8d0a7c94efccd0e36c82cc471b58702c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

POSTGRADUATE MOBILITY Professor G R Tomlinson University of Sheffield, UK 4 th International Conference on Postgraduate Education (ICPE-4) Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia November 2010

A few messages : • International postgraduate research (PGR) students are essential for the success of an economy (worth >£ 600 million per annum to the UK economy direct – much more indirect) • They contribute to the growth of the knowledge economy and enhance / motivate the research output of Universities, supporting aspirations of ‘world-class’ • The need for trained doctoral level staff is growing in the global economy, (India, China, Nigeria, Malaysia) • Have we got the ‘best’ models for sustaining postgraduate mobility?

Some challenges that institutions face with regards to international delivery: • • • Affordability Flexibility Supervision / infrastructure Supply and demand regarding subjects Immigration / visa issues
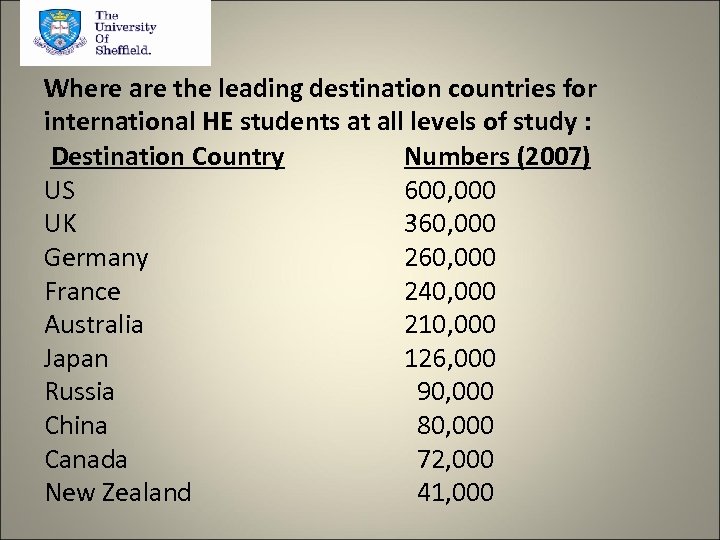
Where are the leading destination countries for international HE students at all levels of study : Destination Country Numbers (2007) US 600, 000 UK 360, 000 Germany 260, 000 France 240, 000 Australia 210, 000 Japan 126, 000 Russia 90, 000 China 80, 000 Canada 72, 000 New Zealand 41, 000

However, we might observe a world where there is likely to be : • more intense international competition • more diverse education ‘products’ and a wider variety of delivery mechanisms • more varied perceptions of the benefits of HE • greater discrimination

• influence of the ‘digital world’ • influence of the private sector re priorities and business models • changing nature of the doctorate (split site, professional, jointly awarded …)
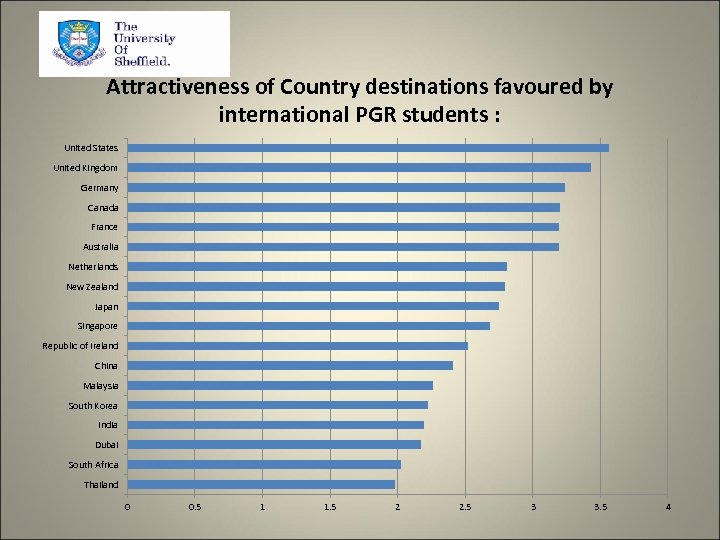
Attractiveness of Country destinations favoured by international PGR students : United States United Kingdom Germany Canada France Australia Netherlands New Zealand Japan Singapore Republic of Ireland China Malaysia South Korea India Dubai South Africa Thailand 0 0. 5 1 1. 5 2 2. 5 3 3. 5 4
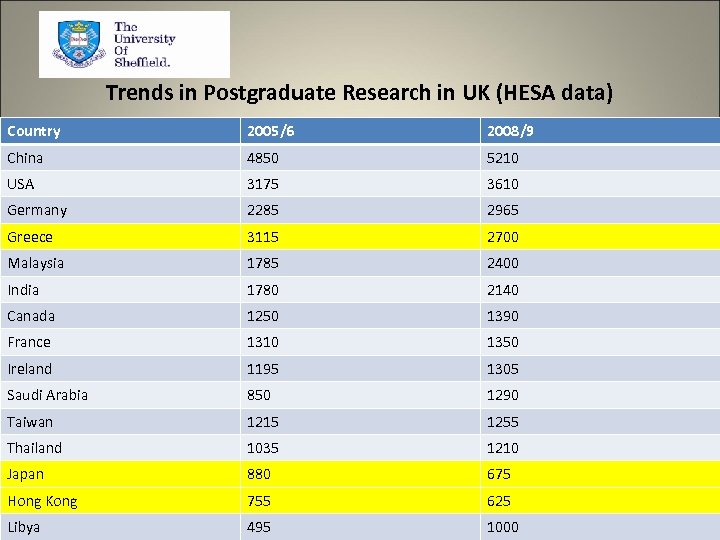
Trends in Postgraduate Research in UK (HESA data) Country 2005/6 2008/9 China 4850 5210 USA 3175 3610 Germany 2285 2965 Greece 3115 2700 Malaysia 1785 2400 India 1780 2140 Canada 1250 1390 France 1310 1350 Ireland 1195 1305 Saudi Arabia 850 1290 Taiwan 1215 1255 Thailand 1035 1210 Japan 880 675 Hong Kong 755 625 Libya 495 1000
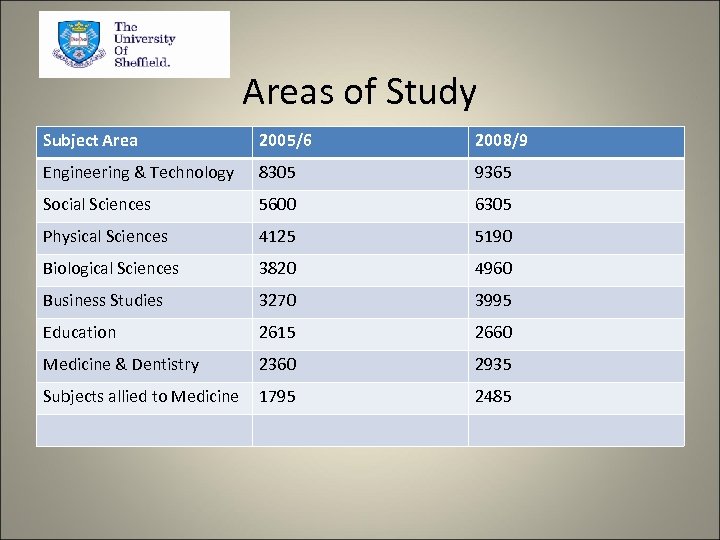
Areas of Study Subject Area 2005/6 2008/9 Engineering & Technology 8305 9365 Social Sciences 5600 6305 Physical Sciences 4125 5190 Biological Sciences 3820 4960 Business Studies 3270 3995 Education 2615 2660 Medicine & Dentistry 2360 2935 Subjects allied to Medicine 1795 2485
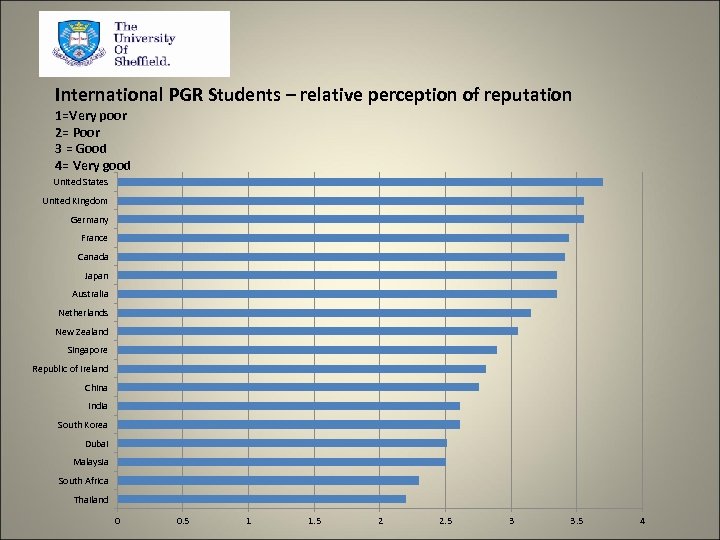
International PGR Students – relative perception of reputation 1=Very poor 2= Poor 3 = Good 4= Very good United States United Kingdom Germany France Canada Japan Australia Netherlands New Zealand Singapore Republic of Ireland China India South Korea Dubai Malaysia South Africa Thailand 0 0. 5 1 1. 5 2 2. 5 3 3. 5 4
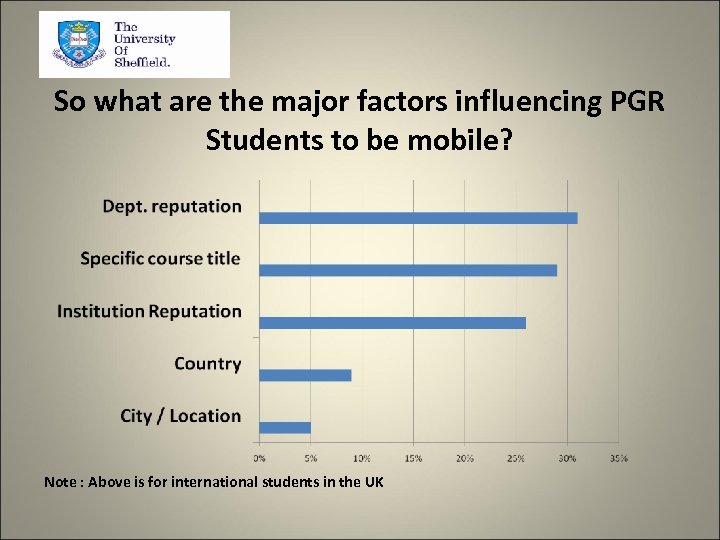
So what are the major factors influencing PGR Students to be mobile? Note : Above is for international students in the UK
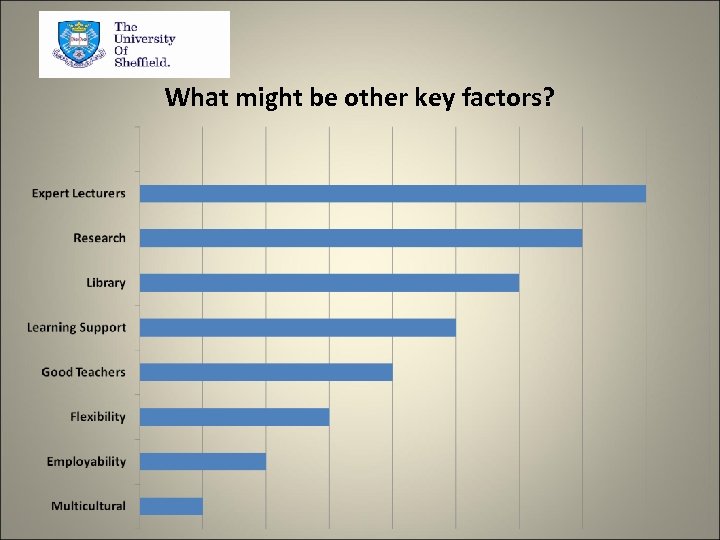
What might be other key factors?
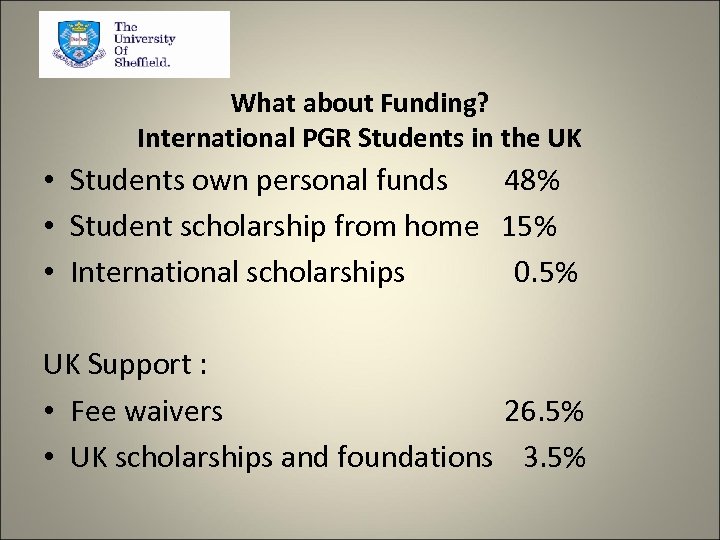
What about Funding? International PGR Students in the UK • Students own personal funds 48% • Student scholarship from home 15% • International scholarships 0. 5% UK Support : • Fee waivers 26. 5% • UK scholarships and foundations 3. 5%
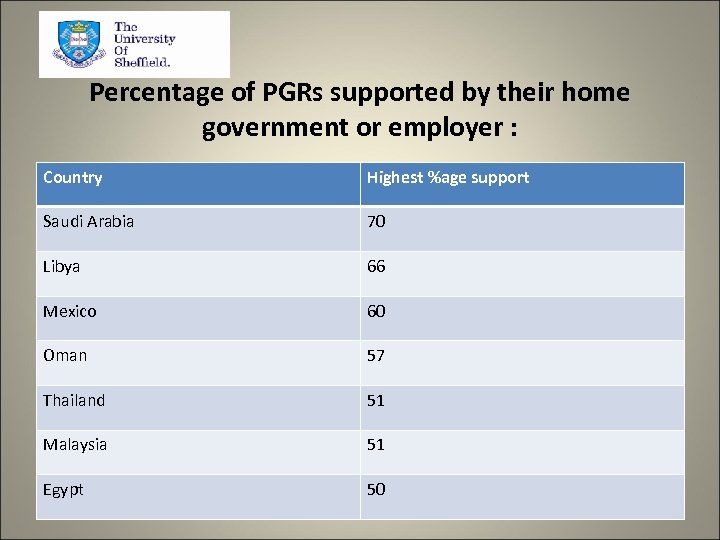
Percentage of PGRs supported by their home government or employer : Country Highest %age support Saudi Arabia 70 Libya 66 Mexico 60 Oman 57 Thailand 51 Malaysia 51 Egypt 50

What is driving global demand? • Fast growth of the provision in lower and middle income countries with a lack of research infrastructure for staff development • Increasing investment in research • Competitive international employment market and its access

What might be the barriers? • Inflexible delivery • Inadequate funding support (including access to part-time work) • What is the doctorate degree? • Quality of the student experience

Flexible Doctorates: JARD – Jointly Awarded Research Degree ARAP – A*Star Research Attachment Programme

JARD : • Developed in partnership with UPM and is a Ph. D programme with a high degree of flexibility • The scheme offers an award (officially on the certificate) from two world class universities • Up to 18 months is spent at both UPM and the Uo. S (minimum of 12 months) • Local fees are paid for the duration of the study period at each University • List of ‘supervisors’ and research areas / key researchers available to UPM to ensure quality co-supervision • Jointly owned IPR (in equal proportion) • Visiting Professor Scheme

ARAP : A*Research Attachment Programme • Developed in partnership with the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*Star) in Singapore • A 4 year Ph. D programme with the Ph. D awarded by the Uo. S • Students typically spend up to 2 years at an A*Star Research Institute in Singapore and up to 2 years in Uo. S • When students are in Singapore, A*Star pays a stipend. When the students are in Sheffield, a scholarship is provided. • IPR is jointly shared • Scheme is only open to UK / European students
8d0a7c94efccd0e36c82cc471b58702c.ppt