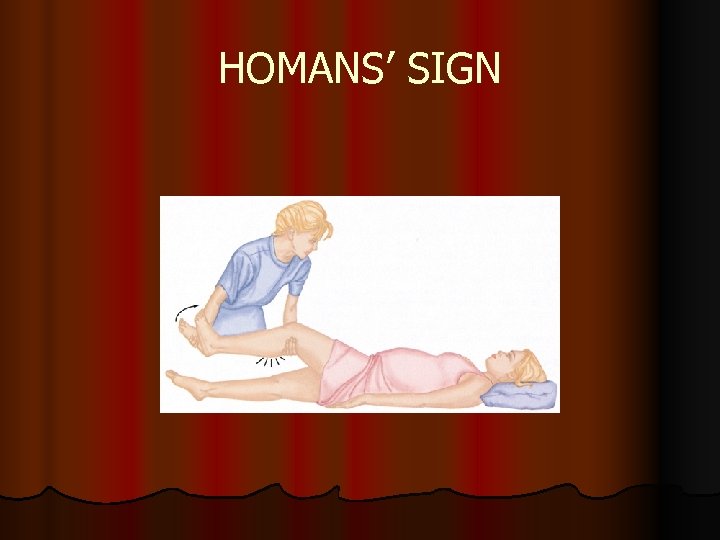
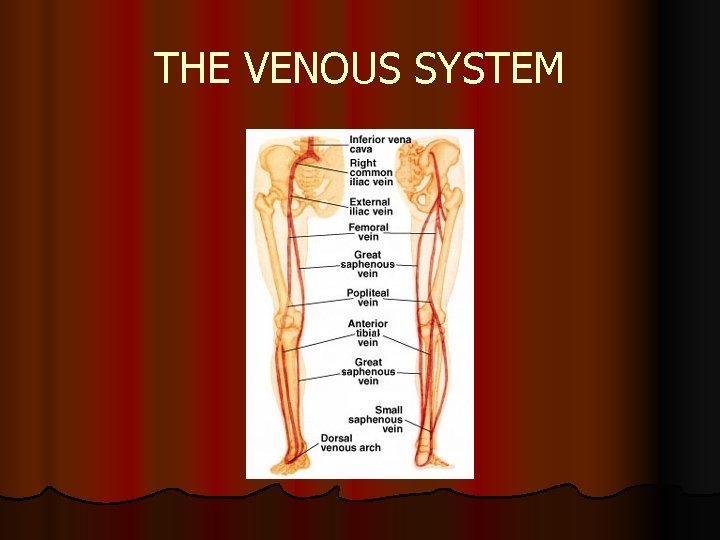
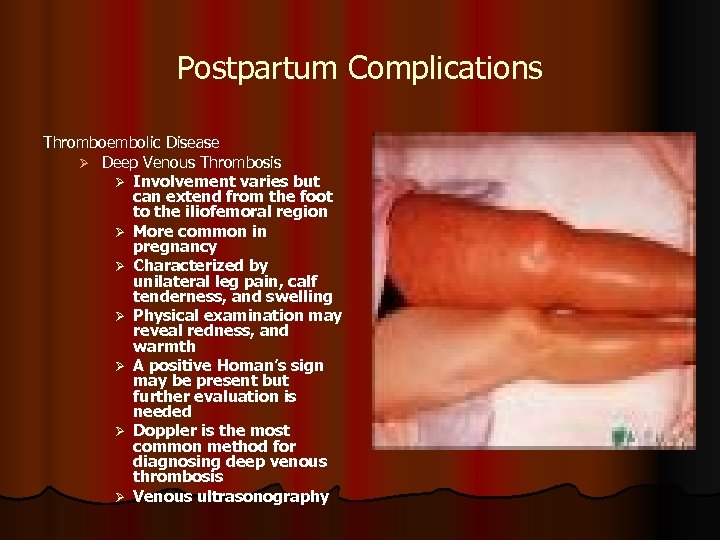 Postpartum Complications Thromboembolic Disease Ø Deep Venous Thrombosis Ø Involvement varies but can extend from the foot to the iliofemoral region Ø More common in pregnancy Ø Characterized by unilateral leg pain, calf tenderness, and swelling Ø Physical examination may reveal redness, and warmth Ø A positive Homan’s sign may be present but further evaluation is needed Ø Doppler is the most common method for diagnosing deep venous thrombosis Ø Venous ultrasonography
Postpartum Complications Thromboembolic Disease Ø Deep Venous Thrombosis Ø Involvement varies but can extend from the foot to the iliofemoral region Ø More common in pregnancy Ø Characterized by unilateral leg pain, calf tenderness, and swelling Ø Physical examination may reveal redness, and warmth Ø A positive Homan’s sign may be present but further evaluation is needed Ø Doppler is the most common method for diagnosing deep venous thrombosis Ø Venous ultrasonography
 A nurse employed in a prenatal clinic is performing prenatal assessments on clients who are in their first trimester of pregnancy. The nurse is concerned with identifying the clients who may be at risk for the development of postpartum complications. Which client would be least likely at risk for the development of thromboembolitic disorders in the postpartum period? l l 1. A 35 -year-old woman who reports that she smokes 2. A 37 -year-old woman in her fourth pregnancy who is overweight 3. A 26 -year-old woman with a family history of thrombophlebitis 4. A 22 -year-old woman in her first pregnancy who states that oral contraceptives taken in the past have caused thrombophlebitis
A nurse employed in a prenatal clinic is performing prenatal assessments on clients who are in their first trimester of pregnancy. The nurse is concerned with identifying the clients who may be at risk for the development of postpartum complications. Which client would be least likely at risk for the development of thromboembolitic disorders in the postpartum period? l l 1. A 35 -year-old woman who reports that she smokes 2. A 37 -year-old woman in her fourth pregnancy who is overweight 3. A 26 -year-old woman with a family history of thrombophlebitis 4. A 22 -year-old woman in her first pregnancy who states that oral contraceptives taken in the past have caused thrombophlebitis
 A postpartum nurse is assessing a mother who delivered a healthy newborn by cesarean section for signs and symptoms of superficial venous thrombosis. Which of the following would the nurse note if superficial venous thrombosis were present l 1. Paleness of the calf area l 2. Enlarged hardened vein l 3. Coolness of the calf area l 4. Palpable dorsalis pedis pulses
A postpartum nurse is assessing a mother who delivered a healthy newborn by cesarean section for signs and symptoms of superficial venous thrombosis. Which of the following would the nurse note if superficial venous thrombosis were present l 1. Paleness of the calf area l 2. Enlarged hardened vein l 3. Coolness of the calf area l 4. Palpable dorsalis pedis pulses
 A nurse is caring for a postpartum client with a diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis who is receiving a continuous intravenous infusion of heparin. Which laboratory result will the nurse specifically review to determine if an effective and appropriate dose of the heparin is being administered? l 1. Prothrombin time l 2. International Normalized Ratio (INR) l 3. Activated partial thromboplastin time l 4. Platelet count
A nurse is caring for a postpartum client with a diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis who is receiving a continuous intravenous infusion of heparin. Which laboratory result will the nurse specifically review to determine if an effective and appropriate dose of the heparin is being administered? l 1. Prothrombin time l 2. International Normalized Ratio (INR) l 3. Activated partial thromboplastin time l 4. Platelet count
 A nurse has provided instructions to a mother at risk for thrombosis regarding measures to prevent the occurrence. Which statement by the mother indicates a need for further instructions? l 1. “I should perform regularly scheduled exercise such as walking. ” l 2. “I should avoid prolonged standing or sitting in one position. ” l 3. “I should avoid using pillows under my knees to prevent pressure in the back of my knee area. ” l 4. “I should apply my antiembolism stockings after I get up in the morning. ”
A nurse has provided instructions to a mother at risk for thrombosis regarding measures to prevent the occurrence. Which statement by the mother indicates a need for further instructions? l 1. “I should perform regularly scheduled exercise such as walking. ” l 2. “I should avoid prolonged standing or sitting in one position. ” l 3. “I should avoid using pillows under my knees to prevent pressure in the back of my knee area. ” l 4. “I should apply my antiembolism stockings after I get up in the morning. ”
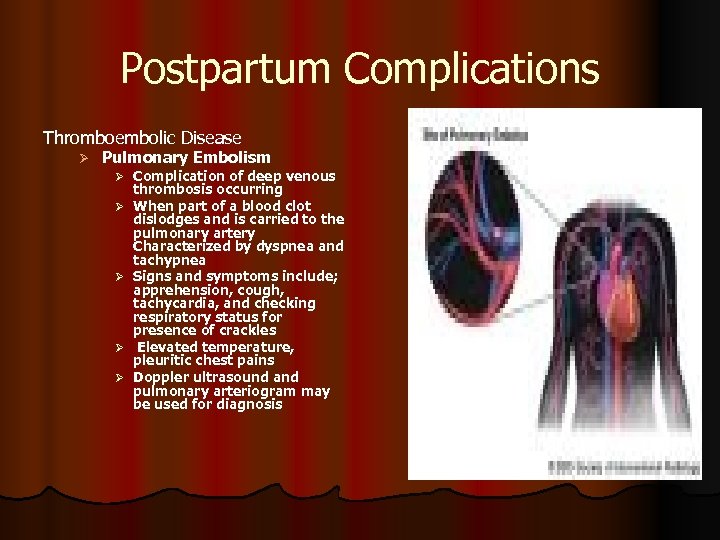 Postpartum Complications Thromboembolic Disease Ø Pulmonary Embolism Ø Complication of deep venous Ø Ø thrombosis occurring When part of a blood clot dislodges and is carried to the pulmonary artery Characterized by dyspnea and tachypnea Signs and symptoms include; apprehension, cough, tachycardia, and checking respiratory status for presence of crackles Elevated temperature, pleuritic chest pains Doppler ultrasound and pulmonary arteriogram may be used for diagnosis
Postpartum Complications Thromboembolic Disease Ø Pulmonary Embolism Ø Complication of deep venous Ø Ø thrombosis occurring When part of a blood clot dislodges and is carried to the pulmonary artery Characterized by dyspnea and tachypnea Signs and symptoms include; apprehension, cough, tachycardia, and checking respiratory status for presence of crackles Elevated temperature, pleuritic chest pains Doppler ultrasound and pulmonary arteriogram may be used for diagnosis
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM l IMPLEMENTATION l Administer oxygen as prescribed l Position client with the head of the bed elevated to promote comfort l Monitor vital signs frequently l Assess respiratory rate and breath sounds frequently and monitor for signs of respiratory distress and for signs of increasing hypoxemia l Administer IV fluids and anticoagulants as prescribed
PULMONARY EMBOLISM l IMPLEMENTATION l Administer oxygen as prescribed l Position client with the head of the bed elevated to promote comfort l Monitor vital signs frequently l Assess respiratory rate and breath sounds frequently and monitor for signs of respiratory distress and for signs of increasing hypoxemia l Administer IV fluids and anticoagulants as prescribed
 A client in the postpartum unit complains of sudden sharp chest pain. The nurse notes that the client is tachycardic and the respiratory rate is elevated, and suspects a pulmonary embolism. The nurse takes which initial action? l 1. Assesses the client’s blood pressure l 2. Initiates an IV line l 3. Administers oxygen at 8 to 10 L by tight face mask l 4. Prepares to administer morphine sulfate
A client in the postpartum unit complains of sudden sharp chest pain. The nurse notes that the client is tachycardic and the respiratory rate is elevated, and suspects a pulmonary embolism. The nurse takes which initial action? l 1. Assesses the client’s blood pressure l 2. Initiates an IV line l 3. Administers oxygen at 8 to 10 L by tight face mask l 4. Prepares to administer morphine sulfate
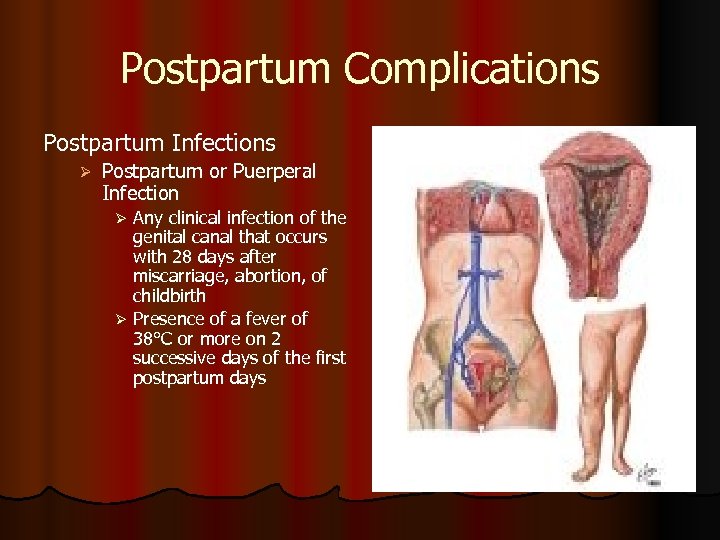 Postpartum Complications Postpartum Infections Ø Postpartum or Puerperal Infection Any clinical infection of the genital canal that occurs with 28 days after miscarriage, abortion, of childbirth Ø Presence of a fever of 38°C or more on 2 successive days of the first postpartum days Ø
Postpartum Complications Postpartum Infections Ø Postpartum or Puerperal Infection Any clinical infection of the genital canal that occurs with 28 days after miscarriage, abortion, of childbirth Ø Presence of a fever of 38°C or more on 2 successive days of the first postpartum days Ø
 A nurse is reviewing the records of the new mothers admitted to the postpartum unit. The nurse determines that which mother would be at least risk for developing a puerperal infection? l 1. A mother with a history of previous infections l 2. A mother who experienced prolonged rupture of the membranes l 3. A mother who had an excessive number of vaginal exams l 4. A mother who underwent a vaginal delivery of the newborn
A nurse is reviewing the records of the new mothers admitted to the postpartum unit. The nurse determines that which mother would be at least risk for developing a puerperal infection? l 1. A mother with a history of previous infections l 2. A mother who experienced prolonged rupture of the membranes l 3. A mother who had an excessive number of vaginal exams l 4. A mother who underwent a vaginal delivery of the newborn
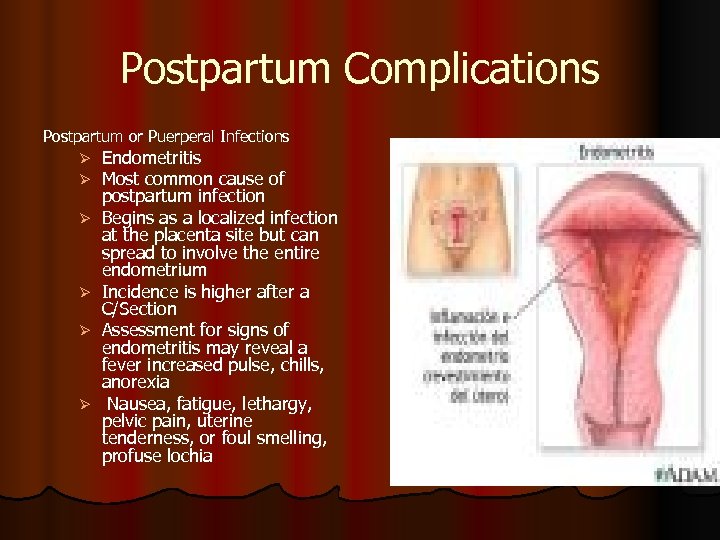 Postpartum Complications Postpartum or Puerperal Infections Ø Ø Ø Endometritis Most common cause of postpartum infection Begins as a localized infection at the placenta site but can spread to involve the entire endometrium Incidence is higher after a C/Section Assessment for signs of endometritis may reveal a fever increased pulse, chills, anorexia Nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pelvic pain, uterine tenderness, or foul smelling, profuse lochia
Postpartum Complications Postpartum or Puerperal Infections Ø Ø Ø Endometritis Most common cause of postpartum infection Begins as a localized infection at the placenta site but can spread to involve the entire endometrium Incidence is higher after a C/Section Assessment for signs of endometritis may reveal a fever increased pulse, chills, anorexia Nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pelvic pain, uterine tenderness, or foul smelling, profuse lochia
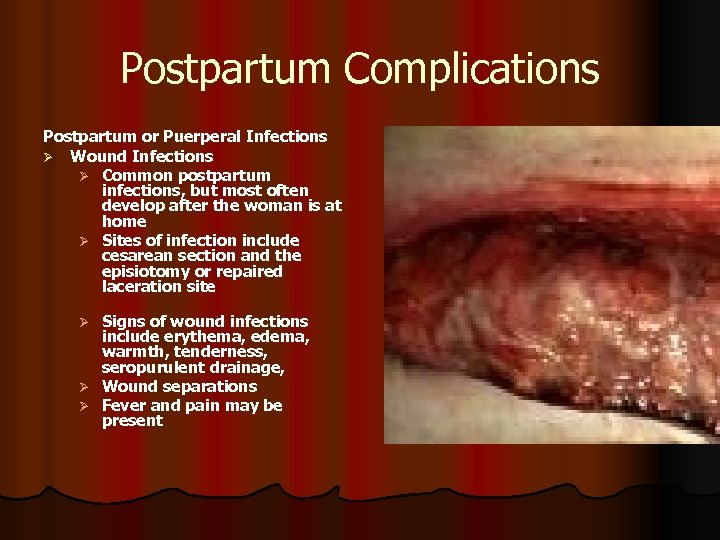 Postpartum Complications Postpartum or Puerperal Infections Ø Wound Infections Ø Common postpartum infections, but most often develop after the woman is at home Ø Sites of infection include cesarean section and the episiotomy or repaired laceration site Signs of wound infections include erythema, edema, warmth, tenderness, seropurulent drainage, Ø Wound separations Ø Fever and pain may be present Ø
Postpartum Complications Postpartum or Puerperal Infections Ø Wound Infections Ø Common postpartum infections, but most often develop after the woman is at home Ø Sites of infection include cesarean section and the episiotomy or repaired laceration site Signs of wound infections include erythema, edema, warmth, tenderness, seropurulent drainage, Ø Wound separations Ø Fever and pain may be present Ø
 Postpartum Complications Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) Ø Ø Occur in 2 to 4% of postpartum women Risk factors include urinary catherizations, frequent pelvic examinations, epidural anesthesia, genital tract injury, history of UTI, and cesarean birth Signs and symptoms include dysuria, frequency and urgency Low-grade fever, urinary retention, hematuria, and pyuria
Postpartum Complications Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) Ø Ø Occur in 2 to 4% of postpartum women Risk factors include urinary catherizations, frequent pelvic examinations, epidural anesthesia, genital tract injury, history of UTI, and cesarean birth Signs and symptoms include dysuria, frequency and urgency Low-grade fever, urinary retention, hematuria, and pyuria
 A 2 -day postpartum woman preparing for discharge complains of burning on urination, urgency, and frequency of urination. A urinalysis is collected and the results indicate the presence of a urinary tract infection. The nurse provides instructions to the woman regarding measures to treat the infection. Which statement by the woman indicates the need for further instructions? l 1. “I need to take the prescribed medication until it is completed. ” l 2. “I need to increase my fluid intake to at least 3000 m. L daily. ” l 3. “I need to urinate frequently throughout the day and not hold my urine. ” l 4. “I need to eat foods and drink fluids that will decrease the acid in my urine. ”
A 2 -day postpartum woman preparing for discharge complains of burning on urination, urgency, and frequency of urination. A urinalysis is collected and the results indicate the presence of a urinary tract infection. The nurse provides instructions to the woman regarding measures to treat the infection. Which statement by the woman indicates the need for further instructions? l 1. “I need to take the prescribed medication until it is completed. ” l 2. “I need to increase my fluid intake to at least 3000 m. L daily. ” l 3. “I need to urinate frequently throughout the day and not hold my urine. ” l 4. “I need to eat foods and drink fluids that will decrease the acid in my urine. ”
 A postpartum client complains of burning and pain on urination, and a urinary tract infection is suspected. The nurse contacts the physician and receives orders for the client. Of the following, which will the nurse implement first? l 1. Administer the prescribed broad- spectrum antibiotic l 2. Obtain urine for culture and sensitivity l 3. Teach the client about proper perineal care l 4. Instruct the client to increase fluid intake
A postpartum client complains of burning and pain on urination, and a urinary tract infection is suspected. The nurse contacts the physician and receives orders for the client. Of the following, which will the nurse implement first? l 1. Administer the prescribed broad- spectrum antibiotic l 2. Obtain urine for culture and sensitivity l 3. Teach the client about proper perineal care l 4. Instruct the client to increase fluid intake
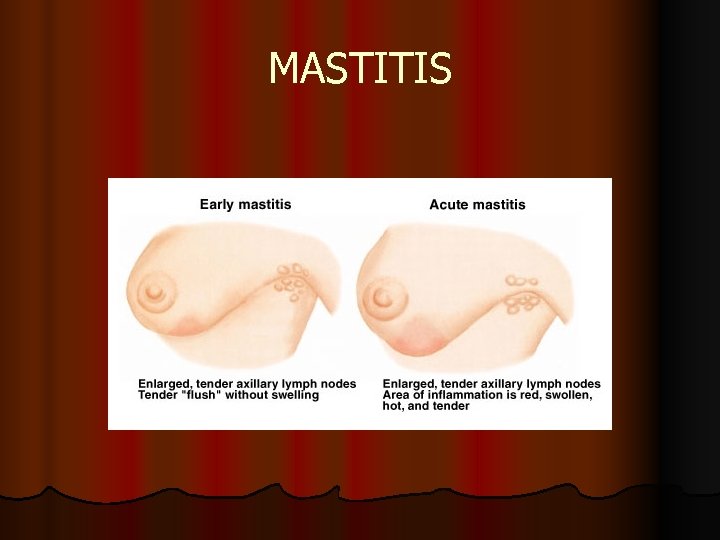
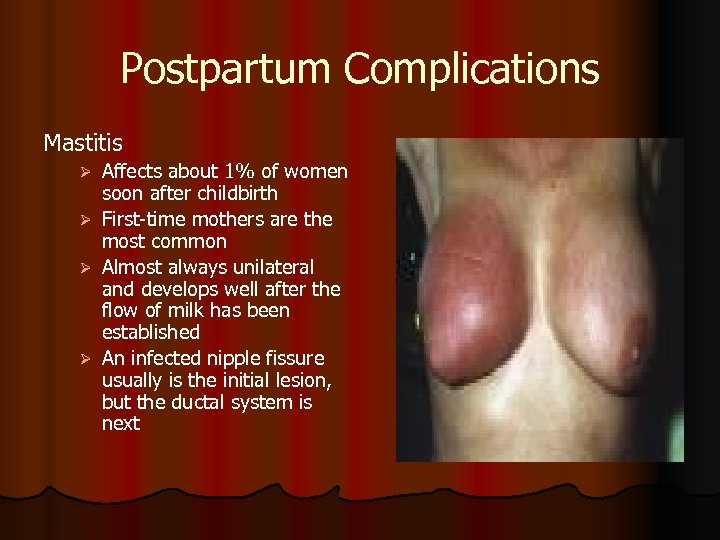 Postpartum Complications Mastitis Affects about 1% of women soon after childbirth Ø First-time mothers are the most common Ø Almost always unilateral and develops well after the flow of milk has been established Ø An infected nipple fissure usually is the initial lesion, but the ductal system is next Ø
Postpartum Complications Mastitis Affects about 1% of women soon after childbirth Ø First-time mothers are the most common Ø Almost always unilateral and develops well after the flow of milk has been established Ø An infected nipple fissure usually is the initial lesion, but the ductal system is next Ø
 MASTITIS
MASTITIS
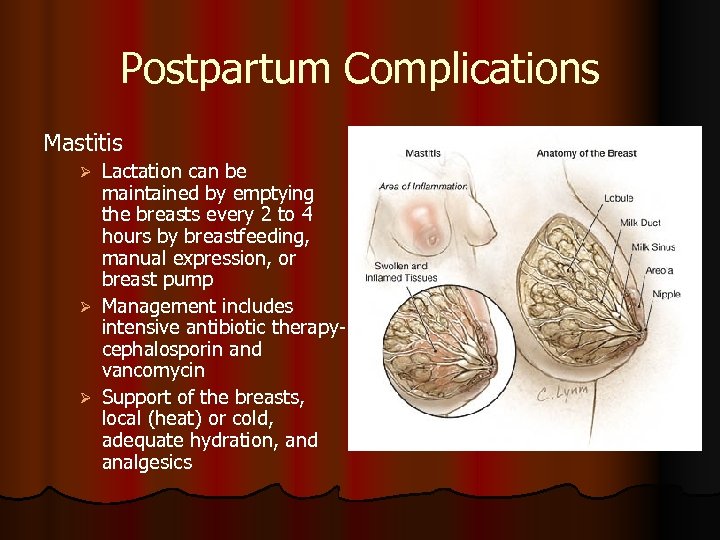 Postpartum Complications Mastitis Lactation can be maintained by emptying the breasts every 2 to 4 hours by breastfeeding, manual expression, or breast pump Ø Management includes intensive antibiotic therapycephalosporin and vancomycin Ø Support of the breasts, local (heat) or cold, adequate hydration, and analgesics Ø
Postpartum Complications Mastitis Lactation can be maintained by emptying the breasts every 2 to 4 hours by breastfeeding, manual expression, or breast pump Ø Management includes intensive antibiotic therapycephalosporin and vancomycin Ø Support of the breasts, local (heat) or cold, adequate hydration, and analgesics Ø
 A new mother is seen in the health care clinic 2 weeks after the birth of a healthy newborn. The mother is complaining that she feels as though she has the flu and complains of fatigue and aching muscles. On further assessment, the nurse notes a localized area of redness on the left breast; the mother is diagnosed with mastitis. The nurse provides information to the mother about the condition and tells the mother that this infection: l 1. Can occur anytime during breast-feeding l 2. Is most common for women who have breast-fed in the past l 3. Always involves both breasts l 4. Is usually caused by wearing a support bra
A new mother is seen in the health care clinic 2 weeks after the birth of a healthy newborn. The mother is complaining that she feels as though she has the flu and complains of fatigue and aching muscles. On further assessment, the nurse notes a localized area of redness on the left breast; the mother is diagnosed with mastitis. The nurse provides information to the mother about the condition and tells the mother that this infection: l 1. Can occur anytime during breast-feeding l 2. Is most common for women who have breast-fed in the past l 3. Always involves both breasts l 4. Is usually caused by wearing a support bra
 A nurse has provided instructions regarding therapeutic management to a mother who has been diagnosed with mastitis. Which statement by the mother indicates a need for further instructions? l 1. “I need to take antibiotics, and I should begin to feel better in 24 to 48 hours. ” l 2. “I can use analgesics to assist in alleviating some of the discomfort. ” l 3. “I need to wear a support bra to relieve the discomfort. ” l 4. “I need to stop breast-feeding until this condition resolves. ”
A nurse has provided instructions regarding therapeutic management to a mother who has been diagnosed with mastitis. Which statement by the mother indicates a need for further instructions? l 1. “I need to take antibiotics, and I should begin to feel better in 24 to 48 hours. ” l 2. “I can use analgesics to assist in alleviating some of the discomfort. ” l 3. “I need to wear a support bra to relieve the discomfort. ” l 4. “I need to stop breast-feeding until this condition resolves. ”
 Case Scenario Laura is in the recovery room. Nursing assessment reveals fundus 3+ above the umbilicus and deviated to the right. Lochia is large rubra with small clots. BP 90/50, P. 120, R 24. She complains of being cold and is shivering and shaking. Her perineum is swollen, especially the right side. AN IV of 1, 000 LR with 10 u Pitocin is infusing into the right arm.
Case Scenario Laura is in the recovery room. Nursing assessment reveals fundus 3+ above the umbilicus and deviated to the right. Lochia is large rubra with small clots. BP 90/50, P. 120, R 24. She complains of being cold and is shivering and shaking. Her perineum is swollen, especially the right side. AN IV of 1, 000 LR with 10 u Pitocin is infusing into the right arm.
 Case Scenario What could be happening to Laura? Explain with pertinent data 2. What interventions should be done immediately? 3. What are the practice standards of vital signs and checking the fundus in this stage? Why is this important? 4. What is Pitocin used for in this stage? 1.
Case Scenario What could be happening to Laura? Explain with pertinent data 2. What interventions should be done immediately? 3. What are the practice standards of vital signs and checking the fundus in this stage? Why is this important? 4. What is Pitocin used for in this stage? 1.


